-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2020; 10(6): 459-465
doi:10.5923/j.economics.20201006.16
Received: Nov. 20, 2020; Accepted: Nov. 27, 2020; Published: Nov. 30, 2020

Re-Emphasising ‘Geography Role’ in Socio-Economic Solutions– A Pedagogical Approach Using Poverty Elimination as a Context
Mohamed Buheji1, Ana Vovk Korže2
1International Inspiration Economy Project, Bahrain
2University of Maribor, Maribor, Slovenia
Correspondence to: Mohamed Buheji, International Inspiration Economy Project, Bahrain.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Geography has always been seen as a classical subject and rarely been linked to realised socio-economic development, or community’s problem-solving. Since literature is scarce about the role of geography in overcoming challenges, the authors bring forth the role of geography based on a collective students’ questions after a class presentation about the role of geography in socio-economic problems. After carrying the literature review, the authors present to students five cases relevant to poverty elimination which represent the type of problems that geography can help to address. The implication of this study is that it opens a new line of research that optimise the utilisation of geography in solving complex problems, besides improving the way geography is presented pedagogically.
Keywords: Geography, Socio-Economic Problems, Community Challenges, Complex Problems, Poverty, Pedagogical
Cite this paper: Mohamed Buheji, Ana Vovk Korže, Re-Emphasising ‘Geography Role’ in Socio-Economic Solutions– A Pedagogical Approach Using Poverty Elimination as a Context, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 10 No. 6, 2020, pp. 459-465. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20201006.16.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- When we deal with socio-economic problems, we are not only targeting to solve the problem, but instead, we are focusing on creating new mindsets that would take risks when learning by exploring. In this paper, we study the influence of geography on our possible achievements, besides enhancing our capacity to engage with socio-economic challenges. The role of geography during COVID-19 pandemic and then its capacity in creating community wealth and its inter-disciplinary approach are discussed. Mishra (2011).The effect of geography on socio-economic issues are reviewed, taking poverty as the context for the geographic locations. The review shows that geographic interpretation helps to collect deeper observations. Buheji and Ahmed (2019).
2. Literature Review
2.1. Influence of Geography Appreciation on Our Possible Achievements
- When we travel, we discover besides appreciates more the history, and the geography that differentiates each country and community. This appreciation raises our curiosity to discover more the community and even get involved with certain projects that are related to this new discovery. In this paper, we review how socio-economic projects could be improved, and involvement could be even more developed through integration with geography. Appreciating geography help us to visualise and look at complex communities’ challenges from multi-perspectives. When we physically discover the geography of the place, we would have no pre-determined solutions. Knowing how to deal with the opportunities discovered and overcome the challenges of geography help us to create a new mindset with new attitudes and behaviours, as shown in Figure (1).
 | Figure (1). Influence of Geography on Curiosity and Mindset |
2.2. Geography Role in Increasing Community Engagement
- Geography improves our capacity to interact, liaise and change the dynamics of the observed environment. When we increase our capacity to confront and explore, we can learn more even from repeating the attempts to explore the possible solutions. These possible solutions enhance our capacity to create a legacy.Socio-economic development helps to bring access to resources that highlight the available or the hidden opportunities. Such access improves our capacities to engage, to produce and to participate, as shown in Figure (2). Gallup et al. (1999).
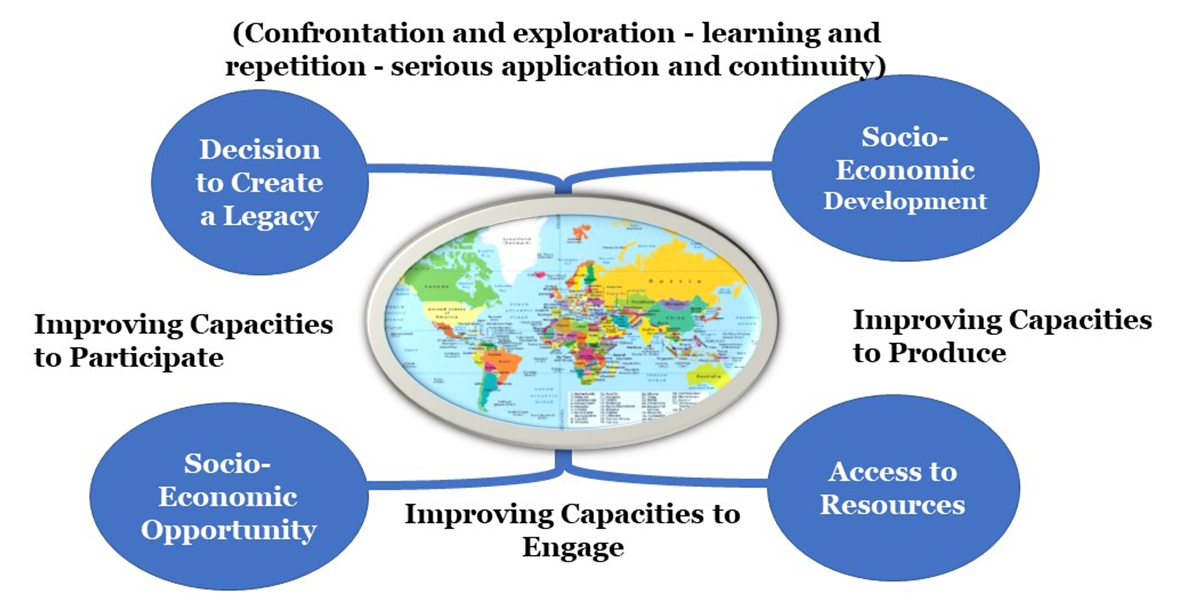 | Figure (2). The Outcome of Appreciating Geography on Engaging with Socio-economic Challenges |
2.3. Self-Sufficiency and Its Relation to Geography
- Self-sufficiency enables any community to be economically inter-dependent, and it helps the socio-economy to regain strength and resilience. When geography is utilised, we can bring the best SF practices in the community through appreciating the available natural resources and assets and this increase our abundant thinking. Buheji (2020a), Buheji et al (2020).When we understand the details of the geography, we can improve the livelihood standards of capital and the rural areas; we can ensure equality in economic affairs and even in communication.
2.4. Role of Geography during COVID-19 Pandemic
- Geography supports the SF project and can play a great role to increase the perseverance of the different communities while ensuring their acceptance to lockdowns. Understanding the challenges of geography also would address the increasing challenges of food availability to challenges in logistics. Understanding how to utilise the geography to enhance the food and logistics distribution is a very important part of the world efforts to mitigate the pandemic negative spillovers. In short, geography can play a great role in empowering for independence, or development, or advancement and thus building vibrant communities. Through the vibrant communities, we can be more prepared to deal with the coming spillovers of COVID-19 pandemic. Gallup et al. (1999).
2.5. Role of Geography in Defining and Creating Community Wealth
- Human Capital, Physical Capital, Natural Capital, Social Capital, Financial Capital.Geographical space represents the real production of nature in a specific region. Taking the spatial space in consideration when defining the wealth or the production process can help to improve the impact on social, economic and cultural spheres of life. Buheji (2019).Gallup et al. (1999) found that both geographic location and climate have large effects on income levels and income growth. The Gallup team routed this cause for many fixed factors as the logistics or transport costs, the disease burdens, and the capacity for agricultural productivity, besides other variable causes. Thus, the geographic location or condition found to affect the economic policy choices and even future foresight. Many geographic regions that have not been conducive to modern economic growth have high population densities which lead to accumulation of migrants from low skilled labour creating a series of slums that would have the hidden effect of the rapid increases on the community services and utilities without being properly accounted for. This disrupts many communities wealth, i.e. the community where the migrant worker migrated and the urban area where the migrant workers in. Hence, geography and geographic condition play a role in creating both opportunities and more disadvantaged people or communities that need would bring with them more complex socio-ec0nomic challenges. Buheji (2019).
2.6. Role of Geography in Enhancing the Inter-Disciplinary Approach
- Mishra (2011) seen that in order to build up an effective economic return from the geographical location while tackling any socio-economic issue we need to utilise inter-disciplinary approaches. Mishra (2011).The inter-disciplinary approaches help us to realise how an appreciation of geography and its intrinsic powers can define specific ways to community prosperity. When we deal with a complex socio-economic problem and then shed light on the geography and its influence economics, supply chain, transportation, community self-sufficiency or self-reliance, etc. then this complexity would be stratified and become part of the norm. When we understand through disciplinarity thinking the cultural aspects of the socio-economic issue of poverty, etc., new paradigms for social sciences originate from multiple causes.
2.7. The Effect of Geography on Socio-Economic Issues (Poverty as an Example)
- In order to eliminate or alleviate poverty, we need first to understand what makes the poverty prevalence in a specific geographical location, despite the availability of different sources of other non-financial wealth. Having the geographic area into consideration would help to observe then exploit the opportunities that could help to overcome the causes for deprivation and in the same enhance the capacity for a certain mode of production. Buheji and Ahmed (2019).The geography of a particular community plays a major role in their level of development. The historicity and the geographical space of a socio-economic problem, like poverty, would help to enhance the outcome of the exploration journey and provide multiple routes. The poverty in a tribal region area, is different than the poverty problem of the urban slums. Therefore, we need to see poverty from through 3-Dimensional perspective: the geographic area, the type of poverty, and the capacity of the resources. The history of the area under study helps to define the type of productive assets that are related to the socio-economic problem. In cases where there is the scarcity of assets with the geographic area, the problem solver should focus on re-inventing the business model to make it more independent became a territorial identity of the tribal in the specific region. In this context, geographical location played a significant role in the manifestations and perpetuation of mass deprivation and poverty. Buheji (2018).
2.8. Exploiting the Advantage of the Geographic Locations
- Like creatures, every geographical location has its beauty, regardless of how fierce or severe it looks. Geography is responsible for the prevalence of poverty and its severances among different communities or groups. For example, the poverty conditions of the Arab nomads or the Amazigh in the Moroccan mountains can be overcome by more holistic self-reliant and self-sufficiency programs.Appreciating and understanding how to deal with the geographic isolation of a community can help to raise the capacity of its economic or socio-economic cycle and create more selective pull thinking strategies. The spatial location can trigger clear breakthroughs or initiatives based on an abundant mindset, that sees the beauty in every condition.
2.9. Geographic Interpretation and Its Role in the Collected Problem Observations
- The spatial pattern of geography helps to collect deep observations that contain both clear and hidden opportunities. The geographical space requires interpretation with the dialectical awareness of the researcher. The different facets of the geographical components help to see different linkages with the problem observations and also appreciate the magnitude of opportunities within this problem. The uniqueness of the area present geographical knowledge.Ramos and Goihman (1989) seen that the geographic interpretation can improve even the household survey, and could help in stratifying better inputs when putting policies or designing quality of life initiatives. In a study conducted in the City of S. Paulo (Brazil), Ramos and Goihman utilised the realisation of the geographic area in assessing and then optimising the most suitable means for improving the health status and social support of elderly people living in this community. The general profile of the elderly was linked that they are living in an urban centre and this helped to stratify their socio-economic status according to the opportunities of their physical and mental health status, or the opportunities of their social support. Thus, the urban space enabled proper interpretation of people's living conditions to be made within the identified urban area of S. Paulo.The geographic interpretation would be of value, especially if we consider the density and the size of the population where the socio-economic problem is investigated. In the Brazilian case study presented by Ramos and Goihman (1989) the characteristics of the city of S. Paulo, being a constantly growing urban city with unique coffee business made the city host 11% of the economically active population of the country and led to its leadership with more than 35% of the Gross National Product. The highly dense population in the city, more than 15 million people are living in an area of 1493 sq.Km also has an ageing society where almost 9% of the population is aged 65 and over, despite the continuous influx of young migrants.The geographic interpretation helps underlines the role of the location in perpetuating the socio-economic problems thus realising the differentiation in the location, be it in its quality, economic opportunities and its cumulative effects on the quality of life. Thus, the geographical location affects the way we can optimise the different sources of none financial wealth and natural factors. Ramos and Goihman (1989).
3. Methodology
- Based on a lecture for Geography students for one of the European Universities that focused on the importance of geography as a subject for socio-economic problem solving; a series of questions were formulated by the students. Answering the questions of the students shed light on the scarcity of literature in the body of knowledge where no lots of work have tried to link between how to utilise the geographic area to tackle a socio-economic problem. Five case studies where identified to show examples of how geography can help in formulating the problem opportunities, or the solutions outcome. The literature reviewed supports the methodology despite its scarcity.
4. Application & Analysis
- Based on a lecture carried for a Geography class student at one of the Eastern Europe Universities, the experience of the researchers of tackling more 300 projects in 69 countries where shared. The researchers focused on the role of geography in helping overcome many socio-economic complex problems. Two outcomes came from this class: One- set of questions that could trigger further research in the future, specifically with the scarcity in literature. Two- a table that could be generalised further that would address the students appreciation of the role of geography in solving socio-economic problems.
4.1. Students Questions about the Importance of Geography in the Life of a Socio-Economic Problem Solving and Inspiration Economy Experts
- Q1: On which continent (Africa or Asia) has the self-sufficiency program been more successful in the fight against COVID-19 and why?A1: Africa is in high need for Self-Sufficiency (SF) programs, but countries as south-east Asia and India is more advanced in implementing SF programs. Q2: How has and will COVID-19 affect self-sufficiency programs in poorer areas?A2: SF helped, especially the rural areas, to survive and even thrive during the pandemic. They are more ready and more resilient since they have been used to poor supply chain and are born to be self-reliant.Q3: How did you start with these projects, or what was your initial motive that led you to this?A3: As an ‘inspiration economy’ experts, we look for opportunities inside each socio-economic problem. Geography can be a source of a problem and can be a source of opportunities. During the travelling of more than 69 countries, I realised the need to sustain the outcome of any change in any community and one of the main of techniques we developed is to build self-reliance according to the geography of the country.Q4: In which areas, or places do you implement the most projects?A4: our projects are focused on any community in need for change, or any community feel they are challenged by a complex problem. But mostly we are focused on under-developed countries or developing countries and specifically in the poor rural areas where the economic cycle is slow, or where there are many geographic resources in the area that are under-utilised.Q5: What do you think are the main reasons for such high unemployment in Arab countries?A5: The Arab countries suffer from a collection of problems that make their problem complex. Political outricity, instable economy linked to depleted resources as petrochemical, and mostly a total dependent culture, i.e. not self-sufficiency driven. Q6: In what way can students participate in your projects, or which projects are intended for students / youth?We have many projects regarding solving problems inside the local communities, or participating in projects in poor communities, or building self-sufficiency program within even organisations and communities. The target of the inspiration economy projects is to help the students understand what it means to create an inspiration economy, self-sufficiency, youth economy, resilience economy, foresight economy, etc. The students are expected to use the challenges of the local area to bring untapped solutions with minimal resources. It is worth to note that we also sponsor, with limited funds, social for non-profit projects that target to create change in the community, provide jobs for the underprivileged, women and youth, or exploit the resources and enhance the profit margin for those who need it. Then, the students were asked to refer to our projects on researchgate to bring further questions or define in what areas they would like work on using geographical information as an important input where codifying or stratifying the type of common good project they want to work on.
4.2. Role of Geography in Solving Socio-Economic Problems
- Table (1) is developed based on realising the literature gap in linking socio-economic problems to the geographic areas.
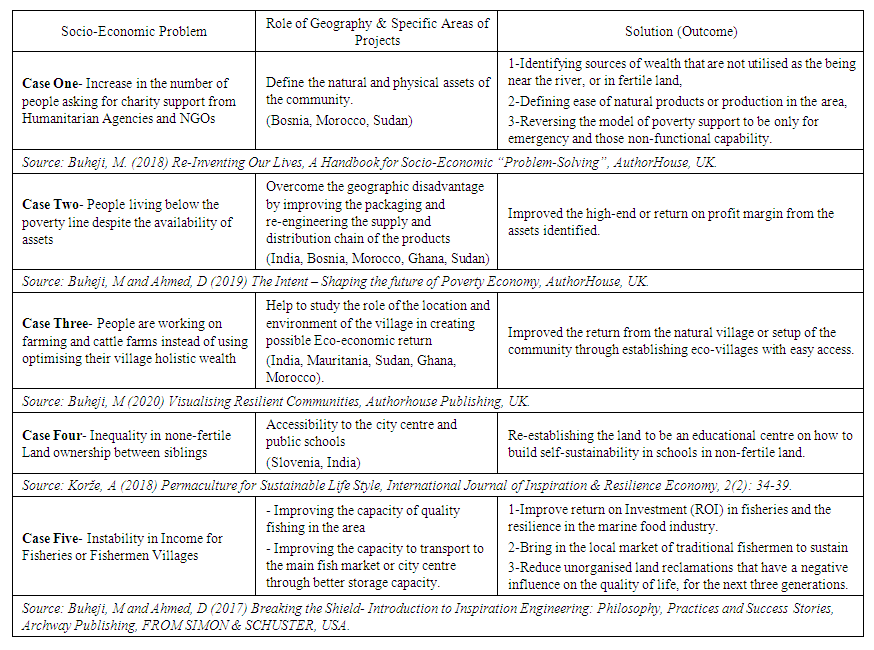 | Table (1). Cases Representing the Role of Geography in Socio-economic Projects |
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Realising Geography in Benefiting Sustained Quality of Life
- The outcome of this paper shows that many challenging problems and even potential valuable opportunities can be achieved through geography. From the past and till today, geography continues to play a source of interdisciplinary thinking that improves people’s lives. On the one hand, it was important to know the space that geography as a subject, represented by its physical capabilities; such as access to water, or fertile land, or the preparedness for the risk of flooding. Mishra (2011).Understanding the urban or rural remoteness were much appreciated for its role in the sustenance of the quality of life and for ensuring supply sites during the. While from another perspective, geography studies help to stratify and then organise the social life of the communities and influenced their socio-economic processes. With the outbreak of COVID-19 pandemic, where life came into a halt, geography has once again proved to be of importance to both physical and social assets.
5.2. Realising Geography in Benefiting Self-Sufficiency Programs
- The pandemic created a demand for change towards many fast response and self-reliance driven plans which optimised the utilisation for geography as a means for enhancing the availability of services and the agility of the supply chain. The importance of geography is expected to increase more folds with the global re-focus on the environmental challenges which now agree to be one of the main sources for the COVID-19 zoonotic virus pandemic. Geography can help to physically decrease diseases and even helping nature to have self-renewal. Another element that has proven to be importance during the pandemic is the accessibility to green areas. While the lockdown has forced people to live in blocks in the cities, between four walls, and today this considered one of the causalities of the mental health risks that came as a spillover after the pandemic. Therefore, access to nature in the rural areas and the countryside has played an extremely important role, and this is reflected in the trend of many people buying lands in the countryside (Vovk Korže, 2011).Today, and after living a wild capital-driven economy that created a materialistic and scarcity thinking mindset that dominated the world for over a century now, many ecosystems came to life again. The geographical space returned to be of high value as they are found they could contribute and create amazing differentiation to the economic cycle.
5.3. Realising Geography for Better Students Empowerment
- The outbreak of the COVID-19 strongly interfered with both the physical and the social space, which would have a great replication in the new normal. Therefore, it is necessary to upgrade geography to inspirational geography, where young people would learn about additional geographical elements, which classical geography does not cover. This was also shown by a short survey among students of geography at the University of Maribor, conducted by dr. Mohamed Buheji with lectures on the new role of geography. The students themselves said that they do not know the higher levels of geography and that they do not know how to connect thinking with spatial components. Using different approaches in education to excite students to the subject of Geography have been well established for a long time; however, the importance of inspirational driven geography, is not well address in literature. Students need to be given geographic observation collection assignments to upgrade their appreciation of the importance of area location and space in the provision of diversified resources that leads to more socio-economic opportunities. Inspirational-driven geography includes systems thinking, trans-disciplinarily, and active experimental learning. Through inspiration-driven geography, we can develop tools to enhance the outcome of the fieldwork, the case studies, the project work, the collaborative work.
5.4. Final Words
- Geography is a holistic discipline that can make a difference in the level of engagement with public life. However, despite the many pedagogical approaches, the role of geography is still not appreciated. In order to create the proper environment for the appreciation for geography a totally new approaches need to be exploited. Despite its limitation in the number of classes piloted, this paper bring an implication for a new line of research that optimise the utilisation of geography in solving socio-economic problems, besides improving the way geography is presented pedagogically. There are yet many opportunities that can be discovered with geography appreciation by further research in the future. Teaching geography with inspiration brings active involvement of all those involved in education and learning process. But what is most important is that geography when integrated with inspirational driven education can bring many changes to one’s mindset and this would help to improve our relationship and coexistence with both nature and people.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML