-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2017; 7(4): 171-176
doi:10.5923/j.economics.20170704.02

Entrepreneurship of Local Student: Online Shopping Behavior Perspective
Hadiyati1, Fatkhurahman1, Eka Armas Pailis2, Bambang Suroto1
1University of Lancang Kuning, Indonesia
2University of Riau, Indonesia
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The purpose of this study is to determine the effect of technology perception and risk perception on online trust and how online trust is related to online shopping satisfaction. The study also examines the impact of online trust in mediating the relationship between perceived technology and online shopping satisfaction. The population in this study are students who study at the University of Lancang Kuning. The sample collection was 372 people by using stratified random sampling method with the criteria of students who had been shopping online, in order to make it easier to get the respondents. Data processing is done by structural equation modeling analysis using Warp PLS 5.0 software. The result of study shows that technology perception and risk perception have an effect on trust and satisfaction of online shopping.
Keywords: Online shupping behavior, Perception Technology, Perception Risk, Confidence, Satisfaction
Cite this paper: Hadiyati, Fatkhurahman, Eka Armas Pailis, Bambang Suroto, Entrepreneurship of Local Student: Online Shopping Behavior Perspective, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 7 No. 4, 2017, pp. 171-176. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20170704.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
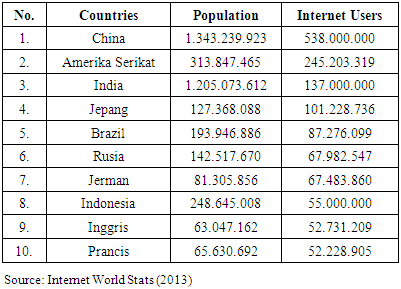
- In today's internet has become a necessity for many people, because with internet network one can search and find various kinds of information quickly and easily. Internet users in Indonesia began in 1995 and continues to grow until 2014 by placing Indonesia as the country of Internet users number 8 as the country's accessor or the highest internet users. The following is explained:
|
2. Framework of Theory and Hypotheses
- Ha and Stoel (2008) argue that perception of technology is the main determinant in determining the intention to buy online. Gefen et. al., (2003) also argue that perceptions of technology are found to have a direct impact on online buying intentions. According to Gefen et. al., (2003), the more useful and easy to use website, the more customers will choose to use it (purchase online). On the other hand, studies from Chen and Barnes (2007) and Gefen et. al., (2003) also shows that online purchasing intentions are influenced by technological perceptions, mediated by online trust. Kamarulzaman (2007) states that the simplicity of website design will help to motivate adoption using the site and increase the intention to use the service (intention of purchasing online).According to Schiffman & Kanuk (2004) perception is a process whereby individuals choose, arrange, and interpret stimuli into a related and meaningful world picture. Meanwhile, according to Chaplin (1999) perception is the process of knowing or recognizing objects and objective events with the help of the senses. This process begins with attention, namely the process of selective observation. In addition, perception is an effort to observe the world, including understanding and recognizing or knowing the objects and events. Based on the above understanding it can be concluded that perception is the process by which a person accepts, recognizes, and understands the stimuli that come to him, whether through the sense of sight, smell, hearing, touch and tasting into a meaningful picture. Furthermore, according to Schiffman & Kanuk (2004) the concept of risk received by consumers is a feeling that decisions made by consumers will produce consequences where it can not anticipate with a definite estimate.Trust is the willingness of a person to rely on others where we have confidence in him. Trust is a mental state based on one's situation and its social context. When a person makes a decision, he chooses a decision based on the choices of people whom he can trust more than unbelievers Moorman et. al., (1992) in Tjiptono (2003).According to Mayer et.al (1995) in Tjiptono (2003), consumer confidence is the willingness of one party to accept the risk of another's actions based on the expectation that the other party will take an important action for those who trust it. This is despite the ability to monitor and control the actions of the trusted parties.According to Kotler (2009) customer satisfaction is "the feeling of pleasure or disappointment of someone who emerged after comparing the perception / impression to the performance (or outcome) of a product and its expectations". Customers will be satisfied with the service or product that will be produced if the service or product can fulfill customer's requirement and expectation, but if the service or product that produced can not fulfill customer requirement or desire, it will cause dissatisfaction for customer.Based on the above description, the research framework with the model as follows:
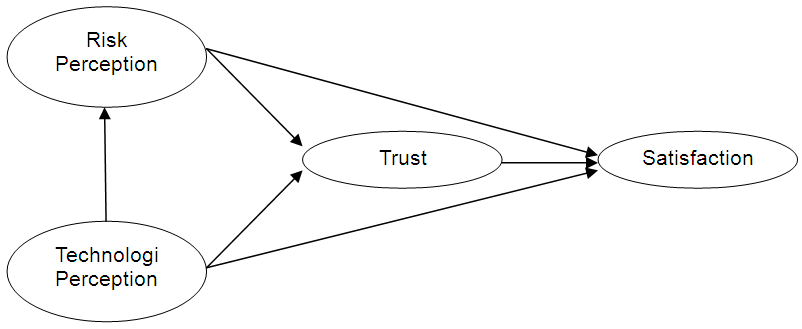 | Figure 1. Research Framework |
3. Research Methods
- This study uses a quantitative approach based on the research gap and the phenomenon that occurs. In the analytical stage used the analytical approach by way of description of the analysis and combine it by using statistical analysis to determine the strengths and weaknesses of the relationship between the variables that affect this study.Sampling technique with questionnaire method, Malholtra (2005) defines "Questionnaire is a structured technique to obtain data consisting of a series of questions, written or verbal, which respondents answered".Questionnaires are distributed by compiling the questions that have been compiled complete with a choice of answers that aims to facilitate the respondent to answer. All questions that have been answered by the respondent will be kept confidential starting from the personal data of the respondent to the answers that the respondent has given. Samples in the form of questionnaires will be distributed directly to respondents as one of the media distributing questionnaires.Methods in sampling in this study by using Proportional Stratified Random Sampling Method. This sampling technique provides equal opportunities for each population to be selected as a study sample. The use of stratified systems to obtain data that is proportional according to the Faculty at the University of Lancang Kuning.The last position of students in 2016 (based on reporting results forlap.dikti.go.id in December) was as many as 10,922 students. So the total population in this study is 10.922 people, while the sample in this study based on Krejcie & Morgan table (1970) is 372 students.This descriptive analysis is used to provide an overview of the respondents in the study and the results of study in the field related to the tendency factor analysis of the influence of student confidence in the risk of online shopping in Pekanbaru. Thus, the descriptive statistical analysis in this study is used to provide an overview of the variables associated with; a) risk perception, b) perception of technology, c) trust, and d) satisfaction.To test the hypothesis of Structural Equation Modeling Partial Least Square (SEM-PLS) analysis is used. The purpose of using SEM analysis in this study is because the variables used in this study are unobserverd variable (variable that can not be observed directly) or in the measurement using indicator for Judge.The SEM-PLS analysis consists of two evaluation phases: (1) outer model evaluation; and (2) inner model evaluation (Abdillah et al., 2016). The first stage is the outer model evaluation, done to see the validity and reliability of the data. Test validity in the outer model evaluation is done by testing the validity of convergent and discriminant validity. Second stage is the inner model evaluation done to test the hypothesis in the study.
4. Results and Discussion
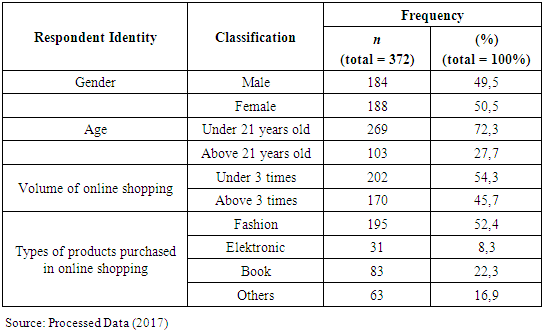
- Before performing the data analysis by evaluating and measuring model (outermodel) and sturctural model (innermodel), then conducted a descriptive statistical analysis consisting of respondents' demography and descriptive research variables. Demographic descriptions of respondents in this study explain the characteristics of respondents consisting of gender, age, volume of online shopping, and types of products purchased in online shopping.
|
|
5. Discussion
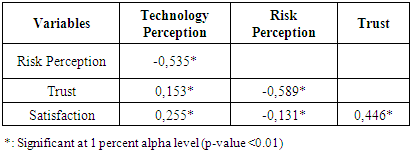
- The result of the study shows the influence of technology perception to the perception of risk directly with the negative significance, it can be assumed that the level of perception of technology in online shopping is high then the level of perception of risk in online shopping will be lower. In contrast to the lower level of consumer risk perception online shopping will increase the level of perception of consumer risk in shopping online. The results of this study support previous study by Ling (2011) the influence of perception level of student technology to the level of perception of student risk in online shopping. The results are in line with Kesyarwani & Bisht (2012) research which explains that a well-designed website is also found to assist in facilitating easier use and also minimize perceived risk concerns regarding internet banking usage.The results of this study also explains the influence of students perception level of technology in a positive or unidirectional direction to the belief of students in shopping online. This means that the technology perceived by students in doing online shopping can increase their trust in online shopping, and vice versa if the perceived technology of students in online shopping is low then it can lower their trust level to do shopping online. The results of this study are supported by Ling et. al., (2011) in his research also explains the perception of technology and perceived risk associated with online trust. This result is in line with the theory According to McKnight et. al., (2002) two factors that may affect consumer trust are perceived web vendor reputation, and perceived web site quality.The results of this study shows the perception of technology positively affect student online shopping satisfaction. Thus means the level of technology perceived by students in high online shopping can increase the level of student satisfaction in shopping online, vice versa If the level of perceived student technology is low then the level of satisfaction in online shopping will be low. The above results are supported by Guo et. (2012) and Loo (2004) who explained that the perceived technology positively influences consumer satisfaction in online shopping, is donated by the user interface and web design. The results of this study also supports Ling research (2011) which suggests the perception of technology affect the intention of online shopping can be concluded that the level of perception of technology affect the intention of online shopping and affect the satisfaction of online shopping. Thus vendors online buying and selling service provider can increase purchasing intentions and online shopping satisfaction by developing strategies to improve perceptions of technology (in terms of web security systems and shopping productivity) to increase satisfaction and intentions of online shopping.The results of this study indicate a negative influence perceptions of risk to student confidence in online shopping. Thus means the high level of perceived risk of students in online shopping can reduce the level of confidence of students in online shopping, and vice versa low level of perceived risk of students in online shopping will increase the level of confidence of students in shopping online. This is in agreement with Ling et. al., (2011) in his research also explains the perception of technology and the perception of risk related to online trust. Also Cheung & Lee (2001) explains the perception of risk has the greatest influence affect the students' trust in online shopping.The results of this study indicate a negative influence of risk perceptions on student satisfaction in online shopping. Thus means the high level of perceived risk of students in online shopping can reduce the level of student satisfaction in online shopping, so otherwise the low level of perceived student risk in online shopping will increase the level of student satisfaction in shopping online. The above results support the research of Bashar & Wasiq (2013) and Lee & Joshi (2007) risk perceptions related negatively to consumer satisfaction, in other words the higher the risk level the lower the satisfaction level. The risk of time-related Internet shopping has a negative impact on satisfaction. Different opinion according to Mulyono (2011) although the level of risk faced by consumers is high but consumer satisfaction is increasing.The results of this study showed a positive influence of trust on student satisfaction in shopping online. Thus the high level of student trust in online shopping can increase student satisfaction in online shopping, and vice versa low level of online shopping trust students will also reduce the level of student satisfaction in online shopping. The above results in accordance with the research of Jin & Park (2004), Kim (2010), Ghalandri (2012), Wiludjeng & Daniarsa (2013) respectively explain that the higher level of consumer satisfaction in online shopping then the higher the level of satisfaction, in other words in Building consumer satisfaction online shopping meal should increase consumer confidence. In addition, according to Lin & Xu (2011) consumer trust and satisfaction has a causality relationship.The results of this study indicate an indirect relationship between the perception of technology to satisfaction mediated trust. Thus means the high technology perceived by students in online shopping increases the level of satisfaction if the level of confidence is also high, so otherwise the low level of technology perceived by students in online shopping will decrease the level of student satisfaction if the trust also decreases.The results of this study indicate an indirect relationship between perceptions of risk to satisfaction mediated trust. Thus means the high perceived risk of students in online shopping increases the level of satisfaction if the level of trust is also high, so otherwise the low level of technology perceived by students in online shopping will decrease the level of student satisfaction if the trust also decreases.
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
6.1. Conclusions
- Based on the results of study and discussion that has been done in the previous chapter then the conclusions of this study are:1) The perception of technology negatively affects the risk perception. This explains that the level of risk perception in the low online shopping is due to the good perception of respondents to the use of technology.2) Perception of technology affects positively to online shopping trust. This explains that the high consumer trust in online shopping is due to the good perception of respondents to the use of technology.3) Perception of technology affects positively toward online shopping satisfaction. This explains that the high satisfaction of consumers in online shopping is due to the good perception of respondents to the use of technology.4) Risk perception negatively affects online shopping trust. This explains that high consumer confidence in online shopping is caused by a low level of risk perception in online shopping.5) Risk perception negatively affects online shopping satisfaction. This explains that high consumer satisfaction in online shopping is caused by the level of perception of risk in low online shopping.6) Trust positively affects online shopping satisfaction. This explains that high consumer satisfaction in online shopping is caused by high consumer trust in online shopping.7) The perception of technology affects indirectly on the satisfaction of online shopping expenditure of trust. This explains that consumer satisfaction in online shopping is due to the good perception of respondents to the use of technology through high levels of high consumer trust in online shopping.8) Risk perceptions affect indirectly to the satisfaction of online shopping expenditure on trust. This explains that high consumer satisfaction in online shopping is caused by the level of risk perception in low online shopping through high levels of consumer trust in online shopping.
6.2. Suggestion
- Things that can be suggested based on the results of study and discussion include:1) Vendor online sales service providers can segment to the products they sell in order to attract consumers to shop that is by targeting segments for women's fashion products that the largest number of consumers than men.2) Regarding the perception of risk, better providers of online trading services provide more assurance of certainty of the products they sell in accordance with what they display on their web either with the improvement of web design, as well as product specifications, and other customer services in order to reduce the level of risk Perceived psychologically by consumers.3) Regarding the trust, increasing the guarantee and compensation to the consumer is highly recommended for providers of online trading services is due to the above results all the respondents still do not trust completely for the safety of shopping online.4) Regarding the satisfaction, the researchers recommend that online purchasing service providers also do relationship marketing to increase consumer loyalty to keep shopping and recommend to others of course with an increase in the points above as well.5) For further research is suggested to perform testing by using other variables outside of the variables used in this study that is like the impact on loyalty, to be able to know how much the level of satisfaction with the vendor online buying and selling service.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML