Clifford James Fagariba
School of Economics, Wuhan University of Technology, China
Correspondence to: Clifford James Fagariba , School of Economics, Wuhan University of Technology, China.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Abstract
One of the greatest problems that have come to force so far as revenue generation is concerned is that of tax evasion. Many Ghanaians especially traders and SMEs willfully or deliberately refuse to honour their tax obligations by distortion relevant figures relating to an assessment after tax liability has been incurred with the intention of reducing the liability. Some also connive with some selfish tax collectors to under declare their tax obligation. Though there had been gains in tax revenue mobilization in recent times, nevertheless the revenue generated from taxes is not enough to support annual government budget for development. This compels the government to continue to rely on donor partners and the international organisations such as World Bank, IMF and European Union to support annual budgets though most of these aid comes with strict and unfavorable conditions mostly not in tune with the country national development plan. If the government is able to generate enough income through various forms of taxes, the country’s ailing economy which is currently facing numerous challenges can be back to a state of good health. Perceptions of causes of tax evasion varies from individual perspective depending on the socio-economic, political, tax administration lapses and other conditions that serve as bottle necks to the taxpayers which influences them to perpetuate these act. There is an inherent tension between the state and the citizen when it comes to tax matters due to poor performance of businesses vis a vis hikes in taxes. Most SMEs and traders which forms about 80% of source of revenue generation to the governments are at the verge of collapsing due to power shortage which serve as their main source of energy to run their business. The research conducted revealed that perception of causes of tax evasion is complex and is related to many socio-economic factors such as high level of corruption in the government, high compliance cost, weak enforcement of tax laws, weak capacity of tax authorities to detect tax defaulters, poor tax education, loop holes in the tax net and issues of tax burden. It was also realised that poor sales coupled with high corruption among government officials influence loyal taxpayers to ignore tax morality and evade tax. Among the recommendation suggested were, bribery and corruption in country should be addressed. The Ghana Revenue Authority (GRA) and Accra Metropolitan Authority (AMA) should also embark on massive campaign against tax evasion. It was also realised that, tax laws and education should be rigorously enforced and offenders should be given severe punishment to serve as deterrent to others.
Keywords:
Tax Evasion, SMEs, Traders, Perceived causes
Cite this paper: Clifford James Fagariba , Perceptions of Causes of SMEs and Traders Tax Evasion: A Case of Accra Metropolis, Ghana, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 6 No. 2, 2016, pp. 116-137. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20160602.04.
1. Introduction
Taxes are vital tools for development and governance of any country. On the one hand, by paying taxes, citizens contribute to building sovereign states and on the other, good governments use this revenue responsibly to meet their obligations in providing essential public services to all citizens. Importance to taxes to every nation cannot be o under estimated. The richest countries in the world mostly generate revenue internally through effective tax administration strategy which ensure that citizens, firms and institutions honour their tax obligation without fear or favour. Globally, government is saddled with the responsibility of providing some basic infrastructures for it citizens. Among these are the provisions of Schools, Hospitals, construction Roads, Bridges, Railway lines, Airports and seaports. More so is the security of the life and properties of the citizens in the country against foreign and or local aggression. Alm et al (2013) stated that, out of tax revenue accrued, most governors are spending huge sum of money to protect their resources and citizens from any external pressure. This enables citizens to go discharge their daily duties without fear or intimidation. Tax is a system of payment that individuals and firms are legally required to pay to the government. Lymer and Oats (2010) defined tax as the compulsory transfer of money from private individuals and groups of institutions to the government. In effect, taxes are compulsory payment made by individuals, companies and business organizations under force without regard to the specific benefits that the tax payer may receive but rather used towards the improvement of the common good of the citizens and the nation as a whole. As a matter of fact, taxation plays tremendous role in every country. It helps the government to raise revenue to be able to fund projects for development. Tax evasion refers to a deliberate refusal of a taxpayer towards his/her tax obligation. Deliberate refusal to disclose one’s sources of income to the tax authority with the intention of paying nothing or something lesser in terms of one’s tax liability is an attempt to evade tax. Tax evasion is also a phenomenon that is present in all societies due to certain factors which include ignorance and noncompliance on the part of taxpayers, poor standard of record keeping and incorrect returns made by small scale businesses. Hence efficient measures should be set and implemented to obtain taxes to be able to fund development projects. According to Benk et al (2015), provision of public services offers a rationale for taxation. Hitherto, taxation and tax evasion in turn influence public expenditure and capital accumulation which affect output and economic growth. It has been noted that tax evasion is directly linked to large budget deficits and hence lower investments in public goods. In the last one and a half decades, tax reforms have been an important component of broader economic reforms in developing countries. The main objectives of these government initiatives have been to increase public revenues by enlarging the tax base, improving tax mobilization techniques, introducing value added tax (VAT), and attempting to improve the efficiency of tax administration by improving transparency and reducing corruption and tax evasion. While governments can do little in the short run to change the structural determinants of tax revenue (such as composition of value added), they can alter other factors that influence tax revenue, such as economic policies, the level of corruption and the quality of tax administration. In many developing countries the wide divergence between the effective and statutory tax rates indicate that there is scope for raising tax revenue without increasing tax rates by reinforcing tax and customs administration, encouraging voluntary tax compliance, reducing and eliminating some tax exemptions, and fighting fraud and corruption.In African countries, experts have warned that tax reform efforts will continue to be modest due to the low levels of development and the heavily agricultural and informal character of their economy. Furthermore, tax mobilization and reform can be achieved only when there is strong political will and leadership to adopt the necessary measures. As all countries across the world, African countries have introduced Value Added Tax (VAT) because it is recognized as a modern and efficient way to collect the revenue needed for a country. The purpose of applying for VAT is to improve the efficiency of tax by facilitating its administrative management and by limiting the possibilities of evasion. A multiplicity of taxation rates would lead to important administrative and control costs that are beyond the tax administrative capacities of most African states. For the structure of taxation, the role of indirect taxation has become increasingly important in Africa, while that of the personal income and other direct taxes remains very low. It is worthy of note however that, there are other sources of revenue generation by the government e.g. borrowing, grants etc but the conditions mostly attached to it hinder economic growth. There are several challenges that bedevil Ghana’s tax and revenue generation sector. The problems are complex and intertwined, for that matter they need to be tackled concurrently. That is to say, the problems that hinder Ghana Revenue Authority efficiency, preventing it from achieving it annual revenue target should be given the needed attention. Ghana’s reliance on donor support to implementation our development agenda is still major issue since the revenue generated from taxation is not enough to fund our annual budget. Despite the improvements in revenue generation, tax revenue has only been enough to finance between 50-60% of total budgetary expenditures.There is an inherent tension between the state and the citizen when it comes to tax matters. Although it is conceivable that citizens should be ready and willing to pay taxes, (which are used for public goods for the benefit of all), in reality, citizens often prefer a free rider’s attitude and avoid taxation as much as possible. Voluntary tax compliance is therefore an issue. Voluntary tax compliance which is one of the main problem in Ghana need to be addressed through education and advocacy that will enable loyal taxpayers to honour their tax obligation without evasion or default. Poor check and balances preventing transparency and accountability in Ghana are the main reasons why tax revenue generated by the government cannot support the nation toward it development agenda. There are also lots of loopholes in the tax administration system which individuals and private sectors are taking advantage of, either pay low or evade tax. Apart from VAT and taxes deducted from sources, individuals, traders and businesses always under declare their profit with the intension of evading or paying less tax. Tax collectors apart from the automated ones mostly take bribes from taxpayers and issue fake receipt so as not to pay the actual tax they ought to pay. Statement of ProblemThe incidence of taxation and the prevalence of tax evasion are complex and cannot be underestimated. Tax evasion by its very nature is not easy to determine unless efficient mechanisms are put in place to monitor all sectors that falls under the national tax net. Tax evasion affects the distribution of the tax burden as well as the resource cost of raising taxes. The resulting tax revenue loss may cause serious damage to the proper functioning of the public sector, threatening its capacity to finance its basic expenses, (James et al, 2014). Research conducted by Shahrodi (2010) revealed that a tax system characterized by widespread noncompliance places an unfair burden on honest taxpayers and this could serve as breeding grounds for tax evasion. Hence, tax evasion by some may lead to tax evasion by others, causing a further loss of revenue. If the government compensates for the loss by raising rates, tax evasion becomes even more attractive. The higher rates in effect penalize honest taxpayers, who comply either because they want to or because they have no opportunities for evasion. If the government, however, takes effective steps to prevent or combat non-compliance, it can raise revenue without increasing taxes or reducing spending.In Ghana, one of the greatest problems that have come to force so far as tax administration is concerned is that of tax evasion. Many Ghanaians especially traders willfully or deliberately refuse to honour their tax obligations by distortion facts and figures relating to an assessment after tax liability has been incurred with the intention of reducing the liability. Deliberate refusal to disclose one’s tax sources of income to the tax authorities with the intention of paying nothing or something less in terms of one’s tax liability is an attempt to evade tax. Tax evasion is an offense as described by the law and so the sanctions could be very severe.Though there had been gains in tax revenue mobilization, the revenue generated from taxes is not enough to support annual budget. There had been a lot of challenges in tax collection and this resulted in loss of government revenue. Most Ghanaian especially traders feel exploited or cheated when paying taxes because they feel paying taxes seem throwing their money away. Most also feel the tax is so expensive looking at the nature of their business and the taxes levied on them to pay either monthly, quarterly or annually. This has compelled businesses and traders to bribe tax collectors to enable them evade tax. Furthermore, due to high rate of corruption among government officials, most taxpayers feel their monies are used for meaningless purpose at the expense of their toil and struggle to make earns meet. Others also feel tax agents who come to their shops to collect taxes exploit them by making them pay unreasonable tax.Ghana is richly blessed with oil and gas among other mineral resources, but the over reliance on oil revenue for economic development of the country has created a lot of challenges to the economy. Over dependence on oil revenue to the total neglect of other revenue source was encouraged by the oil boom which has resulted in Dutch disease. Tax play vital role in Ghana economy because it is the source of revenue that government use to support it budget for development projects such as building schools, hospitals, roads, dams, etc. The government also use part of the revenue generated from taxation to pay workers’ salaries and also provide security for all it citizens. Hence importance of taxation in building a strong economy for that matter Ghana cannot be over emphasized.Greater Accra Metropolis is in the Capital City of Ghana with a population of about 2.4 million people. The metropolis has a lot of small scale business shops for retailing goods and services but most of them invade tax because they claim their businesses does not make enough profit to pay high tax to the government. As a result of poor economic performance coupled with inadequate power supply, most SMEs and traders are facing a lot of challenges to the extent that most small industries who rely on the national grid for power supply have either collapse or produce below capacity. This is because they are not resourced enough to switch to other alternative power supply. This has led most of them to bribe the tax collectors to enable them operate without paying tax hence necessitated the study of perceptions of causes of tax evasion in Accra Metropolis.The study is reasonable on the basis that it would serve as good grounds for theory development which would give insight that would be useful in relation to other interventions for tax administration in Ghana and to add to knowledge by eliciting views on the perceived causes of tax evasion on the Ghanaian economy? This would be a useful resource which would be beneficial to individuals, tax administrators, the government and the academia.Additionally, this study is justified on the grounds that it will provide recommendation for further studies on the perceptions of causes of tax evasion in Ghana and it adverse effect on the economy though a lot of similar research has been done in this regard. Theoretical and Conceptual IssuesThe need for provision of basic infrastructure which is necessary for development and growth of any society is very important for human survival. Therefore denying citizens of infrastructure which they cannot do without is totally unacceptable in human race. This perhaps explains why governments all over the world show great concern for a means through which funds can be made available to achieve their set goals for the society. Governments evidently, need funds to be able to carry out their social obligations to the citizenry. It becomes the responsibility of government to source for the funds to enable her provide these basic amenities to the citizenry who are the beneficiaries. One of the medium through which fund is derived is through taxation. Therefore, the citizens are expected to discharge their civic responsibility by paying their taxes as these contribute to the development and administration of the society at large. This makes the payment of taxes a moral obligation.Research by Bodea (2014) revealed that, taxation is the process or machinery by which communities or groups of persons are made to contribute in some agreed quantum and method for the purpose of the administration and development of the society. This means that revenue needed for development purpose need to be generated by citizens before governments can source funds from donor agencies for support. Though taxes are important to society and public good, tax evasion is part of society and most tax payers cannot do without even if all taxes accrued from taxpayers are efficiently use for public good. As importance of taxation vary from individual perspective so does the perceived causes varies in different perspective. Suspected high corruption in government coupled with over exploitation from tax collectors is one of the motivators of tax evasion by most taxpayers. In such situations taxpayers feel their taxes are used for meaningless purpose and for that matter evasion could be the best option. In general, citizens expect some kind of service or benefit in return for the taxes paid. Research by Everest-Philip (2008) indicated that, if government fails to provide basic public goods and services or provides them insufficiently, citizens may not be willing to pay taxes and tax evasion will be the consequence. As a matter of fact since corruption cannot be ruled out completely in any government especially in developing countries where most government officials have their parochial interest to protect, tax evasion cannot be ruled out. Loop holes which are created deliberately or in deliberately as a result of corruption and poor performance of the tax administration system are also platform for tax evaders to take advantage of. Loopholes can be created by tax collectors or evaders to manipulate tax system to their personal gains. Lack of transparency and accountability in the use of public funds contributes to public distrust leading to tax evasion.High compliance cost, which involves gathering the necessary information, filling out tax forms etc, can be an additional reason for tax evasion. High compliance cost is also one of the challenges that underpin revenue generation in most tax administration system. If the process of filling tax returns is so cumbersome it will deter people from complying with their tax obligations. Most taxpayers especially traders and small scale business owners are illiterate or not highly educated so when the taxpayer see the cost to be problematic or costly; they tend to find opportunity around the tax system to evade it. According to Everest –Philips (2008), low tax compliance cost encourage taxpayers to easily file the tax returns but on the contrary high compliance cost discourage taxpayers from meeting their tax obligation especially in developing countries where there are loop holes in the tax administration system which leads to tax evasion. Weak enforcement of tax laws is also one of the attributes of tax evasion. Taxpayers are rational beings and ready to take any measure to manipulate the tax system to their advantage. In a situation where tax administration system does not have strong legislative backing that can empower them to prosecute or sanction evaders and defaulters, potential taxpayers take the tax laws for that matter the revenue collection agency for granted. When tax laws are well enforced loop holes can be easily be detected and sealed. Also weak capacity of revenue agency to fish out tax evaders could be created when tax laws are not well enforced. Enforcement of tax laws bring about efficiency in service delivery by revenue authority and reduce tax evasion. A well-functioning body of tax investigation is essential for the detection and prosecution of cases of tax fraud. The lack of sufficient capacities in tax administrations reduce the probability of detection that again influences the decision of a taxpayer as to whether evade or not. Additionally, the legal framework is an important prerequisite for any enforcement activity. According to James et al (2014), the size and nature of penalties that are incurred after evasion are mostly determined by legal framework within which tax administration operate. Enforcement of tax laws backed by legal framework can help to determine appropriate sanction which tax evaders will face.Inadequate education on the need for people to pay tax affects tax morality. High moral standard will encourage people to pay tax because they see the need to pay tax to enable government generate revenue for development projects for their own benefits. The importance of taxes for the functioning of the state is not always apparent to the taxpayer. Similarly, individual tax liabilities as well as requirements to comply with the tax system such as filling out different tax forms might be unknown or difficult to understand. By means of taxpayer education and taxpayer service, citizens can be informed and educated about the tax system and be assisted in their attempts to comply with the tax system. Tax education build up tax moral of taxpayers which enables them to file their tax returns without thinking of taking advantage of loop holes or any opportunity that can lead to tax evasion. Empirical Basis of the StudyThe existing literature also seeks to explain why some individuals may evade tax and its effects and consequences on the economy. In seeking to identify how much tax each person pays, it is important to distinguish between the ‘statutory incidence’ (the legal liability to pay the tax) and the economic incidence, which in practice is often the belief regarding who ultimately bears the burden of the tax. Tax evasion affect the ability of those legally liable for various taxes to shift these as traditionally assumed. If the government compensates for the loss by raising rates, tax evasion becomes even more attractive. The higher rates in effect penalize honest taxpayers, who comply either because they want to or because they have no opportunities for evasion. If the government, however, takes effective steps to prevent or combat non-compliance, it can raise revenue without increasing taxes or reducing spending. The resulting tax revenue loss may cause serious damage to the proper functioning of the public sector, threatening its capacity to finance its basic expenses. Provision of public services offers a rationale for taxation. Hitherto, taxation and tax evasion, in turn, influence public expenditure and capital accumulation, which affect output and economic growth Bodea et al, (2014). Tax evasion has had a variety of fiscal effects and also undermines socio-economic growth. Acts of corruption by tax collectors often play a role in promoting or sustaining underground economic activities and in facilitating tax evasion. Tax evasion and fiscal corruption thus contribute to undermining the legitimacy of government. Furthermore, citizens' disrespect for the tax laws may expand disrespect for other laws. Perceived Causes of Tax EvasionThere are various perceived causes of tax evasion. In order to develop methods and instruments for fighting tax evasion, it is important to foremost establish a broad understanding of the different perceived causes underlying these problems. These reasons can be filed in two broad categories. The first category comprises factors that negatively affect taxpayers’ compliance with tax legislation. These factors can be subsumed either contributing to a low willingness to pay taxes (low tax moral) or to high costs to comply with tax laws. The second category of perceived causes contains reasons for the low ability of tax administration and fiscal courts to enforce tax liabilities. These factors can be summarized as resulting from insufficiencies in the administration and collection of taxes as well as weak capacity in auditing and monitoring tax payments which limit the possibility to detect and prosecute violators. These facilitating factors are summarized in figure 1 below.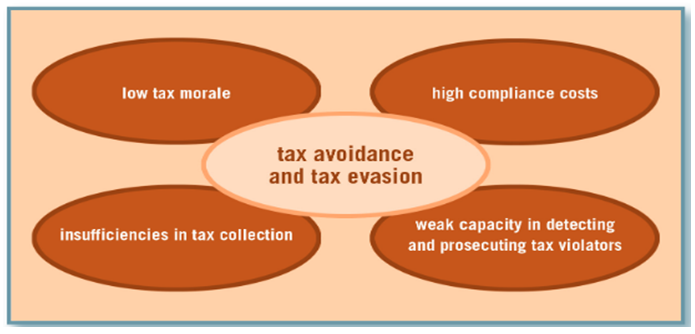 | Figure 1. Facilitating factors for tax avoidance and tax evasion |
2. Study Area
The total population of Accra Metropolis is as at 2010 census was about 2.4 million people made up of females 1.388 million and 1.02 million males giving a population density of 12 persons/sqkm2. It covers a total land area of about 4,11289 km2 which is about 25% of the total landmass of the Greater Accra Region. It population growth rate is 4.2% per annum due to rampant rural urban migration as against 2.7% for the national. The average household size is 10 persons.The population is dominated by the labour force (15 to 64 years) and small proportion of the elderly persons (above 64). The proportion of population below age 15 is about 44.7% while that of the elderly represents about 6.3%. On the other hand, the proportion of the labour force (between 15 and 64 years) stands at 49% of the total population. The sex composition of the population indicates that there are 49.2% males and 50.8% females in the district. The figure 2 and 3 below shows the map of Ghana indicating location of Accra Metropolis. | Figure 2. Map of Ghana. Source: Ghanaweb |
 | Figure 3. Map of Accra Metropolis. Source: Accra Metropolitan Assembly |
2.1. Study Design
The study design adopted was descriptive and analytical sample survey. This design was chosen in view of the fact that the study involves a systemic collection and presentation of data to give a picture of real situation. The descriptive sample survey was used to give clear understanding of what is happening in Accra Metropolis and the methods used to gather concrete information for analyses and recommendation. It aims at getting information on perceptions of causes of tax evasion in the Accra Metropolis. Key ministries, departments, agencies and individuals who matter in taxation evasion and tax related issues were contacted for information. The Officers from Accra Metropolitan Assembly, Ghana Revenue Authority, Ministry of Finance and Economic Planning (MOFE) as well as VAT Service and key informants such as assembly men, chiefs, opinion leaders and focused groups were interviewed. Other elements of the sample were traders.Simple random sampling is a sampling techniques in which each member of the sample population has equal chances of been selected. Justification for using simple random sampling is it ease of assembling the sample. It is also considered as a fair way of selecting a sample from a given population since every member is given equal opportunities of being selected. Another key feature of simple random sampling is its representativeness of the population. Theoretically, the only thing that can compromise its representativeness is luck. An unbiased random selection and a representative sample are important in drawing conclusions from the results of a study as the goals of research is to be able to make conclusions pertaining to the population from the results obtained from a sample. Due to the representativeness of a sample obtained by simple random sampling, it is reasonable to make generalizations from the results of the sample back to the population.A total of 150 respondents were sampled out of 300 sample population and in-depth interview, focus group discussions and key informant interview were the method used to obtain the data from them. Four field assistants were employed to help in the data collection under supervision to avoid biasness and gross errors. Data was analysed using Statistical Product and Service Solution (SPSS), version 19 (2012 edition).
2.2. Study Population and Sampling Techniques
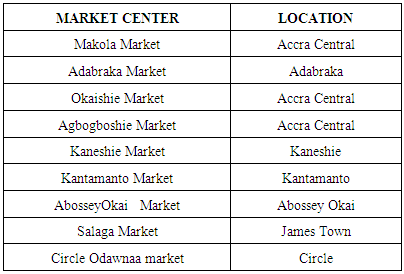
The study population covers 5 main market centers in the central part of the metropolis since it was impossible to cover the entire market centers in the Metropolis. Large numbers do not always guarantee higher degree of precision, validity or success in a research study. The tables 1, 2 below show all the main market centers and their location from which the respondents were randomly selected. Table 1. Main Market Centers in Accra Metropolis
 |
| |
|
Table 2. Sampled Market per the Numbers of Respondents Sampled
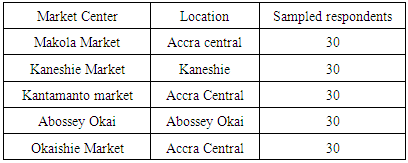 |
| |
|
2.3. Methods of Data Collection
The methods used for collection were In-depth interview, focus group discussion and key informant Interview. In-Depth InterviewOne hundred and fifty (150) respondents comprising 100 SMEs and 50 traders whose activities leads to tax evasion were randomly selected for interview. Due to the large number interviewed and sparse market centers, the study employed four field assistants to help administer the questionnaires under strict supervision. Sampled market centers were selected randomly as well as the respondents from these market centers. The 100 SMEs were sampled from a population of 200 SMEs in the study area and 50 traders were also selected from population of 100 traders. The justification for the in-depth interview was to find answers to as many questions as possible leading to the achievement of the study objectives. Focus Group DiscussionsThe focus group discussion was organized at each of the main market centers mentioned. Discussions were organized separately for groups each consisted of 10 members, the composition of which ensured representation of the categories chosen as sample elements, that is traders and small scale business owners. Respondents were sampled using the purposive sampling method. A discussion guide was designed; it considered research questions and objectives of the study. Justification for the focus group discussions was to ensure that vital information from different sources or group of peoples were obtained. Key-Informant–InterviewKey–informant-interview was also used to obtain information from opinion leaders, officials from the Metropolitan Assembly, Ghana Revenue Authority, VAT Service, Ministry of Finance and Economic Planning (MOFEP). The key informant interview was to get reliable and relevant information that would help achieve objective of the study.
2.4. Types of Sources of Data
Primary and secondary sources of data were used. The bulk of the data collected were from primary source and personal observation of the activities of traders and small scale enterprises. Secondary source of data were obtained from the Accra Metropolitan Assembly, VAT Service, MOFEP and Ghana Revenue Authority.Questionnaires were administered to collect primary information from people (respondents) whose activities leads to tax evasion. A total of 150 respondents were selected randomly, 30 respondents from each market centers to answer questionnaires designed to achieve study objectives. Different questionnaires were designed and used to obtain information from focused groups and key informants with reliable information.
2.5. Data Analysis
After collecting the data by both qualitative and quantitative techniques, editing and coding was done before presentation. In the presentation of the data, descriptive statistics such as frequencies, percent and cross tabulation were used. Data was analysed using Statistical Product and Service Solution (SPSS), version 19 (2012 edition).
3. Results and Discussions
IntroductionThis chapter deals with the analysis, results and discussion of the findings from the survey, focus group discussions and key informant interview. The analysis is guided by the research questions and the objectives of the study. It covers socio-demographic characteristics of the respondents, their perceptions about the causes of tax evasion and solutions to the perceived causes. Socio-Demographic Characteristics of RespondentsThis section presents the characteristics of the respondents sampled. This is done by analyzing the sex, age, occupation, educational background, marital status, daily sales and number of employees of the respondents. This is to give clear picture about the respondents demographic information and how their educational level, sex, daily sales and business influence tax evasion in the metropolis. 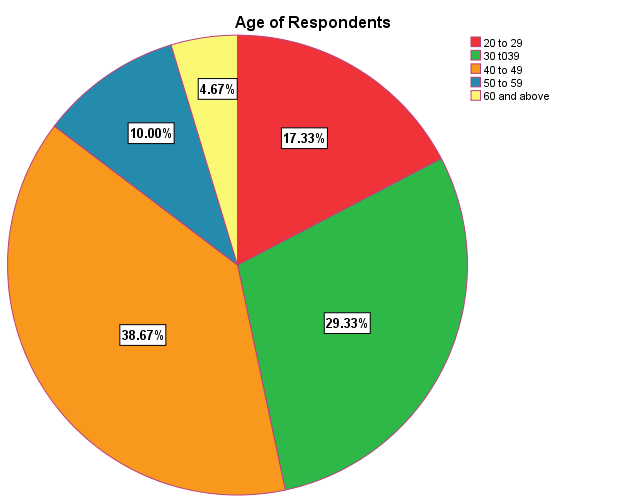 | Figure 4. Age of Respondents. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
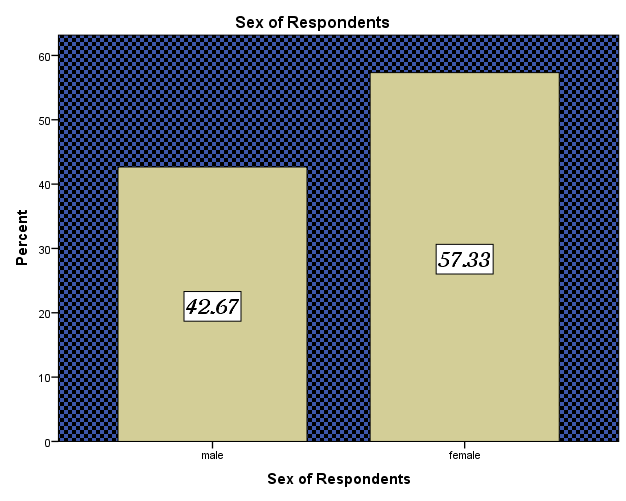 | Figure 5. Sex of Respondents. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
3.1. Age of Respondents
The age of respondents was taken into consideration in the study because it was to determine economic active group whose activities have serious repercussion on the economy for that matter tax evasion. Since age goes with man power, if more active age group engages in trading and businesses, economy activities will be improved to generate revenue for the nation. The study conducted revealed that out of 150 respondents sampled, 15 respondents representing 10% were between 50 to 59 age group. Also 26, 44 and 58 respondents representing 17.3%, 29.3 and 38.3% respectively were between the age group 20 to 39, 30 to 39 and 40 to 49 respectively. The research also revealed that only 4.7% respondents were between 60 and above. The survey conducted showed that the active age group in trade and business were between the age 30 to 39 and 40 to 49. This implies, the active human resource in Ghana fall within this age group. According to Fagbemi (2010), older people comply with tax payment than younger people due to youthful exuberant. He explained that, the relationship between age and tax deviance has attributable to lifecycle variations and generational differences. Younger taxpayers are more risk-seeking, less sensitive to penalties (a life cycle variation), and reflect the social and psychological differences related to the period in which they are raised (a generational difference).
3.2. Sex of Respondents
Sex of respondents was considered in the survey to see how it influences tax evasion. In Ghana, both men and women engage in petty trading and small scale business as income generating venture though the dominant are mostly women. Most ladies in Ghana travel abroad especially China, US and Europe to import and supply goods to retailers. This has created the opportunities for more women self-employment. The research conducted revealed that 86 of the respondents representing 57.33% are females while 64 of the respondents representing 42.27% were males. This implies that females are dominant traders in the Metropolis. Most shops in the Accra metropolis are owned by females who engage in trade such as provisions, groceries, clothes, stationary, cold store, electric appliances etc. Though some of the men also engage in petty trading like the women, most engage in car spare parts. According to Prabhakar (2012), female tax compliance is higher than male. The study further explained that most males are corrupt and find ways to avoid or evade tax. GFI (2010) argued that tax compliance gab between male and female is reducing since generation of women in modern society are liberated and have suffered some deviance or dishonesty. This implies irrespective of gender anybody can evade tax should the need arise.
3.3. Perceptions of Causes of Tax Evasion
Perceptions of causes of tax evasion were one of the main objectives the research was set to access. The perceptions of tax evasion vary from individual perspective depending on political, economic and social problems that influence taxpayer to default. As a result of the challenges of the economy businesses are not doing well as consumers are careful in spending. The economic crises has also compelled the government to broaden it tax net and increase taxes in other to generate income to meet it challenges. Poor sales and low business performance has forced most SMEs to will fully dishonour their tax obligation. Issues which has led to tax evasion are complex in the Metropolis and this has raised concerns in recent times as to how to address it.
3.3.1. Poor Usage of Taxes by Government
There are many perceived causes of tax evasion. While some are deliberate attempt by taxpayers others are within the tax administration agencies. Hikes in taxes nexus and poor economic performance depict the picture of poor tax policy strategy by the government. For instance, frequent and high taxes by government leads to dead weight loss which consequently create more debt for the government. Taxpayers feel exploited and find means and ways to evade tax when they figure out taxes are not put into good use for society benefit. According to Prabhakar (2012) logically, taxpayers and especially those who pay high amounts of taxes, will be sensitive to what the government spends their money on. Although there is limited empirical evidence, it is reasonable to assume that taxpayers will tend to evade tax if they perceive that the government spends tax money unwisely. In a situation when taxpayers money are used for project which most people consider irrelevant, they feel reluctant to honour their tax obligation. The research conducted revealed that 38% of the respondents strongly agree traders evade taxes because the revenue collected from them is not mostly put into good use. They perceived the government use taxes for unworthy purpose which they do not benefit directly or indirectly. The study also showed that 27.33% of the respondents agree that the main cause of tax evasion among traders and businesses is the perception that their taxes do not bring them any benefit. Focus group discussion showed they perceived the government officials enjoy their taxes at the expense of their effort. However to some extent they think their taxes are used for government project but does not meet their expectation. This implies, they believe their taxes are used for projects irrelevant to their present needs unlike the strongly agree respondents who absolutely believe their taxes does not bring them benefits at all. However 16.67% of the respondents are not sure of this perception. They doubt if taxes are put into good use but cannot also ascertain if their tax is used for irrelevant purpose by the government. For them, whether they pay or not they do not enjoy any benefit. The study also showed that 11.33% and 6.67% of the respondents respectively agree and disagree with this perception. They think taxes paid are put into good use but tax evasion is a habit of citizens with bad tax morality hence no matter how efficient government utilise their money they will still evade tax should they get the opportunity.
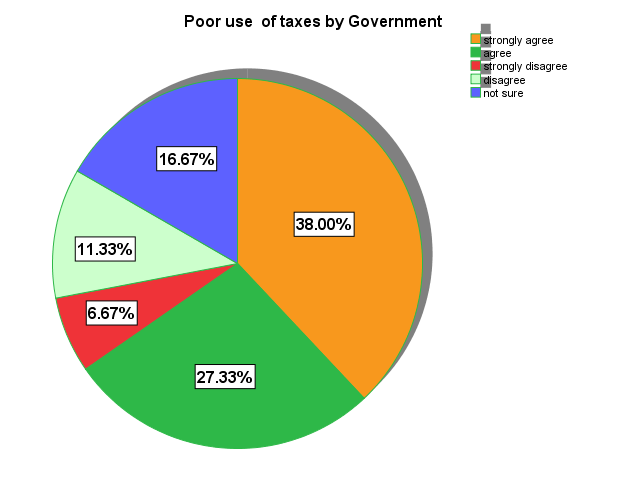 | Figure 6. Poor Use of Taxes by Government. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
3.3.2. Poor Sales Leads to Tax Evasion
Poor sales of goods and services are due to many economic factors such as low income level of consumers, consumer taste and preferences, government policies etc. Poor sales therefore affect performance of businesses and trade. In a situation, where traders make poor sales, paying taxes become a problem which creates likelihood of tax evasion. The research conducted indicated that 18% of the respondents strongly agree is not fair to pay taxes to the government because poor government performance has directly affected their sales. They explained that high fuel prices coupled with rampant power outages affects their business. The study showed that high fuel prices affected prices of commodities which lead to reduction in sales drastically. Also, inadequate power supply from the government which has resulted to load shedding is affecting business leading to poor daily sales. The survey also showed that 11.33% of the respondent also agrees is not fair to pay taxes since they do not make good sales as a result of poor performances of businesses in the metropolis due to economic hardship. They also blame the government for their business downturn. According to the respondents, despite poor sales they keep paying high taxes to the government probably this leads to tax evasion. However, 36% and 26% of the respondents strongly disagree and disagree respectively to the fact that it is not fair to pay taxes to government if businesses are not performing well as a result of poor government performances. They believe taxes are used for development purpose so evading tax due to poor business performance should not be an excuse. They explain that despite poor business performance in the Metropolis in recent times, they can still meet their tax obligation. The survey also showed that 8.67% of the respondents are not sure whether poor sales lead to tax evasion. Meanwhile they also believe poor business performances as result of economic hardships can influence traders to evade tax especially if taxes are so high compared to the sales made.
3.3.3. High Corruption Level in Government
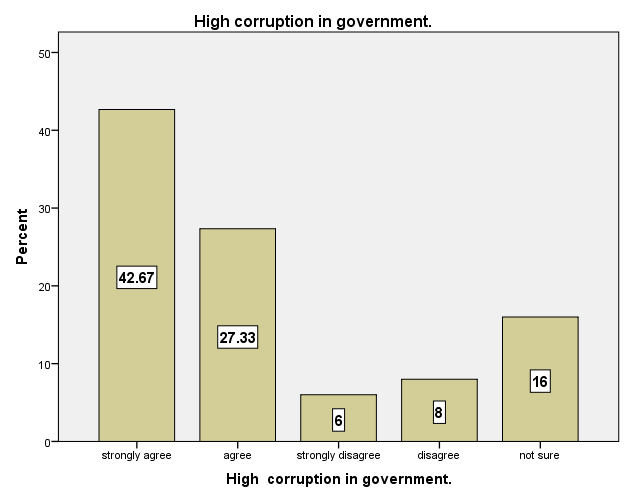
Although corruption and tax evasion are distinct and separate problems, they can easily become intertwined and reinforcing. According to Alm and Martinez (2013) society that is more corrupt may enable more tax evasion as corrupt officials seek more income via bribes; conversely, higher levels of tax evasion may drive corruption by offering more opportunities for bribes. Corruption in government compels people to lose confidence in the government and also find ways and means to also enrich themselves. Wang (2010) found that the strongest argument justifying tax evasion is when the government is corruptive and the tax system unfair. Corrupt government does not seek for the welfare of the people and these create possibilities of tax evasion.In Ghana corruption among government officials is so high and the gap between the rich and the poor keep widening. Therefore the citizens have lost confidence in the current government administration. They believe poor government policies coupled with high corruption has led to economic crises which adversely affected businesses and virtually everything. The research showed that 42.67% and 27.33% of the respondents respectively strongly agree and agree that high corruption in the government compel traders to also evade taxes because they feel their money is not used for good projects that will also bring benefits to them. The survey also indicated that 16% of the respondents are not sure that high corruption in government is the main cause of tax evasion in the country as well the Metropolis. According to them, they are not certain whether corruption in government can influence traders to evade tax. Also the study revealed 6% and 8% of the respondents strongly disagree and disagree respectively with the perception that high corruption is one of the main causes of tax evasion. They believe corruption had been there since time immemorial but tax evasion was not high as recent times. Arguably, tax evasion is rather due to poor performance of tax collectors. Figure 8 below showed perceived causes of tax evasion is due to high corruption in government.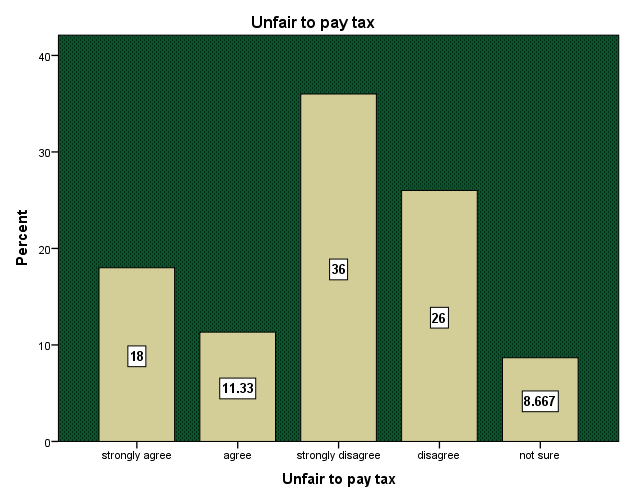 | Figure 7. Unfair to Pay Tax Due to Poor Sales. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
 | Figure 8. High Corruption in Government. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
3.3.4. Loop Holes in Tax Administration System
A tax system consists of tax policy, tax laws and tax administration. Any good tax system should have some fundamental characteristics, among which are equity and fairness, certainty, convenience, and efficiency in administration. A tax system is said to be equitable and fair if taxpayers with equal abilities to pay are made to pay the same amount of tax. There is certainty in the tax system if the tax rules specify when the tax is to be paid, how it is to be paid, and how the amount to be paid is to be determined. Furthermore, the element of convenience demands that taxes should be due at a time or in a manner that is most likely to be convenient to the taxpayer. Moreover, the tax system should be simple and easy to administer and be understood by both tax officials and payers to ensure efficiency in tax administration. Together, these attributes are expected to encourage high levels of compliance on the part of taxpayers. In every country, people always try to look or create loop holes in tax administration system in other to evade or avoid tax. Loop holes could be created if there are inefficiencies in the revenue collection agencies. Research by Whait (2012), indicated that taxpayers behaviour tends to be governed by rule and easily knowable institutions and trust in those institutions can increase tax morality and reduce tax evasion. Loop holes could also be created in an attempt to evade tax when revenue collectors connive with taxpayers to evade tax. The figure 9 below is the respondents’ perceptions about loop holes in the tax net as one of the perceived causes of tax evasion. The study showed that 36.67% of the respondent perceived loop holes in the tax administration system as one of the causes of tax evasion. Also 24.67% of the respondents also agree that loop holes in the tax system contribute to tax evasion in the country. On the other hand, 12.67% and 7.33% of the respondents strongly disagree and disagree respectively that loop holes in the tax net is one of the causes of tax evasion. They perceived high compliance cost coupled with high taxes the government charge traders is one of the main causes of tax evasion. However 18.67% of the respondents are not sure whether loop holes in the tax net is the main cause of tax evasion. They believe corruption, weak enforcement of tax laws and bribery from tax collectors are the main causes of tax evasion.
3.3.5. High Compliance Cost
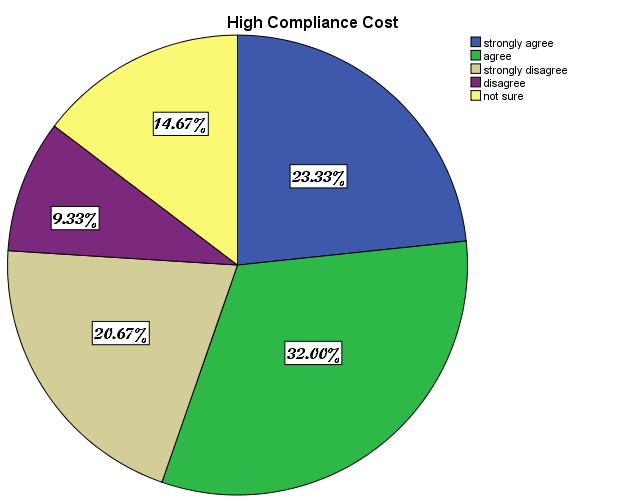
Compliance cost is the cost involve in filling tax returns. Most traders and business owners cannot often make time to file their tax returns in time and mostly face penalties. Treating taxpayers in a professional manner, in other words, more like customers rather than like suspects or thieves, may do much more to promote and improve compliance (Wang, 2010). Tax compliance is a major problem for many tax authorities and it is not an easy task to persuade taxpayers to comply with tax requirements even though ‘tax laws are not always precise’. Also the procedure involve in filling tax is cumbersome and it takes time to read and understand the procedure involve especially if you are not well educated. Studies by GFI (2010), indicated that attitudes and ethics remain important in determining the level of tax compliance. The research conducted showed that 32% and 23.33% of the respondents respectively strongly agree and agree with the opinion that high compliance cost is one of the main causes of tax evasion. According to the research, 20.67% of the respondents strongly disagree high compliance cost is the problem of tax evasion. They think tax compliance cost in the country is not that costly because one can easily file tax returns when the need arise. They think weak enforcement of tax laws to prosecute defaulters or avoiders is the main reason for tax evasion. According to the survey, 14.67% of the respondent is not sure whether high compliance cost is one of the reasons for tax evasion but instead there are other genuine reasons such as corruption, poor sales, poor tax education and poor tax morality. A government that relies on tax revenue to sustain itself will be forced to make implicit or explicit concessions to citizens in order to secure their compliance, whereas financially independent governments will not face the same pressure.Also the experience of paying taxes may give rise to a feeling of ownership of the state; leading citizens to make greater demands for public accountability (Whait, 2012). This implies that high compliance cost could be one of the perceived reasons for tax evasion in the metropolis.
3.3.6. Weak Capacity to Detect Inappropriate Tax Practices
Weak capacities as result of poor human resource in key sensitive positions delivering poor services create problems that prevent efficiency in discharging duties. Weak capacity to detect inappropriate tax practices is of the main problem facing revenue authorities. Taxpayers are rational beings who try to operate everything to their advantage. In a situation where the tax administration has weak capacity due to poor technology or inefficiency, taxpayers take advantage of that. According to Whait (2012) legitimate taxpayers in the formal sector perceive the state as being unfair in pursuing them for taxes while the informal sector continues to operate untaxed. Ignoring informal sector activities will lower compliance morality and increase the risk of generalized non-compliance.The research conducted showed that respectively, 53 and 48 of the respondents strongly agree and agree respectively with the perception that most traders evade tax when the tax administration has weak capacity to detect inappropriate tax practices. This implies that traders perceived that the Ghana Revenue Authority (GRA) is not well resourced to detect tax evaders or defaulters. It was also detected that 28 respondents were not sure whether genuinely the revenue authority has poor capacity to detect inappropriate tax practices. On the other hand they do not also doubt the credibility of the Ghana Revenue Authority. They think their service delivery though not good enough but not also porous to create chance for taxpayers to easily maneuver. However 18 of the respondents strongly disagree while 8 of the respondents disagree. They think the tax revenue collectors are well trained that they can easily detect tax defaulters. They claim though Ghana is not highly technologically inclined, but has good tax administration system to track down tax evaders.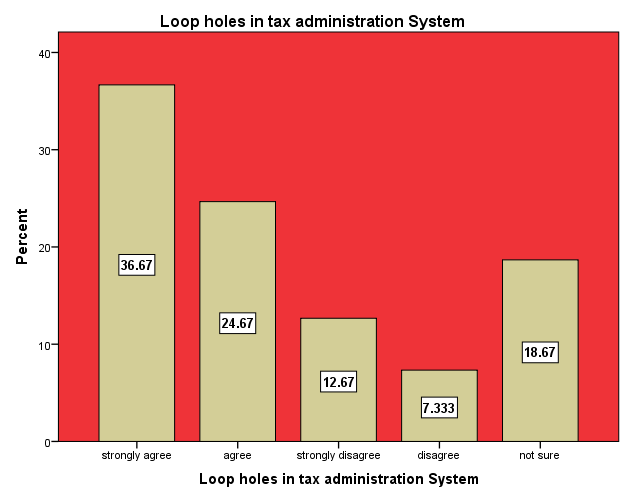 | Figure 9. Loop Holes in Tax Administration System. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
 | Figure 10. High Compliance Cost. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
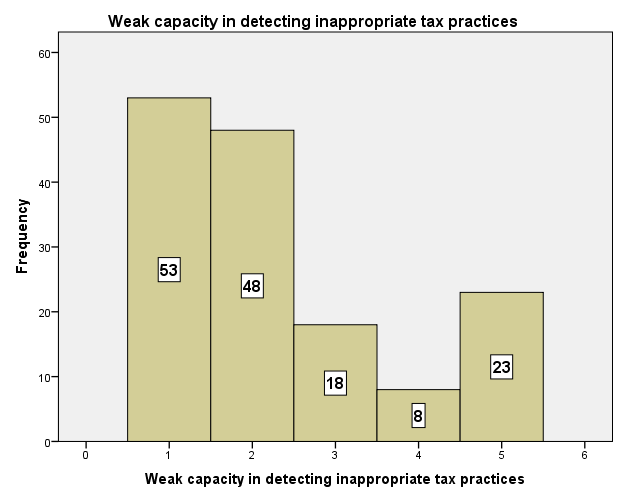 | Figure 11. Weak Capacity to Detect Inappropriate Tax Practices. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
3.3.7. Weak Enforcement of Tax Laws
Weak enforcement of tax laws is one of the challenges of revenue generation authorities. Taxpayers may take their tax obligations for granted if there are no strong laws which bind them to honour their tax obligation. Enforcement of tax laws which are mandatory to revenue authority can lead to poor revenue generation especially when defaulter are not prosecuted to deter others from that act. The research conducted revealed that 44.67% of the respondents strongly agree that most traders perceived weak enforcement of tax laws as main cause of tax evasion. They claim people evade tax when there is no strong laws binding them to pay. If there is strong law that is set aside to deal rigorously with tax evaders or defaulters, the consequences will deter other perpetuators to desist from that act. Furthermore, the research also showed that 27.33% of the respondents also agree that tax evasion could be rampant in situation where both tax collectors and payers engage in activity that leads to evasion or avoidance. The study also revealed that 12.67% of the respondents strongly disagree that weak enforcement of tax laws is one of the main causes of tax evasion. They claimed tax will be evaded if the revenue generation agency is inefficient and has loop holes in their administration system. Meanwhile 8.667% of the respondents are not sure whether weak enforcement of tax laws could be a factor of tax evasion. They are not also sure whether this factor does not also affect tax evasion because they believe as taxpayers are rational beings they could take advantage of prevailing situation to evade tax. The 6.667% percent who disagree said weak capacity of tax administration to detect tax evaders is the main problem that could lead to tax evasion but not enforcement of tax laws.
3.3.8. Inadequate Tax Education and Taxpayer Services
The importance of taxes for the functioning of the state is not always apparent to the taxpayer. Similarly, individual tax liabilities as well as requirements to comply with the tax system such as filling out different tax forms might be unknown or difficult to understand. By means of taxpayer education and taxpayer service, citizens can be informed and educated about the tax system and be assisted in their attempts to comply with the tax system. Previous studies by GTZ (2010) have evidenced that general tax knowledge as a result of tax education, has a very close relationship with taxpayers’ ability to understand the laws and regulations of taxation, and their ability to comply with them. Efforts in this direction will enhance compliance and improve tax morality. Tax education is very important because it improve the tax morality of taxpayers to enable them honour their tax obligation. Education will enable taxpayers know the relevance of tax to the government for development. Services and physical projects such as improvement of the immediate environs of traders to make them realise direct benefit of their taxes. The study showed that 48% and 26.67% of the respondent respectively, strongly agree and agree that inadequate tax education and services could be a cause of tax evasion. They explained if taxpayers are not well educated on the need to pay taxes and do not also receive any good services as benefits they tend to be evasive. The research also indicated that 10.67% of the respondents strongly disagree that inadequate tax education and services is a factor of tax evasion or default. They believe that this could be a factors but the main cause is compliance cost and high corruption in the country which makes tax payers feel exploited. Nevertheless, 6.667% of the respondents are not sure whether this could be a cause for tax evasion.
3.3.9. Heavy Tax Burden on Taxpayers
There is a tendency of taxpayers to perceive tax as burden especially when experiencing poor sales against high taxes and do not also receive any service or meaning benefits directly or indirectly from the government. The idea of an inverse relationship between tax rates and revenue generation is not entirely new as every tax systems has it own challenges. High taxes of certain goods and services encouraging smuggling, frequently afford smaller revenue to government than what might be drawn from more moderate taxes (Marti et al, 2010). Tax also become a burden on taxpayers if the regular taxpayers are compelled to continue to pay high taxes while others evade taxes due to loop holes in the tax net which they take as advantage.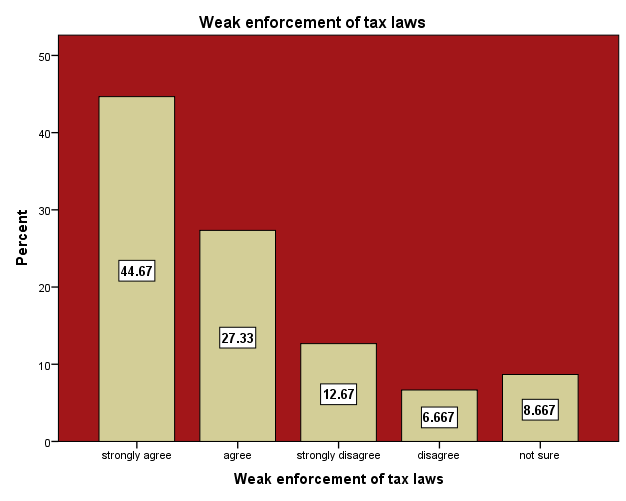 | Figure 12. Weak Enforcement of Tax Laws. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
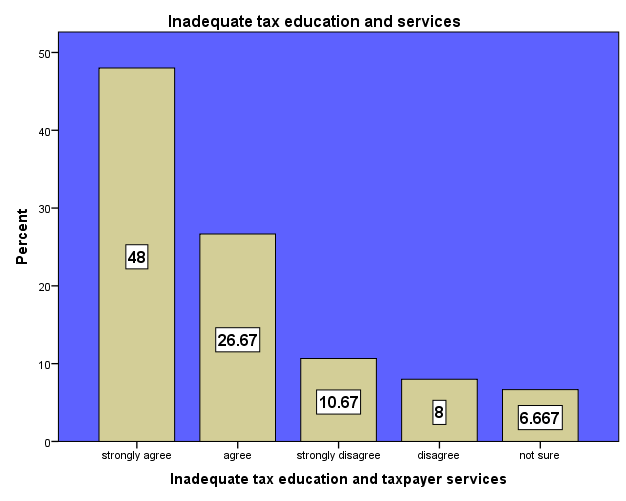 | Figure 13. Inadequate Tax Education and Taxpayer Services. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
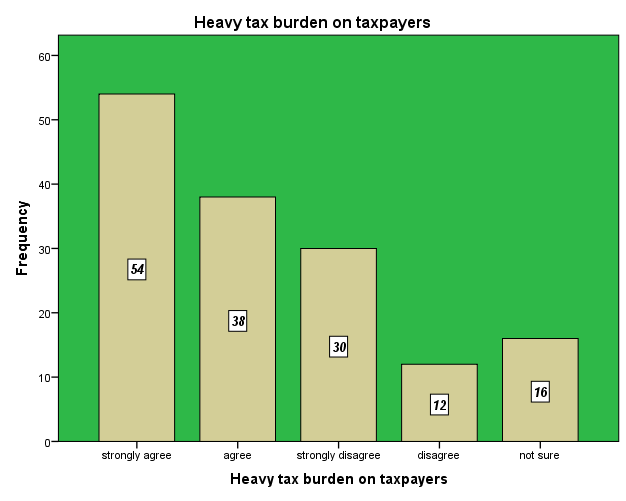 | Figure 14. Heavy Tax Burden on Taxpayers. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
The survey conducted showed that 54 and 38 of the respondents respectively strongly agree and agree that tax is perceived as heavy burden on taxpayers due to high tax rates coupled with poor business performance. Some studies suggest that high tax rates foster evasion. The intuition is that high tax rates increase the tax burden and, hence, lower the disposable income of the taxpayer. Meanwhile 30 and 16 of the respondents respectively strongly disagree and disagree that taxes are not perceived as burden on taxpayers. According to them though taxes are high and businesses are not doing well due to economic downturn, taxpayers can still file good returns should they keep good records of their sales. They also said tax becomes a burden should the tax filing process becomes cumbersome. According to Smulders et al (2010), the “taxpayer compliance burden” includes the time and money spent (i.e., the costs incurred) by taxpayers in order to comply with all aspects of the tax system. This burden includes activities such as record keeping, gathering relevant tax documentation, completion and submission of tax returns, tax planning, using the revenue authorities’ services (offices, help desks, on-line assistance), and/or using the services of tax practitioners. However 16 of the respondents are not sure whether taxpayers perceive tax as heavy burden on traders. Though taxes are high in the country, it becomes a burden when the tax administration system is porous and this compels some taxpayers to evade while regular taxpayers remain committed.
4. Solution to the Perceived Causes of Tax Evasion
4.1. Reduction in Tax Rate
Reduction in taxes could encourage taxpayers to honour the tax obligation so as to curb tax evasion. High tax rates compel taxpayers to look for opportunities that will enable them evade or avoid tax. With recent economic challenges in the country, reduced tax rate will encourage taxpayers to pay taxes without looking for opportunities to evade tax. The study showed that 34.0% and 14. % of the respondents strongly agree and agree respectively that reduced tax rates will encourage taxpayers to pay tax without avoiding or evading. If the rate is reasonable enough, businesses and individual taxpayers will comply with their tax obligation and hence more revenue will be generated. The study also revealed that 17.33% and 8.00% respectively strongly disagree and disagree that reduced tax rate could encourage payment and hence reduce evasion. They believe that, if taxes are reduced to a reasonable rate that every taxpayer could easily pay, some people would still evade tax. This implies that whether taxes are reduced or not, tax evasion cannot be eradicated completely since the administration system is human institution which people can take advantage of their weakness. However 26% of the respondents are not sure that reduced tax evasion can help curb tax evasion. They believe whether tax rates are higher or low, loop holes or any other factors which negatively hinder tax payment will influence taxpayers’ opportunity to circumvent the tax administration system.
4.2. Enforcement of Tax Laws and Penalties
Enforcement of tax laws and penalties will enable taxpayers to have confidence in the revenue authorities. Enforceability of penalties by punishing tax evaders or defaulters will serve as a deterrent to others. The research conducted revealed that,66 and 39 of the respondents respectively strongly agree and agree that enforcement of tax laws and penalties will deter people from evading taxes. They believe when the laws and penalties are made clear to the general public and perpetuators are punished according to the level of their offence, tax evasion could be addressed. However the study also showed that 12 and 8 of the respondents respectively strongly disagree and disagree that enforcement of tax laws and penalties could help curb the rate of tax evasion in the metropolis. They further explained that, no matter how effective tax laws and penalties are enforced, the high corruption among tax collectors and taxpayers coupled with high tax rate and loop holes in the tax net will compel businesses and traders to evade tax so as to enable them feel relieved of tax burden. Nevertheless, 25 of the respondents are not sure whether enforcement of tax laws and penalties can help reduce tax evasion. They explained that with or without enforcement of laws and penalties people will still go their way to evade tax should they get the opportunity. They believe that if corruption in the system is curtailed, tax evasion will be addressed without penalties for evaders or defaulters.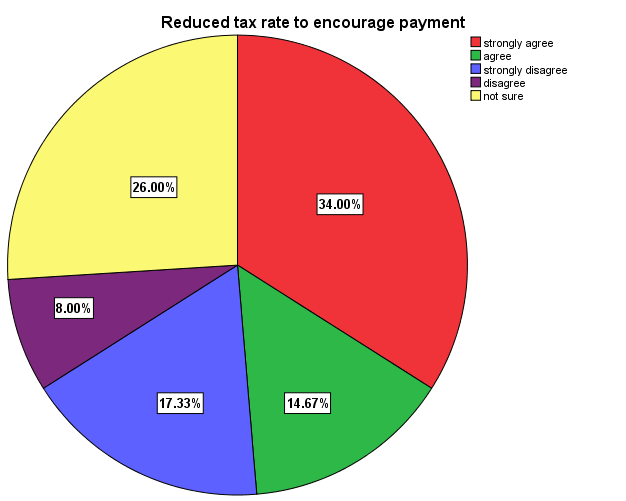 | Figure 15. Reduction in tax rate. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
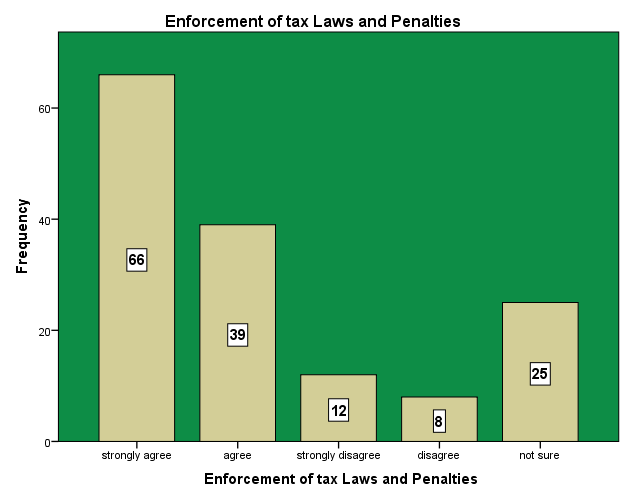 | Figure 16. Enforcement of Tax Laws and Penalties. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
4.3. Improved Tax Education
Tax education enlightens people on the importance of tax to the government for development. It highlights on how taxes are used and it importance to improve the economy. These also help to improve tax compliance which could go a long way to help reduce evasion. The survey conducted revealed that 65 and 45 of the respondents strongly agree and agree respectively that improvement of tax education can help reduce tax evasion. They believe that tax education will throw more light on how taxes are used by the government to build schools, hospitals, roads etc for the well-being of the citizens. This will go a long way to improve tax compliance. Meanwhile 20 of the respondents said they are not sure whether education can help curb tax evasion in the metropolis. They believe, no matter how people are educated on the importance of tax, should they get the opportunity they will still evade tax. They believe effective tax administration system vis a vis rigorous penalties to punish defaulters and evaders could help the government. However 9 and 7 of the respondents strongly disagree and disagree respectively that tax education could help reduce evasion. These respondents believed that so long as there are loop holes in the tax net, no matter how the education, tax evasion cannot be rule out completely. According to Popoola (2009) until the tax administration system seal loop holes and develop effective mechanism to detect defaulters, traders will continue attempting evading tax.
4.4. Improvement of Tax Compliance Cost
High compliance costs, that are the costs the taxpayer has to bear to gather the necessary information, fill out tax forms etc, can be an additional reason for tax evasion and avoidance. This situation led businesses to worry more about the administrative burden than about the actual tax burden. In such a situation it can be assumed that compliance costs are very high and the probability of the taxpayer complying with such a great variety of taxes is low. Particularly small and medium sized enterprises (SMEs) suffer from high compliance costs. This situation is more serious when the taxpayer’s level of education is low and does not understand how to go about filling the tax returns forms.The survey conducted indicated that 40% and 30.37 % of the respondents strongly agreed and agreed respectively that improvement of tax compliance cost will help to reduce tax evasion since the burden of filling the tax returns forms is cumbersome and involves a lot of procedures. However, 10% and 4.667 of the respondents respectively strongly disagree and agree that tax improve tax compliance cost could help reduce evasion. They further explained that, though filling tax returns forms is not that easy, they do get assistance from friends and family. The only problem was most of the administrative work at the revenue offices are done manually and this lead to waste of time when paying taxes. The study also showed that 14.67% of the respondents are not sure whether compliance cost could lead to tax evasion. They said though paying tax involve a lot of procedures and time consuming, taxpayers can still comply with their tax obligation should the need arise.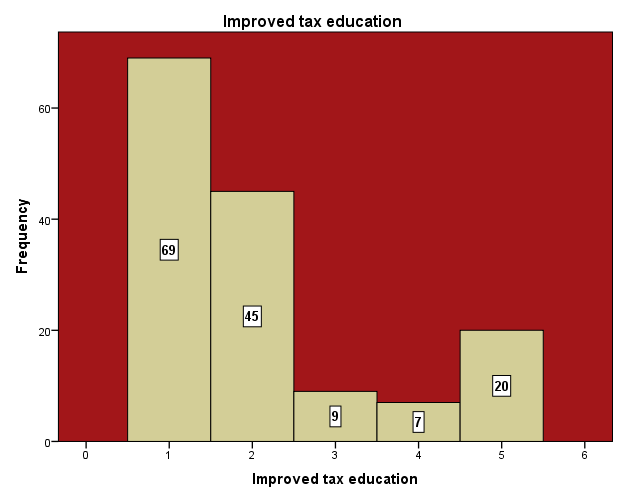 | Figure 17. Improved Tax Education. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
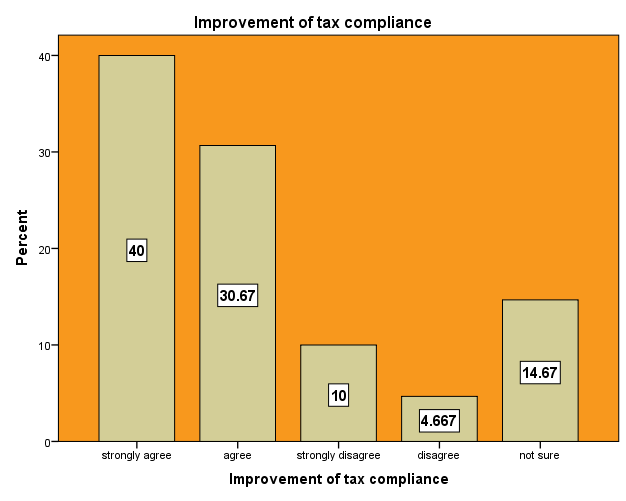 | Figure 18. Improvement of Tax Compliance. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
 | Figure 19. Computerized Tax Administration System. Source: Field Survey 2014 |
4.5. Computerised Administrative Work
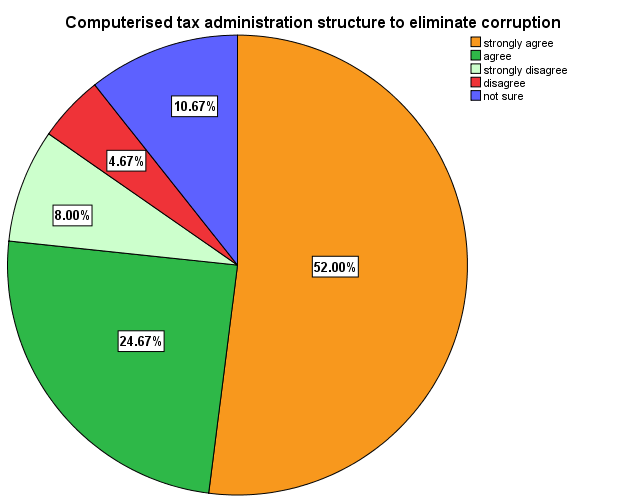
The easy of filing tax returns and payment will enhance compliance and reduce the possibility of tax avoidance or evasion. Taxpayers mostly look for opportunity to default, avoid or evade taxes especially when they do not benefit directly from their taxes. The administrative procedures of Ghana Revenue Authority is mostly manual and most taxpayers try to look for loop holes to connive with some of the tax collecting agencies to evade tax so as to save time and money. The research conducted revealed that 52% of the respondents suggested that when administrative work of the revenue authorities are computerised, it will eliminate or reduce the rate at which people take advantage of the manual system to evade tax. The survey also revealed that 24.67% of the respondent believe that due to manual system of most of the revenue agencies administrative work, it time consuming therefore taxpayers prefer to give bribes so as to evade tax to avoid the trouble of going through long administrative procedures which takes a lot of time. However 8% and 4.7% of the respondents strongly disagree and disagree that computerised tax administrative structure will eliminate corruption which eventually leads to tax evasion. They believe that no matter how the tax administrative system works, some of the revenue collectors are so corrupt and ready to create loop holes in the tax net in other to take bribes and aid tax evasion. Meanwhile the 10.67% of the respondents are not sure whether improvement in tax administrative structure could help reduce corruption among the tax collectors and taxpayers. They explained that, though computerised tax administration system is another way to curb corruption, improved tax compliance cost would also help. The research conducted showed that 54 and 38 of the respondents respectively strongly agree and agree that tax is perceived as heavy burden on taxpayers due to high tax rates coupled with poor business performance and improvement of working conditions of revenue collectors can go a long way to improve efficiency and thereby reducing tax evasion.
5. Summary of Research Findings
The study was to access perceptions of causes of tax evasion in the Accra Metropolis of Greater Accra Region of Ghana. A total of 150 traders (respondents) who engage in small businesses in the metropolis were sampled and in-depth interview, focus group discussions and key informant interview were the methods used to obtain the information from them. Four field assistants were employed to help in the data collection under supervision to avoid biasness and gross errors. Data was analysed using Statistical Product and Service Solution (SPSS), version 19 (2012 edition) and was translated into bar charts, histogram and pie chart for clear illustration of the research findings.Perceptions of causes of tax evasion varies from individual perspective depending on the socio-economic, political, tax administration lapses and other conditions that serve as bottle necks to the taxpayers which influences them to perpetuate these act. There is an inherent tension between the state and the citizen when it comes to tax matters. Although it is conceivable that citizens should be ready and willing to pay taxes, (which are used for public goods for the benefit of all), in reality, citizens often prefer a free rider’s attitude and avoid taxation as much as possible. Voluntary tax compliance is therefore an issue.In Ghana, one of the greatest problems that have come to force so far as tax administration is concerned is that of tax evasion. Many Ghanaians especially traders willfully or deliberately refuse to honour their tax obligations by distortion facts and figures relating to an assessment after tax liability has been incurred with the intention of reducing the liability.Though there had been gains in tax revenue mobilization, the revenue generated from taxes is not enough to support annual budget. There had been a lot of challenges in direct tax collection and this result in lost of government revenue. Most Ghanaians especially traders feel exploited or cheated when paying taxes because they feel paying taxes seem throwing their money away. Most also feel the tax is too high looking at the nature of their business and the taxes levied on them to pay either monthly, quarterly or annually. This has compelled businesses and traders to bribe tax collectors to enable them evade tax. Furthermore, due to high rate of corruption among government officials, most taxpayers feel their monies are use for meaningless purpose at the expense of their toil and struggle to make earns meet. Others also feel tax agents who come to their shops to collect taxes exploit them by making them pay unreasonable tax.Greater Accra metropolis is in the Capital City of Ghana with a population of about 2.4 million people. The metropolis has a lot of small scale business shops for retailing goods and services but most of them invade tax because they claim their businesses do not make enough profit to pay high tax to the government.
5.1. Perception of Causes of Tax Evasion
The research conducted revealed that perception of causes of tax evasion is complex and is related to many socio-economic factors such as high level of corruption in the government, high compliance cost, weak enforcement of tax laws, weak capacity of tax authorities to detect tax defaulters, poor tax education, loop holes in the tax net and issues of tax burden.
5.2. Poor Sales and High Tax Rates
The study showed that poor sales coupled with high tax rates have left most traders with no option than to evade. According to them, poor economic performance has affected income levels of consumers which have affected their business. This has compelled most of them to evade tax. Also the survey showed that high corruption especially among government officials is one of the perceived causes of deforestation. The survey showed that, 42.67% of the of the respondents perceived corruption as the root cause of tax evasion in the metropolis. They explained that paying high taxes without seeing economic improvement makes them feel exploited.
5.3. Loop Holes in Tax Administration System
Loop holes in the tax administration system were also perceived as root cause of tax evasion. The study showed that 36.67% of the respondents were of the view that there are loop holes in the tax administrative system of the Ghana Revenue Authority (GRA) which could be as a result of inefficiencies or poor competence of the tax collectors which taxpayers take advantage of. The study also showed that some of the revenue collectors connive with tax payers for evasion by taking bribes from them.
5.4. High Compliance Cost
High compliance cost was also seen as perceived cause of tax evasion. Most of the respondent were of the view that since most traders are not well educated, filing tax returns becomes a challenge which compel them to bribe tax officials so as to evade since they may not have time to go through all the filling process. In an attempt to assist micro, small and medium-sized businesses to lower or minimise their tax compliance costs and reduce their tax burden, governments often provide these enterprises with a simplified tax regime or a variety of tax concessions (Smulders, et al., 2010). Weak enforcement of tax laws was also realised as one of the perceived causes of tax evasion. The research showed that tax laws are not rigorously enforced and defaulters mostly do not face severe penalty to deter other tax evaders. The research conducted revealed that 44.67% of the respondents strongly agree that most traders perceived weak enforcement of tax laws as one of the underlying main cause of tax evasion. They claim people evade tax when there is no strong laws binding them to pay tax.
5.5. Poor Tax Education
As the study revealed, most self-employed are unaware of the tax system in Ghana. Some people do not even know what constitute an income tax. Also, they do not know much about tax reliefs and incentive, all as a result of lack of or inadequate tax education for the self employed taxpayers. Poor tax education and taxpayer services were also seen as promoter of tax evasion. Most of the traders feel exploited when paying taxes to the government as they think they do not get direct benefit from the taxes they pay. The study showed that 48% and 26.67% of the respondent respectively, strongly agree and agree that inadequate tax education and services could be a cause of tax evasion. They explained if tax payers are not well educated on the need to pay taxes and does not also receive any good services as benefits they tend to be evasive. Tax was also perceived as burden to taxpayers in the research conducted. The research conducted showed that 54 and 38 of the respondents respectively strongly agree and agree that tax is perceived as heavy burden on taxpayers due to high tax rates coupled with poor business performance in the metropolis recent times due to economic downturn.
6. Conclusions
In views of the findings it could be concluded that the perceived causes of tax evasion in the Accra Metropolis were poor tax education, high corruption in the government, poor sales by traders, weak enforcement of tax laws, use of tax for irrelevance purpose, tax perceived as burden and weak capacity in detecting and prosecuting tax defaulters.It was also realised that most of the traders in the metropolis are not highly educated so compliance cost was also seen as one of the main causes of tax evasion. Poor tax education was also seen as the underlying factor that trigger the other perceived causes of tax evasion.The study showed that though taxpayers are aware of that, the main source of funding national projects mostly comes from the taxes but they seem not to bother about the effects tax evasion have on the economy .They prefer evading taxes to better their lives rather than paying taxes to the government they claim corrupt.
7. Recommendations
There are many ways to tackle tax evasion depending on what the underlying causes influencing these acts could be. The following are some recommendations that if stakeholders address could help curb tax evasion in Accra of Metropolis.1. The Ghana Revenue Authority (GRA) and Accra Metropolitan Authority (AMA) should embark on massive campaign against tax evasion and avoidance. They should intensify education on effects of tax evasion on government revenue as well as citizens.2. Corruption and bribery in the country should be addressed and government should improve it infrastructure and other social amenities such as road, market, schools, hospitals and good water for the citizens to repose confidence in the government.3. Tax laws and tax education should be rigorously enforced and offenders should be prosecuted to deter others from that act. 4. The revenue generation authorities or collectors tax should be well trained and resourced to easily detect tax evaders or avoiders. Also the tax administration system should be improved. 5. Most of the tax filling returns should be computerised to enhance easy and efficient service delivery so as to reduce tax compliance cost.6. Tax should be increase reasonably for taxpayers not to perceive tax as burden to prevent creating loop holes for evasion.
References
| [1] | Alm, J. (2013). Expanding The Theory of Tax Compliance From Individual To Group Motivations (pp. 1-24). LA: Department of Economics, Tulane University New Orleans. |
| [2] | Benk, S., Budak, T., Puren, S., & Erdem, M. (2015). Perception of Tax Evasion as a Crime in Turkey. Journal of Money Laundering Control, 18(1), 99-111. |
| [3] | Bodea, C., & LeBas, A. (2014). The Origins of Voluntary Compliance: Attitudes Toward Taxation in Urban Nigeria. British Journal of Political Science, 1, 1-24. |
| [4] | Everest-Phillips, Max. Business tax as state-building in developing countries: applying governance principles in private sector development, International Journal of Regulation and Governance 8(2), pp. 123–154. 2008. |
| [5] | Fagbemi, O. T., Uadile, O. M., & Noah, A. O. The ethics of tax evasion: perpetual evidence from Nigeria. European Journal of Social Sciences, 17(3), 360-371. 2010. |
| [6] | Global Financial Integrity (GFI), Illicit Financial Flows from Africa: Hidden resource for development. 2010. |
| [7] | GTZ – German Technical Cooperation: Benefits of a Computerized Integrated system for Taxation: Tax Case Study – A Handbook for Practitioner Based on GTZ Tax Sector Experience in Tanzania and the Philippines. 2010. |
| [8] | James Alm & Jorge Martinez-Vazquez & Chandler McClellan. Corruption and Firm Tax Evasion, International Center for Public Policy Working Paper Series, at AYSPS, GSU paper1422, International Center for Public Policy, Andrew Young School of Policy Studies, Georgia State University. 2014. |
| [9] | Lymer, A. and Oats, L (2010) Taxation Policy and Practice, 16th ed. Birmingham. Fiscal Publication. 2010. |
| [10] | Marti, L. O. Taxpayers’ attitudes and tax compliance behaviour in Kenya. African Journal of Business & Management, 1,112-122. 2010. |
| [11] | Popoola, N. A Good Tax System’ll Enhance Economic Development. Punch, 31st Jan. Available from: http://www.punchng.com/Articl.aspx?theartic=Art20090131654450#. 2009. of Taxation? Evidence From a Focus Group Study in England. Journal. |
| [12] | Prabhakar, R. (2012). What Do The Public Think of European Social Policy 22(1), 77-89. |
| [13] | Shahrodi, S. M. Investigation of the effective factors in the efficiency of tax system. Journal of Accounting and Taxation. 2010. |
| [14] | Smulders S, Stiglingh M, Franzsen R and Fletcher L. Tax compliance costs for the small business sector in South Africa – establishing a baselinee Journal of Tax Research (Australia). 2012. |
| [15] | Wang, L. A Review of the Determinants of Voluntary Compliance with Tax Laws by South African Taxpayers with Particular Reference to Businesses in South Africa. Unpublished MPhil: Taxation mini-dissertation, University of Pretoria. 2010. |
| [16] | Whait, R. B. (2012). From Responsive Regulation To Dynamic Participation: A New Model For Voluntary Tax Compliance. Australian Tax Forum 27(1), 107-148. |





















 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML

