-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2016; 6(5): 270-279
doi:10.5923/j.economics.20160605.04

Comparison on the Effect of Profit Sharing System between Islamic and Conventional System on Profitability, Wages, and Productivity (A Study on Padang Restaurant Business in Pekanbaru)
Deny Setiawan1, Umar Burhan2, Iswan Noor2, Multifiah2
1Doctoral Program of Economics Sc, Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
2Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Brawijaya, Indonesia
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Based on the definition of profit sharing system, there are two different understanding concerning the matter. In Islamic profit sharing system, the distribution of profit or wage between capital owners and capital managers is calculated after the company reaches profit. The portion of profit distribution between capital owners and capital managers is based on previously formulated contract. In conventional profit sharing system, the distribution of profit in a form of wage, and the award of compensation, is set by the owner of capital. The objectives of this study are to assess the effect of both profit sharing systems on profitability, wages, and productivity in Padang restaurant business in the city of Pekanbaru and to identify the difference of profit-sharing system between the economy of Islam and conventional economy.The population of this study is 429 Padang restaurants in the city of Pekanbaru, which spread to 12 districts. The samples of the study are 81 restaurants obtained from the use of Slovin formula. Further, sets of samples is determined, using proportional random sampling method, to represent each of the districts. The respondents of this research are capital managers of Padang restaurant business in the city of Pekanbaru. The analytical method used in this research is quantitative descriptive analysis using PLS (Partial Least Square) tool, which is used to see the effect of each variable, and Independent Sample Test, which is used to see the difference between the variables of both systems regarding profit sharing system.The results of this study indicate that Islamic profit sharing system and conventional profit sharing system provide a significant and positive impact on profitability, wages, and productivity of restaurant business in the city of Pekanbaru. The results of Independent Sample Test show that apparent differences are present in each of the tested variables. The profit sharing system according to the economy of Islam works better in generating profitability, in distributing fairer wages between the capital owners (shahibul mal) and capital managers (mudharib), and in creating higher corporate productivity.
Keywords: Profit Sharing System, Profitability, Wages, and Productivity
Cite this paper: Deny Setiawan, Umar Burhan, Iswan Noor, Multifiah, Comparison on the Effect of Profit Sharing System between Islamic and Conventional System on Profitability, Wages, and Productivity (A Study on Padang Restaurant Business in Pekanbaru), American Journal of Economics, Vol. 6 No. 5, 2016, pp. 270-279. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20160605.04.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Islam as a religion also teaches people to do productive activities. AnasZarqa (in Madnasir 2010) suggested that Islam recognize the term distribution as the transfer of the income of wealth among the people by way of the exchange (by the market) or by way of heritance, alms, endowments and zakat. There are some differences that have been determined in running the economic system of Islam with other economic systems. For example, the economic system of Islam forbids usury, the obligation to pay zakat, profit sharing mechanism between the owners of capital (shahibul mal) and workers (mudharib). Profit sharing mechanism in the economic system of Islam known as profit sharing system.There are many verses in the Qur’an that describe the implementation of profit sharing system in Islam itself. First, the doctrine of cooperation in Islamic economy can create productive work everyday from people (Qur'an, 2: 190). Second, increase welfare and preventing social misery (Qur'an, 3: 103) (Qur'an, 5: 3) (Qur'an, 9: 71, 105). Third, to prevent economic oppression and unequal distribution of wealth (Qur'an, 69: 25-37), (Qur'an, 89: 17-20), (Qur'an, 107: 1-7). Fourth, build a reputable principled organization, resulting in the strong help the weak (Qur'an, 4: 5-10, 74-76) (Qur'an, 89: 17-26). Fifth, the division of cooperation or specialist based on interdependence and exchange of goods and services because it is impossible to stand alone (QS, 92: 8-10) (Qur'an, 96: 6).Islam requires and directs Muslims to take action in accordance with what is permitted and forbidden by Allah SWT. Similarly, in carrying out trading activity, the values of Islam has always been a main runway. Anyone who wants to socializing (muamalah) been allowed unless prohibited. It provides a broad space for Muslims to perform their economic activities so as to improve the welfare and standard of living (Subhan, 2003). Islam as a religion also teaches people to do productive activities. AnasZarqa (in Madnasir 2010) suggested that Islam recognize the term as the transfer of the income distribution of wealth among the people by way of the exchange (by the market) or by way of inheritance, alms, endowments and zakat.There are some differences that have been determined in running the economic system of Islam with other economic systems. For example, the economic system of Islam forbids usury, the obligation to pay zakat, profit sharing mechanism between the owners of capital (shahibul mal) and workers (mudharib). Profit sharing mechanism in the economic system of Islam known as profit sharing system.There are many verses in the Qur’an which highlighted the implementation profit sharing within Islam itself. First, the doctrine of cooperation in Islamic economy can create productive work everyday from people (Qur'an, 2: 190). Second, increase welfare and preventing social misery (Qur'an, 3: 103) (Qur'an, 5: 3) (Qur'an, 9: 71, 105). Third, to prevent economic oppression and unequal distribution of wealth (Qur'an, 69: 25-37), (Qur'an, 89: 17-20), (Qur'an, 107: 1-7). Fourth, build a reputable principled organization, resulting in the strong help the weak (Qur'an, 4: 5-10, 74-76) (Qur'an, 89: 17-26).The verses of the Qur’an above explains that in Islam has taught a complete economic system, be it the process of cooperation, prosperity and social equality, equity, public organizations and unity, as well as the division, specialization, as well as the exchange of goods and services. The economic system forming a concept with functions that show that through Islamic profit sharing system will create a more equitable economic order. Islamic economic system is a problem related to the division of net income determined at the beginning of the cooperation contract, which is determined is the portion of each party.The profit sharing system in the conventional economy, for example in the form of compensation, stock dividers, and a bonus for workers is not referred to in the sharing system in Islamic economics. The profit sharing system of Islamic economics in which an investors made an accounting agreement with workers of profits in accordance with the deal. The results of the count will applicated after gains obtained.In carrying out economic activities in the field of trade micro (real sector) are generally implemented a conventional profit sharing system or identical with the capitalist economic system. Not many Muslims who implementing the Islamic profit sharing system in their business. It proven of the small number of studies conducted on the application of the sharing system of Islam in the real sector in the community. Even if there is, the current profit sharing system is now generally carried out by Islamic banking, Islamic insurance and Islamic financial market.Padang restaurant business is one of the many trading businesses that implement both systems, both the profit sharing system of Islamic and conventional system. It also happens to Padang restaurant in Pekanbaru city of Riau province. Padang restaurant is very popular among the people the city of Pekanbaru. With the increasing population and per capita income of urban Pekanbaru, restaurant business in Pekanbaru city is growing by leaps and bounds. In general, the restaurant business is done with conventional profit sharing system. Conventional profit sharing system that is distribution advantage of the wages of the owners of capital to employees is done by giving wages for workers on a monthly basis for a nominal amount plus the compensation that has been agreed or not. This is commonly done by employers restaurant or other business.While business in the Padang restaurant in terms of the distribution of profits in the form of wages between capital owners and managers have own way. Generally, owners of capital Padang restaurant did wage as do venture capitalists in general. Owners of capital and managers in Padang restaurant would get a reward from the profit-sharing percentage profit sharing they had set at the beginning of this business. It is identical to the profit sharing system of Islam as described in the literature of Islamic economics. In percentage of profit share, known as profit sharing there are a fixed and certain returns as interest, but done in a way to share profits and losses based on real productivity of such products (Karim, 2001).In running the restaurant business, each employee has a different task. For that wages will be given to each worker will be different. Sharing a percentage (ratio) for the results of Padang restaurant business in general is 40:60 between the owners of capital with a manager or a 40 percent gain for the investor and 60 percent for managers. Distribution of this percentage is not absolute, depending on the initial agreement with the manager of the restaurant financiers. This strengthens the foundation of that system is the result of efforts undertaken by Padang restaurant is synonymous with the concept of profit sharing in Islam. The second application of the profit sharing system, the profit sharing system both Islamic and conventional in Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru will affect profitabilitty, wages and productivity of the business being operated.
2. Research Methods
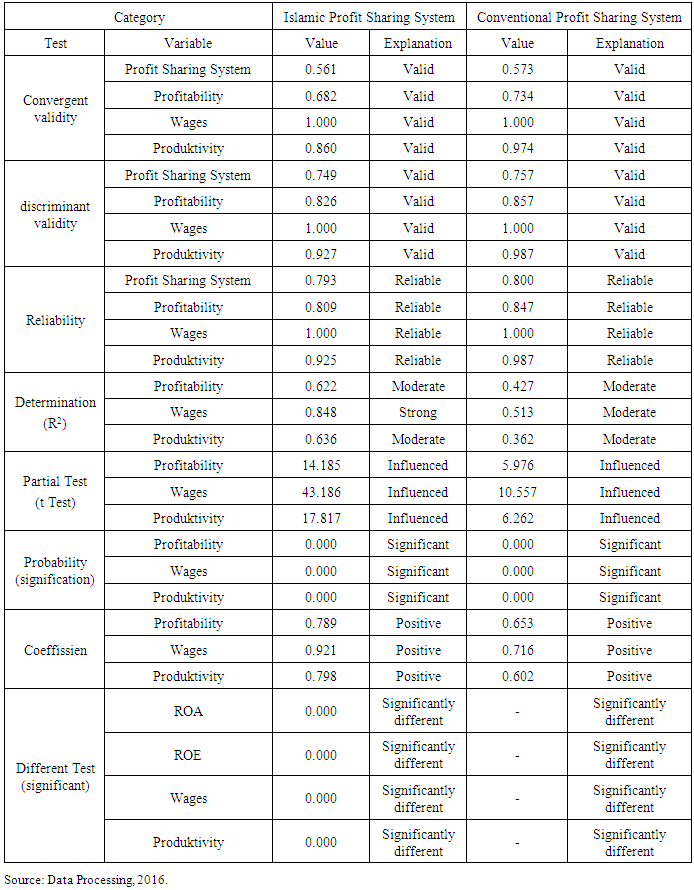
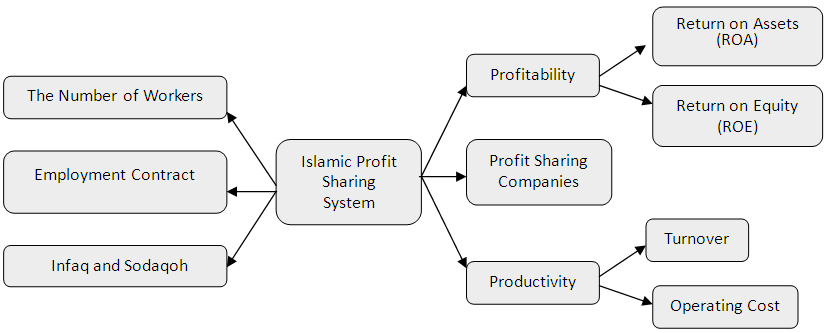
- This study aimed to analyze the comPadangon effect of Islamic profit sharing and conventional to profitability, wages, and productivity in Pekanbaru. The choice of location using criterion-based selection, the choice is based on certain criteria. (Le Compte and Preissle in alwasilah, 2003). This study uses analysis tools Partial Least Square (PLS). That is a structural equation analysis (SEM) based variants that can simultaneously perform testing at the same measurement model structural model testing. Measurement model used for validity and reliability, while the structural models used to test causality (hypothesis testing predictive models). Structural equation for the Islamic Profit Sharing and conventional production sharing system can be illustrated in Figures 1 and 2.
 | Figure 1. PLS Model for Islamic Profit Sharing System |
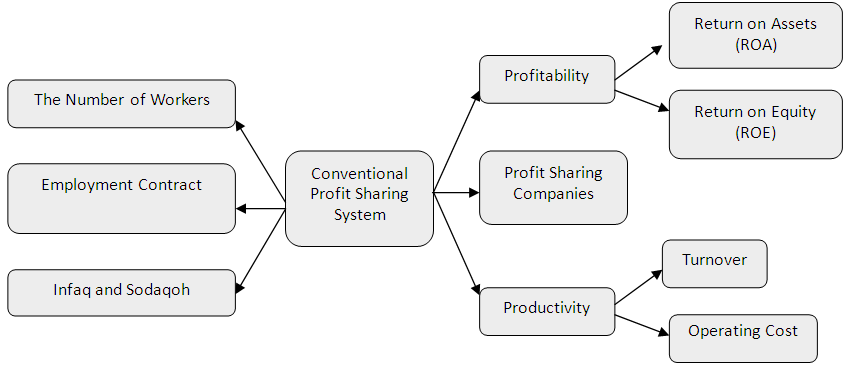 | Figure 2. PLS Model for Conventional Profit Sharing System |
 | Figure 3. Research Location Map |
3. Empirical Result
- I. Analisys DataPath coefficients describes the impact of the independent variable on the dependent variable. In this case, the path coefficients see the effect of variable profit-sharing system of Islam on profitability, wages and productivity, as well as the effect of a conventional system on profitability, wages and productivity at the business Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru. The results of calculations using the application path coefficient obtained SmartPLS 3.0 sharecropping system of Islam on profitability, wages, and productivity of the business Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru is as follows:From the picture above, may explain the effect of variable profit-sharing system of Islam on profitability, wages and productivity at the business Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru is as follows:Sharing System 1. The Effect of Islamic Profit Sharing System to Profitability on Padang Restaurant in PekanbaruThe effect of Islamic profit sharing system to profitability on Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru is very strong. This is seen in the amount of path coefficients produced, which is equal to 0.789. Profit sharing system of Islam with indicators of the amount of wages, contract or work rules, and worship in terms of donation and alms giving a significant positive effect on the level of profitability of the company, both in the aspect ROA companies, as well as the company's ROE in the Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru. The magnitude of the effect of profit-sharing system of Islam to the level of profitability of the company is not independent of the value of R2 is formed on these variables, the greater the value of R2 on a variable, the smaller the effect of other variables to effect it. Path coefficient on this variable adequately address the hypothesis 1 is in the form of Islam that is the profit sharing system significant positive effect on the profitability of the business Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru. Path coefficient value of 0.789 is a positive effect, while T-count> T-tables as well as for 0.000 P-values of <0.05 interpret the independent variables have a significant effect on the dependent variable.2. The Effect of Islamic Profit Sharing System to Wages on Padang RestaurantThe effect of Islamic profit sharing system to wage on Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru is very strong. Compared with the results of the effect of Islamicprofit sharing system to profitability, its effect on the wage level is greater. This is seen in the amount of path coefficients produced, which is equal to 0.921. Profit sharing system of Islam with indicator of the number of labor, contract or work rules, and worship in terms of donation and alms giving a significant positive effect on the wage levels of the company, where wage levels are measured by indicators of the amount of salary or profit sharing business received by employees in the Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru. The magnitude of the effect of profit-sharing system of Islam to the level of profitability of the company is not independent of the value of R2 is formed on this variable, wherein R2 wage level is also greater than R2 profitability. Path coefficients on these variables adequately address the hypothesis 2 is in the form of Islam that is the profit sharing system significant positive effect on wage levels in the company's Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru. Path coefficients value of 0.921 are positive effect, while T-count> T-tables as well as for 0.000 P-values of <0.05 interpret the independent variables have a significant effect on the dependent variable.3. The Effect of Islamic Profit Sharing System to Profitability on Padang Restaurant in PekanbaruThe effect of Islamic profit sharing system on the productivity of companies Padang restaurant in Pekanbaru also strong. This looks at the magnitude of the resulting path coefficient, which is equal to 0.798 is greater than the other variables. Islamic profit sharing system with the indicators of the amount of labor, contract or work rules, and worship in terms of donation and alm giving a significant positive effect on the level of productivity of the company, as measured by indicators of turnover and operating costs of companies in the Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru. In addition to the value of the path coefficients, the value of R2 in the variable productivity is also the largest R2 value compared to other variables. This shows the strong effect of Islamic profit sharing system on the productivity of the company compared its effect on other variables. Path coefficient on this variable enough to answer hypothetical 3 is in the form of Islam that is the profit sharing system significant positive effect on the productivity of the Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru. Path coefficient value of 0.798 is a positive effect, while T-count> T-tables as well as for 0.000 P-values of <0.05 interpret the independent variables have a significant effect on dependent variables. While, the value of the path coefficients in the conventional profit sharing system has results that little different than the value of the path coefficients on the Islamic profit sharing system. Basically, the value of the path coefficients for conventional profit sharing system also has a positive effect, as in the following picture:From the picture above, may explain the effect of system variables for conventional profit sharing system on profitability, wages and productivity at the Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru is as follows:1. The Effect of Conventional Profit Sharing System to Profitability on Padang Restaurant in PekanbaruThe effect of conventional profit sharing system has a strong effect on the profitability of companies Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru. This is seen in the amount of path coefficients produced, which is equal to 0.653. Profit sharing system with the conventional indicators of the amount of labor, contract or work rules, and worship in terms of donation and alms giving a significant positive effect on the level of profitability of the company, where the company's profitability measured by ROA of the company, and also the value of the company's ROE in Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru. The magnitude of the effect of conventional profit sharing system on the level of profitability of the company is not independent of the value of R2 which is included into the strong category.The effect of the system for conventional on profitability is better than the effect on productivity of the company, but when compared with the effect on wage levels, the effect of conventional profit sharing system on profitability still has path coefficient value smaller. Path coefficient on this variable is sufficient to answer the hypothesis 4 is in the form of profit-sharing system that is conventionally significant positive effect on the profitability of the Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru. Path coefficient value of 0.653 is a positive effect, while T-count> T-charts and P-values of 0.001> 0.05 define independent variables have a significant effect on the dependent variable.2. The Effect of Conventional Profit Sharing System to Wages on Padang Restaurant in PekanbaruThe effect of conventional profit sharing system to Wages on Padang restaurant company in the city of Pekanbaru is very strong. Compared with conventional profit sharing system effect on the profitability and productivity of the company, its effect on wage levels are the greatest effect. This is seen in the amount of path coefficients produced, which is equal to 0.716. Profit sharing system with the conventional indicators of the amount of labor, contract or work rules, and worship in terms of donation and alm giving a significant positive effect on the wage levels of the company, where the wage rate is measured by the amount of wages fixed and coupled with incentives or compensation received by employees on Padang restaurant on the city of Pekanbaru. The magnitude of the effect of conventional profit sharing system to wage the company is not independent of the value of R2 is formed on this variable, wherein R2 wage level is also the largest R2 value compared to the value of R2 in the variable profitability and productivity of the company. The value of path coefficients on these variables adequately address the hypothesis 5 were in the form of a conventional profit sharing system havesignificant positive effect on wage levels in the Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru. Path coefficients value of 0.716 is a positive effect, while T-count> T-tables as well as for 0.000 P-values of <0.05 interpret the independent variables have a significant effect on the dependent variables.3. The Effect of Conventional Profit Sharing System to Productivity on Padang Restaurant in PekanbaruThe effect of the conventional profit sharing system on the productivity of Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru has a strong effect though when compared with the effect on profitability variable and variable wages, conventional profit sharing systems effect on the productivity of the company is the smallest effect. The magnitude of the resulting path coefficient shows a relatively strong effect, which is equal to 0.602. Conventional profit sharing system with indicators of the amount of labor, contract or work rules, and worship in terms of donation and alm giving a significant positive effect on the level of productivity of the company, as measured by indicators of turnover and operating costs of companies in the Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru. The effect of conventional profit sharing system is not independent of the value of R2 generated. Path coefficient on this variable enough to answer hypothetical 6 in the form of conventional profit-sharing system that is significant positive effect on the productivity of the Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru. Path coefficient value of 0.602 is a positive effect, while T-count> T-tables as well as for 0.000 P-values of <0.05 interpret the independent variables have a significant effect on the dependent variable.From the above calculation, the profit sharing system both Islamic and conventional has a significant positive effect on the variable profitability, wages and productivity. But the effect on the show by each of the variables differ depending on the relative magnitude of the path coefficients and R2 value generated by each variable.
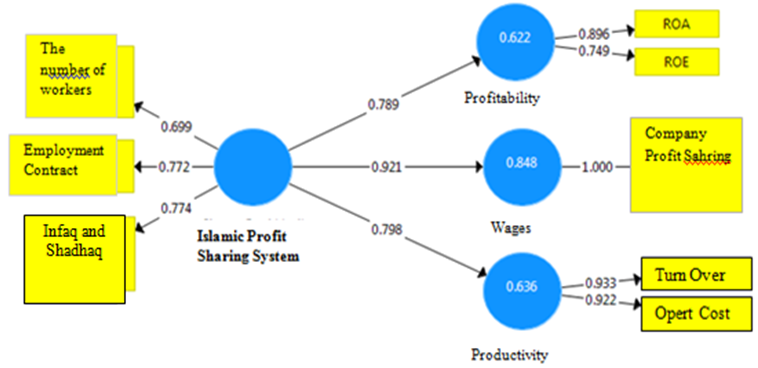 | Figure 4. Path Coefficients of Islamic Profit Sharing System |
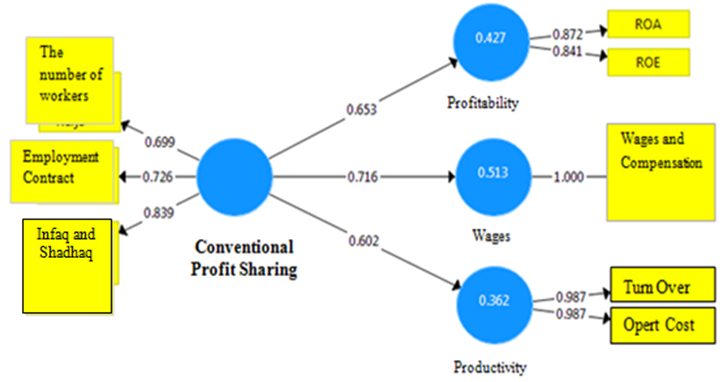 | Figure 5. Path Coefficients of Conventional Profit Sharing System |
|
4. Discussion and Results
- Islamic profit sharing system to be trending in decades is getting warmer in talking, especially after the reform the existing market failures. Islamic profit sharing system is expected to be a solution amid the crisis that hit Indonesia in the reform period. Until now, the sharing system of Islam has its own charm, what else in the world of banking. Islamic profit sharing system in the banking world, better known as profit sharing. In contrast to conventional production sharing system aimed at obtaining the maximum benefit, the sharing system of Islam prioritize welfare, where profits are divided between capital investors in accordance with a specified percentage of employees. In the world of Islamic banking, the sharing system aims to avoid the establishment of the system of interest, where interest in Islam is "usury".From the statistical test result explains that these two systems provide benefits in the restaurant business in the city of Padang Pekanbaru. The two systems for this result, both the Islamic profit sharing system and conventional has a significant impact on profitability, wages and productivity. Despite having a significant effect, but the sharing system of Islam gives a greater effect than the conventional system for results.1. The Effect of Islamic Profit Sharing System to ProfitabilityProfit sharing system whose application is a benefit sharing between investors and employees are a major factor in the high proftability acquired by the company. Employees will be motivated to work, so that the output or total sale of the business will increase, which means clappers company also increased. The calculation of the profitability of companies using ROA and ROE that is used as the main source of corporate profits in the company's return on capital.Application of Islamic profit sharing system in Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru also significant positive effect on the profitability of its business. Similarly studied by Hassoune, Anggadanni and Sheptiyani get thestudy that sharing system of Islam profits become larger, because the employees who work oriented to the greater business profits earned, the greater part of which was obtained by the employees.2. The Effect of Islamic Profit Sharing System to WagesStatistical analysis showed that the effect of Islamic profit sharing system of wages is significantly positive. The relationship between the two variables is also very powerful indicated by the value of determination (R2) obtained. In the Islamic profit sharing system, wages earned by the employee depends on the sale of its business due to the wages received a benefit sharing between investors and employees. The more that is able to sell, the higher the profits. The higher the profit earned by the company then the remuneration given to employees are also getting bigger.Kuncoro (2002) suggests that there are positive effect between the system of profit sharing with employees' wages. In this study, said the implications of the results of the labor-intensive industries in Indonesia in 1990 and 1998 can be concluded that the application of the sharing system to increase wages (welfare) for employees. In addition it is said that, if the system for these results goes well, in the long term will support efforts to improve the living standards of employees in particular and the distribution of income between employees and employers in general.In line with the above Kuncoro research, the effect of Islamic profit sharing system to wage the Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru significant positive effect. The concept of profit sharing system of Islam which is a division of clappers between investors and employees to be the cause, where the greater profits of their business the greater the profits of investors, as well as the wages received by employees will be greater.3. The Effect of Islamic Profit Sharing System to ProductivityIslamic profit sharing system applied to the Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru showed significant positive effect on the productivity of the company. This means that the system is applied to the Islamic profit sharing system, the employees in the Padang restaurant business in Pekanbaru was able to increase the productivity of companies in order to obtain the maximum profit.The results of this study are also consistent with previous research that has been studied. Kato (2010) in his study show that implementation of the profit sharing system and team incentive plan in the company South Korean companies can improve productivity 10%. In addition, another study conducted by Lentz and Mortensen (2003) concluded that the difference between the company's productivity is closely related to differences in wages, and the relationship between labor productivity and wages measured individually can be well documented. This further confirms that the sharing system of Islam has great effect shaping the company's productivity. The employee's desire to increase its profit making employees to be more productive in managing existing resources.4. The Effect of Conventional Profit Sharing System to ProfitabilityThese results indicate that the effect of conventional production sharing system to profitability of the restaurant business in the city of Padang Pekanbaru significant positive effect. The results of this study supported the statement Harahap (2004) that the profitability ratio describes the ability of companies to profit through all the existing capabilities and resources such as sales activities, cash, capital, number of employees, number of branches. The ability to see a return can be seen from the ROA and ROE. Conventional profit sharing system prioritizes the maximum profit, so that by applying a system that rewards can still increase the company's profits and therefore contributes to the profitability of the company.5. The Effect of Conventional Profit Sharing System to Wages In the Conventional Profit Sharing System, wage determination was fundamental. Wages still provided in this system have an effect in achieving its business objectives, namely profit. When it is the remuneration given too big an impact on the growing costs to be incurred, where the cost of employee wages given by the initial agreement and the amount does not change until the contract agreed between venture capitalists and employees ends. Conversely, if the wage is too small lead someone working interest is very low which will also have an impact on their business profitability. These results indicate that the effect of conventional production sharing system have a significant effect on wages. These results are in line with research conducted by Afrooz danRahim (2010) in their study entitled effect of gender, age and education on wages and productivity gain that there is a positive relationship between productivity and real wages. Mangkunagara (2000), argued that the compensation granted to employees affects the satisfaction and motivation, where motivation and ability to work would affect the work.Implementation of the Conventional Profit Sharing System on a Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru, besides setting wages, some business units provide compensation or incentives to motivate their employees beyond salary. This is done so that employees are able to meet their needs and keep morale so that maximum benefit can be achieved.6. The Effect of Conventional Profit Sharing System to ProductivityIn this study, the effect of Conventional Profit Sharing System on the productivity of Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru significant positive effect. The results are consistent with what is observed by Afrooz and Rahim (2010) in their study entitled effect of gender, age and education on wages and productivity gain that there is a positive relationship between productivity and real wages. Besides other research conducted by Patra and Ranjan (2012) states that productivity associated with wages based on the output produced by the employees. In applying the conventional revshare system at Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru implement a fixed wage according to the contract or agreement at the beginning of the work and does not change until an agreement or employment contract ended. Implementation of the system for the results of this conventional permanent effect on productivity because the wages granted by venture capitalists to employees has been assessed able to meet the needs of its employees, in addition to several business units provide compensation or incentives beyond the fixed wage to improve the productivity of his company.
5. Conclusions
- The results of this study explains that theoretically and empirically, gives the following conclusions: (1). Businesses or corporate houses in the city of Pekanbaru tends to apply the Islamic profit sharing system, (2). Islamic profit sharing system and conventional production sharing system has positive and significant impact on profitability, wages and productivity. Although the two systems for this result a significant effect, but the sharing system of Islam have a more powerful effect against profitabiitas, wages, and productivity compared with wages for conventional results, (3). Islamic profit sharing system generate levels of profitability and productivity levels for businesses Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru higher. This proves that the application of the Islamic profit sharing system for Padang restaurant in the city of Pekanbaru better than conventional system application. For the average wage received by workers, based on the results of this study find that average wages of workers who implement the Islamic profit sharing higher than the average wage of workers that implement the conventional system. This led to a fairly even distribution of income is better and (4). There are significant differences between profitability, wages, and productivity on the Islamic profit sharing and profit sharing conventional. This is due to the implementation of the Islamic system for better results led to higher average profitability, wages, and productivity compared to conventional profit sharing system.The results of this study also provide advice to continue to maintain the principles of business in accordance with Islamic law. Padang restaurant business actors are also advised to be careful to make your choice for the system adopted in its business results. Selection of the appropriate system will affect the profitability and sustainability of their business. In this case the business actor can make your choice for the results of the Islamic system because it proved to be better than the conventional profit sharing system. In terms of the relationship between capital owners and employees will create a partnership that is mutually beneficial. This is because there is a value that is fair in terms of the distribution of income.The results of study show the application of the sharing system of Islam better in improving profitability, wages and productivity in the restaurant business Padang compared to the conventional application of the sharing system for businesses hence recommended to implement the sharing system of Islam as an alternative to running a restaurant business.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML