| [1] | Acaravci, A., & Ozturk, I. (2010). Electricity consumption-growth nexus: Evidence from panel data for transition countries. Energy Economics, 32(3), 604-608. Retrieved 7 16, 2020, from https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0140988309001996. |
| [2] | Alam, A., Malik, I. A., Abdullah, A. B., Hassan, A., Faridullah, Awan, U., . . . Naseem, I. (2015). Does financial development contribute to SAARC'S energy demand? From energy crisis to energy reforms. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 41, 818-829. Retrieved 7 23, 2020, from https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s1364032114007576. |
| [3] | Alam, F., Alam, Q., Reza, S., Khurshid-ul-Alam, S., Saleque, K., & Chowdhury, H. (2017). A Review of Hydropower Projects in Nepal. Energy Procedia, 110, 581-585. Retrieved 7 3, 2020, from https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s1876610217302187. |
| [4] | Alam, M. J., Alam, M. J., Begum, I. A., Buysse, J., & Huylenbroeck, G. V. (2012). Energy consumption, carbon emissions and economic growth nexus in Bangladesh: Cointegration and dynamic causality analysis. Energy Policy, 45, 217-225. Retrieved 7 16, 2020, from https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0301421512001395. |
| [5] | Anwar, M. A., Zhou, R., Asmi, F., Wang, D., & Hammad, A. (2019). Mapping The Evolution Of Energy‐Growth Nexus: Synergies And Trade‐Offs. Journal of Economic Surveys, 33(3), 968-998. Retrieved 7 24, 2020, from https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/joes.12306. |
| [6] | Arminen, H., & Menegaki, A. N. (2019). Corruption, climate and the energy-environment-growth nexus. Energy Economics, 80, 621-634. Retrieved 7 24, 2020, from https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s014098831930060x. |
| [7] | Asian Development Bank. (2016). Basic Statistics. Manila: ADB. |
| [8] | Aydin, M. (2019). Renewable and non-renewable electricity consumption–economic growth nexus: Evidence from OECD countries. Renewable Energy, 136, 599-606. Retrieved 7 23, 2020, from https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0960148119300084. |
| [9] | Bashier, A.-A. A. (2016). Electricity Consumption and Economic Growth in Jordan: Bounds Testing Cointegration Approach. European Scientific Journal, ESJ, 12(1), 429. Retrieved 7 16, 2020, from http://eujournal.org/index.php/esj/article/download/6909/6628. |
| [10] | Baz, K., Deyi, X., Ampofo, G. M., Ali, I., Khan, I., Cheng, J., & Ali, H. (2019). Energy consumption and economic growth nexus: New evidence from Pakistan using asymmetric analysis. Energy, 189, 116254. Retrieved 7 24, 2020, from https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0360544219319498. |
| [11] | Benkraiem, R., Lahiani, A., Miloudi, A., & Shahbaz, M. (2019). The asymmetric role of shadow economy in the energy-growth nexus in Bolivia. Energy Policy, 125, 405-417. Retrieved 7 23, 2020, from https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0301421518307146. |
| [12] | Central Bureau of Statistics. (2015, November 24). Nepal in Numbers. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal. |
| [13] | Dinç, D. T., & Akdoğan, E. C. (2019). Renewable Energy Production, Energy Consumption and Sustainable Economic Growth in Turkey: A VECM Approach. Sustainability, 11(5), 1273. Retrieved 7 23, 2020, from https://mdpi.com/2071-1050/11/5/1273. |
| [14] | Galadima, M. D., & Aminu, A. W. (2020). Nonlinear unit root and nonlinear causality in natural gas - economic growth nexus: Evidence from Nigeria. Energy, 190, 116415. Retrieved 7 26, 2020, from https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0360544219321103. |
| [15] | Halisçelik, E., & Soytaş, M. A. (2019). Sustainable development from millennium 2015 to Sustainable Development Goals 2030. Sustainable Development, 27(4), 545-572. Retrieved 7 6, 2020, from https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/sd.1921. |
| [16] | Hassan, S. T., Xia, E., Latif, K., Huang, J., & Ali, N. (2019). Another Look at the Nexus Among Energy Consumption, Natural Resources, and Gross Capital Formation: Evidence from Pakistan. Natural resources research, 1-12. Retrieved 7 26, 2020, from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11053-019-09607-0. |
| [17] | Mahi, M., Phoong, S. W., Ismail, I., & Isa, C. R. (2019). Energy–Finance–Growth Nexus in ASEAN-5 Countries: An ARDL Bounds Test Approach. Sustainability, 12(1), 5. Retrieved 7 24, 2020, from https://mdpi.com/2071-1050/12/1/5. |
| [18] | Marques, L. M., Fuinhas, J. A., & Marques, A. C. (2017). On the Dynamics of Energy-growth Nexus: Evidence from a World Divided into Four Regions. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy, 7(3), 208-215. Retrieved 7 24, 2020, from https://dergipark.org.tr/tr/pub/ijeeep/issue/31922/351241. |
| [19] | Ministry of Finance. (2016). Economic Survey 2015-2016. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal. |
| [20] | Mustafa, G., Latif, I. A., Shah, S. Z., & Bashir, M. K. (2016). Nexus between CO2 Emission, Energy Consumption and Economic Growth in ASEAN Countries Plus China. American Journal of Environmental Sciences, 12(4), 299-307. Retrieved 7 24, 2020, from https://thescipub.com/abstract/10.3844/ajessp.2016.299.307. |
| [21] | Nazlioglu, S., Kayhan, S., & Adıgüzel, U. (2014). Electricity Consumption and Economic Growth in Turkey: Cointegration, Linear and Nonlinear Granger Causality. Energy Sources Part B-economics Planning and Policy, 9(4), 315-324. Retrieved 7 16, 2020, from https://tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/15567249.2010.495970. |
| [22] | Nepal Electricity Authority. (n.d.). Retrieved 7 3, 2020, from http://www.nea.org.np/about-us.html. |
| [23] | Nepal, R., & Paija, N. (2019). A multivariate time series analysis of energy consumption, real output and pollutant emissions in a developing economy: New evidence from Nepal. Economic Modelling, 77, 164-173. Retrieved 7 24, 2020, from https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0264999317316863. |
| [24] | Ozturk, F., & Ozturk, S. (2018). Exploring the Nexus of Coal Consumption, Economic Growth, Energy Prices and Technological Innovation in Turkey. Asian Economic and Financial Review, 8(12), 1406-1414. Retrieved 7 24, 2020, from https://ideas.repec.org/a/asi/aeafrj/2018p1406-1414.html. |
| [25] | Pachauri, S. (2014). Energy access, poverty, and development: the governance of small-scale renewable energy in developing Asia | Energy access, poverty, and development: the governance of small-scale renewable energy in developing Asia, Benjamin K. Sovacool, Ira Martina Drupady (2012). Energy, 68, 1007-1008. Retrieved 7 6, 2020, from https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0360544214002187. |
| [26] | Pandit, A., Pandit, A., Ishaq, S., Mamnun, N., Ahmad, B., & Jamil, M. (2019). Hydropower development in the Hindu Kush Himalayan region: Issues, policies and opportunities. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 107, 446-461. Retrieved 7 23, 2020, from https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s1364032119301431. |
| [27] | Parajuli, R., Østergaard, P. A., Dalgaard, T., & Pokharel, G. R. (2014). Energy consumption projection of Nepal: An econometric approach. Renewable Energy, 63, 432-444. Retrieved 7 29, 2020, from https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/s0960148113005272. |
| [28] | Pesaran, M. H., Shin, Y., & Smith, R. J. (2001). Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. Journal of Applied Econometrics, 16(3), 289-326. Retrieved 7 24, 2020, from https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/jae.616. |
| [29] | Pradhan, R. P. (2010). Energy Consumption- Growth Nexus in SAARC Countries: Using Cointegration and Error Correction Model. Mathematical Models and Methods in Applied Sciences, 4(4), 74. Retrieved 7 16, 2020, from http://ccsenet.org/journal/index.php/mas/article/view/4927. |
| [30] | Proposal for Sustainable Development Goals .:. Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform. (n.d.). Retrieved 7 3, 2020, from Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform: http://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/focussdgs.html. |
| [31] | Rahman, M. M., & Velayutham, E. (2020). Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption-economic growth nexus: New evidence from South Asia. Renewable Energy, 147, 399-408. Retrieved 7 26, 2020, from https://sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0960148119313370. |
| [32] | Rana, B. (2020). A SWOT Analysis of Nepalese Hydropower Policy. Advanced Journal of Social Science, 7(1), 71-80. https://doi.org/10.21467/ajss.7.1.71-80. |
| [33] | Rashid, A., & Yousaf, N. (2015). Linkage of financial development with electricity-growth, nexus of India and Pakistan. EuroEconomica, 34(2), 151-160. Retrieved 7 24, 2020, from https://ideas.repec.org/a/dug/journl/y2015i2p151-160.html. |
| [34] | Rauf, A., Zhang, J., Li, J., & Amin, W. (2018). Structural changes, energy consumption and Carbon emissions in China: Empirical evidence from ARDL bound testing model. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, 47, 194-206. |
| [35] | Sbia, R., Shahbaz, M., & Ozturk, I. (2017). Economic Growth, Financial Development, Urbanization and Electricity Consumption Nexus in UAE. Retrieved 7 16, 2020, from https://tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/1331677x.2017.1305792. |
| [36] | Sen, A., Nepal, R., & Jamasb, T. (2018). Have model, will reform: assessing the outcomes of electricity reforms in non-OECD Asia. The Energy Journal, 39(4), 181-209. Retrieved 7 6, 2020, from http://dro.dur.ac.uk/24193. |
| [37] | Shahateet, M. I., Al-Majali, K. A., & Al-Hahabashneh, F. (2014). Causality and Cointegration between Economic Growth and Energy Consumption: Econometric Evidence from Jordan. International journal of economics and finance, 6(10), 270. Retrieved 7 12, 2020, from https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/59067/1/mpra_paper_59067.pdf. |
| [38] | Shakya, S., Nepal, R., & Sharma, K. (2018). Electricity consumption and economic growth: empirical evidence from a resource-rich landlocked economy. International Journal of Global Energy Issues, 41, 226-247. Retrieved 7 3, 2020, from http://ecite.utas.edu.au/129844. |
| [39] | Sharma, K., Bhattarai, B., & Ahmed, S. (2019). Aid, Growth, Remittances and Carbon Emissions in Nepal. The Energy Journal, 40(1), 129-141. Retrieved 7 23, 2020, from https://researchers.cdu.edu.au/en/publications/aid-growth-remittances-and-carbon-emissions-in-nepal. |
| [40] | Sikdar, C., & Mukhopadhyay, K. (2018). The Nexus Between Carbon Emission, Energy Consumption, Economic Growth And Changing Economic Structure In India: A Multivariate Cointegration Approach. Journal of Developing Areas, 52(4), 67-83. Retrieved 7 24, 2020, from https://muse.jhu.edu/article/678189. |
| [41] | Solarin, S. A. (2011). Electricity consumption and economic growth: trivariate investigation in Botswana with capital formation. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy, 1(2), 32-46. Retrieved 7 16, 2020, from http://r6a.cn/a9tN. |
| [42] | Sustainable Development Goals .:. Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform. (n.d.). Retrieved 7 6, 2020, from Division for Sustainable Development Goals, United Nations: http://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/?menu=1300. |
| [43] | Zeren, F., & Akkuş, H. T. (2020). The relationship between renewable energy consumption and trade openness: New evidence from emerging economies. Renewable Energy, 147, 322-329. |
| [44] | Zeshan, M., & Ahmed, V. (2013). Energy, environment and growth nexus in South Asia. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 15(6), 1465-1475. Retrieved 7 24, 2020, from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10668-013-9459-8. |
| [45] | Zortuk, M., & Karacan, S. (2018). Energy–growth nexus revisited: an empirical application on transition countries. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 20(2), 605-623. Retrieved 7 23, 2020, from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10668-016-9901-9. |



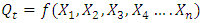 where
where 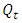 is the quantity of output, while
is the quantity of output, while 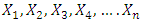 are the quantities of factor inputs (such as capital, labor, land or raw materials). Since this study focuses on the dynamic relationships between economic variables, electricity consumption and trade openness, we will apply the following functional form, which is also used by numerous other studies as highlighted above:
are the quantities of factor inputs (such as capital, labor, land or raw materials). Since this study focuses on the dynamic relationships between economic variables, electricity consumption and trade openness, we will apply the following functional form, which is also used by numerous other studies as highlighted above: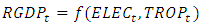
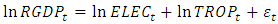
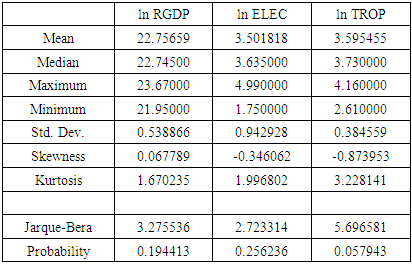
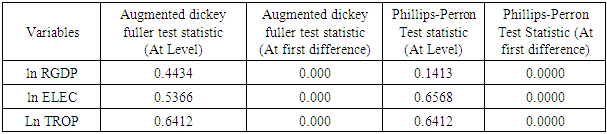
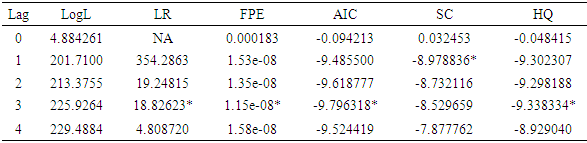
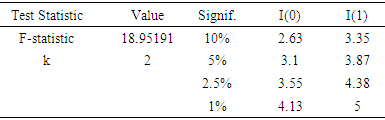
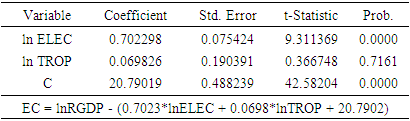
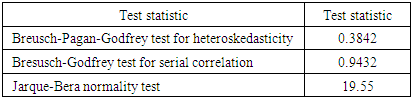
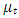 is the error term. Since the data are yearly figures, we need to apply the unit root test to check the stationary of the variables. Augmented Dickey–Fuller (ADF) test, an augmented version of the Dickey-Fuller test. Thereafter, ARDL co-integration test is used to examine the existence of a long run relationship between the variables. The ARDL cointegration approach was developed by Pesaran and Shin (Pesaran, Shin, & Smith, 2001). This approach has three distinct advantages. Firstly, this approach can be effectively used to estimate the long-run and short-run relationship simultaneously. Secondly, the method can be applied even when the variables have mixed integration orders. And thirdly, the method is found to yield better results for finite data sets. Since we are using a 30 years period, this method is suitable for our study. In addition, the ARDL model take care of endogeneity issue by adding lags of dependent as well as in-dependent variables in the model. The Autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) model is written as
is the error term. Since the data are yearly figures, we need to apply the unit root test to check the stationary of the variables. Augmented Dickey–Fuller (ADF) test, an augmented version of the Dickey-Fuller test. Thereafter, ARDL co-integration test is used to examine the existence of a long run relationship between the variables. The ARDL cointegration approach was developed by Pesaran and Shin (Pesaran, Shin, & Smith, 2001). This approach has three distinct advantages. Firstly, this approach can be effectively used to estimate the long-run and short-run relationship simultaneously. Secondly, the method can be applied even when the variables have mixed integration orders. And thirdly, the method is found to yield better results for finite data sets. Since we are using a 30 years period, this method is suitable for our study. In addition, the ARDL model take care of endogeneity issue by adding lags of dependent as well as in-dependent variables in the model. The Autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) model is written as 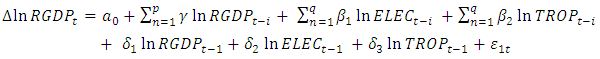
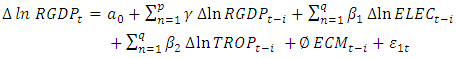
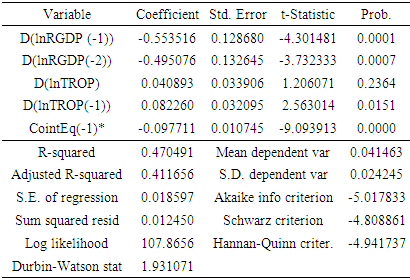
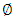 captures the speed of adjustment,
captures the speed of adjustment, 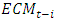 represents disequilibrium or the error correction term, and
represents disequilibrium or the error correction term, and  denotes first difference. The error correction coefficient indicates the speed of re-adjustment to the long-run equilibrium after short-run shocks lead to disequilibrium. After ECM, we finally conduct some diagnostic tests including the cumulative sum (CUSUM) of recursive residual and cumulative sum of squares (CUSUMSQ) of recursive residual tests to examine the stabilization of estimated coefficients in the long run and short run.
denotes first difference. The error correction coefficient indicates the speed of re-adjustment to the long-run equilibrium after short-run shocks lead to disequilibrium. After ECM, we finally conduct some diagnostic tests including the cumulative sum (CUSUM) of recursive residual and cumulative sum of squares (CUSUMSQ) of recursive residual tests to examine the stabilization of estimated coefficients in the long run and short run.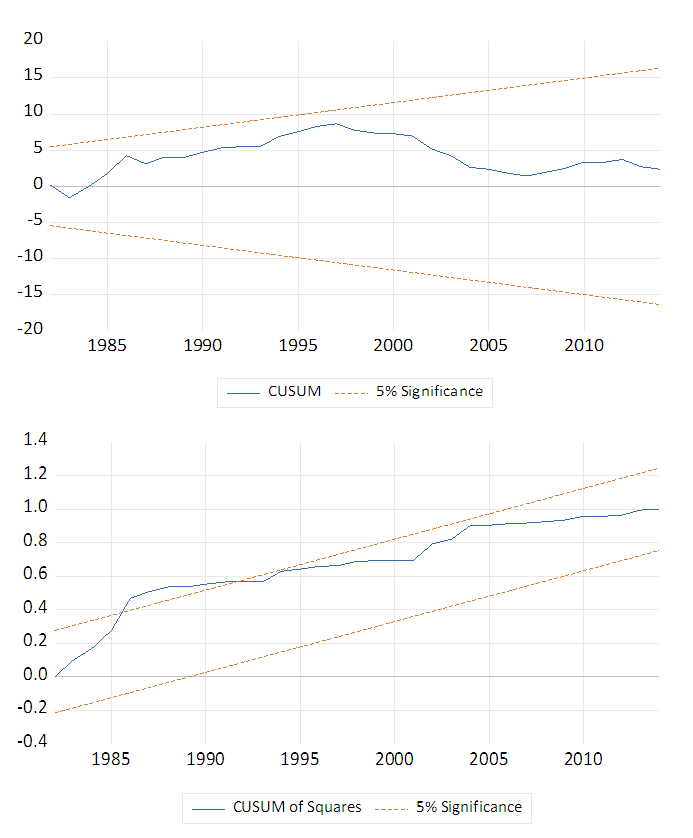
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML