-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2023; 13(3): 71-77
doi:10.5923/j.economics.20231303.01
Received: Dec. 13, 2021; Accepted: Mar. 10, 2022; Published: May 12, 2023

Relationship between Financial Inclusion, Financial Development and Economic Growth in Nigeria
Onoh Chukwunonso Francis1, Longtei Muanzem Henry2
1National Open University of Nigeria
2Central Bank of Nigeria
Correspondence to: Onoh Chukwunonso Francis, National Open University of Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The work examined the Impact of financial inclusion on economic growth in Nigeria from 1990-2020. The objectives of the study are to examine the Impact of financial inclusion on economic growth of Nigeria and to examine the causality relationship between financial inclusion and economic growth of Nigeria. Ordinary Least Square Method (OLS) regression analysis was employed for the study. The variables used for the research are; Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR), Broad money ratio to GDP (MGDP), credit to private sector ratio to GDP (CPSP), Deposits of rural branches of deposit money banks (DRC) and Loans of rural branches of deposit money banks (LRC). The data for the study was collected from Central Bank of Nigeria statistical bulletin. Bounds Testing cointegration was carried out which shows that there is long run relationship between the variables. The error correction mechanism, which indicates the speed of adjustment is -0.676412 which means that the speed of adjustment in the short run is 68%, and it is statistically significant at 0.0030. The findings of the study showed that financial inclusion has significant impact on economic growth in Nigeria. It is on this ground that the study recommended that the authorities in Nigeria should educate rural dwellers on the importance of banking as it would facilitate the success of CBN financial inclusion policy.
Keywords: Financial Inclusion, Finance Development, Modern banking, Peaceland
Cite this paper: Onoh Chukwunonso Francis, Longtei Muanzem Henry, Relationship between Financial Inclusion, Financial Development and Economic Growth in Nigeria, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 13 No. 3, 2023, pp. 71-77. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20231303.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
1.1. Background of the Study
- The debate on financial system services as how it impact on the economic growth and development of Nigeria have increased since the literacy level of the most populous nation in Africa is on fast increase. According to (Leyshon and Thrift, 1995) in Oruo (2013) Financial inclusion is a system in which all people have access to appropriate desired financial products and services in order to manage their money effectively, in Otiwu, okere, uzowuru and ozuzu (2018), Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) in 2005 introduced a microfinance framework to enhance access financial services to low income earners and by extension the financial excluded people. In Oruo (2013), Sinclair (2001) defined financial exclusion which is the opposite of financial inclusion as the inability to access necessary financial services in the right time and in the desired form. Access to financial services have been an issue of contention and much deliberation is on the topic as it is believed to positively impact on the economic growth and development of nations. In Bigirimana and Hongyi (2018) Rwandan government in expanding the economic growth and development of the nation has set a target of getting 90% of Rwandans to be financially included by 2020. The target of most developing nations is to expand the financial product and services of the nation to the people. This is believed to give a boost to the economic development, growth and sound financial system of any nation. In Nigeria financial inclusion will help integrate the masses into the vast financial services available in the country financial sector, such will help poverty eradication and increase in development index of the nation, this will also boost the nations ease of doing business statues. The nation has developed tools to increase the financial included people, which include Agent banking, Know Your Customer, Financial literacy and mobile money operation. But the issue is not devising a means to it but sustaining it. The electronic payment system which have taken a solid shape in the country in the past two decades, have not been able to break the barrier of the largely financially excluded Nigerians and in most cases the electronic system has not taken care of the other aspects of financial inclusion such as insurance and pension. The impact of the electronic payment system has also been affected by low literacy and challenges of multiple chargers and complications in resolving undelivered services.If Nigeria can increase the population of people with access to financial services, it is certain that the financial sector will be able to mobilize the needed capital that is needed to spur the economy to high rate of growth vis-a vis development of the people and the nation. It is in an attempt to resolve these challenges and offer a sound solution that this research is carried.
1.2. Research Questions
- 1. What is the impact of financial inclusion and financial development on economic growth of Nigeria?2. What is the causality relationship between financial inclusion and financial development on economic growth in Nigeria?
1.3. Objectives of the Study
- 1. To examine the impact of financial inclusion and financial development on economic growth of Nigeria. 2. To examine the causality relationship between financial inclusion and financial development on economic growth of Nigeria.
1.4. Statement of the Hypotheses
- H01: Financial inclusion and financial development has no significant impact on economic growth in Nigeria.H02: There is no causality relationship between financial inclusion and financial development on Economic growth in Nigeria.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Theoretical Literature
2.1.1. Schumpeter Theory of Economic Development
- The theory is based on the circular flow model of Schumpeter concept. According to Schumpeter in (Suman of economic discussion), the circular flow is a stream that is fed from continually flowing springs of labor, power and land and flow in every economic period into the reservoir which we call income. In order to be transformed into satisfaction of wants Schumpeter emphasized the essence of innovation and entrepreneur in advancing economic growth. According to Suman, the features of the circular flow are (1) all economic activities are essentially repetitive and follow a familiar routine course (2) all the producers know the aggregate demand for goods and adjust the supply of output accordingly. This means that demand and supply are in equilibrium at each point of time. The economic system has the optimum level of output and its maximum use and there is no possibility of wastage of resources and the firms working in a system are in a state of competitive equilibrium. In adhering to Schumpeter’s circular flow theory model, it is expected that innovation will lead to gain in financial development which will lead to economic growth and development.
2.1.2. Financial Liberalization Theory
- Mekinnon (1973) and Shaw (1973) developed a seminal work to advance financial policy in developing countries. According to Williamson (1998) the authors listed the six dimensions which repression occurs: 1) the government, not market determined who received credit (2) the government, not market determined interest rates (3) the government determined whether new institutions would be allowed to enter the financial sector (4) the government laid down details of bank operations such as who they hired and what salaries were paid (5) the government owned the financial institutions and (6) the government decided who would be allowed to borrow and lend abroad and the terms. Mekinnom and Shaw contended that the listed repression retards growth and add extra cost on the nations that are practicing it. But in projection of these conditions on the topic which is financial development, inclusion and economic growth. It is evidenced that if government minimizes much control on the financial sector, but use the regulatory extension to deliver financial services to the excluded through much private sector participation, the much needed growth of the developing nations will activated From the financial sector as the achieved result in financial inclusion will aid the capital formation of those nations.
2.2. Empirical Literature
- Bigirimana and Hongyi (2018) examined the relationship between financial inclusion and economic growth in Rwanda using ARDL. They applied the ARDL method because of the small sample size of their research (2004-2016). The research established a long run relationship between financial inclusion and economic growth of Rwanda. It also established a cause-effect relationship of economic growth measured by Gross Domestic Product and Financial inclusion due to the positive effect of financial inclusion on economic growth of Rwanda. The research recommended that barriers to loan access should be braked by the government, thus to encourage more people to take loan and be financially included.Adu, Marbuah and Mensuh (2013) empirically examined financial development and economic growth in Ghana. The research employed the ARDL method using GDP as the dependent variable while the key independent variables are financial deepening indicators. The research found out from varying output that the effect of financial development on economic growth is dependent on the on the variables of choice proxies for financial development. It recommended that polices that will make access to funds by the real sector should be initiated and implemented by the government.Otiwu, okere, uzowuru and ozuzu (2018) studied financial inclusion and economic growth in Nigeria with a particular reference to microfinance bank, the study employed the ordinary least square method while laying more efficacies on rural areas to capture the unbanked population. The study found out that microfinance bank is a vital tool that enhances financial inclusion impact on economic growth. It further suggested that microfinance activities should be increased in the rural areas while also encouraging the microfinance banks on low cost deposits and avoid fixed deposit rush, so as to achieve more in the financial inclusion drive.Ayinde and Yinusa (2016) examined the financial development and inclusive growth in Nigeria using a threshold analysis. Financial deepening indictors were employed as the regressors. The research found out that inclusive growth Granger causes financial development; hence this by extension means that openness of the economy will enhance financial development through investment. The research recommended that efforts should be placed more on inclusive growth drivers, thus small and medium scale enterprises.Nwafor and yomi (2018) on the nexus between financial inclusion and economic growth used two staged least square regression method, the research found a relationship between financial inclusion and economic growth using coefficients of regression of 48% as a prove. It further recommended the development of more financial products to cover the financially excluded population while it also encouraged the regulatory body to influence low interest rate so as to encourage financial participation.Onaolapo (2015) analyzed the effects of financial inclusion on the economic growth in Nigeria. The research hampered more on the effect of financial inclusion on poverty reduction, thus the research variables include financial deepening, and financial intermediation and proxies for poverty index, the research found out that increase inclusiveness in financial activities reduces poverty and impact on economic growth of the nation. It recommended increased opportunity of financial activities to the poor and the unbanked.Madichie, maduka, oguanobi and Ekesiobi (2014) on financial development and economic growth in Nigeria, established a varying relationship between financial development and economic growth of Nigeria in the short run and long run. Positive in the short run and negative in the long run. The study which utilized the OLS method, also applied the Granger causality method. It found there is no bi-directional causality between financial development and economic growth. It concluded and recommended that government should support the micro credit providers so as to include those who cannot access credit from the conventional creditors.Odeleye and Olusoji (2016) on financial inclusion and inclusive growth in Nigeria used econometrics methods; the research found that financial inclusion variables such as money supply, liquidity ratio and credit to private sector positively influence economic growth in Nigeria. The research also found out that there exist long run relationship between financial inclusion and economic growth in Nigeria. Hence it recommended that government should provide a conducive environment for increase participation of the population on financial activities.Okoye, Adetiloye, Erin and Modebe (2017) on financial inclusion as a strategy for enhanced economic growth and development used Ordinary least square method to analyze the sourced time series data. From the findings, the effect of rural credit was outlined, thus financial inclusion through rural credit was found to have aided poverty reduction in Nigeria and should be encouraged. It recommended increased funds to the private sector to enhance financial inclusion.Olaniyi (2015) researched on the effects of economic and financial development on financial inclusion in Africa using panel data from 44 African Countries. The study found out that financial inclusion has impact on economic growth and development of African nations, the study also outlined that income level influences participation in financial activities which means that low income of most African nations affects its financial inclusion, thus economic growth and development. The research recommended that deposit interest rate should be more attractive to encourage financial inclusion. It further recommended financial literacy to educate and attract people to financial activities.Oruo (2013) examined the relationship between financial inclusion and GDP growth in Kenya. The research found out that there exist positive relationship between economic growth and financial inclusion in Kenya. The study recommended increase in microfinance establishments in Kenya and increase in Bank branches as well.Puatwoe and Piabuo (2017) researched on financial sector development and economic growth in Cameroon using ARDL Method, the research found a long run positive relationship between financial sector indicators and economic growth. The research recommended improves in financial institutions and upholding the financial reforms in Cameroon.Paun, Musetescu, Topan and Danuletin (2019) on the impact of financial sector development and sophistication on sustainable economic growth on selected 45 low income, middle income and high income countries using fixed panel with 450 observations. The result found out that expansion of financial services and foreign assets influences economic growth and that sophistication of financial services and inclusion impact on the economy positively.
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Design
- The research design that will be adopted for this research is cause-effect also known as ex-post facto research design.
3.2. Variable Measurement and Definition
- In analyzing the relationship between financial inclusion, financial development and economic growth in Nigeria we adopted the OLS method, real Gross Domestic Product Growth Rate (GDPGR) is the dependent variable, while proxies for financial inclusion and Financial developments; Broad money ratio to GDP (MGDP), credit to private sector ratio to GDP (CPSP), Deposits of rural branches of commercial banks (DRC) and Loans of Rural branches of commercial banks (LRC) are independent variables.
3.3. Model Specification
- The functional relation of the model is given as:
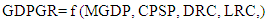 | (1) |
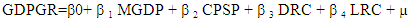 | (2) |
3.4. Data Analysis Method
- The study will make use of regression analysis method, first stationarity test will be conducted to test the if the data can be used in it normal state or differenced, then it will incorporate bound testing co-integration test in order to undertake a thorough examination of the data which is expected to be of different stationarity level, the bound test will solve the cointegration qusetion. Granger causality test will also be conducted to test the predictive properties of a variable over the other.
3.4.1. Co-integration Test
- Empirical Model: GDPGR= f (MGDP, CPSP, DRC, LRC)The Bound cointegration test model:
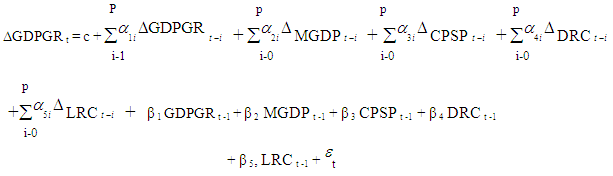 The Error Correction MechanismEmpirical Model: GDPGR = f (MGDP, CPSP, DRC, LRC)
The Error Correction MechanismEmpirical Model: GDPGR = f (MGDP, CPSP, DRC, LRC)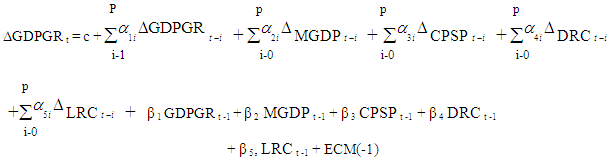
3.4.2. Granger Causality
- Granger causality test is a statistical test conducted to test the predictive properties of a variable over the other. Decision Rule:If the computed F value exceeds the critical F value at the chosen level of significance, we reject the null hypothesis; otherwise, we do not reject it.
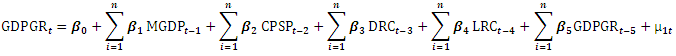 | (1) |
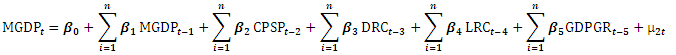 | (2) |
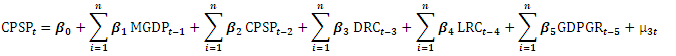 | (3) |
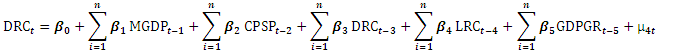 | (4) |
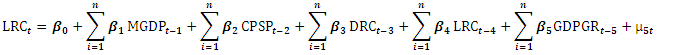 | (5) |
3.5. Sources of Data
- The data (GDPGR, MGDP, CPSP, DRC, LRC) used in this research are from secondary sources. All the data employed were sourced from Central Bank of Nigeria statistical bulletin 2020. Eviews 9 econometric software will be utilized for the analysis.
4. Data Presentation and Analysis
4.1. Stationarity Test
- Unit root test
|
4.2. Bound Test Output
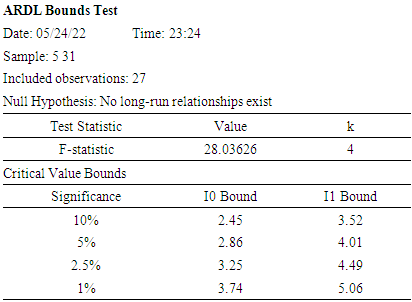
- According to Pesaran, Shin and Smith (2001) if the F-Statistics of a Bound test is greater than the lower bound and the upper bound of the chosen level of significance, then there is long run relationship. From the ARDL result, F-statistic value of 28.03626 is greater than I0 (2.86) Bound at 5% level of significance and the upper bound I1 (4.01) Bound at same level of significance. Hence there is long run relationship between the variables. Since the variables are cointegrated on the long run, we therefore estimate the ECM.
4.3. ARDL Cointegrating and Long Run Form
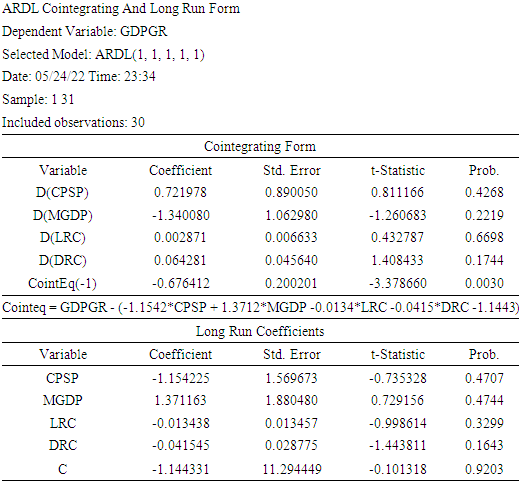 Discussion of the Results(i) From the estimation result a change in credit to private sector ratio to GDP (CPSP) will lead to Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR) to increase by 0.721978 in the short run and decrease by 1.154225 in the long run.(ii) A unit change in Broad money ratio to GDP (MGDP) will lead Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR) to decrease by 1.340080 in the short run but increase by 1.371163 in the long run.(iii) A Unit change in Loans of Rural branches of deposit money banks (LRC) will lead Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR) to increase by 0.002871 in the short run but decrease by 0.013438 in the long run.(iv) A change in Deposits of rural branches of deposit money banks (DRC) will lead Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR) to increase by 0.064281 in the short run but decrease by 0.041545 in the long run.(v) The error correction coefficient, which indicates the speed of adjustment, has a negative sign. This is expected as it is the condition for accepting the model. From the result of the model presented above, the ECM is -0.676412 which means that the speed of adjustment in the short run is 68%, and it is statistically significant at 0.0030.
Discussion of the Results(i) From the estimation result a change in credit to private sector ratio to GDP (CPSP) will lead to Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR) to increase by 0.721978 in the short run and decrease by 1.154225 in the long run.(ii) A unit change in Broad money ratio to GDP (MGDP) will lead Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR) to decrease by 1.340080 in the short run but increase by 1.371163 in the long run.(iii) A Unit change in Loans of Rural branches of deposit money banks (LRC) will lead Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR) to increase by 0.002871 in the short run but decrease by 0.013438 in the long run.(iv) A change in Deposits of rural branches of deposit money banks (DRC) will lead Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR) to increase by 0.064281 in the short run but decrease by 0.041545 in the long run.(v) The error correction coefficient, which indicates the speed of adjustment, has a negative sign. This is expected as it is the condition for accepting the model. From the result of the model presented above, the ECM is -0.676412 which means that the speed of adjustment in the short run is 68%, and it is statistically significant at 0.0030.4.4. Granger Causality Tests
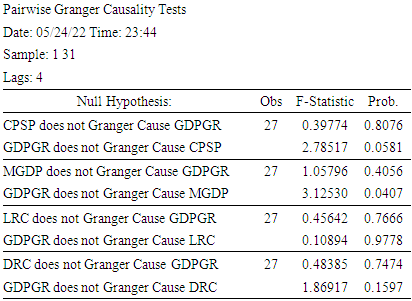 Interpretation of the Granger Causality Test(i) There is unidirectional causality between credit to private sector ratio to GDP (CPSP) and Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR). Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR) Granger causes credit to private sector ratio to GDP (CPSP).(ii) There is also unidirectional causality between Broad money ratio to GDP (MGDP) and Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR). Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR) Granger causes Broad money ratio to GDP (MGDP).(iii) There is no Granger causality relationship between Loans of Rural branches of deposit money banks (LRC), Deposits of rural branches of deposit money banks (DRC) and Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR).
Interpretation of the Granger Causality Test(i) There is unidirectional causality between credit to private sector ratio to GDP (CPSP) and Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR). Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR) Granger causes credit to private sector ratio to GDP (CPSP).(ii) There is also unidirectional causality between Broad money ratio to GDP (MGDP) and Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR). Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR) Granger causes Broad money ratio to GDP (MGDP).(iii) There is no Granger causality relationship between Loans of Rural branches of deposit money banks (LRC), Deposits of rural branches of deposit money banks (DRC) and Gross Domestic product Growth Rate (GDPGR).4.5. Test of Hypotheses
- H01: Financial Inclusion has no significant impact on the economic growth of Nigeria. Result of the error correction model showed that the variables of DRC, CPSP and LRC were significant determinants of economic growth in Nigeria. Therefore, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that financial inclusion has significant impact on economic growth of Nigeria. H02: There is no causality relationship between Financial Inclusion and Economic Growth of Nigeria. From the result of the causality test, we reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is causality relationship between Financial Inclusion and Economic Growth of Nigeria.
5. Recommendations
- 1. The rural dwellers should be encouraged to access credit facilities with reduced single digit interest rate. 2. The most effective way to improve financial inclusion, is through the incorporation of Information and communication services based financial players into the system, this will aid quick access to financial services as it known that the telecommunication sector has penetrated the Nigerian zone more than the financial services. This method will involve the microfinance banks and mobile money operators.3. Increase in financial participation involves not only opening account, but education on financial services and loans to the excluded and disadvantaged people. Therefore there is urgent need to educated more the non-urban dweller on the importance of banking so as to capture those group.4. The promotion of collaboration between Deposit Money Banks (DMBs), Microfinance Banks (MFBs) and Communication services providers for enhanced intermediation of financial services should be encouraged.5. Financial inclusion and development Promotes innovations that allow us to build credit, savings insurance and pension products for low-income households thereby helping drive inclusive growth and economic development. Therefore more infrastructures should be put in place to make financial services available to all.6. General increases in level of economic activities, income levels relative to communities that do not have access to financial services. Therefore Government should strengthen the public-private partnership so as to make more catalysts of economic development to get to more places.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML