-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2020; 10(3): 163-171
doi:10.5923/j.economics.20201003.06

Influential Factors on Consumers’ Online Purchasing Decision in Bangkok, Thailand
Benjawan Suppasilp1, Chaiyawat Suppasilp2
1School of Economics, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China
2Department of Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Mahidol University Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital, Thailand
Correspondence to: Benjawan Suppasilp, School of Economics, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

With the development of technology like electronic devices and the internet has invented a new channel of commerce, Electronic commerce (E-commerce). Countless consumers had changed their shopping behavior and consider online shopping channel as the convenience of living. The online shopping channels are new opportunities for investors and retailers to get benefits and advantages of selling goods and services. However, there are still some challenges and obstacles for online retailers to maximize consumer satisfaction and replace the traditional shopping behavior. This research is the study on influential factors affecting online shopping decisions in Bangkok, Thailand, by using Factors, Filtering element and Filtering buying decision theory (FFF model). The surveys were collected in different districts in Bangkok, where is the capital city of Thailand, and the high percentage of mobile penetration and internet users. Also, Thailand’s E-commerce had been growing statistically in the past few years. The study had collected the total number of 419 surveys for analysis. The results found that gender, occupation, address, educational background, income, and privacy are statistically significant factors affecting online shopping decisions in Bangkok. Analyzing by theorized FFF model, the results found that privacy of consumers is the most concerned while security factors and trust and trustworthiness factors were less affected. Therefore, to overcome all challenges and obstacles and maximize online consumer satisfaction, E-marketplace should invent a high security platform and prevent consumers’ personal information and protect consumers’ privacy.
Keywords: E-commerce, Online shopping, Consumer behaviors, Factors - Filtering elements - Filtering buying behavior model (FFF model)
Cite this paper: Benjawan Suppasilp, Chaiyawat Suppasilp, Influential Factors on Consumers’ Online Purchasing Decision in Bangkok, Thailand, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 10 No. 3, 2020, pp. 163-171. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20201003.06.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Electronic commerce (E-commerce) historically meant the process of execution of electronic commercial transactions with technologies such as Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT). The EDI requires agreement between trading partners in order to govern their electronic trading relationship [1]. It gave a massive opportunity for users to exchange business information, do electronic transactions, and share commercial documentation electronically. In 2000, the definition of E-commerce was changed to the process of purchasing of available goods and services over the internet using secure connections and electronic payment services [2]. Since then, E-commerce has been using as an online channel for business and transformed traditional shopping beyond expectations. E-commerce today gained a high level of popularity since its convenience and reliability. People highly accept in online shopping, and it becomes the shopping nature of consumers. In the foreseeable future, E-commerce will be the ultimate tool for commerce with sales boom around the world. E-commerce business types can be classified into four basic types of commerce, which are B2B, B2C, C2C, B2G. Business-to-Business (B2B): the online transactions of goods or services through online channels between company to company. It does not engage in sales to the consumer public. Business-to-Consumer (B2C): companies sell their goods or services through online channels to consumers who are the end-users. Consumers buy products or services for self uses. The shop websites open for any users or visitors. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C): this type of E-commerce encompasses all electronic transactions of goods or services between individuals through the third-party platform. Business-to-Government (B2G): the government offers a project and put out tenders1 which companies bid for. Then the government reviews and selects the company that meets their price expectation.
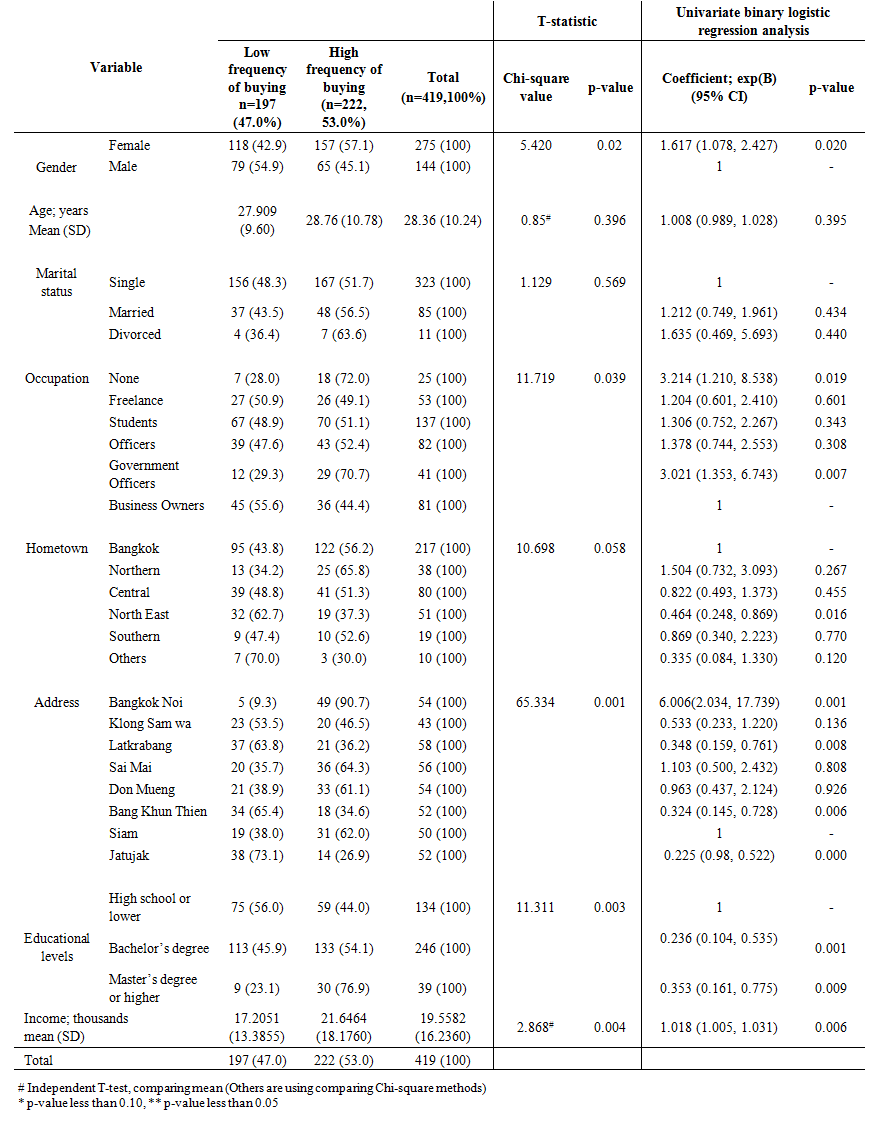 | Table 1. Demographic data and Univariate binary logistic regression analysis |
2. Factors, Filtering Elements, Filtering Buying Decision (FFF Model)
- The consumers' behavior model is a base theory for consumers who would like to purchase a product or services. This theory is used and applied to most of consumer behavior theory, including Factors, Filtering elements, Filtering buying behavior model (FFF model). The FFF model is developed by Dr. Ujwala Dange and Professor Vinay Kumar [6]. The FFF model is developed based on the consumers' behavior model, but the developers had noticed the differences in buying behavior between the physical store and online store. Therefore, the developers decided to include concerned elements and buying behavior of consumers when they would like to purchase online, which are filtering elements and filtering buying behavior.
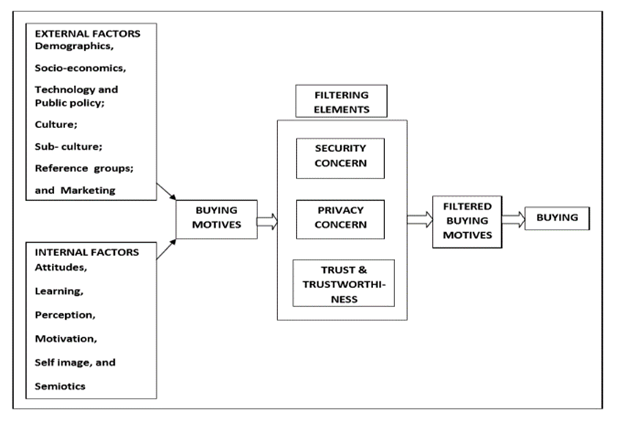 | Figure 1. Online consumer buying behavior motive model, Factors (F), Filtering elements (F) and Filtered buying motive (F); (FFF Model) |
3. Research Methodology
- The methodology for this paper is qualitative and quantitative analysis, using survey questionnaires as tools for collecting data. Survey questions will be about general information of participants (demographic information and socio-economic characteristic) and opinions towards online shopping (influential factors and others) to identify the relationship to an online purchasing decision.ParticipantsTargeted participants will be Thai people who live in Bangkok and have online shopping experiences by E-marketplace. The reason for choosing Bangkok as the target city because Bangkok is the capital of Thailand, and people in Bangkok adapt and use the internet and technology in their daily living. The number of participants is calculated from Cochran’s sample size formula [10].
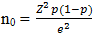 n0 = the sample sizeZ2 = the abscissa of the normal curve that cuts off an area α at the tails (1 - α equals the desired confidence level, e.g., 95%, Z value will equal to 1.96)e = the desired level of precision,p = the estimated proportion of an attribute that is present in the population, q =1-p. As mentioned, we want to calculate a sample size of a large population by assuming the maximum variability, which is equal to 50% (p =0.5) and taking 95% confidence level with ±5% precision the calculation for required sample size will be
n0 = the sample sizeZ2 = the abscissa of the normal curve that cuts off an area α at the tails (1 - α equals the desired confidence level, e.g., 95%, Z value will equal to 1.96)e = the desired level of precision,p = the estimated proportion of an attribute that is present in the population, q =1-p. As mentioned, we want to calculate a sample size of a large population by assuming the maximum variability, which is equal to 50% (p =0.5) and taking 95% confidence level with ±5% precision the calculation for required sample size will be 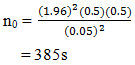 From the calculation, the total number of participants should be 384 participants for survey questions. Nevertheless, to prevent the information lost and incomplete information, I would like to collect 460 surveys for this research, which is approximately 20 percent of the calculated participants number. Participants selection methods will be random sampling selection by using districts in Bangkok as an edge of these surveys. There are 51 districts in Bangkok; however, the researcher would like to select eight districts for selecting survey information since these eight districts are the highest population density area in Bangkok.
From the calculation, the total number of participants should be 384 participants for survey questions. Nevertheless, to prevent the information lost and incomplete information, I would like to collect 460 surveys for this research, which is approximately 20 percent of the calculated participants number. Participants selection methods will be random sampling selection by using districts in Bangkok as an edge of these surveys. There are 51 districts in Bangkok; however, the researcher would like to select eight districts for selecting survey information since these eight districts are the highest population density area in Bangkok. 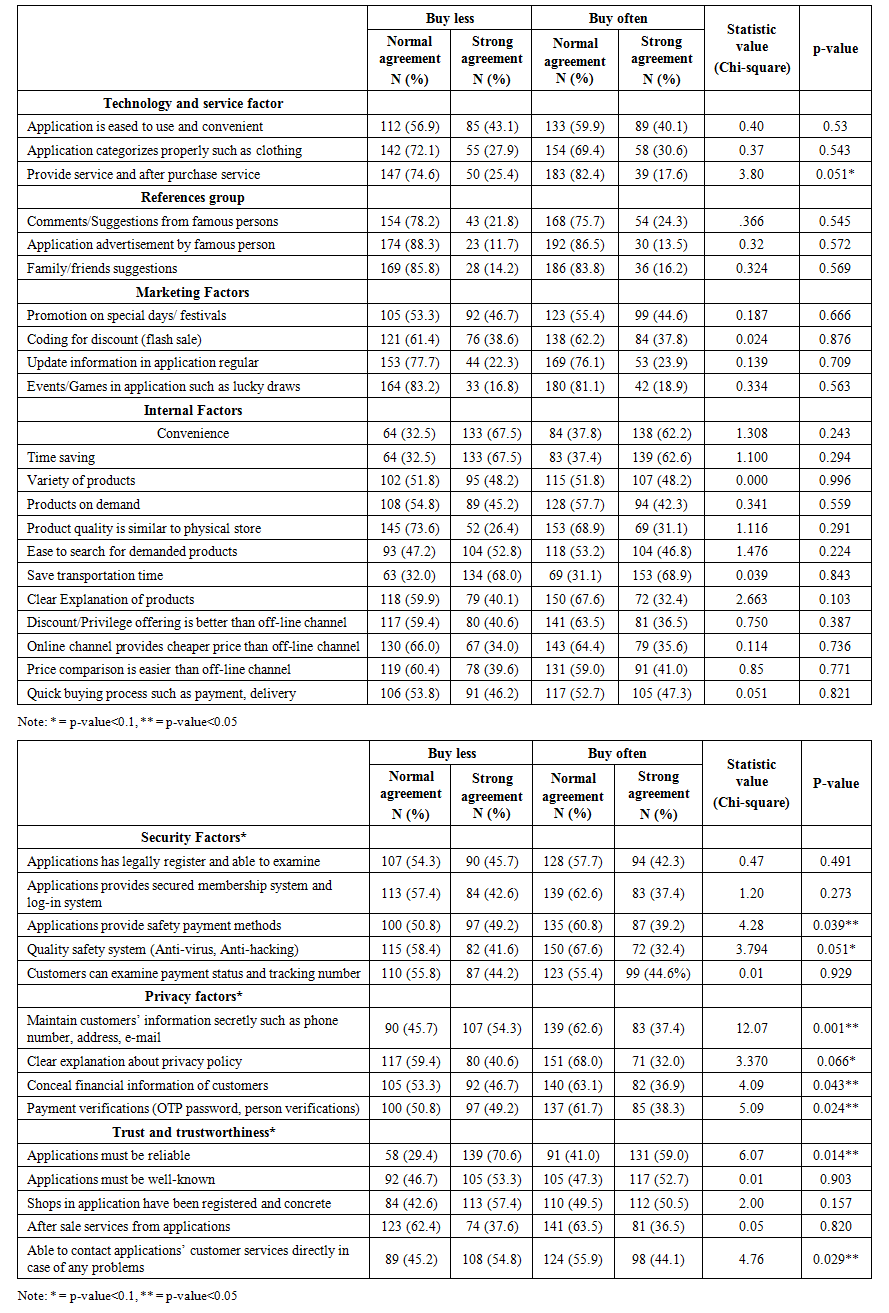 | Table 2. External factors, Internal factors and filtering elements’ s statistic value |
4. Result of Study
- The total of the sample population is 275 females, 65.65%, and 144 males 34.36%. The average age of total sample participants is 28.36 years old, with a standard deviation of 10.24. The marital status of total participants is single (77.08%), married (20.28%), and divorced (2.62%). The occupations of total participants are none (5.96%), freelance (12.64%), students (32.69%), officers (19.57%), government officers (9.78%), and business owners (19.33%). The hometowns of total participants are Bangkok (51.78%), Northern (9.06%), Central (19.09%), North East (12.17%), Southern (4.53%), and others (2.38%). The current address of total participants is at Bangkok Noi (12.88%), Klong Sam Wa (10.26%), Lat Kra Bang (13.84%), Sai Mai (13.36%), Don Muang (12.88%), Bang Khun Thien (12.41%), Siam (11.93%) and Jatujak (12.41%). The educational backgrounds of total participants are primary (3.34%), high school (28.63%), Bachelor’s (58.71%), Master’s (7.15%) and Ph.D. (1.67%). The average income of total participants is 19,558.2 baht, with the standard deviation of 16.236.Regarding to Chi-square and Univariate regression analysis, the results shows that gender has statistically significant affected online shopping decision, which means female has higher opportunity to be in high frequency of buying group than male by 1.617 times. The marital status does not statistically affect online shopping decision. By using univariate regression analysis, comparing to divorced group as a dummy variable, the single and married group have higher opportunity to be in high frequency of buying group by 1.212 and 1.635 times; however, it is not statistically significant at 0.005. The different in occupation does affect online shopping decision statistically. Comparing to business owner’s occupation, unemployed, government officers have high opportunity to be in high frequency of buying group by 3.214 and 3.021 times. Other occupations also have higher opportunity to be in high frequency of buying group at 1.204, 1.306 and 1.378 times, comparing to business owners’ group. The hometown slightly does not affect online purchasing decision. Comparing with Bangkok as a dummy variable, Northern has higher opportunity to be in high frequency of buying group by 1.504 times, while other hometowns have high opportunity to being low frequency of buying group. The current addresses have statistically and significantly affected consumer’s online shopping decision. Comparing with the Siam district, Bangkok Noi and Sai Mai districts have higher opportunity to be in high frequency of buying group. While other districts have higher opportunity to be in low frequency of buying group. For the educational background, it does affect online shopping decision. Comparing to high school or lower degree, Bachelor;s degree and Master’s degree or higher have high opportunity to be in low frequency of buying group with statistical significance at 0.005. The different age does not affect online purchasing decisions statistically; however, the study found that the increase in age for one year, the opportunity of online shopping increase by 1.008. The monthly income also affects online shopping decisions statistically, which means the growth of monthly income in every thousand baht, the higher the opportunity to increase the online shopping decision by 1.018. To analyze individual variables from external factors, internal factors, and filtered elements. The statistical study found that consumers in Bangkok concern about technology and services factors, particularly in services and after-sale service, with a statistical value of 3.80 and asymptotic significance (P-value) less than 0.100. In addition, the safety system, such as anti-virus and virus protection, is another consumers’ concern, at statistic value at 3.794 and P-value less than 0.100. The privacy policy also has a statistical significance value at 3.370 and a P-value less than 0.100, which consumers slightly concern about the privacy policy of application. Other factors that consumers concern, and they are statistically significant toward online shopping decisions at P-value less than 0.050. There are safety payment methods, concealing consumers’ financial information, payment verification, application’s reliability, concealing consumers’ personal information, and application’s customers' services. Analyzing all independent variables simultaneously by using Multivariate binary logistic regression analysis. To see which variables are the most concern for customers in the high frequency of buying group when analyzing all variables at the same time. The results showed that gender still is a crucial variable for consumers, and females have higher opportunities to be in high frequency of buying group than males. The monthly income is still the significant variable that affects online shopping decisions, but the exponential Beta had changed from 1.018 to 1.033. This means every increase in a monthly income of thousand baht, the increase in online shopping will be 1.033. The last factor that statistically affects online shopping decision is internal factors, which are the perception and attitudes of consumers toward online shopping decision. This implies an increase of one score in internal factors will increase the online shopping decision by 1.061. After using multivariate binary regression analysis, there are some changes in the significance of variables such as occupation, hometown, current address, education, and filter elements such as security factors, privacy factors, and trust and trustworthiness of application. The results from the analysis are consistent with the study of Baubonienė and Gulevičiūtė [11], researchers from Lithuania, their study is about E-commerce factors influencing consumers’ online shopping decision. The reasons consumers would like to shop online are internal factors such as convenience and simplicity as the first reason. For second reason is the lower price of products through online channels. Also, gender plays another significant variable affect online shopping decisions. However, the study is not consistent with the study of Miss Jutarat Kaidrasamee [5]. The study shows that the only variable affects online shopping decision is occupation, and there are no statistical association with age, gender, monthly income, and educational background.
5. Discussion
- The increase of uses of smartphones and the internet impacts an individual’s daily life, also the shopping behavior. Many consumers start using online shopping channels for convenience and time-saving. Since anyone can access to the internet and use the online shopping application, there are some influential factors causing consumers whether to buy or not. From the study, the online consumers mostly are freelance, students, officers, government officers, and business owners with an average age at 20s years old and in 8 different districts in Bangkok. The researcher found that three main issues should be focused.
|
6. Conclusions
- Online shopping channels have become a new alternative for people to purchase goods and services. Comparing offline shopping behavior, online shopping channels had changed consumers’ behavior in terms of variety of products alternative, price comparison, and expected quality of products. Consumers might have positive or negative experiences from online shopping. To maximize consumers’ satisfaction, studying of influential factors affecting online shopping decision is significant for companies and online sellers. The FFF model is designed for consumers’ online shopping behavior due to the filtered elements, security, privacy and trust and trustworthiness of application or online channels that consumers concern. To summarize all influential factors affecting online shopping decision, external factors (demographic information, socioeconomic, technology and services), internal factors (convenience, time-saving and transportation cost), security factors ( anti-virus system and payment methods), privacy factors (concealing personal information, financial information, payment verification and privacy policy), and trust and trustworthiness factors (reliability of application and application’s services) are the most concerned factors for consumers in Bangkok, Thailand.All in all, any factors could not be significant if consumers have negative attitudes and perception toward online shopping. Companies and online sellers should provide quality products and services to impress consumers and create positive experiences and perception toward online shopping. Thus, consumers will have trust in online shopping channels.
Note
- 1. To put out a tender means to ask companies to say formally at what price they would like to charge for a project.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML