-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2017; 7(5): 211-215
doi:10.5923/j.economics.20170705.02

Foreign Direct Investment, International Trade and Economic Growth in Pakistan’s Economic Perspective
Najabat Ali, Li Xialing
School of Economics, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China
Correspondence to: Najabat Ali, School of Economics, Shanghai University, Shanghai, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Today globalisation is increasing global economic integration and interdependence of world economies through the movement of goods, services, capital flows and new technologies across borders. International trade and foreign direct investment is being considered the vehicle of economic growth in developing countries. FDI stimulates economic growth of developing countries by capital formation, transfer of technology, adding skills of labour, increasing competition in the domestic market and creating new job opportunities. On the other hand, international trade results in more effective production facilities of goods and services through shifting production to those countries which have comparative advantage in producing them. The current research study attempts to analyse the relationship of international trade, foreign direct investment and economic growth in Pakistan’s economic perspective. The study utilizes time series data over the period of 1991 to 2015 to analyse the relationship among the variables. The results of the study clearly show that there is a positive relationship among international trade, foreign direct investment and economic growth in Pakistan’s economic perspective.
Keywords: Pakistan’s Economy, Exports, Foreign Direct Investment, Imports, International Trade
Cite this paper: Najabat Ali, Li Xialing, Foreign Direct Investment, International Trade and Economic Growth in Pakistan’s Economic Perspective, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 7 No. 5, 2017, pp. 211-215. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20170705.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The process of rapid economic integration among the countries of the world has increased the importance of international trade and foreign direct investment in recent years. Trade and foreign direct investment (FDI) are considered as drivers of economic growth for developing countries. Foreign direct investment (FDI) is a main source of technology transfer from developed economies to developing ones and it also stimulates the economic growth by enhancing domestic investment, increasing labour skills and creating new job opportunities in the host countries. Trade is also considered as an important catalyst of economic growth. It promotes more efficient and effective production of goods and services to the countries which have comparative advantage in producing them.1Trade and Foreign direct investment is not only essential for the economic growth of developing countries but also very crucial for developed countries. For instance, OECD (1998) reports: “Trade and foreign direct investment are major engines of growth in developed and developing countries alike”. The volume of trade has been dramatically increased in the recent years and trade has tremendously outclassed the domestic investment. Due to integration of world economy, FDI flows have also been increased. Formerly, centrally planned developing economies have become the part of world economy. In this situation, countries with more open trade and foreign investment regimes will outclass those countries which have restrictive trade and foreign direct investment policies.2 Although a lot of empirical and theoretical studies support the idea that trade and FDI have a positive impact on the economic growth of the developing countries but there are several studies which are of the view that the impact of FDI and trade totally depends on the human capital and absorptive capacity of the host country. Even several studies came up with the conclusion that FDI and trade have negative impact of the economic growth of the developing countries.3
2. Review of Literature
- According to neoclassical growth model, technological progress and labour growth are exogenous, FDI inflows simply increases the investment rate, that results in a transitional increase in per capita income growth but it has no long-run growth effect. The new growth theory indigenizes technological progress and FDI has been considered to have permanent growth effect in the host country through technology transfer and spill over effect. (Hsiao and Hsiao, 2006) The theoretical and empirical literature studying the relationship of foreign direct investment (FDI), international trade and economic growth is huge. The impact of the both variables FDI and international trade on the economic growth has been studied for various countries using different sample periods and econometric methods. A considerable amount of literature supports the idea that the impact of FDI and trade is positive on the economic growth. Balasubramanyam et al. (1996); Karbasi et al. (2005) concluded that FDI and trade both stimulate economic growth. They found that FDI and trade have positive impact on the economic growth. De Mello (1997) and World Bank (2001) also emphasises on the positive impact of FDI on the economic growth. Borensztein et al. (1998) analysed the impact of foreign direct investment (FDI) on economic growth in a cross-country regression framework by using data of 69 developing countries. The results of the study suggest that FDI is an important source of technology transfer and contributes comparatively more to the economic growth as compared to the domestic investment. The study further suggests that higher productivity of FDI is dependent on the threshold stock of human capital. So, FDI contributes to the economic growth when the host country has substantial absorptive capacity to absorb foreign modern technology efficiently. De Mello (1999) argues that the impact of FDI on economic growth is expected to be twofold. First, economic growth can be achieved with the help of capital accumulation in the recipient economy. The FDI inflows may add new technology and inputs in the existing stock of domestic physical capital available in the host country. Secondly, FDI stimulates the economic growth by technology transfer, labour trainings, alternative management practices and organizational arrangements. Tintin (2012) investigated whether foreign direct investment (FDI) spur economic growth and development by using economic freedoms index to proxy the quality of host country institutions. The study analysed 125 countries as samples including 38 developed, 58 developing and 29 least developed economies over the time period of 1980-2010 by using panel least squares method with fixed effects. The results obtained from the study show that FDI spur economic growth and development in developed, developing and least developing countries. The study further shows that FDI enhances the economic growth and development in developing countries relatively higher than the developed and least developed countries. Fan (2002) pointed out that the domestic firms in the host countries acquire benefit through spill over effects. Through spillovers, FDI can transfer new ideas, modern technology, and modern working practices to domestic firms in the host countries. So FDI promotes economic growth of the host countries by spillover effects. After realizing the benefits of FDI, the governments of the host countries encourage foreign direct investment inflows. Belloumi (2014) examined the relationship among foreign direct investment (FDI), trade openness and economic growth in Tunisia for the period of 1970-1980 by using ADRL model. The results of the study show that there is cointegration among the variables specified in the model when FDI is taken as dependent variable. In the long run trade openness and economic growth promote foreign direct investment in Tunisia. The results further show that there is no significant Granger causality from FDI to economic growth or from economic growth to FDI in the short run. Turning to the Granger causality test results for economic growth and trade openness, there is also no significant Granger causality from trade to economic growth or from economic growth to trade in the short run. Makki (2004) analysed the role of FDI and trade in promoting economic growth and the study came up with the conclusion that FDI, trade, human capital and domestic capital play a crucial role in the economic growth of developing countries. There is a significant positive interaction between FDI and trade in stimulating and advancing economic growth of developing countries. The results further show that foreign direct investment also stimulates the domestic investment in the developing countries.Carkovic and Levine (2002) studied the impact of FDI on the economic growth and the results of the study found that FDI does not exert a robust and positive impact on economic growth. The study further explains that there is not reliable cross- country empirical evidence supporting the claim that FDI accelerates economic growth. Klasra (2011) During the last few decades government of Pakistan has taken many measures to attract foreign direct investment in Pakistan. The government has been liberalizing economic and trade policies to get maximum benefit from international trade and foreign direct investment. The government of Pakistan has been adopting economic reforms with the objective to set a good pace of economic development. Until 1980 Pakistan was following import substitution policies and import substitutions were very high but until 1995 Pakistan reduced tariff from 150 percent to zero percent. Pakistan has strengthened export incentive system and liberalised the import licencing system. Khan (2007) analysed the link of foreign direct investment, domestic financial sector and economic growth in Pakistan over the period of 1972-2005 by using bound testing approach of co-integration. The results of the study suggest that foreign direct investment has a positive impact on the economic growth of Pakistan both in the short run and long run if the domestic financial system has attained a certain minimum level of development. The study also suggests that a better financial system not only stimulates FDI but also increases the benefits of foreign direct investment. Iqbal et al. (2010) investigated the causality relationship among FDI, Trade and Economic growth in Pakistan over the period of 1998 to 2009. The integration and co-integration analysis in VAR model suggests that there is a long run relationship among the variables. The results obtained from VECM causality test suggest that there is bidirectional causality among FDI, export and economic growth, with are two important factors which boost the effect of economic growth of Pakistan.So, the impact of trade and FDI on the economic growth is still an unresolved issue. There are various studies which came up with the conclusion that trade and FDI exerts a positive impact on the economic growth of developing countries. There are various studies which oppose the claim that trade and FDI have a positive impact on the economic growth while some studies conclude that the impact of trade and FDI totally depends on the absorptive capability of the host countries.
3. Methodology and Data
- Annual time series data covering the 1991 – 2015 period have been used in this study. Data has been taken from World Bank Indicators. E-views software has been used for the analysis of data. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) has been taken as dependent variable while Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), Imports and Exports have been used as independent variables. The Model is as follows
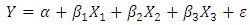 Where,
Where, 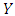 = Gross Domestic Product (Dependent Variable)
= Gross Domestic Product (Dependent Variable)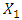 = FDI
= FDI 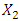 = imports
= imports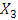 = exports
= exports 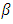 = coefficient of independent variable, α= constant
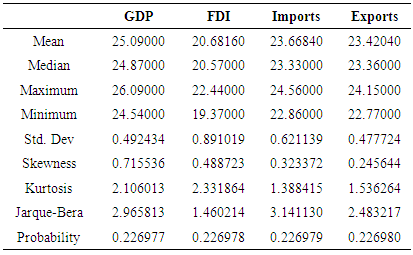
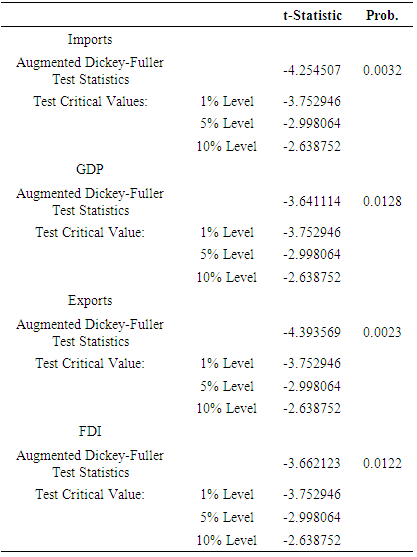
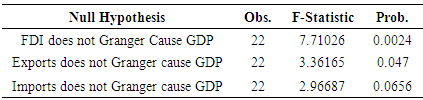
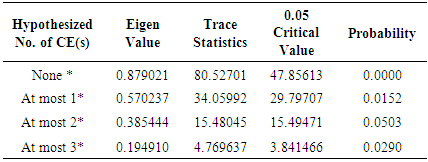
= coefficient of independent variable, α= constant 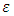 = error termThe paper adopts following techniques for the empirical analysis of data. Descriptive statistics technique has been used to present summary of observations and samples. It also describes and summarizes features of a collection of data. The empirical study which is based on time series data can never be assumed as stationary time series. So, there is a test of stationarity that has become widespread nowadays is the unit root test. Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) has been used to test the stationarity of the series. It was proposed by Dickey and Fuller (1981). ADF test is a standard unit root test and analyses the order of integration of the data series. After determining the order of integration of data, the study applies test of co integration to check the integration between two or more variables. Engle and Granger (1987) suggested the method of two steps to analyse the equilibrium relationship of variables for long period having same level of integration. But this technique has a drawback i.e. it only helps to determine the possibility of one co integration vector. To eliminate this drawback, Johansen and Juselius (1990) introduced Johansen co-integration to eliminate the drawback. Engle and Granger (1987) suggested the granger causality test which is used to determine the causality between two variables in a time series and it determines whether one time series variable is useful in forecasting another or not.
= error termThe paper adopts following techniques for the empirical analysis of data. Descriptive statistics technique has been used to present summary of observations and samples. It also describes and summarizes features of a collection of data. The empirical study which is based on time series data can never be assumed as stationary time series. So, there is a test of stationarity that has become widespread nowadays is the unit root test. Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) has been used to test the stationarity of the series. It was proposed by Dickey and Fuller (1981). ADF test is a standard unit root test and analyses the order of integration of the data series. After determining the order of integration of data, the study applies test of co integration to check the integration between two or more variables. Engle and Granger (1987) suggested the method of two steps to analyse the equilibrium relationship of variables for long period having same level of integration. But this technique has a drawback i.e. it only helps to determine the possibility of one co integration vector. To eliminate this drawback, Johansen and Juselius (1990) introduced Johansen co-integration to eliminate the drawback. Engle and Granger (1987) suggested the granger causality test which is used to determine the causality between two variables in a time series and it determines whether one time series variable is useful in forecasting another or not.4. Results and Discussions
|
|
|
|
5. Conclusions
- The paper aims to analyse the relationship of foreign direct investment (FDI), international trade and economic growth of Pakistan. The results of the study show that there is a positive relationship between FDI, international trade and economic growth of Pakistan. By using time series data over the period of 1991 to 2015, the study concludes that there is a significant and positive link among FDI, international trade and economic growth. FDI and trade both are the vehicles of economic growth of Pakistan. FDI stimulates economic growth by capital formation, transfer of technology, adding labour skills, increasing competition in the domestic market and creating new job opportunities.
Notes
- 1. See Makki and Somwaru (2004), Busse and Königer (2012), Das (1987), Din (1994), Rodriguez-Clare (1996), Balasubramanyam et al. (1996) and Borensztein et al. (1998) for details. 2. See OECD (2002, 2006, 2008 and 2009), Dollar (1992), Sachs et al. (1995), Lipsey (2004). Tintin (2012), Ozturk (2007), Sun (2002), Lewer and Berg (2003) for more details about the impact of trade and FDI. 3. See (Balasubramanyam et al. (1996), Borensztein et al. (1998), Lipsey (2000), De Mello (1999), Xu (2000), Meschi (2006), Darrat et al. (2005).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML