-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2018; 8(2): 69-75
doi:10.5923/j.economics.20180802.01

Automated Teller Machine (ATM) Service and Customer Satisfaction in the Upper East Region of Ghana
Ignatius Abasimi1, Atirikatua A. Evans2, Agbassou Y. A. Martin1
1Department of Economics, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China
2Department of Banking and Finance, University for Development Studies, Wa, Ghana
Correspondence to: Ignatius Abasimi, Department of Economics, Northeast Normal University, Changchun, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2018 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

One of the cardinal components of the banking industry is ATM service and the extent to which customers feel comfortable to patronize its service. This study therefore investigates ATM service and customer satisfaction in the Upper East region of Ghana. More specifically, the study looked at ATM service quality and customer satisfaction and factors that influence ATM usage. The study uses primary data collected from 200 respondents using convenience and simple random sampling methods. The logistic regression model was used to analyze the data. Multicollinearity and heteroskedasticity were corrected using the variances inflation factor (VIF) and robust standard errors respectively. The results suggest that customer’s satisfaction could be improved by convenience, security and privacy and reliability of the ATM services, as evidenced by a p-value of 0.0000 at 1% significance level. The results further indicate that convenience, security and privacy have positive effects on customer satisfaction at 1% significant levels, whereas reliability has negative effects on customer satisfaction at 1% significant levels. Also, security and privacy, ATM user fees, educational level and location of the ATM are found to be the major factors that influence customers’ willingness to use a particular ATM services in the studied area.It is recommended that, management of the various banks in the region should use participatory approaches to ensure active involvement of its customers with regards to ATM operations and policies safeguarding it usage.
Keywords: Automated teller machine, Customer satisfaction, Logistic regression, Ghana
Cite this paper: Ignatius Abasimi, Atirikatua A. Evans, Agbassou Y. A. Martin, Automated Teller Machine (ATM) Service and Customer Satisfaction in the Upper East Region of Ghana, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 8 No. 2, 2018, pp. 69-75. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20180802.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Banking system can be traced to medieval and early renaissance Italy, to the rich cities in the north like Florence, Venice and Genoa, the Bardi and Peruzzi families dominated banking in the 14th century Florence, establishing branches in many parts of Europe. The most famous Italian Bank was the Medic banks, established by Giovanni medic in 1397. During the 20th century, developments in telecommunication and computing resulting in major changes to ways banks operated and allowing dramatically increasing size and geographical spread. The late 2000’s financial crisis saw significant number of bank failures including some of the world’s largest bank and thereby raising much debate about banking regulations (Walter, 2012). The first decade of the 21st century also saw the culmination of the technical institution in banking over the previous thirty (30) years and saw a major shift away from traditional bank branches to internet banking (Charles, 2006).Banking in Africa has long been problematic because local banks are often unstable and corrupt as such governments and various industries rely on international banks (UN report, 1995). In the years after independence, African governments heavily regulated the banking sector and placed its limit on international competition. In recent decades, banking reforms has been a priority of International Monetary Fund (IMF) and World Bank (Walter, 2012).Banking services in the Gold Coast was exclusively provided by two expatriate banks functioning as Commercial Banks and the Central Gold Coast Bank (Vidal et. al, 1999). Since the inauguration of the Gold Coast Bank as the Central Bank of the then Gold Coast (1953) and its maturity to the Central Bank of Ghana after independence in 1957, there has been the influx of a number of Commercial, Investment, Merchant, Development and Private Banks among others. Banking services contribute to the socio-economic development of every country. Banking creates employment opportunities to citizens of various countries. That is, banks helps in the day to day transactions of businesses and also provides security to customer’s income. Banking facilitates many developmental projects by granting loans. Banks in Ghana contribute to the development of the country. They perform a lot of functions in the economy amongst which includes issue of money (in the form of bank unit and current accounts subject to cheque or payment at the customer’s order), netting and settlement of payments, credits intermediation (banks borrow and lend back - to - back on their own account as middleman), credit quality improvements through diversification of the bank’s assets and capital and maturity transformation [that is banks borrow more on demand debt and short term debt, but provide more long term loans] (ibid).Rafiqul et al (2005) noted that the banking industry like any other industry faces a lot of challenges in its operations that minimize the level of customer satisfaction. Some of the challenges include; accessibility of accounts when customers are not near their mother banks and long waiting time in the banking hall. This can be minimized by widening the infrastructural base of the banks. It has also been observed overtime that management of banks put their focus on treasury and corporate business whiles the operational side is often ignored. The operational side is as important as other segments of banking and banks should strengthen and give incentives to those involved in the operational business. Another area in the banking industry where a lot of progress should be made is the e-banking. Although small and medium banks are now offering online services to their customers, the large banks with more expanded branches network and a large number of customers are required to move more expeditiously so as to optimally utilize the e-banking network. This will not only lower the transaction cost but will also help in improving the customer services (Rafiqul et al., 2005).
1.1. Problem Statement
- Automated teller machine (ATM) is an innovative service delivery mode that offers diversified financial services like cash withdrawal, funds transfer, cash deposits, payment of utility and credit card bills, cheque book requests and other financial enquiries (Muhammad 2010). The concept of automated teller machine (ATM) has been quite old and has been developing throughout the world. Undoubtedly, a fair number of theoretical and empirical researches have been made worldwide, because of increase in scale of ATMs and consequently to convert the economy into a cashless one (Pohwa and Saxean, 2010). Yazeed Abdul (2014) noted that in Ghana, ATM is commonly use by customers of various banks for cash withdrawal and account balance enquiry. The other functions of the ATMs such as funds transfer, cheque-book requests and payment of utility bills among others which are collectively aimed at increasing customers’ satisfaction are not fully utilized. This inability on the part of customers to exploit these opportunities provided by the ATM is mainly due to reasons such as inadequate knowledge about the functions of the ATMs apart from cash withdrawals and balance enquiry, inability of some banks to render diversified ATM services, among others. However it should be noted that ATM services offered to clients differ among banks (Islam et al, 2007).A couple of empirical studies have being conducted on ATM services and customer satisfaction across different countries of the globe. For instance, Rafiqul et al (2005) conducted a study on Customer satisfaction with ATM service; a case study of HSBC ATM. Pahwa and Saxeen (2010) also analyzed the satisfaction levels of customers of ICICI bank holding ATM cards with respect to some aspects of ATM service quality in their study of the analysis of customer satisfaction at ICICI bank with special reference to ATM. Aborampah (2010) also focused on the levels of customer satisfaction in the banking industry in his research customer satisfaction in the banking industry: a comparative study of Ghana and Spain.There are however, disparities with regards to these empirical studies; they based their studies only on ATM users without considering non-ATM users and the factors that influence the usage of ATMs. In view of these shortcomings, this study seeks to address the following questions:1. How does ATM services quality affect the level of customer satisfaction in the Upper East Region?2. What factors influence the usage of ATM in the Upper East region? The study is organized in five sections; section one comprises of the introduction and statement of the problem, section two talks about the literature review on ATM service and customer satisfactions, section three outlined the methodology employed in collecting and analyzing the data, section four presents the results and discussions of findings and section five is based on the conclusion and recommendation of the study.
2. Literature Review
- Mcandrews (2003) outlined that; the various utility of ATM’s has gained worldwide popularity. The utilities include withdrawal of cash as per convenience of the customer than during the banking hours of various branches. Besides providing off-time and off-shore services, there is reduction of cost servicing. Ones access is gained, it offers several retailed banking service to customers. They are normally located outside the banks and also found at airports, malls and places far away from the home bank of customers. They were introduced first to function as cash dispensing machines; however, due to advancements in technology, ATM’s are able to provide a wide range of services such as making deposits, funds transfer between two accounts and bill payments. Banks tend to utilize the ATM as all others, for competitive advantage (Abor 2004). ATM’s are a cost–efficient way of yielding a higher productivity as they achieve higher productivity per period of time than human teller (an average of about 6400 transactions per month for ATMs compared to 4300 for human tellers(ibid).Stuart (1999) pointed out that the total number of ATM transaction have more than doubled over the last ten years and its estimated to reach near eleven million and total number of terminals in the united states has tripled over the last ten years.Several empirical studies have being carried out on ATM services and customer satisfaction. Saxeam and Pahwa (2009) for instance, analyzed customer satisfaction at ICICI bank with special reference to ATMs in Udaipur city. Their study looked at some aspects such as the service quality of ATM personnel, location, sufficient number of ATM in the city, the regularity in working of ATMs, their impacts on overall performance and their options on various other related issues. Their study revealed that the quality of ATM services provided was marginally above average and hence customers’ satisfaction with the ATM service was also above average. Chelliah et al, (2010) also studied service quality delivery and its impact on customer satisfaction in the banking sector in Malaysia. His study reveals that assurance, reliability, tangibles, empathy and responsiveness contributed to 62.1% effect on customers’ satisfaction. Only tangibles have significant effect on customer satisfaction and hence indicated it with a P-value of less than 0.01.Asif-Khan (2010) in his study; determinants of ATM service quality and its effects on customer satisfaction concluded that convenience, efficient operation, security and privacy, reliability and responsiveness have a significant dimension on ATM service quality.Rafiqul et al, (2005) also conducted a study on customer satisfaction of ATM services: case study of HSBC ATM. This study provides information for analyzing ATM scenario of HSBC. Hence the study investigated the satisfaction levels of HSBC ATM card holders with respect to various aspects of using HSBC ATM and their opinions on various other related issues. The main objective of their study was to examine the level of satisfaction of staff and non-staff customers of HSBC ATM. In their study, they categorized the various aspects of HSBC ATM as the promptness of card delivery, performance of HSBC ATM and the service quality of ATM personnel. After their survey and analysis of data, the study revealed that the average satisfaction levels of ATM users is more than that of non-staff ATM users in all respects or aspects of HSBS ATM.
3. Research Methodology
3.1 Source of Data
- Primary data constitutes the main sources of data for this research. The sample size considered is 200 bank staffs and non staffs (customers) in the studied area. Convenience and simple random sampling techniques was used to select the sample units and both structured and semi structured questionnaires were administered to collect the data.
3.2. Theoretical Framework
3.2.1. Logistic Regression Model
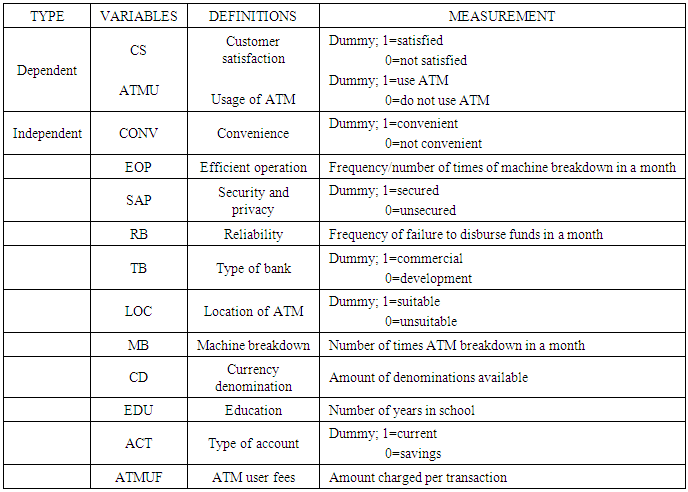
- The logit model is used to analyze the quality of ATM service and the level of customer satisfaction as well as the factors that influence the usage of ATM service in the studied area.In this study, most of the variables to be used are dummy hence the need for the usage of dummy variable regression models. In such models it is assumed implicitly that the dependent variable is quantitative whereas the explanatory variables are either qualitative or quantitative (Vasisht, 2010). In statistics, logistic regression, or logit regression, is a regression model where the dependent variable is binary (Fox, 2010). This study covers the case of binary dependent variables—that is, it takes only two values. Logistic regression measures the relationship between the binary dependent variable and independent variables by estimating probabilities of these independent variables, using a logistic function, which is the logistic cumulative distribution function. The logit model is given by;
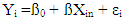 | (1) |
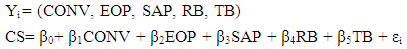 | (2) |
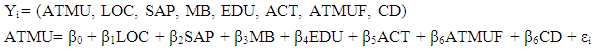 | (3) |
|
4. Results and Discussions
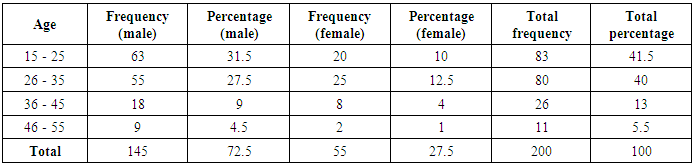
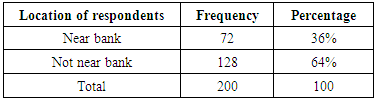
4.1. Demographic Characteristics of Respondents
|
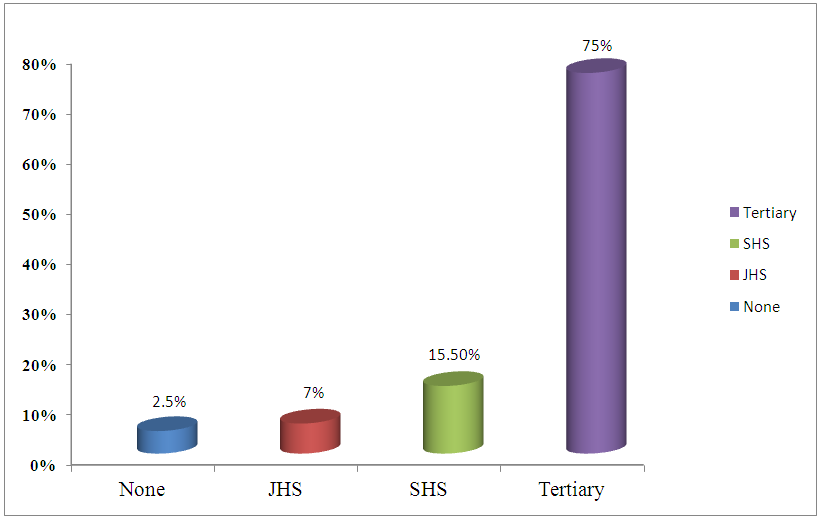 | Figure 4.1. Educational Statuses of Respondents |
|
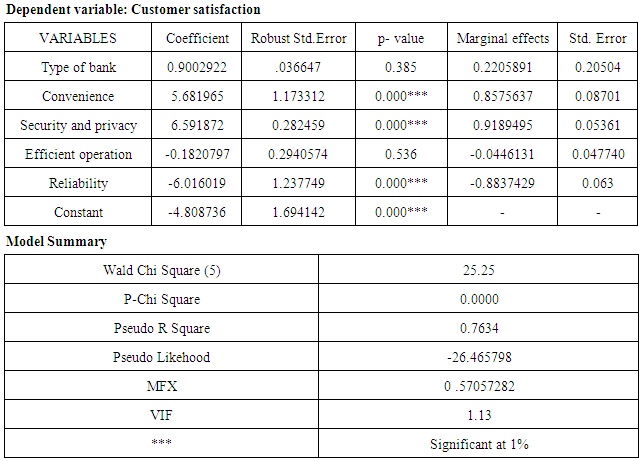
4.2. Logistic Regression Estimates of the Study Objectives
|
|
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
- This study investigates ATM service and customer satisfaction in the Upper East region of Ghana. More specifically, the study looked at ATM service quality and customer satisfaction and factors that influence ATM usage. The study uses primary data collected from 200 respondents using convenience and simple random sampling methods, Multicollinearity and heteroskedasticity were corrected using the variances inflation factor (VIF) and robust standard errors respectively.The results suggest that customer’s satisfaction could be improved by convenience, security and privacy and reliability of the ATM services, as evidenced by a p-value of 0.0000 at 1% significance level. The results further indicate that convenience and security and privacy have positive effects on customer satisfaction at 1% significant levels, whereas reliability has negative effects on customer satisfaction at 1% significant levels. Also, security and privacy, ATM user fees, educational level and location of the ATM are found to be the major factors that influence customers’ willingness to use a particular ATM services in the studied area. Security and privacy, educational level and location were found to influence ATM usage positively, whiles ATM user fees has negative influence. Base on the findings, it has been realized that customer satisfaction is influenced by convenience, security and privacy and reliability of the ATM services in the studied area while customers’ willingness to use ATM services is influenced by security and privacy, ATM user fees, educational level and location of the ATM in the studied area.It is recommended that banks should increase the number of ATM installations at the banks premises and at vantage points where customers can have full access to it more easily. This will prevent customers from travelling long hours before having access to some banking services and hence, reduce pressure on one ATM.Banks should put some vital mechanisms in place and intensify the educational problems on the ATM. They should provide personnel who are well resourced in the operation of the ATM to assist customers who are not able to use the machine.Participatory approaches should be put in place to ensure active involvement of customers with regards to ATM operations and policies safeguarding its usage.Banks should provide lower or lesser denominations in the ATM for customers who want smaller denominations to withdraw at anytime. The ATM should also be able to always issue receipts after transactions for customers to know their accounts balances.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML