-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2014; 4(6): 240-256
doi:10.5923/j.economics.20140406.03
The Relationship between the Tabulation Method of Real-Time Input-Output Table and the Modernization of Enterprise Management
Kang Ning
Senior Engineer (Retired), Guizhou Power Grid Company Training and Evaluation Center, China Southern Power Grid
Correspondence to: Kang Ning, Senior Engineer (Retired), Guizhou Power Grid Company Training and Evaluation Center, China Southern Power Grid.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The science-based tabulation method of real-time input-output table is market-oriented, thus, basic data is hoped to be calculated accurately to formulate a micro input-output planning model beforehand to accomplish a real-time analysis to instruct the business operation of enterprises and also to formulate a micro input-output statistic model afterwards to accomplish a just-in-time analysis to inspect the enforcement of business plans without any other additional data collection and process. On the basis of this method, the corresponding macro planning and statistic model can hence be established and through the real-time analysis and just-in-time analysis of the macro models, new budgeting (planning) and accounting methods can be used as a “supporting system” to create both micro and macro management techniques to direct economic construction and development with the help of scientific economic policy making. By doing so, not only challenges like Enron Event can be dealt with, but also the root of financial crisis can possibly be eliminated before it is going to spread.
Keywords: Enterprise Input-Output Model, Financial Management, Supply-Demand Chain Management, ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), Lean Production, Agile Manufacturing, TFP (Total Factor Productivity), Goal Management
Cite this paper: Kang Ning, The Relationship between the Tabulation Method of Real-Time Input-Output Table and the Modernization of Enterprise Management, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 4 No. 6, 2014, pp. 240-256. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20140406.03.
Article Outline
1. Theoretical Background
- Science and technology, as the core elements of productivity, infiltrate into and have a direct influence on other elements of productivity. The development of productivity is a result of interaction with various elements. To better understand how the overall productivity is improved, the concepts of “real-time input-output table” and “modernization of enterprise management” will be introduced in this article. From this, we will get to know their critical status and functions in the national economy. But first, there are several theoretical terms need to be made clear.
1.1. The Technological and Economic Relations between Different Sectors of the National Economy
- As Diagram 1.1 shows, there are complicated technological and economic relations among and between different sectors of the national economy. The so-called “technological relations” are generated during the process of production and are restricted by the technological level, which is demonstrated by actual technological allocation and exchange of raw materials (iron and steel), fuel, power and auxiliary materials. The “economic relations” are also generated during the process of production, while it takes the form of value relations through product allocation and exchange. Technological and economic relations between different sectors of the national economy reflect the inner law of the national economy system. Thorough understanding and application of the national economic law will be crucial to full development of society. It must be pointed out that the improvement of social productivity and the innovation of relations of production can also “update” people’s cognition and their way of thinking. To further illustrate how people recognize the inborn national economic law, there will be four phases concerning people’s knowledge of the national economic law.
1.1.1. Phase One Perceptual Knowledge
- Long ago, people noticed that during the production process, different sectors or different products of the national economy were interrelated, influencing and restricting each other. One tiny change in a specific sector might affect the whole economy. Such kind of interrelation was not only circular but also recurrent.
1.1.2. Phase Two Conceptual Knowledge
- With the development of science, technology and social productivity, people had some new understandings about the national economy. There were two representative theories in this conceptual period. One was Karl Marx’s theory of “planned proportional development of the national economy”. Karl Marx (1868) once stated that the amount of product corresponded to different needs and different needs quantitatively determined the amount of society’s aggregate labor. It is self-evident that this necessity of the distribution of labor force in specific proportions is certainly not abolished by the specific form of social production; it simply changes its form of manifestation (in Marx/Engels Selected Publications, Vol.4. P.368). Developing economy proportionally is an objective need of all forms of society. Another theory was Walras’ statement of “all equilibrium”. When pointing out that “all equilibrium” was different from partial equilibrium, Walras expanded the marginal utility analysis from two goods to all goods and pointed out that the prices of all goods should be determined simultaneously by total supply-demand in the overall economic system. Hence, the supply and demand of any kind of goods should not only be the function of this goods’ price, but also the function of all other goods’ prices. And, when the prices of all goods on the market would just make the supply of all goods and services be equal to the demand, the whole price system on the market would be in an equilibrium position. This was considered by Walras as “all equilibrium”. Moreover, he regarded such goods’ prices in the “all equilibrium” as being equal to their value.
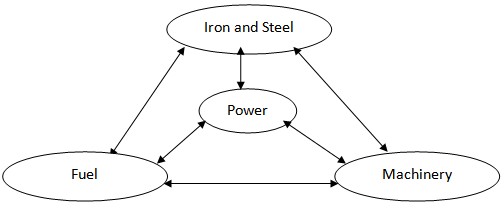 | Diagram 1.1. Structure of the National Economy |
1.1.3. Phase Three Quantitative Analysis
- The relations, direct and indirect, between different sectors of the national economy are complicated. Direct consumption coefficients reflect direct relations between economic sectors but it can not reflect indirect relations. Only with complete consumption coefficients, can the direct and indirect relations between different sectors in a whole be reflected. Although the complete relations of consumption between economic sectors are already known, there is no scientific method to calculate complete consumption coefficients accurately. Now, with the mathematic model established by input-output table, the direct consumption coefficients and computer aid, the complete consumption coefficient can be worked out. Leontief’s contribution of input-output table objectively reflects the approach of quantitatively analyzing the interrelations between each sector of the national economy, proves the necessity of promoting Marx’s theory of planned proportional development of the national economy in all forms of society, and utterly solves the problems posed by Walras’ “all equilibrium” which was not solved before. The input-output model coordinates the development of economic sectors (products). It is a tool of macro-economic control and also a scientific method of overall economic management. The input-output table provides three different approaches, namely, accounting framework, policy analysis and budgeting method, and it is a unique systematic analysis tool which can objectively reflect the interrelations between the object of labor, means of labor and labor force. Through the establishment of input-output table, the input-output analysis reflects studies and quantitatively analyzes the technological and economic relations between all stages (production, allocation, exchange and consumption) of social reproduction, all sectors and regions of the national economy, and between nations as well. Therefore, the input-output approach is an important tool to make development plan of the national economy and predict its trends. It is worth pointing out that establishing a macro input-output model, regional or national, is to make sensible economic policies, while establishing a micro input-output model for a company or an enterprise to enhance its management and increase profits.
1.1.4. Phase Four Real-time Analysis
- The input-output analysis is based on formulating the input-output table, in this process, the most difficult, complicated and work-demanding part is the collection and reorganization of reliable and relevant statistic data. A reliable and relevant data system ensures the quality and accuracy of an input-output model. Hence, it is very crucial for anyone who dedicates to input-output analysis and to establish a high-quality and precise input-output model in accordance with the present needs of the modern economic management, while at the same time to save the time, labor, resources and money as much as possible when the method of real-time input-output table is attempted to be a scientific, simplified and practical approach. The basic theory of real-time analysis is that, starting from the framework of micro-scale input-output analysis, it tackles traditional tabulating problems, such as formulated tables are not up-to-date and the data is presumed rather than accurately provided. And as it applies to the analysis of micro-scale input-output model, input-occupancy-output model and dynamic input-output model, the flexibility of the tabulating approach, the up-to-date accounting, the scientific policy analysis, and the real-time budgeting (planning) are therefore guaranteed. Furthermore, macroscopic input-output model, input-occupancy-output model and dynamic input-output model on a regional or national basis will be respectively formulated, and a reliable data base will be formed. Although the theory of real-time analysis has gotten rid of the restriction of traditional tabulating method and the way of fixed thinking, it is impossible for an enterprise’s input-output planning model to provide real-time analysis, nor for enterprise input-output statistic model to provide up-to-date analysis. It may be exaggerated to consider real-time analysis as a reform in the study of economics. It seems more appropriate to take real-time analysis as a necessary part of the quantitative analysis phase and a supplement for micro-scale input-output model, input-occupancy-output model and dynamic input-output model, to help the three models play a dominant role in enterprise management. However, the creation of real-time analysis has been very significant and instructive for the modernization of enterprise management, for it triggered the second-time evolvement of enterprise resource management information system and helped to guide an enterprise toward a more scientific, systematic and standardized development in the sense of its technological level and core competition ability. Therefore, it is reasonable to view real-time analysis as an important stage of the modernization of enterprise management which has its competitive advantages, as the president of Newgrand Software, Mr. Shi Zhongshao has pointed out that competition in the 21st century is neither the competition between one each individual enterprises, nor between an individual enterprise and an enterprise chain, but rather between one each enterprise chain. In the Internet age, though the competition environment has changed, the basic principles of competition between enterprises have not yet changed. According to Michael E. Porter’s principles of competition, either differentiation advantage or low-cost advantage or both must be achieved for one enterprise to succeed in competition. In a modernized management environment, which consists of enterprise resource planning, lean production, agile manufacturing, TFP (total factor productivity), and management by objective, real-time analysis, on the both micro and macro levels, there is an incomparable strategic advantage in that it enhances management, increases profits and solves the problem of competitive mechanism. The economic profits brought by real-time analysis can be shown in an internal flow matrix of enterprise input-output model. In this matrix, entries in each row represent the amount of output one sector produces and allocates for other sectors, while entries in each column represent the amount of input this specific sector consumes, such as raw materials, materials, power, and fuel. If basic data from an enterprise input-output model is provided precisely for production and management, waste of logistics, information and money in the supply-demand chain can be fully avoided and cost in each step of production and management can be minimized so as to help the enterprise realize the desire of “completely solving the waste of needed resources, forever controlling the product cost the lowest, and nobody can play tricks” (Wassily W. Leontief: Input-Output Economics, pp.12~13, Beijing, the Commercial Press, 1980). It can not be hard to imagine how much money and resources can be saved for enterprises, for nations and for all human beings.
1.2. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Started from the 1960’s, and represented by the application of computer for storage management in the USA, ERP has gone through four stages of development, which is stated as follows.
1.2.1. Stage One the Common MRP
- The common MRP, a short term for material requirement planning, is a planning method aimed to reduce storage while maintain a sufficient supply of materials. It mainly applies to manufacturing industry. On the basis of product structure (components) or bill of materials (for food, pharmaceutical and chemical industry, the term “formula” is used), data of materials needed is collected so as to guarantee an efficient and sufficient supply of materials, and at the same time, to reduce storage and improve productivity.
1.2.2. Stage Two Closed-loop MRP
- Closed-loop MRP introduces functions as resource planning and resource guarantee, execution planning and monitoring and readjustment of planning according to factual situation and feedback. It has become a tool for managing production and making comprehensive logistic plans.
1.2.3. Stage Three Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II)
- MRPII, also known as manufacturing resource planning, is a management information system focusing on planning and controlling and aiming to achieve the overall benefit of enterprise. Based on the theory of closed-loop MRP, it combines sub-system of production (the logistic system) with sub-system of financing (the capital-flow information system) into one system so that resource account and capital account are generated simultaneously, achieving the information integration of logistics and funds.
1.2.4. Stage Four Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- ERP is an information integration orienting to the process of supply-demand chain, achieving communication and exchange between cooperating partners. Developed on the basis of MRPII, ERP is a highly-intensified information management system which integrates the information of inner-corporate resources with the information of outer-corporate resources. ERP breaks the boundaries created by MRPII (restricted to traditional manufacturing industry) and expands the application to many other industries such as financial, sanitation, IT, transportation, food and beverage, retailing and service, etc.. The major change of modern management has been the change of relationships between enterprises and suppliers, retailers, service providers and customers from a simple business relationship to partnership in which all parties share profits and interests.
1.3. Supply-Demand Chain Management, Value Chain Management and Value Chain Accounting
- In a new economy featured by the internet technology and knowledge management, enterprise management has gone through tremendous changes. The traditional way of organizing a corporation according to different functions is clearly outdated, while a new trend of enterprise management emerges: the supply-demand chain management, value chain management and value chain accounting which are defined as follows:
1.3.1. Supply Chain Management
- The supply-demand chain is the flow of materials starting from the suppliers, and moving through raw materials, in-process materials, semi-finished products, finished products, goods until delivering to the end customers, and with one attaching to the other. The substance of supply-demand chain management is value chain management and value chain accounting.
1.3.2. Value Chain Management
- The value chain management is a newly emerged management method which can plan, organize, coordinate and control the logistics, information and capital in the chain respectively, coping with logistic flow and information flow in a network consisting of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, service providers and customers. In such kind of network, a variety of challenges is posed and the value added ability of itself for enterprises increases.
1.3.3. Value Chain Accounting
- The value chain accounting is a management information system and an adjustment to the value chain management, which can account, analyze, evaluate and assesse the logistics, information flow and capital flow in the chain respectively, aiming for the value-add of enterprises.
2. Technical Problems That Must be Solved to Construct a Better Economy, Save Resources and Prevent Corruption
- In traditional Chinese culture, “economy” means “managing the world to finance the people”, or “managing the nation to provide treasure”, in other words, a country well managed is a country well governed. In general terms, economy is about how to grant maximum output with minimum input, that is, how to make the best choice in multiple options when restricted by conditions of the subjective and the objective, of the nature and the humans. Therefore, it is a common will of different social economies to gain equivalent values with the least labor consumption and labor occupancy, or to gain maximum value with the same labor consumption and labor occupancy. To run the economy, it is hard to imagine if problems of economic construction are not well solved, how can we manage the country well to achieve economic goal of all human concerns? Therefore, these technical problems mentioned above will be elaborated to build the economy, save resources and prevent corruption.2.1. The input-output analysis table, created by the Nobel Prize winner, American Economist and Harvard Professor Wassily W. Leontief, is considered as the modern time Francois Quesnay’s economic table by some western economists, and they also take it as a reform in economics, like Newton’s theory on gravity in physics. However, the input-output table has one big weakness that is, when it is being accounted, a long time will be taken to collect, sort out and process reliable and accurate statistic data before the table is formed, causing the table to be out-of- date. During the reporting period, when using the mathematic model “X = (I - A) -1 Y” to make an input-output planning table, it is assumed that the direct consumption coefficient, i.e. “A” in the model, stays unchanged in the planning period, however, it fluctuates with changes brought by factual factors such as product variety, product price, technological progress and management level. Thus, it is quite possible that the planning table will not be able to reflect the real-time situation of the social reproduction process. Although “A” can be modified with techno-economic analysis method, Delphi method, RAS method and regression analysis method, basic data information in the input-output planning table still lacks real-time accuracy and can not objectively reflect real-time situation. As pointed out by the 7th International Input-Output Conference, this is due to the limitation of each method.2.2. The single classification and double cross classification, also known as the pure input-output approach in the system of national accounts (SNA) recommended by the United Nations Statistics Division, has one obvious shortcoming when data is collected and processed. The reason is the neglect of the relations between ex post statistic data and previous planning method, management and monitoring approach, and neglect of possible changes and subsequent influences, which will lead to a common mistake. The noticeable problem is whether the ex post statistic data from real life is true, accurate and reliable.2.3. According to the input-output approach, we collect, calculate and process accurate and reliable data. Since they are from different channels in the internal flow matrix, there will be two numerical values for each single data and the problem will be which one to choose.2.4. The input-output table consists of material-type and value-type. The material-type is classified by products and takes the quantity of material as measurement unit. The value-type is classified by sectors and takes value as measurement unit. Because product in the material-type (physical) table is calculated by turnover method, while the overall production value is calculated by factory method, there will be the lack of connection between material-type table and value-type (value) table.2.5. Although the management information technology has gone through four different phases: common MRP, closed-loop MRP, MRPII and ERP, none of them has a mathematic model. Take MRPII, an important part of the EPR system, as an example, MRPII takes the advantage of modern computer, simulating the status quo of an enterprise through timely process of mass amount of data from the whole process of production and operation. Activities as engineering design, manufacturing and operating management have developed their own separate and computerized system. Each system owns high automation of internal information and material processing and so acts like an isolated automatic island. There is still the lack of connection and coordination between each other and this problem still remains to be solved.2.6. ERP emerged and corresponded with flows of management method flourished in the late 1980’s such as Lean Production, Agile Manufacturing and supply-demand chain management. They were all led by market and controlled by total quality management, aiming to combine MRPII, Just-in-time Operation and flexible production to achieve information integration and communication internally and externally, to promptly react to market change and to organize a more flexible production to reduce risks and increase profits. Like ERP, either the communication between three cooperating parties of Lean Production: demander, producer and supplier, or the information integration and simultaneous operation of a virtual factory (dynamic alliance) in agile manufacturing, requires the division of MRP into independent demand plan and related demand plan, the integration of logistics information and capital flow information, the integration of supply-demand chain information, and the support from internet communication technology. Lean Production, Agile Manufacturing and supply-demand chain management integrate related resources and make a complete system. However, because of the lack of internal connection, it is not the best or even a relatively good system.It is obvious that the problems clarified above will be the breeding ground for waste and corruption, and will be the biggest obstacle to the integration of industry management and information management.
3. An Important Method to Practice Scientific Development and Build a Harmonious Society
- Émile Zola once said that the smallest finding of scientific truths makes more contribution than fifty years’ social struggle to technical progress. For the convenience of clarification, the smallest findings of scientific truths in this piece of writing will be divided into several parts. Being objective and independent of man’s will, these findings are not only the theoretic foundation of the “real-time input-output table tabulation” approach, but also a very important method to realize scientific development and to build a harmonious society.3.1. As known to all that the direct consumption coefficient A is introduced on the basis of the data of input-output table. In order to make “A” change in accordance with the objective factor of enterprise environment and productivity, the basic data in the input-output table must change. The real-time input-output table is made to reflect such real-time situation of a corporation. On the ground of combining engineering design, manufacturing and producing and operating management with the enterprise input-output model, we will take the advantage of the theory and power of information management technology and use the computer science and technology. The tabulation method of real-time input-output table tackles the problem of an outdated table using the reference of the data from micro economic information flow such as MRP, MRPII (e.g. product mix, technological line, consumption norm, man-hours norm, capacity resources and inventory information) as the basic data of macro economic information flow, which is needed by the enterprise input-output analysis. In this way, a real-time input-output planning table and a just-in-time input-output statistic table can be made. The smallest finding of such a scientific truth is the theoretical background for the uniqueness of real-time input-output table. It not only solves the problem of an outdated and presumed input-output analysis, but also has a great theoretical and practical meaning for changing the way of thinking, accounting method and management method of the traditional tabulating.3.2. Now we will focus on the enterprise’s physical input-output planning table. According to the "3-same" (same consumption structures, same process technologies and same use values) principle and the demand of the "pure" departments (classifying the departments and products to achieve the correspondence of product and department one by one) of the input-output model, once the enterprise input-output model has been designed, the basic data of the constructing table can be divided into two categories: “independent demand” and “related demand”. The basic data of independent demand is a predicted value, while the basic data of related demand is a calculated value. In the enterprise physical input-output table, the end product in the second quadrant is the independent demand data which is presumed, while the end product in the first and third quadrant is the related demand data which is calculated. Led by the market demand, once the type, quantity of the end product and its corresponding quantity of material have been determined, according to the relationship between the structure of end product (component) or bill of materials and production line, whether it is the structure of the end product which determines the production plan of preorder and pushes the production of post-order, or it is the production line which is determined by the production demand by the post-order about when and what the preorder begins and produces. Since in the whole producing and manufacturing circle from the input of materials until the end of production, it is clear before the production that which components are self-manufactured and which are purchased, and also in which production sectors those self-manufactured components are produced and processed, in which production sectors those purchased components are assembled. Therefore, the type, quantity and corresponding material quantity of the intermediate products of each physical production department needed to produce, process and assemble can be calculated precisely. Secondly, according to the type, quantity and corresponding material quantity of the intermediate products of each physical production department, with the basic data of corresponding consumption norm and man-hours norm, the type, quantity and corresponding material quantity of the purchased products of each department can be calculated precisely. Lastly, based on the balance relations between the horizontal rows, the total amount of output of each material production department can be calculated which in the end makes an enterprise’s physical input-output table. This smallest finding of a scientific truth avoids the problem that in the enterprise physical input-output table, the direct consumption coefficient A in the reporting period remains unchanged as in the planning period.3.3. Now let us focus on the tabulation method of a physical input-output statistic table. According to the connection and difference between the physical input-output statistic table and the physical input-output planning table, we can timely formulate the material-type input-output table without having to collect the process and organize reliable statistic data at the end of the planning period. It is easy to understand that, in the physical input-output statistic table and planning table, when the variety, quantity and the corresponding material quantity of the end product are determined, the variety, quantity and the corresponding material quantity of the intermediate product can be determined accordingly. The variety, quantity and the corresponding material quantity of the intermediate product must be adequate to ensure efficient, sufficient and just-in-time production, otherwise, it will either cause the waste of material or the deficiency of the end product. It can be concluded that in the physical input-output statistic table and planning table, except that in the third quadrant of the external purchasing flow matrix, the basic data of the variety, quantity and the corresponding material quantity are different, the basic data in the first quadrant of the internal flow matrix and the basic data in the second quadrant of the end product vector are identical to the basic data of the total output vector. This finding has laid a solid theoretical foundation for the real-time input-output table, reflecting both the connection and difference between the ex post statistic data and the previous planning data, i.e., the connection and difference of the basic data between the reporting table and the planning table. 3.4. Then we will move on to the tabulation method of value input-output planning table and value input-output statistic table. Both of them are formulated on the basis of the corresponding physical input-output planning table and statistic table. As to create the enterprise’s value input-output plan statement, we will use the basic data from the physical input-output statement to calculate the direct consumption coefficient and the complete consumption coefficient, based on the variety, quantity and corresponding quantity of material of the end product of different production plans. In the planning period, since the variety, quantity and corresponding material quantity of the end product of each production sector are given (price- or value-based), the material quantity of outsourcing goods in the flow matrix sheet that each production sector puts in (consumes) during the self-manufactured production can be converted into magnitude of value by specific inventory management methods, such as First In First Out, Last In First Out, Moving Weighted Average Method and Specific Cost Identification Method. Similarly, as the depreciation cost of fixed assets row vector and labor cost matrix of each production sector are given, and the public apportionment of the depreciation cost of fixed assets, other expenses, deferred expenses, withholding expenses, and also profits can be figured out according to management requirements and specific apportionment ways. Therefore, the initial input and profits of each production sector can be worked out. It needs to point out that product cost and product value are fundamentally formulated by the initial input cost and profits accumulated during the production. To calculate the product cost, we should first have the price of the self-manufactured product from the cost category, in other words, the price of the self-manufactured product must be figured out before we have the cost of the self-manufactured product. The product cost is formulated during the production process when the initial input cost transfers and accumulates, and the product price is formulated during the production process when the initial input cost and profits transfer and accumulate. So long as we use the direct consumption coefficient or the complete consumption coefficient to conduct parallel carry-over method (the object is the initial input cost and profits of each production sector), the composition of product price as well as the product price can be worked out. Price here is the factory price of self-manufactured product, reflecting profits whether it is the semi-finished product or the finished product. As the product price and quantity of each production sector are known and are based on the balance relations between rows and columns, the material quantity in the internal flow matrix can be converted into corresponding magnitude of value. Furthermore, by using the intermediate product magnitude of value of each production sector and corresponding initial input cost and profits, the total input of each production sector can be figured out. In this way, we can also calculate the total output of each production sector with the use of the intermediate product magnitude of value and corresponding magnitude of value of the finished product. As a result, on the basis of material-type input-output planning table, a corresponding value input-output plan statement is made, reflecting the real-time environment and status of a corporate during the planning period. The above mentioned two types of input-output planning table are similar in terms of approaches, except that the value-type takes into account the accumulation and allocation of production expenses between the semi-finished product and finished product. This finding shows that the scientific theory, principle and approach of the real-time input-output table are objective and feasible in its real-time budgeting (planning) method and its timely accounting method.3.5. The creation of an enterprise’s input-output model and the realization of real-time analysis of financial management and supply-demand chain management. This can also be illustrated as: 1) the enterprise’s input-output plan statement and real-time analysis of value chain management and financial accounting, and 2) the enterprise input-output statistic statement and just-in-time analysis of management accounting and value chain accounting. The realization of input-output planning model and real-time analysis of financial accounting, or the realization of the input-output statistic model and just-in-time analysis of management accounting are based on the basic data (how many to be used), inventory (how many), implementation (how many wanted) and purchasing (how much needed) with the basic data of the ability resources (fixed assets, current assets and current funds) and the basic data from balance sheet and income statement that are needed by the financial accounting. With all these data, the basic data required for drawing up the enterprise’s input-output model can be calculated precisely (referring to products’ and equipment’s varieties and quantities) and accurately (referring to the products’ physical quantities of varieties and quantities and the equipment’s varieties and quantities and its corresponding value). The realization of input-output planning model and real-time analysis of value chain management or the realization of input-output statistic model and just-in-time analysis of value chain accounting is based on the value chain constructed by the logistics, information and cash flow within each physical production sector and within different sectors of an enterprise, connecting enterprises with suppliers before production, and with distributors, service providers and customers after production. The inner and inter value chain of each production sector reflects the whole process of the supply-demand chain and it is the foundation and core of the supply-demand chain management theory. This finding indicates that as long as the real-time analysis of input-output planning model is achieved, the real-time analysis of financial accounting and value chain management can be achieved, and, as long as the just-in-time analysis of input-output statistic model is achieved, the just-in-time analysis of management accounting and value chain accounting can be achieved.3.6. The tabulation method of the input-occupancy-output model and dynamic input-output model. The basic data needed by the input-occupancy-output model is based on the basic data (how many to be used) in the input-output model, inventory (how many) , implementation (how many wanted) and purchasing (how many needed), along with other basic data such as the ability resources, products’ and equipment’s varieties and quantities and the products’ physical quantities of varieties and quantities and the equipment’s varieties and quantities and its corresponding value can be calculated accurately. The basic data needed by the dynamic input-output model is obtained through the approach of dynamic conversion of static model or static conversion of dynamic model, either of which plays similar roles and can achieve the aim of using static mathematic approach to interpret dynamic economic issues and can therefore link the input-output models of each production cycle within or close to a month. Then, we will get the basic data needed for dynamic analysis of input-output model, measured in month or in production cycle close to a month. This finding indicates that, according to the designing approach of model analysis, model design and model management information system, once the input-output model is created, the corresponding input-occupancy-output and dynamic input-output model will be created.3.7. The organic combination and connection between the input-output optimal planning model and modern management methods such as ERP, lean production, agile manufacturing, TFP, and goal management can be established with the shared basic data such as product mix (component) or bill of materials, technological line, consumption norm, man-hours norm, ability resources and inventory information and under a unified “data environment” (e.g. input-output planning table and input-output statistic table). If we work with world-class software engineering companies working on the research and development of ERP, lean production and agile manufacturing etc., or if these companies can put the theory and approach of real-time input-output table into practice, commercialized systematic software can be developed within two years of time. This finding not only solves the problem of lack of correlation and harmonious development between engineering design, manufacture and production and operating management, but also lays a scientific foundation for realizing an effective combination of various management theories, standards and techniques.3.8. A scientific and satisfactory apportionment of other expenses, deferred expenses, withholding expenses, auxiliary production expenses and manufacturing expenses is crucial to the quality of the a value input-output planning table and statistic table. Therefore, we construct a matrix with the amount of money each production sector puts in or consumes for external purchasing of fuel, power and auxiliary materials in the process of producing, processing and assembling and with the depreciation cost of fixed assets and labor cost when using the characteristic value of the matrix as the weight coefficient of the public apportionment to ensure its scientific nature. This finding avoids the disadvantage of evaluation standard from psychological factors, therefore, ensures the scientific nature of the real-time input-output table.It needs to point out that in old days, basic conditions for formulating enterprise input-output model were: 1) mass production was comparatively complicated in terms of technological process; 2) technological process of producing was fairly stable; 3) the enterprise’ accounting system was regulated, all original record and accounts were completed and accounting data concerning business, statistics and finance was integrated. However, the “tabulation method of real-time input-output table” based on management information technology can work perfectly well regardless of the above limitations. It can be applied not only to enterprises of production technology type but also to the ones of non-production-technology type. For enterprises of either engineering project manufacturing type or workshop task type or streamlined production type, when scientific theories and achievement methods from the “tabulation method of real-time input-output table” are applied to process-oriented manufacturing(such as chemical industry, pharmaceutical industry and serial fertilizers production) and discrete production and assembly(such as construction, shipbuilding, machinery manufacturing and repetitive manufacturing of TV products), no matter how was and is the management level, these scientific thoughts and methods can be of help to establish enterprise input-output model and meanwhile, can all at once optimize enterprise management level to the best of system management and model management. The same is applicable to enterprises of non-production-technology type (such as financial industry), that is to say, the enterprise’s management level can also be optimized all at once to the best of real-time and just-in-time analysis level. In conclusion, of the above mentioned scientific findings, though all of them are very important as a whole, the material-type (physical) input-output planning table is particularly crucial because none of the subsequent studies could be possible without it. As long as the physical input-output planning table, the value input-output planning table, the physical input-output statistic table and the value input-output statistic table are drawn up, the input-occupancy-output planning table, the dynamic input-output planning table, the dynamic input-output statistic table and the real-time analysis of financial accounting and value chain management, the just-in-time analysis of management accounting and value chain accounting can be formulated and achieved. Real-time and Just-in-time are two key factors of the information system which consists of input-output model, financial management and supply-demand chain management. The two key factors accomplish the real-time analysis of the physical input-output model, the physical chain budgeting, the value input-output model and the value chain budgeting to guide the running of enterprises at the beginning of the planning period. Meanwhile, they accomplish the just-in-time analysis of the physical input-output statistic model, the physical chain accounting, the value input-output statistic model and the value chain accounting without collecting, processing and organizing reliable statistic data to monitor the execution of plans at the end of the planning period.
4. Processing and Sorting-out Methods Concerning the Basic Data of “Model Analysis, Model Design and Model Management”
- Connection exists between the structure of end product (component) or bill of materials and the technological line, how to convert this connection to numerical information that can be processed by computer is a critical issue. Meanwhile, the same is true to the way as how to obtain basic data required for drawing up worksheets through simplified calculation and processing. This would be not only one of the basic work for the “model analysis, model design and model management” method, but also an impact on the time and space for collecting, processing and sorting out relevant basic data which will consequently determine the quality of whole systems.1. Theoretical basis for the basic data processing and collating methods: it can be said that the slightest discovery of the scientific characteristics of “The Tabulation Method Of Real-Time Input-Output Table” and the methods concerning model analysis, model design and model management are the theoretical basis for processing and collating basic data. It needs to point out that in the context of the realization of modern enterprise management concerning “nine-must”, tabulating the material-type (physical) input-output planning table in the first place is fundamental and innovative as well as original. Therefore, theoretical basis in here will be illustrated only through basic data required by real-time analysis in the realization of the material-type (physical) input-output planning table. For example, once the varieties and quantities and corresponding physical volumes of end products would be verified, then during the whole processes of production and manufacturing, starting from input until the withdrawal of the production cycles, no matter the production plan issued to the front procedures by the former, with the output as the input for the rear procedures to promote the production of the rear procedures;or the latter would put forward the demand on the front procedures due to the production demand of the rear procedures by the latter, to determine what to produce and when to produce the front procedure then based on the quantitative interdependent relationship of the end products and intermediate products per unit, and the manufacturing technological level of the enterprise’s various production departments, we can accurately (referring to the products’ varieties and quantities) and precisely (referring to the products’ physical volumes of varieties and quantities) obtain the inputs’ varieties and quantities required to be input by the enterprise’s various production departments and their corresponding physical volumes, and the outputs’ varieties and quantities and their corresponding physical volumes; they should be the basic data to constitute the internal flow matrix sheet for the enterprise’s material type (physical)input-output model and to reflect the technical and economic connections between the enterprise’s various internal production departments.2. Scientific methods for basic data processing and collating: The introduction of the enterprise’s internal flow input matrix sheet and the enterprise’s internal flow output matrix sheet can not only transform the relationship between the structure (component) of end products or bill of materials and the technological line into the numerical information that can be processed by computer, but also obtain the basic data required for drawing up the sheet through simple calculation and process. Since the enterprise’s internal flow input matrix for the enterprise’s input-output model should be a square matrix, and often an upper triangular square matrix; so within any a production cycle, according to the varieties and quantities of the end products per unit and their corresponding physical volumes, the inputs’ varieties and quantities required to be input by various production departments and their corresponding physical volumes and the outputs’ varieties and quantities and their corresponding physical volumes can be calculated out. While drawing up the sheet with the computer methods, in order to obtain the general rules for the algorithm, we may regard the inputs’ physical volumes by the enterprise’s various production departments as the enterprise’s internal flow input matrix sheet; and regard the outputs’ physical volumes of the enterprise’s various production departments as the enterprise’s internal flow output matrix sheet; if using the related elements’ physical volumes in the enterprise’s internal flow input matrix statements divides the corresponding elements’ physical volumes in the enterprise’s internal flow input matrix sheet, then we can get a ratio is always > 1 (for some special products, if their differences would be very tiny and can be ignored between the inputs’ physical volumes and the outputs’ physical volumes, such ratio may be regarded = 1), and an upper triangular matrix sheet with the structures and forms of completely the same. Using the ratio of the upper triangular matrix sheet, predications would be carried out starting from the end products, from up to down, from right to left, and forwarding one by one; until the first production department would input; then we can get the basic data required. During the process of predications, there is a principle: the outputs’ varieties and quantities from the former production department is the inputs’ varieties and quantities of the latter production department, according to this principle, if the inputs’ varieties and quantities would be equal to the outputs’ varieties and quantities, then it would show that during the process of production and processing only the form of products yet not the structures should be changed, at this moment using the outputs’ physical volume multiples their ratio, we can get the inputs’ physical volume; if the inputs’ varieties and quantities would not be equal to the outputs’ varieties and quantities, then it would show that during the process of the production and processing not only the form of products, but also the structures of products should be changed, at this moment using the outputs’ physical volume multiples their ratio, what we would get in the inputs’ physical volume should be the quantum of all inputs. That is, in this production department, besides containing the physical volumes of the outputs’ varieties and quantities produced by the former production department, there would still contain the physical volumes of other inputs’ varieties and quantities input by this production department.3. Practical significance of the basic data processing and collating: In our opinions, by introducing the enterprise’s internal flow input matrix sheet and the enterprise’s internal flow output matrix sheet to get the upper triangular matrix with completely same structures and shapes, it would be the scientific basis for algorithm design and programming. Once upon the establishment of such science basis, while helping the enterprise to develop the system, it can not only make the basic data processing and collating become very simple and feasible for the enterprise’s management personnel, but also only by using the two-layer DO statement and conditional statement, make it an easy job to realize the desire of compiling the sheet while the enterprise’s relevant professional and technical personnel programming the computer system. It must be pointed out that for those engaged in enterprise management and professional and technical personnel concerned, as long as through trainings for a certain period of time, they can compile the needed input-output statements based on the characteristics of their own enterprises. Thus it can be seen, for a scientific view of point, that the simpler and more practical the better!
5. The “Nine-Must” in the Light of Enterprise Management Modernization
- The practice of management can be dated back to early human history, and it flourishes with the abundance of human culture. The project of real-time input-output table and enterprise management modernization, i.e., the study of enterprise input-output model and real-time analysis of financial management and supply-demand chain management is the fruit of crystallization of modern management thoughts, management norms and management techniques. It involves the fundamentals of scientific fields such as economics, accounting, management and future factory automation and it embodies the basic ideas in all of the applications of information theory, control theory and system theory in modern enterprise management. The basic theory and scientific tabulation method of real-time input-output model is the theoretical basis for scientific research while the substance of the “nine-must” regarding enterprise management modernization is the core. The accounting theory, principles, norms, accounting and management methods based on the real-time input-output planning model and just-in-time input-output statistic model are the essence of scientific research programs. The method and solution of model analysis, model design and model management are ways to how scientific research programs can be accomplished. In this chapter, we will focus on the substance of the “nine-must” concerning enterprise management modernization. It must be pointed out that the basic content of the “nine-must” and its referred system logic structure model are designed and demonstrated according to different production technology type and the “commonness” residing in both process-oriented manufacturing and discrete production. As long as the basic relation of related functions in this referred system logic structure model is clear, no matter how different the production technology type is, the design and development issues, according to a specific enterprise’s type and demand, will be easy to handle. In addition, the basic substance of modern enterprise management concerning “nine-must” is just the tip of the iceberg in the scientific research of tabulation method of real-time input-output model and modern enterprise management - enterprise input-output model and the realization of real-time analysis of financial management and supply-demand chain management. For an enterprise, the essence of research is valuable and meaningful. It will not only be the theoretical fundamentals for building up modern enterprise accounting system, but also be the accounting methods globally accepted. 5.1. Why must it be necessary to draw up the production and management plans with the input-output model? Because the production and management planning of an enterprise is a large-scale, complicated, multifunctional and multifactor system which makes the traditional ways of planning incompetent for guiding modern time production, finance and purchase under the circumstances of economic globalization and tense competition. A more innovative and efficient system engineering theory and approach must be introduced. By using the systematic planning method of the input-output table, we can make production and management plans; predict economic trends in a much more practical and up-to-date way so that our goals can be achieved. In the input-output model, harmonious development between different sectors or products is the guarantee of best economic profits and if it is combined with the quantitative management technology (operations research) to establish the optimal planning model, it will help enterprise make maximum economic benefits with minimum inputs. And, since the input-output model builds an efficient connection between systems, resources and labor force, linking the production, supply, marketing, labor, funds and materials, it enhances the core competition ability of an enterprise comprehensively and systematically. So, a management information system based on the input-output model will become a key approach to increase enterprise’s profits.5.2. Why must it be necessary to draw up inventory strategies with the input-occupancy-output model? Because any form of productivity would not be possible without the occupation of fixed assets (e.g. plant, machines, transportation tools, instruments and apparatus and computer networks), current assets (raw materials, fuel, power and auxiliary materials), natural resources (land and mineral reserves) and all kinds of labor force. Therefore, the establishment of an enterprise input-occupancy-output management information system is necessary for efficient use of all resources, for it analyzes the relations between occupancy and input and occupancy and output, so that rational purchasing plans, high-quality inventory management and low inventory expenses can be ensured.5.3. Why must it be necessary to establish the grey input-output model to study the connection between grey factor input and output? Grey factors refer to non-material environment factors, such as policy, climate, market, overall scientific level, workers’ education and expertise level, workers’ involvement degree. These non-material factors coexist with material factors in any economic system and are independent of man’s will. They will not change during the running of the system and they play an important role in the economic system. So, they can not be underestimated. To establish the grey input-output model and to analyze the influence of grey factors on economic system are also a theoretical basis for scientific strategy decisions.5.4. Why must it be necessary to establish the dynamic input-output model to carry out dynamic analysis? Because the planning of a specific production period is not isolated from other periods, earlier or later. Only by conduct a thorough study which covers both the earlier period and the later period, can it be complete and comprehensive. The dynamic input-output model displays the development of investment and production connecting and their constraining of each other in a circular mode, so that it will correlate the investment demand and economic development of the past, present and future to establish an organic whole. Therefore, it will help review the relation between investment and reproduction of national economy in a certain time series consecutively so that the study of the inner relations between reproduction of productive investments (e.g. fixed assets, current assets and renewing of fixed assets) and reproduction of enterprise’s products can be carried out and can be reference to the making of reproduction decisions and productive investments.5.5. Why must it be necessary to realize the organic combination and connection between the enterprise’s input-output optimal planning model and the business management modes such as ERP, lean production, agile manufacturing, etc.? Because the input-output optimal planning model emphasizes on the best macroeconomic profits while those modern management methods emphasize on best productivity of microeconomic activities. If the latter is conducted on the basis of the former, then the combination of the micro with the macro will play each of their own roles of overall advantages, management theory, norms and techniques to the fullest. A well-designed combination of an enterprise’s input-output optimal planning model with modern management methods will help to further the enterprise management modernization.5.6. Why must it be necessary to realize the organic combination and connection between the enterprise’s input-output optimal planning model and the modern management methods such as TFP (total factor productivity) and goal management? Because the TFP is a comprehensive index measuring economic benefits, it can not only quantitatively describe the contribution of technological innovation and management advancement to the productivity increase, but also can analyze factors influencing input and the change of productivity. As to the scientific approach of comprehensive management method, the management by objective is featured with objectivity, clarity, integrity, gradation and democracy. Therefore, an organic combination and relation of an enterprise’s input-output optimal planning model with modern management methods such as TFP theory and goal management will help itself to gain experience, find out shortcomings, reveal and clarify principles of operation and eventually, through improving management and technology level to promote economic development. Also, a scientific, systematic, standardized and regularized management and an integrate system of management by objective that we expect for modern enterprise management will be established.5.7. Why must it be necessary to realize the real-time analysis for the enterprise’s input-output optimal planning model and the financial management? For engineering design, production and manufacturing, and operation management are keys to production and the achievement of production goals. An enterprise’s accounting, statistic accounting, business accounting and economic activity analysis all together not only create a fundamental system supervising production and operation but also help to seek economic regulations, improve productivity and save time, producing more products with less labor, material and resource. Therefore, the realization and enforcement of an enterprise’s input-output optimal planning model and real-time analysis of its financial management with its engineering design, manufacturing and production and business management will make an integrate and complete system with common “basic data” under circumstances of unified “data environment” and only after this, can an enterprise conduct unified budget, accounting and analysis of its economic activity and can it enhance internal management and supervision. 5.8. Why must it be necessary to realize the real-time analysis for the enterprise’s input-output optimal planning model and the supply-demand chain management? Because the supply-demand chain management connects enterprise and market by focusing on customer demand and close cooperation between trade partners and applying modern science and technology (e.g. the bar code technology, scanning technology, POS system and EDI technology) to conduct management. With the spread of ERP - an information integration theory, to the process of supply-demand chain of more and more enterprises, the meaning and application of supply-demand chain also extends- from the internal core enterprises(refers to a series of links and activities experienced by an enterprise from its establishment to putting into production and management,i.e., the formation process for an enterprise’s internal product value ) forwards to suppliers and extends backwards to distributors, service providers and customers. Therefore, the realization of the input-output optimal planning model and real-time analysis of supply-demand chain management, and the integration of supply-demand chain with the model, together with common “basic data” and under the circumstances of unified “data environment” to conduct real-time and just-in-time analysis will ensure core competitive ability of an enterprise.5.9. Why must it be necessary to use the input-output model to conduct the analysis of policy? Because correlation, mutual influence and mutual restriction exist among different sectors of the national economy. Changes in a single sector will influence other sectors. when using the input-output model to conduct the analysis of policy, resources can be allocated with the theory of “harmonious development” of related sectors. Clearly, this organic combination and relation of policy analysis and resource allocation will have the supervision and control function over sectors so that the best defense system can be realized and all the resources needed can be calculated to regulate production of all sectors. This kind of regulation not only renders transparent scientific management and administration system, but also lays a scientific foundation for an enterprise’s standardization, systematic management with strict principles and procedures. The theory of harmonious development reflects both natural and social attribute and their mutual infiltration from the scientific point of view. Furthermore, this regulation is an indispensable part of modern enterprise management system. Therefore, allocating resources in the context of applying the input-output model to analyze policy and to realize the organic combination and relation of policy analysis and resource allocation will achieve two basic functions of enterprise management: the realization of both labor supervision and labor command.In conclusion, though the input-output table cannot achieve total optimization, combining with the quantitative approach (operations research), it can still establish the input-output optimal planning model. The major optimal planning models in common use include: 1) production plan, 2) monthly allocation of annual production task, 3) machine load, 4) rational material input, 5) rational material allocation, 6) distribution, 7) productivity arrangement, 8) optimal allocation of power load, 9) optimal allocation of investment, 10) making of transportation plans, 11) production scheduling, 12) single objective planning and 13) multiple objective planning. Currently, when we need to make choices among these grey factors and evaluate them, the heaviest task of the “nine-must” realization is the formulation of input and output table concerning grey factors that involves grey system theory and fuzzy mathematics methods. However, with further research, we believe solutions can be found in the near future.
6. To Eliminate the Possibility of Financial Crisis before It is Going to Spread
- As we all know that the subprime lending crisis originated from the end of twentieth century, marked by the New Century Finance’s bankruptcy in April 2007. This financial disaster spread from New Century Finance, the second biggest subprime mortgage company in the USA, to credit market and went further to trigger a global financial crisis. In September 2008, when Lehman Brothers and some other important financial organizations were blown into collapse, subprime lending crisis joined, bringing adverse consequences to banks and financial markets around the world. After subprime lending crisis, major economies around the world kept printing money. Worldwide excess liquidity was inclined to drown the world. The ongoing financial crisis reveals the root of shortcomings in financial supervision and the global financial system. After the “911” in 2001, in order to stimulate balky consumer spending and the national economy, the American government advocated vividly to adopt consumer credit, encouraged its people to borrow heavily and at the same time, it used varieties of financial derivatives to disperse and shift loan risk to collect huge funds from every corner of the world for its domestic consumption. Eventually, its two parallel policies which tended to promote each other went into a vicious cycle and showed that :1) although falling house prices were the fuse of subprime lending crisis, the hidden reason was the excessive rise of house prices in a short period of time which derailed severely; 2) the root of credit crisis was the global accommodative monetary policy went with economic globalization which brought about worldwide excess liquidity and inflation pressure; 3) the direct reason of subprime lending crisis resulted from irrational investment enthusiasm because of the flush of hot money, excessive pursuit of returns, slackness of risk control, overestimation of the power of the financial innovation products lever; 4) the crucial reason of financial crisis was the defect of credit evaluation system brought about by rating agencies on structured financial products, agencies’ interest drive, lack of risk control of investment on data model. Many people blamed the crisis on the error made by financial supervision institutions. In fact, it was made on purpose somewhat by both supervision department and financial institutions. The current economic situation tells that the tip of Wallstreet’s “modern alchemy” is to shut their eyes to bubble economy or even to produce new “bubbles” to shift risk and crisis, which become a trick tacitly approved and encouraged by American financial authorities. In addition, judging from the above statements concerning root and reasons of subprime lending crisis, economic crisis in financial sphere can be demonstrated by overproduction in macro field or the insufficiency of effective demand which belongs to mismatch of market supply and demand created by economic structural contradiction. Solutions such as adjusting market price or expanding monetary credit are temporary but can not cure. Currently, the flood of the currency worldwide has been infuriatingly worse. Therefore, finding a way to cure is crucial. Traditionally, economic crisis normally occurs in real economy domain, demonstrated by surplus production capacity, while financial crisis occurs in fictitious economy domain, demonstrated by a series of deterioration of financial indicators. Currently, it is hard to set these two kinds of crisis apart for they are related so closely. Financial crisis is often a prelude to economic crisis, in a sense, financial crisis itself is economic crisis in fictitious economic domain and it can trigger crisis in real economic domain. They seriously damage socioeconomic life through interaction. It is not hard to say that current economic and financial problems are more associated with mechanism problems, so to eliminate the root of financial crisis is to improve or even establish new mechanisms. Finance is a part of economy, the solution of financial problems relies on that of economic problems. Meanwhile, a nation’s financial situation exerts influence on economy and the two together are related to policy. So the improvement and establishment of new mechanisms depend on how to study the above factors altogether organically and comprehensively. Hence, the key to eliminate financial crisis is to balance the economic growth and profit pursuit properly. As far as the structure of national economy is concerned, development in harmony between/among departments (products) is crucial and indispensable: it is not only a tool for macroscopical control of supply-demand match and surplus production capacity but also a scientific method for overall management of structural contradiction. Input-output model is designed mainly for balancing development between/among departments, resource allocation through this model is not only the key of improving core competitiveness of an enterprise, a region and a nation, but also “the Great Wall” of stabilizing economic structure, therefore, with the micro input-output model being a base and macro input-output being a guide and with the unique function of the whole input-output model, it can be used to analyze policies(such as analysis of product variety, quantity, price, salary, cost, profit, taxes) and consequently to make plans for national economy development. That is to say, on the one hand, policies incompatible with objective situations can be adjusted by real-time analysis; on the other hand, plans of national economy development can be recreated according to policies readjusted. In this way, there would be repeated analysis, repeated adjustment, repeated comparison and repeated demonstration and proof, and each repetition regards others’ existence as the premise of its own existence when building scientific foundation to improve and establish new mechanisms, which can not only find a proper balanced point between economic growth and profits pursuit but also can highly possibly eliminate the root of financial crisis before it spreads. This is because the related fields are different owing to basic information required by related macro input-output model in the “Tabulation Method Of Real-Time Input-Output Table” , for different production technology type, basic data required by the “nine-must” basic content of modern enterprise management can not only accurately calculate in advance product variety, quantity and the corresponding products’ physical quantities, but also can gather all the needed data and information afterwards without processing. Therefore, the industry may be financial, sanitation, Information technology services, transportation, food and beverage, retailing or service, real-time and just-in-time analysis can both be realized through the R&P of MIS management information system according to various enterprise type and demand. To be exact, this kind of thinking embodies in H. Igor Ansoff’s strategic management theory and methods, that is, according to predicted results, three levels of an enterprise: decision-making, planning and executive levels need to base themselves on the realization of real-time analysis of the micro input-output planning model and of just-in-time analysis of the micro input-output statistic model, and then render basic data for worksheets making according to the real-time analysis of macro input-output planning model and the just-in-time analysis of macro input-output statistic model respectively. To make out worksheets in this way can not only conform to game rules of market economy but also is irreplaceable. The adoption of the method of real-time input-output table acts like the ERP’s application, which breaks fixed concept that MRP II can only be limited to traditional manufacturing business. The fact is: the method of real-time input-output table functions quite well in various industries as mentioned above on the basis of integrating all relevant real-time and just-in-time theories and design methods and techniques of MIS. By doing so, an enterprise’s own management system can be strengthened, economic benefits can be enhanced and the supervision of financial regulators can be effectively activated. On this base, the method which requires basic data rendered by the real-time analysis of macro input-output planning model and the just-in-time analysis of macro input-output statistic model also conforms to game rules of market economy but also is irreplaceable. Therefore, it is clear that the real-time analysis of macro input-output planning model and the just-in-time analysis of macro input-output statistic model can also be realized because on the basis of realization of micro input-output planning model and micro economy real-time analysis, and micro input-output statistic model and micro economy just-in-time analysis, basic data required to establish macro input-output planning model and macro input-output statistic model can be accessed. Obviously, as for the micro- and macro-input-output model, micro- and macro-economy budget (planning) and accounting method concerned once a production cycle within or close to a month is launched on the basis of real-time analysis and just-in-time analysis, two basic functions (labor supervision and labor command) can be realized. Consequently, there is no room for fraud at all. Or one step back, even fraud or corruption happens that will cause crisis concerning financial asset, institutions or markets. With the above methods, the spread, influence and consequence from this finance-related crisis can be timely reduced to the minimum together with rebalancing between demand and supply, thus, related problems could be solved rapidly.
7. The Theoretical and Practical Meaning of the Real-Time Input-output Table and Enterprise Management Modernization
- Entering the 21st century, global economic restructuring has been heated up since the Enron Event and international financial crisis. Following the trend to promote scientific and harmonious development of economy, how to make changes to build economy, to save resources and to prevent further corruption is a global concern. The study of “real-time input-output table and enterprise management modernization - the practice of enterprise input-output model and real-time analysis of financial management and supply-demand chain management” concords the global trend for economic growth, not only does it lay a scientific foundation for economic construction, resources reservation, corruption prevention, scientific and harmonious development, but also it renders an important approach for overall administration and effective supervision. It must be pointed out that since basic data come from the material-type input-output planning model and the material-type input-output statistic model, the percentage of accuracy of the basic data of product variety and quantity is 100% and the corresponding product variety and quantity can be as accurate as 0.01, 0.001, 0.0001, etc. All can be determined according to factual specific business management situation. Therefore, not only the quality of the input-output model can be perfectly guaranteed, but also great amount of time, labor, materials and financial resources can be saved. In this sense, this study has its theoretical and practical meaning and will be elaborated below.7.1. It has changed people’s view on the input-output model since the last 50+ years and has become a new focus of people’s attention, for it not only solves the problem of being unable to update analysis and of running business with presumed data, that is to say, it achieves both real-time analysis of input-output planning model to guide business operation and just-in-time analysis of input-output statistic model to inspect the enforcement of business plans, but also it helps enterprise save resources, minimize input of production cost. The theory of the real-time input-output model has been widely accepted by the academic circles in China and around the world and it can be a scientific achievement above reproach. 7.2. It is the interface merging the natural attribute with the social attribute of enterprise management that is based on the modern enterprise management system。 Under an unbiased and unprivileged system of acknowledged principles independent of anyone’s will during the whole process of production and operation, the real-time input-output model encourages a harmonious interpersonal relationship, and at the same time removes the soil of waste and corruption. It is a right way of enterprise management. 7.3. It is a scientific approach that coordinates a harmonious development of enterprises and helps to get maximum output with minimum input, so that resources can be used to the fullest to produce more products, satisfying more needs.7.4. It creates a competition mechanism urging enterprises to top and to lead in international competitions with optimal resource allocation and a set of combination of elements. 7.5. It is a management method focusing on maximizing the benefit and minimizing the cost. Through accounting, statistical accounting, business accounting and economic activity analysis with common “basic data” and under unified “data environment”, the input-output model and the design of financial management and supply-demand chain management information system all together supervise the whole process of production and business operation so that problems can be easily discovered and solved on time, and the auditing afterwards would be unnecessary. 7.6. It is a theory guided by modernization of management philosophy, measured by systematization of administration and based on quantification of management methods that it makes use of the automation of management approaches and aims for the integration of supply, production and marketing. It will grant leaders of management and training, CEOs, entrepreneurs, MBAs, professional managers and administrative staff the expertise of management.7.7. It is an approach that can be easily applied to enterprises and companies by training technical staff who takes charge of administration, production planning, cost accounting, process design and computer and law for just around 15 days and two class hours each day. This will help build up management information system based on input-output model which is specifically adjusted to circumstances of each enterprise or company and which will finally achieve real-time analysis of physical input-output optimal planning model and just-in-time analysis of physical input-output statistic model in about three months. For those large or medium-sized enterprises and companies with talents, if the theory and approach of self-study of real-time input-output table is thoroughly carried out, it would be easy for those enterprises to achieve intended production goals.7.8. It is an approach that can not only be applied to micro-scale input-output analysis and to provide basic data for micro-scale input-occupancy-output model and dynamic input-output model, it can also be applied to regional or national macro-scale input-output analysis if the basic data of each production sector is known.7.9. It is an approach that can not only be applied to regional or national input-output analysis; it can also be applied to regional or national input-occupancy-output and dynamic input-output analysis when basic data is provided.
8. Systematic Evaluation
- The development of civilization and society is fundamentally triggered by technology that dominates social life. The content of technology here is defined as natural technology (or instrumental technology) and social technology (or social management technology). For quite a long time, people have been fascinated and amazed by natural technology, while neglecting the power of social technology. Social technology is a practical supporting system with which we improve and manage social life, regulate and improve social relationship and tackle social contradictions. After we have gone through the Enron Event and global financial crisis, though the importance of social technology has aroused lots of attention from countries around the world, there still lacks a proper approach to establish a competent supporting system that could take the responsibility of social management. And this is an issue worth studying. But if the theory and approach in this thesis about 1) micro-scale input-output model, 2) input-occupancy-output model, 3) dynamic input-output model, specifically, 4) the micro-scale management technologies (e.g. the accounting theories, principles, methods and management methods based on real-time analysis of the input-output planning model and just-in-time analysis of the input-output statistic model) are taken as the scientific foundation of accounting management system and developing strategy of modern enterprises and companies to perform scientific and effective managements for countries around the world, the overall administration level of enterprises and companies around the world will change dramatically. By realizing the above mentioned micro- and macro- scale management technology and their mutual combination and relation, and by applying it as the foundation for social management technology, we will have the following conclusions during the process to make efforts to construct a better economy, save resources, prevent corruption and realize scientific development and harmonious society.8.1. When we perform accounting, policy analysis and budgeting (or planning) with input-output model, the chain reaction brought by the national economic accounting system ill reach the far end of the economic system if the analysis is still outdated and the data is not accurate. The consequences will be terrible, for not only will the real-time situation of the economy be completely unknown, the interaction of different sectors, the analysis of various important relevant proportional relationships, the deep-rooted correlation and essence of problems will be out of control. Effective economic policies and industrial policies would also be impossible. Furthermore, important decision-making against problems like low economic returns, poor-functioning industry structures, inappropriate revenue allocation,flawed financial system and population pressure on resources and environment will be troubled unless it is conducted on the basis of reliable data. Meanwhile, the national economic accounting system which is established on the basis of macro-scale input-output model is difficult to show a high degree of perfection and integration because inaccurate and unreliable basic data will be awkward reference to the efficiency of instruction, organization, supervision and control and to the implementation of scientific management such as planning management, production management, cost management, price study and analysis of economic activity. As a result, it would be highly impossible to find out the real financial situation, improve management level, and perform accurate and reliable budgeting and accounting of product cost, not to mention the unawareness of problems in management which will hinder steps to gain product competitive advantages and to increase economic benefits. It is obvious that accuracy and precision of basic data is the key to successful input-output analysis. 8.2. Since 1936, people have dedicated to input-output analysis following the footstep of American economist Wassily W.Leontief, Nobel Prize winner and professor in Harvard University. His tabulation method, micro-scale input-output model or a macro-scale input-output model, is carried out in this order: 1) tabulating an input-output statistic table, and then 2) tabulating an input-output planning table with the mathematic model “X = ( I - A ) -1 Y”. Therefore, we take it for granted that the input-output analysis is inevitably outdated and presumed as birth defects. Moreover, because the tabulating method of the micro-scale input-output model is deemed to be extremely complicated for wider spread, the organic integration and connection between macro-scale input-output model and micro-scale input-output model are then deemed as impossible. The approach of real-time input-output table, however, is to tabulate an enterprise’s input-output planning table firstly, then tabulating an enterprise’s input-output statistic table accordingly, so that the analysis is up-to-date and the data used is precise and accurate. And, as the micro-scale real-time input-output tabulating method is simplified and easy for popularization, the basic data can then be used for tabulating a macro-scale input-output model so as to establish the organic integration and connection between the micro and the macro. The tabulating method of the real-time input-output model is distinct from the traditional way in that it is done from bottom to top and with the combination of the two, it integrates the micro with the macro by adhering to tabulation order and principle. Therefore, the macro input-output model can be more efficient to meet management demand and its quality is guaranteed as well. 8.3. For nearly half of a century, the tabulating technology and method of input-output analysis has improved and developed a lot, however, the problem of outdated analysis and lack of accuracy and precision of data has not been solved thoroughly. It has been questioned why, in such a long period of time, the theory of management information technology has not aroused the attention of experts who are engaged in input-output analysis and econometrics, and why the theory of input-output analysis has not aroused the attention of experts who are engaged in ERP, lean production and agile manufacturing? The reason is that the input-output analysis and the management method of ERP, lean production and agile manufacturing are two completely different concepts: the former deals with the coordinated development of different sectors or products which takes time, while the latter deals with the real-time management of the production process and must be flexible and accurate. Thus, this results in inconsistency between the two. The real-time input-output table accomplishes the integration and connection of input-output analysis and management information technology (ERP, lean production and agile manufacturing), improving the social management technology. 8.4. The establishment of an enterprise’s input-output model and the realization of real-time analysis of financial management and supply-demand chain management hinge on: 1) the basis of business strategy, 2) the instruction of the systematic engineering theory, 3) the reference to the scientific method of “model analyzing, model designing and model managing” to design and develop management information system. Specifically, because the accounting theory, principles, standards, methods and management methods are based on real-time analysis of enterprise input-output optimal planning model and just-in-time analysis of enterprise input-output statistic model and meet the conditions and requirements of the Three-Tier Model Of Corporate Transparency (which includes: first, a set of global generally accepted accounting principles focused on principles-based, not rules-based reporting standards; second, standards for measuring and reporting information that are specific to respective industries and consistently applied; third, guidelines for company-specific information including items such as strategies, plans, risk management practices, compensation policies, corporate governance, and performance evaluation) brought up by the chief executive of PricewaterhouseCoopers Samuel Dipiassa in the wake of the collapse of Enron. They will be a solution to constructing a better economy, saving resources, preventing corruption, performing the scientific and harmonious development of society - all of which is our obligation.8.5. The characteristic of commercial enterprises is that they aim to make profits. For outsourcing products, except for transportation and storage cost, they are sold without any processing. The characteristic of government departments and institutions is that they are nonprofit organizations providing grassroots-oriented, public-oriented and community-oriented services within their functional scopes. To meet the needs of market economy and economic globalization, we can take the number of commercial departments of the basic structures (i.e. basic structures of internal flow matrix) of the enterprise input-output model as the special case of “N = 1” while since government departments and institutions are nonprofit, their profit can be taken as “N=0” so that both commercial enterprises and nonprofit organizations can use basic structures, basic theory, economic content, economic significance, inherent connections and management demand of the input-output model to regulate their design and development of the management information systems and at the same time comes to the realization of the real-time analysis for the financial management and the supply-demand chain management. Eventually, uniform data standards could be provided for drawing up macroeconomic input-output models at the regional and the national levels. The realization of financial management and supply-demand chain management modeling will be an important symbol of internal management system of national economy in the 21st century.8.6. The United States is known for its advanced theory of economic management in that its economic construction in the world economy goes side by side with an integrated law system. However, it is still in the same country of strict regulations and laws where the financial crisis broke out and spread all over the world, collapsing the world economy. Whether it is the event in succession of Enron, WorldCom, Xerox, Ernst & Young, KPMG engaging in business fraud or accounting fraud since 2001, or it is the subprime lending crisis of 2007 and global financial crisis of 2008, all of these have something to do with decay of integrity, righteousness and morals. The financial foundation lies in credibility. Especially in the global economy, credibility becomes more important for a stable financial environment. To avoid human’s greed and business fraud, apart from an integrated law system and strict regulations, more effective measures should be put into practice. The “nine-must” regarding enterprise management modernization could be a proper solution.8.7. The essence of financial industry is to coordinate the allocation of resources and help people achieve their goals more effectively. However, under the circumstances of subprime lending, such coordination has become a predatory tool. Although the phenomenon of excessive investment has little to do with the free market, it is closely related with high profits. As early as 232 years ago, Adam Smith once pointed out in The Wealth of Nations that “when the trading profit is higher than usual profit, immoderation will become a common mistake.” He said that the countries with the highest margins would be destroyed fastest. Will the unlimited credit expansion bring about unlimited wealth? Facts have proved that whether it is sea commerce, stocks, bonds or mortgages, excessive trading will turn into a speculative disaster. In other words, to obtain high profit is the cause of excessive speculation. Violating the objective requirement of coordinated development is not only the soil for high profit but also the cause of financial crisis. At present, the very acts of all countries in the world reacting to financial crisis, whether it is the financial assistance, tax relief, financing assistance or investment incentives, are only temporary but not permanent in the long run. Only by urging coordinated and harmonious development of different sectors (products) of the national economy and by rooting out the very causes of high profits, can financial industry perform its duty. 8.8. As the impact of global financial crisis on the real economy deepens and broadens, the unprecedented market turbulence and complexity raise a harsh test to operating capacity, management level and risk prevention ability, etc. of enterprises and companies. Although improving system and mechanism and management level, strengthening risk management and control and enhancing innovation capability and team performance are the fundamental measures to cope with the challenge of financial crisis, working out a more scientific and efficient approach is much more crucial. The “nine-must” concerning enterprise management modernization reflects three classic mainstreams of ancient Chinese philosophy, namely, the compliance of the objective law by Taoism, the compliance of morals by Confucianism, and the compliance of principles and laws by Legalism, these all together render a practical solution to financial crisis and will help enterprises and companies build up a stronger internal management system.8.9. The investigation report from Shanghai Targi Management and Consulting Co., Ltd. shows that Chinese enterprises rise or fall all in a few years. Normally, enterprises heavily rely on marketing strategies and capital operation to gain success so if their foundation is not strong enough, even the slightest risk will cause collapse. Thus, without scientific management system and core ability, enterprises will not stand long. In this context, the large-scale enterprises or companies in developed countries such as the United States are without exception. Although many experts and scholars have expressed their views on how to establish a scientific management system and enterprises’ core ability, their views are partial. If we can not integrate the vertical gradations with the horizontal sectors (products) well and can not establish a unified and systematic management system, it is very difficult to deal with complex and changing market environment. The accounting theory, principles, standards, methods and management method based on the real-time analysis of enterprise input-output planning model and just-in-time analysis on enterprise input-output statistic model will be the theoretical foundation of establishing both scientific management system and core ability of modern enterprises. 8.10. Apart from the competition of production elements, the international competition is more about the competition of combination of all elements. In many cases, enterprises collapse not because of the failure of elements implementation, but because of the failure of combining elements. The responsibility of the executives is to establish and improve an effective system through which management performs rather than instructs. Without an effective system, even a correct instruction will lose its function when it intends to help to solve problems because the system fails. The scientific thought of enterprise real-time input-output tabulation method is market-oriented. In a rapidly changing competition situation, it instructs an enterprise’s factual operation through establishing the optimal input-output model and integrates elements of supplying, producing, marketing, resources and labor to achieve the optimized combination. To examine implementation using enterprise just-in-time input-output statistic model analysis, problems can be timely found out during manufacture and business process and scientific foundation for decision-making can also be laid to establish a combination system to lead enterprises towards management goals. Apparently, such combination of all elements, with organic integration of “real-time” and “just-in-time” analysis which aims to realize management goal is a noticeable mark of an enterprise core competition. 8.11. The law itself is not a panacea. The ultimate solution to some problems (such as waste and corruption) in real social life can not solely rely on the power of law. In many cases, the solution to real life problems is more about politics, economy, culture and technology. We believe that if we respectively basic laws, rules and regulations related to the “dependable aspects” of politics, economy, culture and technology on the technical level of micro- and macro-scale management technologies as well as of their organic combination and relation, then laws, rules and regulations will yield twice the result with half the effort during the process of constructing politics, economy and culture in terms of solving many problems in real social life, on the precondition of being helpful to social supervision.For the limit of my knowledge and academic level, flaws and mistakes in this thesis are inevitable. I appreciate any criticism and modification. Thank you.Note: This paper was presented at the 19th International Conference of Input-Output, and is a suggestion for economic construction, prevention of corruption, reservation of resources, development of scientific and harmonious society. All are of great concerns to the general public.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML