-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2019; 9(2): 65-69
doi:10.5923/j.economics.20190902.04

The Evolution of the Theory of Value: from Marx to Crypto Currency
Saif Ahmed Abdulhakeem, Wang Qinmei
International Business School, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China
Correspondence to: Saif Ahmed Abdulhakeem, International Business School, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

A commodity, according to Marx, is any good or service within which a socially necessary labor time is needed so that its value is being derived from the time spent by the laborer. A given commodity has an exchange value and can play the role of medium of exchange, as well as fulfil all the other functions of money, precisely because it is a commodity. This applies to the precious metals, gold and silver, in the same way it applies to all the various commodities which, throughout history, have functioned as money. In today’s world, there are some commodities in the shape of services cryptographically provided, like Bitcoin, but the value derived from the labor time is barely noticed causing others to view the face-value of such commodities equal to ZERO. Though in reality some digital currencies, in which the labor time is scarcely rooted, have more value than gold or fiat money, yet others see it as only a bubble and it won’t last too long until it goes back to zero. This paper is an attempt to view and discuss the evolution of the theory of value from the classical to the modern aspect with Crypto Currencies. The paper starts off with an introduction to the Bitcoin system viewing the process that it followed to become a so-called currency. Then it proceeds to analyze the nature of bitcoin according to Marx’s theory of money as it looks at the reasons behind bitcoin getting this value, and last looks at the difference in fluctuation between cryptocurrencies and fiat money as well as the reasons behind the high volatility experienced in Bitcoin.
Keywords: Bitcoin, Cryptocurrencies, The evolution of the theory of money
Cite this paper: Saif Ahmed Abdulhakeem, Wang Qinmei, The Evolution of the Theory of Value: from Marx to Crypto Currency, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 9 No. 2, 2019, pp. 65-69. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20190902.04.
Article Outline
- Hypothesis of the study: It is hypothesized that Bitcoin is not a currency but a digital version of what we call collectables.
1. Introduction
- Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer electronic cash system that facilitates transactions between two parties without any central oversight. Though it works as a medium of exchange, yet with no physical location. This system was lunched almost ten years ago, 2009, by Satoshi Nakamoto, the father of Bitcoin whose real identity remains unknown. The first and only objective for this system was just to work as a medium of exchange providing two willing parties with cryptographic proof instead of trust when dealing online and without the need for a trusted third party. Such system is meant to protect both sellers and buyers from fraud as it provides a solution to the double-spending problem experienced in online trading. This system depends on computational power and it is secure as long as honest nodes collectively control more CPU power than any cooperating group of attacker nodes.The unit of account of this system is bitcoin as a digital currency, cryptocurrency referred to as BTC. This coin is being generated as a reward to miners who devote their computers and CPU power to solving complex mathematical puzzles while processing transactions. Miners are rewarded with BTC for each new block (Complex mathematical puzzle) discovered. Satoshi’s system employs algorithm that increases the difficulty of the work needed as more mining capacity is added to the pool. The top limit of bitcoins in the system is 21 million bitcoins, but it is estimated that it will need at least 100 years to mine all bitcoins available due to the doubled increase in effort required to mine each new bitcoin.Though it’s been less than a decade since BTC has come to existence, yet it is now the most popular and valuable digital currency in the market as it is today, 29th of Jan 2019, $3.425. The BTC, functionally, serves the same purpose as fiat money like U.S. dollars or Chinese Yuan, except that it’s not tied to a central bank and is not regulated by a specific government or a treasury. Bitcoin transactions take place entirely over the internet and offer a great deal of anonymity to users. These transactions are securely recorded in a public ledger called a blockchain, and users trade bitcoins in an exchange as they have the option to store them in a digital cryptocurrency wallet.Since bitcoin transactions are mostly anonymous and unregulated by a central bank, it has gained a great reputation for being the currency of choice on the dark-web when trading illicitly. Online marketplaces like the Silk Road became even notorious for selling drugs and weapons, netting their owners millions in the process and drawing away the attention of federal authorities.Like any other currency, bitcoins are bought, sold, and even traded on currency exchange platforms. Some stores and businesses have even accepted it as a payment method for years now, but recently especially with the great devaluation witnessed this year just gone, from almost $20.000 to $3.425 per 1 BTC, much doubts have arisen concerning bitcoin whether it would continue devaluing or instead gaining its power back. Some others even started to trade their tokens back to fiat money speculating that bitcoin would keep devaluing as others started to believe that such a currency is only a bubble existed in the air for a short period of time and its fair value is just ZERO.
2. Bitcoin Analysis Based on Marx’s Theory of Money
- A commodity, in Marx’s dictionary, is a good or service that requires a particular amount of time, exactly like gold needing time for being digged out of the ground. The value that gold carries is being derived from the value of the socially labor time spent on mining it. The father of Marxism, Marx, presented his theory of money as being a true application of the labor theory of value that defines the value of any good or service being ultimately determined by the amount of labor used to produce it. The theory of money is, in one way or another, a commodity theory of money that states “a given commodity can play the role of a medium of exchange trading for another commodity in proportion to the labor time they contain”.Gold is known as a precious commodity and any given commodity can be a medium of exchange for other commodities. Money, during the "underdeveloped" stages of the economy, was presented in the shape of gold since the latter could be measured in precise amounts, and this alone made gold more opportune than other commodities. And therefore, the value of gold was adopted by society as a universal measurement for other commodities and that’s how a commodity like gold became commodity money.Since a precious commodity like gold was once money, money then is a special commodity within which a specific amount of labor time is rooted. But in today’s world with the developing technologies and business virtualization, money no longer has the gold standard form but does have different ones. The standard that money is represented by still serves as a store of value but that value remains somehow tied to the socially necessary labor time. Moreover, today’s money is no longer tied to the value of a specific commodity but rather it measures the value of commodities internationally.The value of a given commodity, according to Marx, is defined by the labor time used to produce it. And modern economists see that the value of a commodity is not only determined by the labor time, but also by the subjective valuation of consumers, the willingness of buyers wishing to pay for a specific item. The one obvious item that refutes the labor theory of value is bitcoin, the most famous cryptocurrency so far. Bitcoin has no physical appearance and there is no labor time rooted in so, yet it is backed by the power of educational technology and the energy security of the computing processes and capabilities. This coin is being generated every 10 minutes as a reward to users processing a number of transactions. The actual work done in processing these transactions is conducted by high-powered computers, machines, and not by human beings. Sure, those computers were produced by human beings in the first place, but computers can’t add new value to a specific commodity because only living labor can. Machines just pass a percentage amount of their value to the bitcoins, so each generated bitcoin has a proportion of the machines’ total value. And since there’s no direct labor time rooted in such a thing, according to Marx, then the fair value of bitcoin as a commodity is ZERO. Bitcoin’s value, like any other goods or services, is derived from the willingness of us wishing to pay for it.Moreover, money is a financial instrument, and the value of any financial instrument comes from being redeemable to its issuer, or from having a collateralized value. And since bitcoin has no collateralized value and is not redeemable, then it is not a financial instrument and therefore its fair value is zero.Though Bitcoin is based on the power of educational technology and the energy security of the computing processes, its value, to some extent, is still driven by speculation and there’s no state or basket of currencies that back this value as it is in all today’s currencies. Bitcoin is not a currency but a speculative bubble that most participants expect to gain returns from, and that’s why its price is so volatile. A person might get very rich by just speculating in bitcoins or lose everything.Bitcoin is not a real currency but instead a sort of digital version of what people call collectibles, same as original paintings by Picasso. There’s no amount of human labor that could create a unique new painting that is valuable as the original one of Picasso’s, just like no amount of human labor will do to the bitcoin system. The true copies of Picasso are easy to produce, but not like the original ones of Picasso’s. To create another system similar to Bitcoin is possible, but the original value of bitcoin would not be inherent to the new created one. It’s true that the original paintings of Picasso do not serve as a currency, same as bitcoin, though there’s nothing that could prevent their holders of swapping them for valuable commodities or other forms of currencies. Collectors buy collectibles, bitcoin or Picasso paintings, assuming that the price of their collectibles will appreciate and go up in the future taking into account that original copies will not flood the market.Bitcoin is a bubble and as the bubble grows, the capital gains from Bitcoin become larger. And during a bubble, it becomes very rational for investors to pay a little price for Bitcoin if they are sure that it could be sold later for a higher price to another willing investor. So accordingly, the Bitcoin’s value is again derived from the willingness of us wishing to pay for it and not from the working time rooted in it.
3. Bitcoin as a Currency is not Backed by a State, but where does It Get Its Value from?
- The value seen in bitcoin is mainly derived from its utility and scarcity, and that’s why people are ready to pay tons of dollars for it. Marx writes; “Nothing can have value, without being an object of utility. If the thing is useless, so is the labour contained in it; the labour does not count as labour, and therefore creates no value.” Bitcoin is the currency of the black-web as it could be used in illegal activities and money laundering. Its utility in paying and keeping one’s identity anonymous is what gives it such value. Some people who love gambling also find utility in bitcoins.Unlike fiat money being printed at will of governments, Bitcoin has a limited supply of coins that is 21 million bitcoins that will never be changed or manipulated. When more money is printed and put into an economy, it decreases the value of the same currency already in circulation. Another trait that adds value to the Bitcoin is its acceptability. Yuan & Yen or any other currency can only be accepted within a country’s border and not outside. But since bitcoin is based on the internet and not limited to a specific government, it is widely accepted. The structure of the Bitcoin system with the power of energy security are what also make this project successful and has such value.
4. Bitcoin & Fiat Money Fluctuation
- Price fluctuation in both Fiat money and cryptocurrencies is driven by many reasons. The volatility of a currency in traditional markets is measured by an Index, and we are not here to study that volatility, but just to quickly read it. Here and in this part, we will try to view the Chinese Yuan as a fiat money and Bitcoin as a cryptocurrency, according to the USD Exchange Rate, to see the fluctuation happened in both currencies during the last year 2018. Fiat money (Chinese Yuan)Looking at the opposite graph, figure 1, we see that the Chinese Yuan has experienced fluctuation during the last year, 2018, but that volatility is low and remains between 6 & 7 USD. It’s true that there are many reasons behind such volatility, but the one and only factor that makes this volatility somehow stable and rational is because Yuan currency is based on the credit of the economy and is backed by a government.
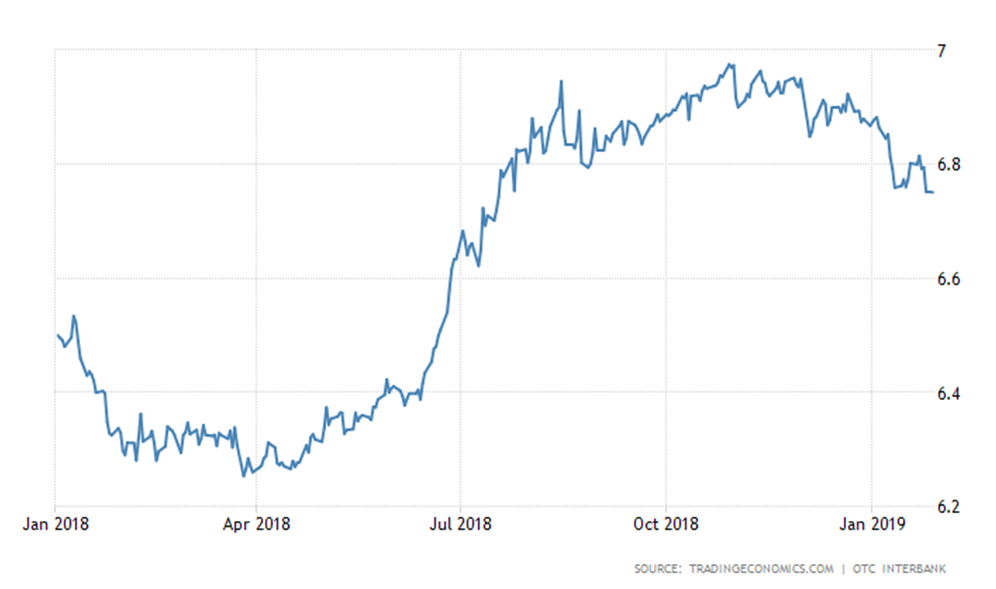 | Figure 1. Price volatility in Chinese Yuan against USD during 2018. Graph taken from https://tradingeconomics.com, accessed on Jan 29, 2019 |
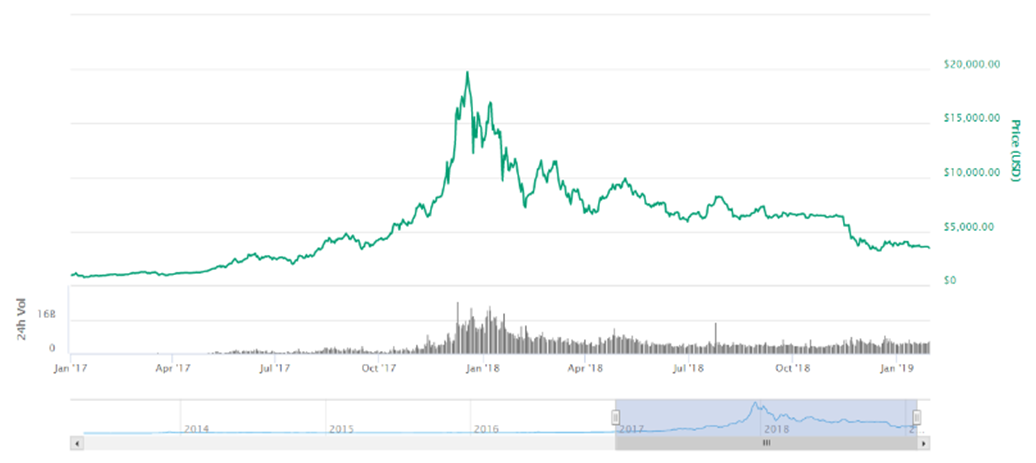 | Figure 2. Price volatility in Bitcoin against USD from 2017 to 2019. Graph taken from https://coinmarketcap.com, accessed on Jan 29, 2019 |
 | Figure 3 |
5. Conclusions
- The value sorted in any given commodity, according to the theory of value by Marx, is mainly derived from the amount of labor time it contains, and therefore there will be no value in a commodity if there is no labor time needed to produce it. Yet in a time like this being surrounded by high technologies, some commodities like Bitcoins have a great value whereas there is no labor time rooted in them. Moreover, the present value of crypto currencies is a hundred percent derived from machine’s total value, not from the labor time value, and bitcoin is valuable because of the power of technology and the energy security it provides. Bitcoin fails to meet the standard of financial instrument, and therefore it is not a currency but instead a digital version of collectibles that could be swapped for other commodities or currencies. And because of its high volatility, Bitcoin is not a well-trusted store of value.
6. Recommendations
- Based on the conclusion provided above and with the high volatility witnessed, it recommended for bitcoin holders to swap their tokens back to a more reliable store-of-value like fiat money or gold. And for those with the interest in cryptocurrencies, caution should be there when trading.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML