-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2017; 7(1): 29-40
doi:10.5923/j.economics.20170701.04

Purchase Intention towards Counterfeiting Luxuries Fashion Product among Undergraduate Student in UniKL
Selvarajah Krishnan1, Fakhrul Hisyam2, Shah Ramlan2, Nur Diyana2, Nur Salihah2, Zareth Atiqa2
1International University of Malaya-Wales, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
2University Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Correspondence to: Selvarajah Krishnan, International University of Malaya-Wales, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

This study aims to measure the factors that affecting Universiti Kuala Lumpur (UNIKL) undergraduate students’ attitudes toward counterfeiting luxurious fashion products and attitudes effect on the purchase intention. Self-administered questionnaires were distributed by online to individuals in UNIKL. The findings focused on brand image, social influence, price-quality inferences, Integrity, novelty seeking, status consumption that influence toward purchase intention. Finding shown that correlation between attitudes and intention of purchase counterfeiting luxurious fashion product is significant. In addition, the research will also found that the difference between attitude and purchasing intention of the consumer in monthly income and genders. Furthermore, elaborates the demand of counterfeit goods through the attitudes that effects of purchase intention to consumer.
Keywords: Counterfeit Product, Luxury Fashion Product, Attitudes, Purchase Intention
Cite this paper: Selvarajah Krishnan, Fakhrul Hisyam, Shah Ramlan, Nur Diyana, Nur Salihah, Zareth Atiqa, Purchase Intention towards Counterfeiting Luxuries Fashion Product among Undergraduate Student in UniKL, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 7 No. 1, 2017, pp. 29-40. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20170701.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- According to (McCarthy, 2014) counterfeiting has been defined as “the act of producing or selling a product containing an intentional and calculated reproduction of a genuine trademark”. Counterfeiting originated with the piracy of elite consumer products such as branded clothing and accessories but now has expanded to the music, video, pharmaceutical industry and even to food products such as Coffee Beans drinks. In 2011, the international trade of counterfeit goods is estimated to be worth $650 billion and is expected to increase to $1 trillion in 2015 (Frontier Economics, 2011). Piracy has recently become a rising trend in China, Thailand, India and Malaysia, making them known as the ‘home for piracy’ due to being regarded as the world’s worst violators of intellectual property rights and worst counterfeit offenders (Haque, Khatibi and Rahman, 2009). In a report on the “adequacy and effectiveness of U.S. trading partners’ protection of intellectual property rights (IPR)”, Malaysia was among the countries listed in a watch list and was invited to cooperate in developing action plans to resolve IPR issues of concern, amongst which is the piracy over the internet and digital piracy (United States Trade Representative, 2011). Datuk Ismail Sabri Yaakob (2011) 858 Entrepreneurship Vision 2020: Innovation, Development Sustainability, and Economic Growth also reported that there has been an increase in the number of counterfeit cases investigated in Malaysia as compared to the previous year which resulted in a higher value of confiscated pirated goods. According to Trade.ec.europa (2006), Malaysian authorities are improving their efforts to battle against piracy through increased raid actions, amendments to relevant laws, allowing filing of complaints to the trade ministry and even containment of import and export of these goods. However, Trade.ec.europa (2006) suggests that the “level of infringement remains exceptionally high and trade in counterfeit goods is generalised”. Thus, the research aims to analyze factors affecting the attitudes toward counterfeiting luxurious fashion products, and attitudes’ effect on the purchase intention of consumer. An online survey was conducted with 100 respondents in Universiti Kualal Lumpur (UniKL) student. This research paper highlights the attitudes that effecting the purchase intentions of (UniKL) students on counterfeit goods, particularly on luxury products which have multiple regression and testing difference factors, such as brand image, social influence, price-quality inferences, integrity, novelty seeking, status consumption that influence to attitudes toward counterfeiting luxurious fashion product. The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: The next section gives a brief literature review. Section 3 describes the research methodology, and Section 4 presents the findings. Finally, Section 5 concludes the paper and draws managerial implications.
2. Literature Review
- Counterfeiting appears in two types: deceptive and non-deceptive counterfeiting. Deceptive counterfeit products are presented in the marketplace as being genuine with the intent to deceive the purchase (Penz & Stottinger, 2005). This research focused on non-deceptive counterfeit goods, which no intent to deceive the purchaser and their purchasing are entirely intentional. According to Cordell et al. (1996), counterfeiting products is “any unauthorized manufacturing of goods whose special characteristics are protected as intellectual property rights (trademarks, patents and copyrights) constitutes product counterfeiting.”
2.1. The Attitudes toward Counterfeiting
- Attitude is a learned predisposition to behave in a consistently favorable or unfavorable manner with respect to a given object (Schiffman & Kanuk, 1997). Meanwhile in Bagozzi et al. (2002) attitude is defined as reviews, it is “...a psychological tendency that is expressed by evaluating a particular entity with some degree of favor or disfavor”. The attitude is closely related with the intention of a person, it is a reasonable factor to predict that person's behavior (Ajzen & Fishbein, 1975). Therefore, the attitude of consumers against counterfeiting goods is supported, then most likely they will have the intention of buying it and vice versa (Nordin, 2009).
2.2. Intention to Purchase Counterfeiting
- According to Fishbein and Ajzen (1975), intending to buy is the decision to act or psychological status representing for the awareness of individual participants and a particular behaviour. According to the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) of Ajzen (1991), the purchasing behavior of consumers is measured by intentions of purchasing, whereas the intention of buying is measured by the attitude of consumers according to the Theory of Reasoned Action (Ajzen & Fishbein, 1975). Although performing an act of buying also need to have other elements of the opportunities or resources such as money or the accessibility of goods, the intention is the major measurement factors for purchasing behavior of consumers (Phau & Teah, 2009).
2.3. Brand Image and Attitudes
- Brand image is “consumer’s perception of the brand” (Aaker, 1996), in other words it is the way that brand exists in consumers’s mind (Nguyen & Tran, 2013). Brand image significantly contributed to the decision to buy or not to buy that brand personally (Bian & Moutinho, 2011). Phau et al. (2009) also indicate if luxurious goods on which consumers know about its brand and reputation, they will tend to favor its counterfeiting. However the survey data hasn't proved it yet. In high fashion field, the better the product image is, the more helpful it would be to strengthen consumers willingness to purchase its counterfeiting (Nguyen & Tran, 2013). Therefore, the hypothesis H1 is proposed: Hypothesis H1: Brand image has a positive significant influence on favorable attitudes toward counterfeiting luxurious fashion product.
2.4. Social Influence and Attitudes
- Consumers often refer groups and consulting before making their purchasing behavior. Reference groups have potential in forming a person attitudes or behavior in goods and its brand name (Bearden & Etzel, 1982). Social factors also impact the buying behavior of consumers (Ang et al., 2001). Consumer's choice is influenced by others whether they acknowledge about it or not, on the other hand, consumers are interested in impressing or influencing others (Ang et al., 2001). According Phau et al. (2009), consumers have supportive attitudes if their friends or relationships around them supporting it and vice versa. Nguyen Van Phuong and Tran ThiBaoToan (2013) found a positive relationship of social influence to favorable attitudes toward counterfeiting fashion products. H2 hypothesis is proposed: Hypothesis H2: Social influence has a positive influence on favorable attitudes toward counterfeiting luxurious fashion product.
2.5. Price-Quality Inference and Attitudes
- To have the inferences from the price-quality, consumers consider price as “light” then they perceive that a higher price will reflect good materials and better skills, so in this situation the price will play an important role for their purchasing intention (Lichtenstein et al., 1988). However, when they feel that their high cost consuming expense is not as equal quality as they expected, they accept other products with lower rates (Lichtenstein et al., 1988). Consumers believe that “high prices, good quality” and “low prices, poor quality”, this is precisely the inference of consumers from the price-quality (Huang et al., 2004). Huang et al. (2004) proved that the more consumers understand the theory “they will get exactly what they paid”, the less they supported counterfeit. Research of Phau et al. (2009) found that inference from price-quality has a strong impact and negative to favorable attitudes toward counterfeiting. Hypotheses H3 is set as follows: Hypotheses H3: Price-quality inference has a negative influence onfavorable attitudes toward counterfeiting luxurious fashion product.
2.6. Integrity and Attitudes
- Integrity has a strong effect on purchase intention (Ang et al., 2001; Matos et al., 2007; Phau & Teah, 2009). Integrity is determined by personal ethical standards and obedience toward law. If consumers view integrity as crucial, the chances of them viewing counterfeits of luxurious brands in a positive light would be much smaller (Ang et al., 2001). Consumers, who are lawfulness or legality when using counterfeits good, will have more intention to purchase counterfeits. In other words, integrity showed to be a significant predictor of consumers’, they willingness to pay more for purchase genuine goods. (Nordin, 2009). Ang et al. (2001) found a negative effect of integrity to favorable attitudes toward counterfeits. Matos et al. (2007) also found the reverse impact of integrity to favorable attitudes toward counterfeits of consumers in Brazil. Consumers have integrity is as high as it had favorable attitudes toward counterfeits (Phau & Teah, 2009). H4 hypothesis is proposed: HypothesesH4: Integrity has a negative influence to favorable attitudes toward counterfeiting luxurious fashion product.
2.7. Novelty Seeking and Attitudes
- The new favorite is people’s curiosity in search of diversity and difference (Wang et al., 2005). Consumers seek novelty (try to use new goods) is the following strong influence factor after price (due to genuine is too expensive) (Cheng et al., 1997; Wang et al., 2005). For fashion products, there are many factors affecting buying behavior of consumers, in particular to trend or change, consumers quickly forget the product and want novelty (Yoo & Lee, 2009). Consumers follow fashion trends, and always look for the latest products, from which they tend to choose and buy counterfeit goods for more reasonable prices (Nordin, 2009). For updated fashion consumers, the more they like new trend, the higher they support to counterfeit goods (Harun et al., 2012). Hidayat and Diwasasri (2013) found a positive relationship between the new favorite of consumers and their attitudes toward pro fakes. Hypothesis H5 is set as follows: Hypothesis H5: Novelty seeking has a positive influence on favorable attitudes toward counterfeiting luxurious fashion product.
2.8. Status Consumption and Attitudes
- Consumers buy products high fashion to express class and individual images. it is like being shown “how others see me” (Yoo & Lee, 2009). The present status of consumer is defined as a group of people to express their prestige, and to influence others by using certain brands. When a person has a status, which means that people have a certain position in society, and may be jealous by someone else (Phau & Teah, 2009). Those consumers who have lower status, they have an idea of buying counterfeit goods to present a higher position (Budiman, 2012). Phau and Teah (2009) have found a positive effect of status of consumers to attitudes and intention to purchase toward counterfeiting product of consumers. Hypothesis H6 is set as follows: Hypothesis H6: Status of consumers has a positive influence on favorable attitudes toward counterfeiting luxurious fashion product.
2.9. Attitudes and Intention to Purchase toward Counterfeiting Luxurious Fashion Product
- Attitude is a factor to predict intentions and behavior of consumers (Fishbien & Ajzen, 1975; Ajzen, 1991). Although attitudes toward behavior are recognized as a predictor of consumer behavior better than attitudes toward the product (Fishbien & Ajzen, 1975; Ajzen, 1991), but the attitudestoward counterfeit goods is also seen as a factor has an important influence to the idea of buying counterfeit goods (Phau & Teah, 2009). Counterfeit is financial risk, however, if it meets the expectations and satisfies the needs of consumers, it can also feel satisfied when using. So the attitudestoward counterfeit goods is an vital factor to predict the intention of buying counterfeit goods, especially for luxurious fashion brands (Nordin, 2009). There is a positive relationship between favorable attitudes and intention to purchase toward counterfeiting goods (Ang et al. 2001; Huang et al., 2004; Matos et al., 2007; Phau & Teah, 2009; Nguyen & Tran, 2013). Hypothesis H7 is set as follows: Hypothesis H7: Favorable attidues has a positive influence on intention to purchase counterfeiting luxurious fashion product.
3. Methodology
3.1. Methodology
- This study was intended to investigate The Attitudes and Purchase Intention towards Counterfeiting Luxurious Fashion Products among Undergraduate Student in University Kuala Lumpur (UNIKL). Therefore a descriptive research was conducted through a process of collecting 100 self-administered online surveys starting from 25th October until 27th October in order to test the hypothesis. A convenience sample was chosen among students from UNIKL. As counterfeit purchase intentions area is a sensitive topic, people might have been reluctant to answer the questionnaires sincerely. In order to reduce this potential worry, the respondents were notified that this research is purely for academic purposes and their names and information would remain confidential. This study focused on determining if undergraduate students’ purchase intention of luxury counterfeit goods is affected by their ethical and materialistic values. We collected the data through quantitative method (questionnaire). The questionnaire has 2 parts. Part I required respondent to fill up their personal profile and part II required respondent to measure their purchase intention towards the counterfeiting luxurious fashion products. Five point likert scale “1-Totally disagree”, “2-Disagree”, “3-Neutral “, “4-Agree”, “5. Totally agree” is used to measure observed variables in each factor.This is how we calculated to know the sample size of 100 questionnaires to undergraduate student in UNIKL.

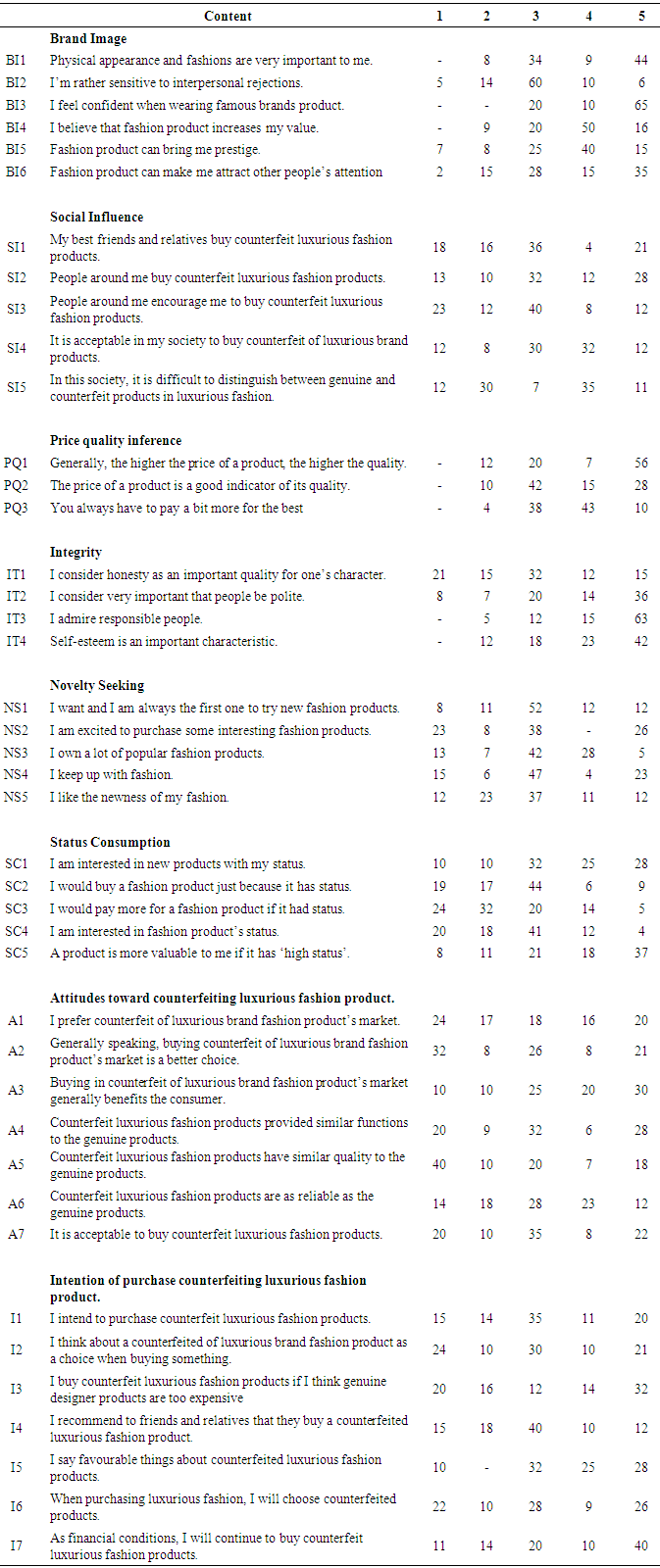
3.2. Research Model
- To study factors that influence attitudes toward counterfeiting luxury, this research will analyze the impact of factors of two groups: factors that influences from outside and inside of consumer: • Outside individual factors: Brand image; Social influence; • Inside individual factors: Price-quality inference; Integrity; Novelty seeking; Status consumption. The research will analyze the degree of influence of these factors on the attitude toward counterfeiting luxurious fashion products, then explore the influence of attitudes on intentions to purchase luxurious fashion products of consumers in Vietnam. The proposed model is as follows:
 | Figure 1. Research Gap Proposed Research Model |
4. Findings
- There are 100 self- administration questionnaires was distributed and collected, after sorting out unsatisfied forms due to lack of information, the remaining 95 valid questionnaire forms (95%) used to analyze this data.
4.1. Statistics
- Genders: In the sample, the majority of the respondents are female, accounting for 66.3%. Male accounting for 33.7%. Age: Respondents, who aged from 19-21 years old, account for 45.3%; from 22 to 24 years old account for 50.5%; from 25-27 years old account for 3.2%; and 28-30 years old account for 1.1%. Marital Status: Respondents who are married, account for 17.9% while single status has the highest number account for 82.1%.Monthly Income: The demographic summary also reported 73.7% of the respondents have the monthly income between RM601 – 1000 while there are only 16 respondents who have the monthly income lower than RM600, accounting for 16.8%. The respondents have monthly income between RM1001 – 5000 accounting for 9.5% and there is no undergraduate student who have monthly income higher RM5001.
|
|
4.2. Bar Graph
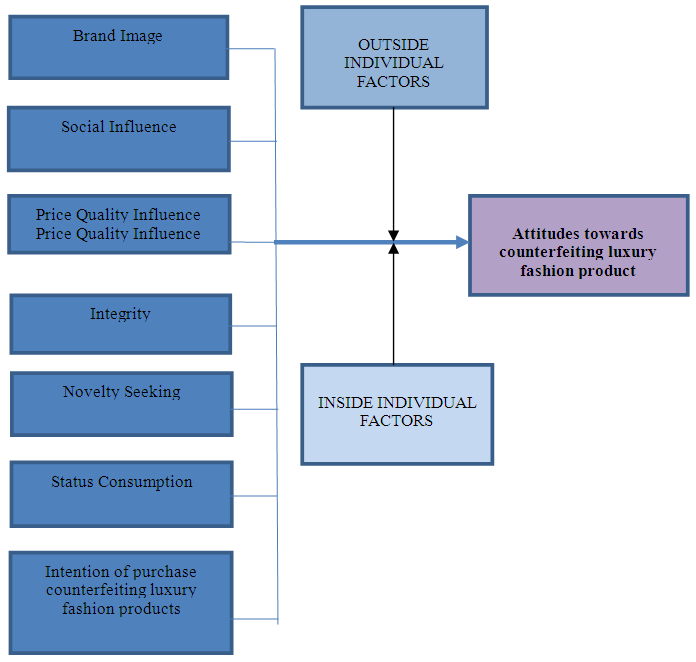
- Bar graph in figure 2 shows that, BI1 got the maximum rate for totally agree (44.4%) while totally disagree got no one rate for this question. BI2 most respondent rate for neutral (63.2%) while only (5.3%) vote for totally disagree. BI3 got the highest rate for totally agree (68.4%) and no one rate for totally disagree. BI4 the maximum vote and minimum vote each got (52.6%) for agree and (0%) for totally disagree. BI5 most respondent vote for agree (42.1%) while less respondent vote for totally disagree (7.4%). BI6 the maximum vote was totally agree (36.8%) while the minimum vote was totally disagree (2.11%). In this question most respondent vote for totally agree. So, the consumer prefer receiving praise for their fashion, but don’t feel that fashion can bring them credibility.
 | Figure 2. Brand Image |
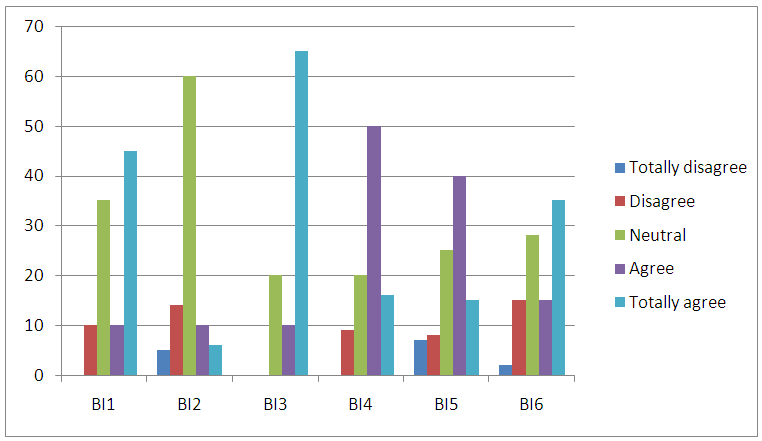
 | Figure 3. Social Influence |
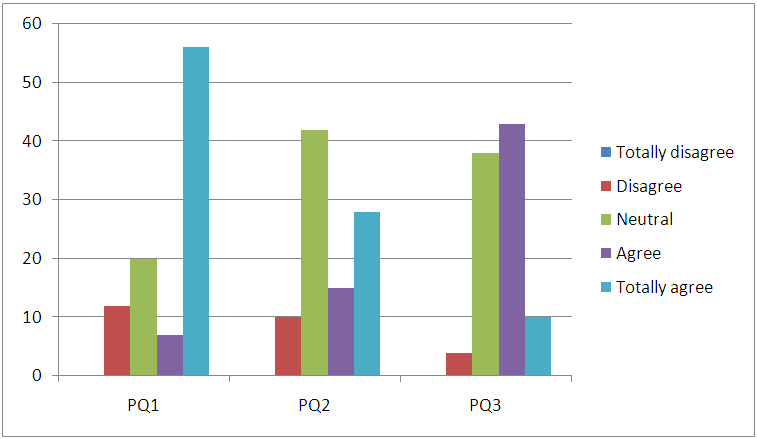 | Figure 4. Price- Quality Inference |
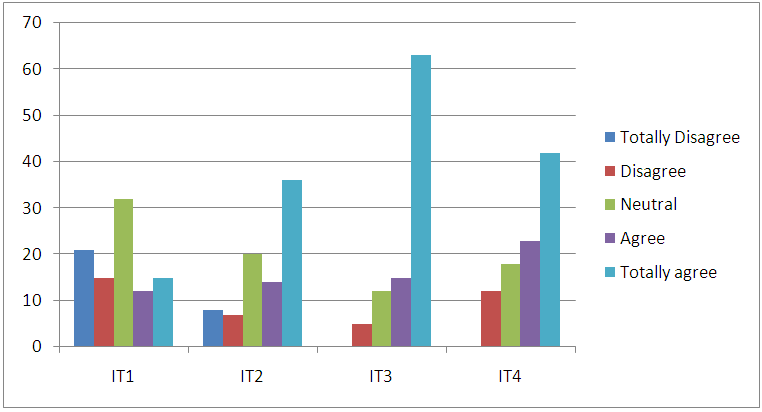 | Figure 5. Integrity |
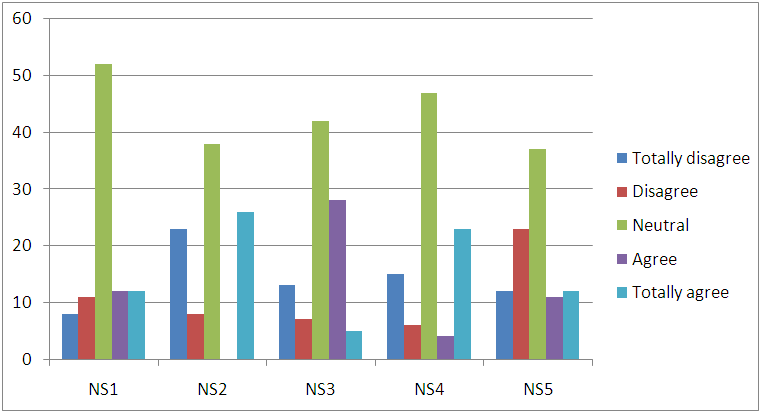 | Figure 6. Novelty Seeking |
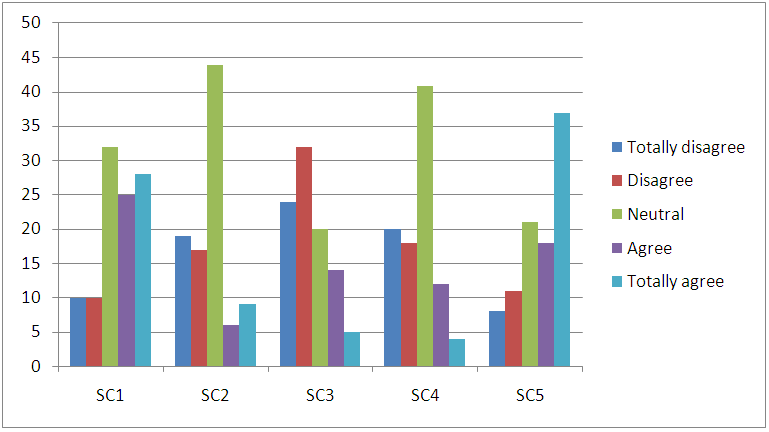 | Figure 7. Status Consumption |
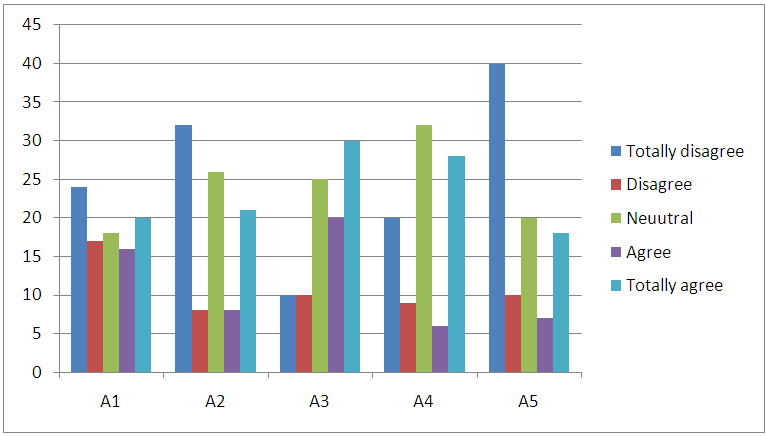 | Figure 8. Attitudes toward counterfeiting luxurious fashion product |
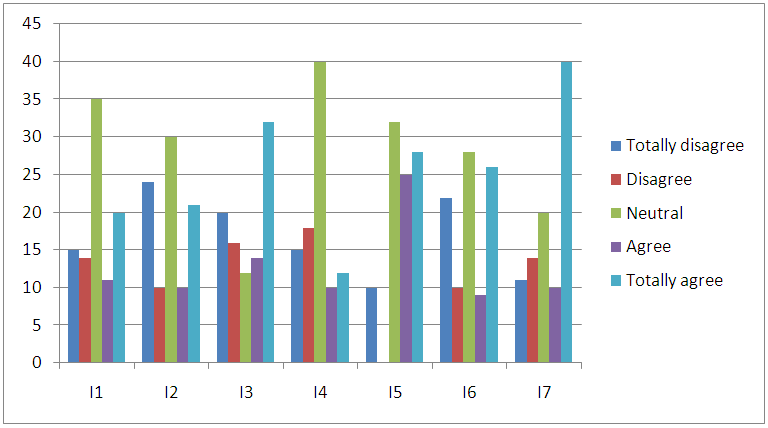 | Figure 9. Intention of purchase counterfeiting luxurious fashion product |
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
- The research was conducted in one phase which is formally research by quantitative method. Qualitative research was conducted using data from distributed questionnaire to UniKL student. Quantitative research was conducted through data from 100 individuals. All data was being cleaned, evaluated, and processed using Microsoft Excell. The results show six factors affecting the attitudes toward counterfeiting luxurious fashion products: brand image, social influence, novelty seeking, status consumption, price-quality inference, and integrity. The first four factors have positive relations to the supportive attitudes. The highest impact factor is expression of consumption status; social influence factor is following. In the other hand, integrity and price-quality inference describe a negative relation to that attitudes; in details, the integrity factor shows higher impact. Regression analysis result also confirms that supportive attitudes strongly adds to the intention of buying those counterfeiting products.From outside individual factor group, including social influence and brand image, both have strong impact to support to counterfeiting luxurious fashion products. Regarding inside individual factor group, according to this research, managers need to make moves to change consumers’ awareness, thus adjust to more appropriate consumption following regulations, society, and their own income. According to experience from other, entrepreneurs-patent owners-play an important role in implementation. Collaboration between entrepreneurs- managers, business owners, distribution representatives of luxurious fashion products in particular-needs to be more forceful in fighting against counterfeits. In details, brand managers could make more community activities, more social responsibility programs, such as in order to attract more consumers. At the moment, they can spread more information of penalty cases to gain more supports from society against counterfeiting products. Secondly, spreading more advertisements how to differentiate genuine and counterfeiting products. It would probably be easier for consumers to differentiate between original products and counterfeits. Lastly, manufacturer of origin branded products should design products congaing rare and high quality materials, associated with value and brand, thus making it more difficult to counterfeit them.Similar to any other research, this paper has its limitations. Due to the method of convenience sampling in the collection of data and a limited scope of time, data could only be collected from 12 campus of University Kuala Lumpur around Malaysia. Furthermore, since data was collected from students of universities from seven campus of UniKL only, the findings of this study cannot be generalized for all UniKL students across Malaysia. In addition, the data was collected from a sample of that predominantly consisted of Malay respondents and lack of Indian and Chinese respondent thus further limits the generalisation of the findings. Also, this research had focused only on luxury non-deceptive counterfeits goods. However, to fully understand consumers’ perception and purchase intentions of counterfeit goods, it is suggested that future studies further explore a wider range of counterfeit products. This could then help in gaining a better understanding of the perception of counterfeit goods.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML