-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2024; 14(3): 67-74
doi:10.5923/j.economics.20241403.01
Received: Oct. 23, 2024; Accepted: Nov. 9, 2024; Published: Nov. 12, 2024

Analysis of the Role of Stakeholders in the Sustainability of Marine Capture Fisheries in Jember Regency
Moch Fachrur Roziq, Herman Cahyo Diartho, Riniati
Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Jember, Jember, Indonesia
Correspondence to: Herman Cahyo Diartho, Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Jember, Jember, Indonesia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The sustainability of marine capture fisheries is essential for economic development, social welfare, and environmental preservation, particularly in regions like Jember Regency, East Java. This study analyzes the role of various stakeholders in ensuring sustainable fisheries in this region. Key stakeholders include the Jember Regency Fisheries Service, Supervisory Com-munity Groups, Village Heads, Fishermen Groups, Fisheries Assistant, Non-Governmental Organizations, and Fishermen's Cooperative. Using the MACTOR method, this research identifies each stakeholder's influence and involvement. Results indicate that Jember Regency Fisheries Service, Supervisory Com-munity Groups, Village Heads, Fishermen Groups, Fisheries Assistant, Non-Governmental Organizations, and Fishermen's Cooperatives show lesser involvement. Key challenges include overfishing, ecosystem damage, and a lack of investment in fishing port infrastructure. The study highlights the importance of collaboration between all stakeholders to enhance the economic, social, and ecological sustainability of the fisheries sector in Jember. By aligning the efforts of both governmental and non-governmental actors, the fisheries sector in Jember can ensure long-term sustainability, increasing productivity and improving the welfare of the fishing community.
Keywords: Marine Capture Fisheries, Sustainability, Stakeholder Analysis, MACTOR Method
Cite this paper: Moch Fachrur Roziq, Herman Cahyo Diartho, Riniati, Analysis of the Role of Stakeholders in the Sustainability of Marine Capture Fisheries in Jember Regency, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 14 No. 3, 2024, pp. 67-74. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20241403.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The area of waters in Indonesia is 6.4 million km with a coastline length of 108,000 km, 17,504 islands, and a population of 140 million people living in coastal areas (Kementerian Kelautan dan Perikanan, 2024). In the sea, there are marine resources that are divided into four groups, namely renewable resources, non-renewable resources, marine energy, and environmental services, where the potential of these marine resources is still not optimally managed (Tangke, 2023). The capture fisheries and aquaculture sectors are included in the category of marine resources that can be recovered, so they require the development of various aspects which can provide great contribution value in regional economic development (Kaison et al, 2021). According to Todaro (1997), economic development is a part of development that has meaning as a process involving major changes in social conditions, an attitude of getting used to something new, and the task of national institutions, as well as the acceleration of economic growth, poverty reduction or eradication (Hasan & Azis, 2018).According to data from the Ministry of Maritime Affairs and Fisheries of the Republic of Indonesia, in 2023 East Java ranks second in the production volume of marine capture fisheries of 568,955 tons. Data from the Jember Regency Fisheries Office, states that Jember Regency is one of the regions in East Java that produces marine capture fisheries, which in 2023 will see an increase in production of 13,593 tons with skipjack fish, cob, shrimp, and other types of fish caught. There are 5 fish-catching sub-districts, namely Kencong, Gumukmas, Puger, Ambulu, and Tempurejo Districts. According to Muhartono and Nurlaili (2019), Jember Regency is an area that is a vital fish landing center with great potential in the fisheries sector, supported by abundant marine resources and developing marine product processing activities. Quoting from Radar Jember (2024), the Regent of Jember Regency is the only regional head in East Java Province to obtain the Satya Lencana Wira Karya in the field of fisheries, because of his innovation, and many other programs such as moving the ocean to the mainland.The direction of catch management tends only to increase production without paying attention to the value-added aspect which will have an impact on the overexploitation of fish resources, therefore, management in the fisheries sector must be carried out in a sustainable manner in order to maintain the sustainability of fishery resources so that overfishing does not occur, and affects the increase of business productivity, increase income, and the welfare of actors in the fisheries sector (Imelda et al, 2019). Sustainability is something important in fisheries development which is expected to improve resource conditions and the welfare of the fisheries community itself (Tuhuteru et al, 2015). According to Suharno et al (2020) Stakeholder involvement is very important in the sustainability of small-scale capture fisheries. The involvement of stakeholders can anticipate excessive utilization of fish resources and coupled with the destruction of ecosystems such as coral reefs.According to Rahmayanti (2018), stated that currently there are still not many fishery companies investing in fishing ports, this is due to several factors including weak support for legal instruments, fish production capacity in the area around the port, incentives for local governments or area managers for investors who will invest in the area, as well as capacity on existing land. Meanwhile, according to Ramlah et al (2022), it is stated that the emergence of threats to the sustainability of fish resources and the capacity of business actors is still the main concern in realizing capture fisheries, because if there is excessive fishing, it will have an impact on fishermen's economic problems, in addition, there are problems with the level of education, lack of data recording, and lack of understanding related to the use of geographic position systems (GPS) when going to sea. This indicates that it requires the role and attention of all stakeholders so that fisheries sustainability and fishermen's welfare are achieved. From this phenomenon, it is the background in researching the role of stakeholders in the sustainability of marine capture fisheries in Jember Regency. The role of stakeholders will be analyzed using MACTOR, which will identify the preferences of each stakeholder and the level of their role towards the goals that have been identified (Mafruhah et al, 2021). There are seven actors that will be analyzed, namely the Jember Regency Fisheries Service, Supervisory Community Groups, Village Heads, Fishermen Groups, Fisheries Assistant, Non-Governmental Organizations, and Fishermen's Cooperative.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Sustainable Development Concept
- According to Todaro (1995), development must have several main objectives, namely increasing supplies and expanding equitable access to basic material needs, raising living standards including increasing income, providing adequate employment, better education, paying greater attention to cultural values and human values, increasing awareness of self-esteem both individually and nationally. and to expand the range of economic and social options for the whole society through liberation from dependency not only in relation to other people and other countries, but also from the sources of human ignorance and suffering (Afandi et al, 2023). Development is essentially a process of transforming society towards a state that is close to the goals of the aspired society as stated in the constitution, in which the process finds two things that need to be considered, namely sustainability and change (Yamin & Haryanto, 2017). Based on the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA, 2013) Sustainable development has an approach to three pillars, namely trying to achieve equality of economic development, social welfare, and environmental preservation in a development system that is related to each other (Widuri, 2021).
2.2. Concession Stakeholder
- According to Handayani and Warsono (2017), the definition of stakeholders is divided into 3 groups, namely:1. Primary stakeholders are stakeholders who are directly affected, both positive and negative impacts of a plan and have a direct interest in the activity.2. Key stakeholders, namely those who have legal authority in terms of decision-making.3. Secondary stakeholders, namely stakeholders who do not have a direct interest in a plan but have a great concern for the development process. Stakeholders are any individual or group that has an interest in, and involvement in a certain organization, where these stakeholders will influence and influence each other to achieve a goal (Gravitiani et al., 2022). Stakeholders in marine capture fisheries in Jember Regency are: 1. The Jember Regency Fisheries Service has a role in setting policies, supervising, and providing technical support for sustainable capture fisheries management.2. The Supervisory Community Group plays a role in supervising fishery activities to ensure compliance with rules and the preservation of marine resources.3. Village Heads have a role in facilitating communication and collaboration between fishermen, communities, and the government to support sustainable management of marine resources.4. Fishermen groups play a role in carrying out marine capture fisheries activities responsibly and collaborating in the joint management of marine resources.5. Fisheries Assistant plays a role in providing technical assistance and logistical support for fishermen to ensure the continuity of capture fisheries operations.6. Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) play a role in providing education and advocacy about sustainable fisheries and fighting for the rights of fishermen.7. Fishermen's Cooperative have a role to organize and support the welfare of fishermen through the provision of sustainable economic facilities, such as access to capital and markets.
2.3. Capture Fisheries Concept
- National capture fisheries are still characterized as small-scale capture fisheries, which are synonymous with poverty and always lose competition with large ships in the use of fish resources (Kusdiantoro et al, 2019). According to (Berkes, Mahon & McConney, 2008) poor management of small-scale capture fisheries will result in conflicts so that they are not able to keep up with the speed of economic progress, population growth, food needs and poverty (Ikhsan & Arkham, 2020). Capture fisheries are fishing activities carried out by humans in marine waters or public waters such as rivers, lakes, swamps, or coastal waters using capture fisheries methods that involve the use of fishing gear such as nets, fishing rods, nets, nets, bubu, and other fishing gear (Kurniawan, 2024). Marine capture fishery products provide approximately 54 percent of the total demand for animal protein sources consumed by people in Indonesia, therefore the great potential of capture fisheries is in line with the many requests from various countries, so that it is a great opportunity for business actors in the field of capture fisheries, both large-scale companies and traditional business actors, to improve the quality standards of handling and processing of catches in the sea that can meet the demand of the export market by adjusting the quality standards of each destination country (Munarko et al 2023).
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Research Design
- This research design uses a quantitative descriptive analysis method. This method is used to analyze and test the role of stakeholders in the management of the small-scale marine capture fisheries sector, both Regional Government Institutions, Private Sector, and the community. The research was conducted in July - September 2024. The method of determining the location of the research was carried out purposively (intentionally). The area chosen as the object of research and sample is Jember Regency where Jember Regency is a producer of capture fisheries that has quite large potential as indicated by receiving an award from the East Java Provincial Government related to the sustainability program for capture fisheries and protection of fishermen in the form of fisherman insurance facilities.In addition, Jember Regency is one of the regencies that has the potential for capture fisheries to be developed in order to have a greater impact/influence on the development of the Jember Regency area. Jember Regency has potential in terms of capture fisheries but still needs integration between stakeholders involved in the sustainability of fisheries in Jember Regency, so it is necessary to analyze the role of actors/stakeholders and factors related to the sustainability of fisheries in Jember Regency.
3.2. Data Collection Method
- The sampling method in this study uses the Non-probability sampling type with the Purposive sampling technique. According to Sugiyono (2018) Non-probability sampling is a sampling technique that does not provide equal opportunities or chances to each member of the population when being selected as a sample. While the Purposive sampling technique according to Sugiyono (2018) is sampling using several specific considerations according to the desired criteria to be able to determine the number of samples to be studied.Sampling in this study used the purposive sampling method or deliberate selection of respondents. The sample consisted of 93 respondents including the Fisheries Service, Community Supervisory Groups, Village Heads, Fishermen's Groups, Pengamba', Non-Governmental Organizations, Cooperatives. Sample selection was based on the role and synergy between actors and factors in implementing sustainable capture fisheries policies. In addition, the samples taken also have a full relationship to the sustainability of capture fisheries in Jember Regency.The type of data used in this study is primary data that is descriptive quantitative in nature, namely data obtained from the Fisheries Service, Community Supervisory Groups, Village Heads, Fishermen's Groups, Fishermen, Non-Governmental Organizations, Cooperatives as stakeholders in the sustainability of capture fisheries using structured questionnaires, while secondary data uses published data from the Fisheries Service of Jember Regency and previous research results.The problem is investigated through focus group discussions (FGD). The results of the FGD are used as analysis material with a factor and actor (stakeholder) approach using a prospective structural analysis (PSA) tool using Mactor software. Furthermore, the results of the analysis are used as a reference for formulating a sustainable capture fisheries policy plan that will be proposed.
3.3. Data Analysis Methods
- The data analysis method used to analyze and test the role of stakeholders in the management of the small-scale marine capture fisheries sector uses prospective structural analysis (PSA) with Mactor software. The use of the Prospective Structural Analysis (PSA) method with Mactor software in this study is to observe the relationship and influence between variables that allow the classification of variables to understand the most relevant variables for the sustainability of capture fisheries. Prospective structural analysis (PSA) with Mactor software is a comprehensive analysis in mapping the synergy between actors and factors in implementing sustainable capture fisheries policies compared to other analyzes.The use of Prospective Structural Analysis (PSA) with mactor software has been widely used to conduct sustainability-related analysis. Several studies on the use of Prospective Structural Analysis (PSA) with mactor software include: Ahmed, Saleh, Abdellkadir, Abdelrahim (2009) conducted a sustainability analysis of desert areas in Egypt. Jaziri & Bousafa (2010) conducted a sustainability analysis of tourism in Tunisia, while Raju, Delaere, Lindmark, Stamatelatos & Ballon (2011) conducted a sustainability analysis of business in energy networks. Fauzi, (2019) used the Prospective Structural Analysis (PSA) method with mactor software to conduct a policy analysis on the prohibition of Cantrang fishing gear.Prospective analysis is used to rank the positions of stakeholders on many strategic issues, assess convergence and divergence, and anticipate coalitions and conflicts (Omran, Khoris & Saleh, 2014). The prospective analysis method with Mactor software conducts a comprehensive analysis of the strategies and initiatives of actors. Mactor (Alliance and Conflict Matrix: Tactics, Objectives and Recommendations) is based on the influence between actors. The Mactor method attempts to provide a global picture of the importance and possible outcomes of various issues, as well as the expected actor strategies, power relationships and potential alliances and conflicts. This method is intended to obtain the possibility of the evolution of the system being studied to build better and more coherent scenarios (Fauzi, 2019).The stages in prospective structural analysis (PSA) with Mactor software (Fauzi, 2019) include: (i). identification related to the topic to be analyzed; (ii) conducting Focus Group Discussion (FGD) with key informants consisting of the main actors (fishermen groups, Village Heads, Cooperative Fishermen, NGOs) and representatives from the Jember Regency Fisheries Service and Community Monitoring Groups by conducting structured interviews to collect data. (iii) identifying the actors involved and the objectives to be achieved. After these stages are carried out, the tables for analysis are filled in (Matrix of Direct Influence/MDI Table and Actor-Objective/2MAO Table).Actors involved in prospective structural analysis (PSA) using Mactor software, namely;1. Fisheries Service2. Community Supervisory Group3. Village Head4. Fishermen Group5. Fisheries Assistant 6. Non-Governmental Organization7. Fishermen's CooperativeMeanwhile, the objectives set in prospective structural analysis (PSA) using Mactor software are:1. Sustainability of the Economic Dimension2. Sustainability of the Social Dimension3. Sustainability of the Environmental/Ecological Dimension
4. Results and Discussion
- The initial stage in the prospective structural analysis (PSA) analysis using Mactor software is to build a direct influence matrix or MDI (Matrix of Direct Influence) and MAO (Matrix of Actor Objective). The MDI matrix describes the influence between actors on other actors which is indicated by a score of 0 to 4, the greater the value indicates the greater the influence, while the MAO matrix shows the actor's attitude towards the objective.Table 1. MDI (Direct Influence Matrix Between Actors) shows the level of influence of each actor on other actors. For example, the Fisheries Service has a large influence on the Community Monitoring Group and the Fishermen Group. This is in accordance with the strategic role of the Fisheries Service as a policy distributor. In contrast, other actors such as Pengamba', Non-Governmental Organizations and Cooperatives do not have significant influence on other actors. The relationship between actors is measured by a scale that shows the level of influence, where the Fisheries Service acts as the main authority in the region. Meanwhile, other actors such as Non-Governmental Organizations and Cooperatives show lower influence.
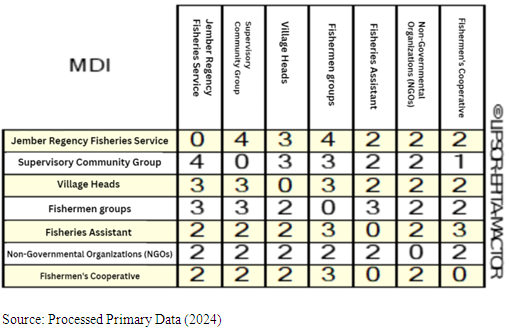 | Table 1. MDI: Analysis of Direct Influence Between Actors |
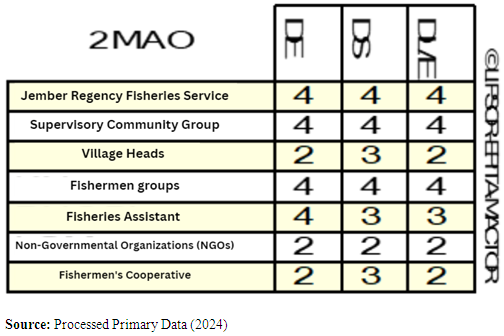 | Table 2. 2MAO: Actors' Attitudes Towards Capture Fisheries Sustainability Objectives |
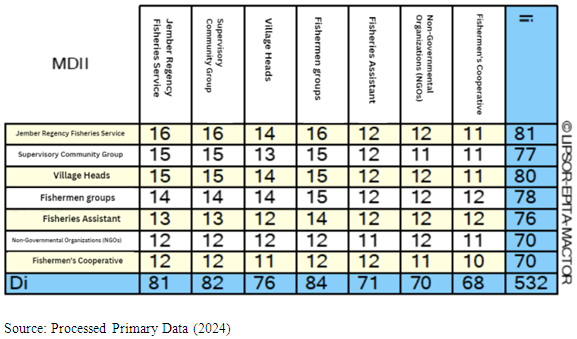 | Table 3. Level of Direct and Indirect Influence and Dependence |
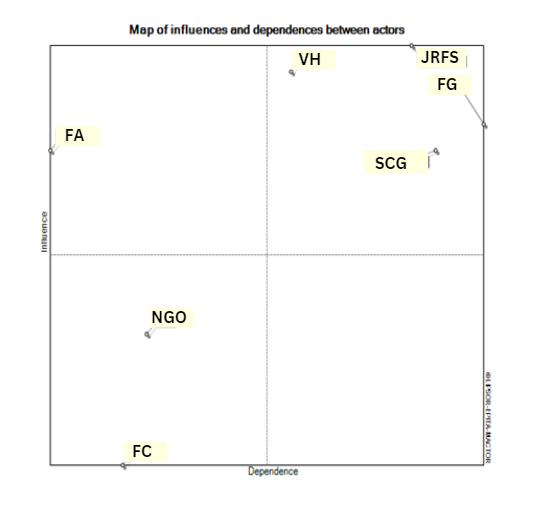 | Figure 1. Mapping of Actor Roles in Quadrants: Level of In fluence with Level of Dependence (Source: Processed Primary Data (2024)) |
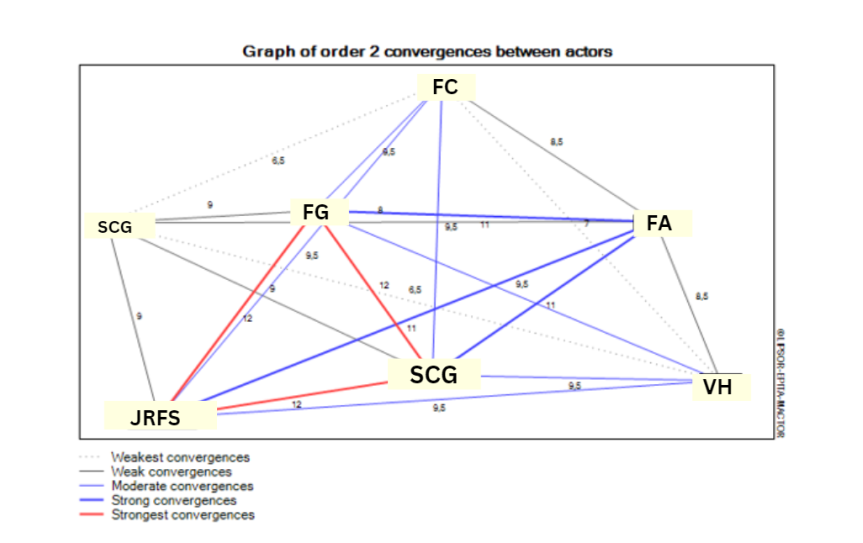 | Figure 2. Image of Convergence Between Actors (Source: Processed Primary Data (2024)) |
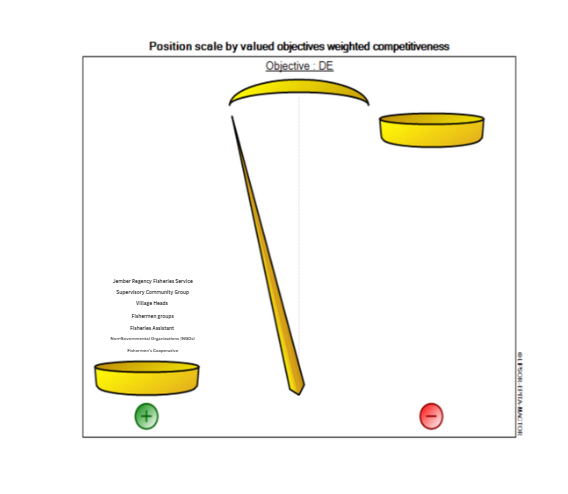 | Figure 3. MDII Competitiveness Scale – Objective: Sustaiability of Economic Dimension (Source: Processed Primary Data (2024)) |
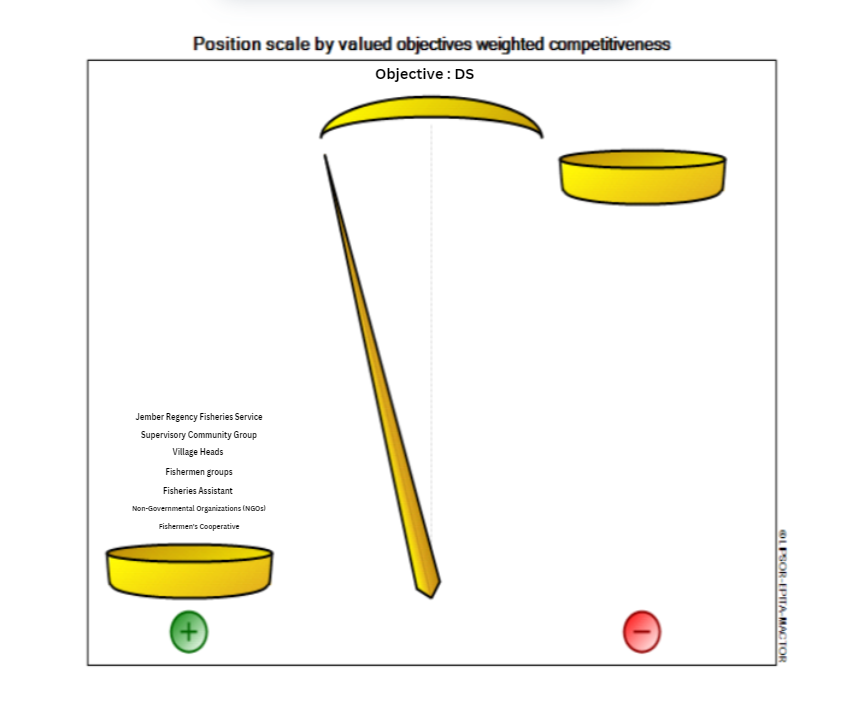 | Figure 4. MDII Competitiveness Scale – Objective: Sustaiability of Social Dimension (Source: Processed Primary Data (2024)) |
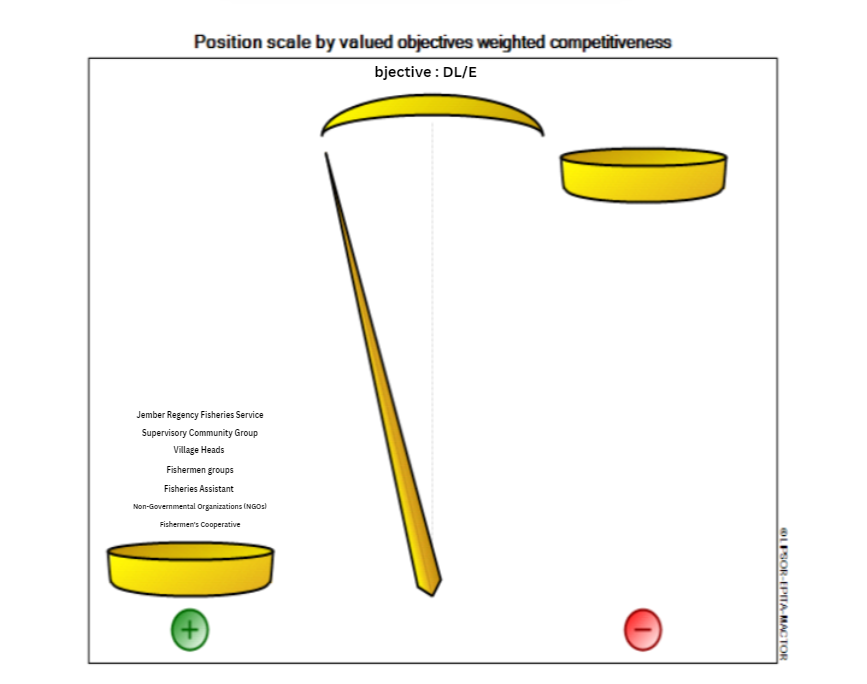 | Figure 5. MDII Competitiveness Scale – Objective Sustaiability of Ecologi Dimension (Source: Processed Primary Data (2024)) |
5. Conclusions
- The sustainability of marine capture fisheries in Jember Regency is heavily influenced by the active role of various stakeholders, including government institutions, fishermen groups, and NGOs. The study indicates that key actors, such as the Jember Fisheries Service and Community Supervisory Groups, play a pivotal role in maintaining sustainable fisheries practices, while other stakeholders, such as cooperatives and NGOs, need further involvement. Effective collaboration is essential for managing fishery resources, as overfishing and environmental degradation pose significant risks. The implementation of sustainability strategies has led to improved economic outcomes for local fishermen, yet challenges such as lack of infrastructure investment and education for fishermen remain. Involving all actors in a balanced way can ensure that fisheries not only provide economic benefits but also contribute to social and ecological well-being.
6. Policy Recommendations
- Strengthening stakeholder collaboration through a multi-stakeholder approach should be promoted by strengthening partnerships between stakeholders. This can be done by holding regular coordination meetings to align sustainability goals and strategies. Develop infrastructure by encouraging public and private sector investment in fishing port infrastructure. The provision of better facilities will not only support large-scale fishery operations but also improve the quality and handling of fish products. Supporting education and technology such as providing training programs for fishermen that focus on sustainable practices, modern fishing techniques, and the use of GPS for navigation. This will increase the sustainability and economic competitiveness of small-scale fisheries. Regulation and oversight by strengthening regulatory frameworks to prevent overfishing and ensure compliance with sustainability measures. Regular oversight by the supervisory group must be supported with modern technology to improve resource management. Encourage economic incentives through the development of incentive schemes for sustainable fisheries practices, including subsidies for environmentally friendly fishing gear and access to markets for sustainably sourced products. This will help ensure that sustainable fisheries remain economically viable. By implementing these policies, the marine capture fisheries sector in Jember can achieve long-term sustainability that benefits both the local economy and the environment.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML