-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2014; 4(6): 226-239
doi:10.5923/j.economics.20140406.02
Capital Controls, New IMF Policies and the Practice of Turkey
Mehmet Nar
Faculty of Economics and Administrative Sciences, Department of Economics, Artvin Çoruh University, Turkey
Correspondence to: Mehmet Nar, Faculty of Economics and Administrative Sciences, Department of Economics, Artvin Çoruh University, Turkey.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
In parallel with the phenomenon of globalism, especially portfolio flows have become in a way to be carried in a distant of a computer button from one country to another; in this respect, the portfolio investments have constituted the most unstable part of global financial flows. In the forthcoming days, a clearly visible rise in portfolio or hot money flows has increased with discourses and practices supported especially by IMF. For this purpose, since the early 1990s, it has been seen that favorable solutions towards removal of capital controls have been brought to the agenda. However, opinions towards the fact that full liberalization doesn’t always result in positive consequences have gained importance just after the crisis of 2008. Consequently, this study aims to question the fact that IMF, which used to support financial openness up until yesterday, has become in a way to support controls with a controversial discourse after the crisis of 2008 and the efficiencies of capital controls based on the experiences of Turkey.
Keywords: Globalism, Capital Controls, IMF Policies, Liberalization, Crisis
Cite this paper: Mehmet Nar, Capital Controls, New IMF Policies and the Practice of Turkey, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 4 No. 6, 2014, pp. 226-239. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20140406.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- “Globalization” refers to the growing interdependence of the countries resulting from their increased economic integration via trade, foreign investment, foreign aid, and international migration of people and ideas. However, the important fact is the expansion in the volume of international investment and the extent of the financial flows, which are highlighted by the concept of globalization. Considering that the financial flows are practiced through the main channels such as foreign direct investment, private capital or portfolio flows, remittances from migrant workers, debt flows and official development aids, the significance of the portfolio investments in this classification becomes more prominent [42].Controlling capital flows is one of the most difficult issues that policymakers have to face in the developing economies. Thus, the complexity of capital flows and the problems surrounding the control of them make it difficult to present the most suitable choices regarding these policies. In parallel with the globalization process, apparently, the rise in the capital flows and especially hot money flows have increased with the discourses and practices supported especially by IMF. In this regard, since the early 1990s, it has been seen that favorable solutions towards abolishing capital controls have been brought to the agenda. Therefore, it is uttered that while rising capital flows, which have been helping to close the saving gaps in the developing countries, investments will increase and the countries will develop faster as a result of decreased interest rates. According to the people who agree in this idea, the capital flows to these countries will be increased as a result of increasing capital returns in the developing countries. The interest rates will drop down, because the rise of the capital is more than the rise of labor force; thus, the growth rate of the poor countries will be higher than the rich countries and these poor countries will reach them sooner or later. Although the ones who support the opposite opinion accept that financial globalization presents broad opportunities between those, who supply funds and for those who demand funds; experiences until today show that at the same time, speculative capital flows result in some macro-economic problems such as financial crisis, balance of payments deficits, debt crisis and exchange rate overvaluation. In this respect, it is also seen that there are various techniques and practices on the agenda towards the control of capital flows [1, 15, 18].
2. A General View of the Capital Controls
- Capital control means all restrictions and arrangements that are imposed by governments to domestic residents and non-residents in order to restrict its mobility during the transfer of “capital” in the country or out of the country. It has been observed that until the 20th Century, capital controls were practiced occasionally; however, it has gained more importance in many countries over time. After World War II, it is seen that only Switzerland, Canada and USA accepted open capital regimes (considerably). Despite this fact, it is understood that other rich countries still continue to have strict controls and during the period of 1960-1970, they insisted on these political practices [8].The main reason for this insistence is the Bretton Woods system, signed in 1944 in the town of Bretton Woods, in New Hampshire, which has defined the exact rules to be obeyed regarding international payments, structures “international money system” [17]. Within this system, independent nation states leagued together and accepted the Bretton Woods system (fixed exchange rate regime) in order for realizing global trade and wealth after the war, and signed the treaty, which reigned during the period of 1945-1971. The aforesaid treaty is known as the one which established International Monetary Fund (IMF) [30]. However, along with the end of the Britton Woods system in 1971-1972, the aforesaid structure started to change. Continents and countries such as developed North America, Europe and Japan switched to floating exchange rate from fixed exchange rate. This case has led the capital accounts to be liberalized and brought functionality to cross-border flows of financial investments [5]. Thus, it is possible to make a dual classification of world economy regarding financial regimes as Bretton Woods Period and Free Capital Period. According to this, while “the Bretton Woods Period” is generally refers to the structures based on fixed exchange rates and capital controls in terms of international financial regimes, it is a period in which this kind of practices are confirmed by IMF. Nonetheless, “Free Capital Period” has become very popular since mid-1970s that refers to a period, in which fixed exchange rates were abandoned and floating exchange rates were accepted in terms of international financial regime, and the capital has gained free mobility by releasing controls of governments [25]. In parallel with these improvements, it is seen that capital controls, which are practiced by the developed countries, have started to change in the early 1980s, and the present controls were either removed or minimized. The main reason for the removal of capital controls in the developed countries can be classified under two headings. The first one is that the capital controls have become out of the date as a result of proliferation of market practices worldwide, and the second one is that the financial providers and investors have become experts on finding solutions by using various methods instead of the controls. This process was also seen in the developing countries in a similar way. Especially in Latin American and Asian countries (such as Argentina, Indonesia, Mexico, Turkey, Thailand and Malaysia), the common capital controls were loosened during the late 1980s; and in 1990s, the liberal practices towards removal of capital controls have been accelerated [8].According to Rawi Abdelal, this financial liberalization process is an extension of political and financial hegemony, which is imposed by the developed countries, and aforesaid process was supported constantly by international organizations such as IMF (International Monetary Fund) and OECD (Organization For Economic Cooperation and Development) [29]. After financial deregulation and the removal of capital controls, in parallel with the rivalry phenomenon experienced in almost all the industrialized countries, cross-border capital mobility increased considerably. Because of low interest rates in their own countries, the developed countries have canalized their investments to the emerging market economies, which offer higher security conditions. While this situation was turning back to developing countries as growth and low interest rates, also it enabled the occurrence of a “respectable asset class” swiftly in the developing markets. The hot money flows canalizing to developing countries have contributed significantly to provide necessary funds in terms of having macro-economic stability and maintaining structural adjustment programs. On the other hand, commercial and financial deregulation decreased the risk perception that had existed in the developing countries up until yesterday, and this situation made a great contribution about reducing the external debt burdens. The renewed feeling of trust and confidence in the international scale has turned economical perspective into a positive direction in many developing countries. This situation revealed itself in a form of a dramatic rise in the capital flows by conducting investors to be deceived. As a result, while total explicit capital inputs were flowing into the developing countries in 1983, the capital flows almost reached to a level of explosion between the years of 1990-1994. In 1993, the capital or hot money flows have peaked with an amount of 155 billion dollars, which is equal to the total amount in the former five years period [31]. A general classification containing developing countries (emerging market economies) and sample countries, which need to be evaluated in another category along with developed countries, was carried out by Glick and Hutchison given in Table 1 [37].
|
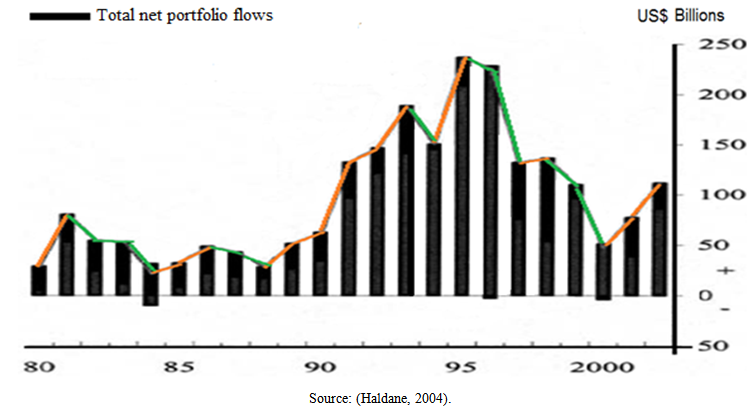 | Figure 1. Capital flows to emerging markets |
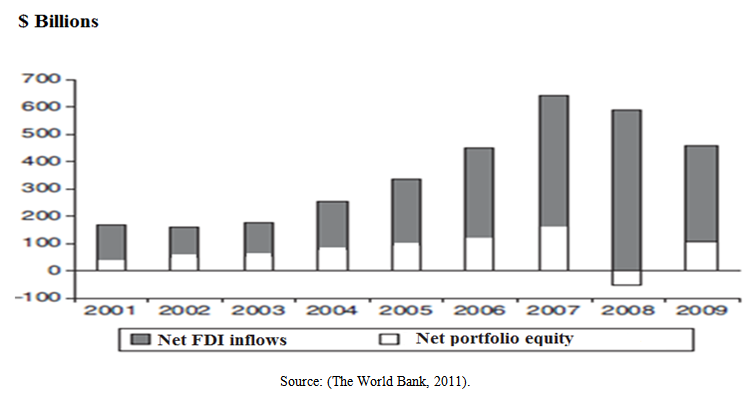 | Figure 2. Net equity flows to developing countries, 2001-09 |
3. Types of Capital Control
- Short term capital inflows, which constitute a significant part of international capital mobility and occur as a reflection of international financial liberalization in a way, can rapidly flow into a country and at the same time, they can leave the economies at the same pace. This emerging financial volatility may cause territorial and regional crisis, and also may penetrate all global markets by means of contagion effect as it was the case during Asian crisis. This situation forced especially the developing country governors to take the initiative over the economy of the country. As a result of these efforts, it was seen that real practices towards taking control of short term fund flows came into force in Malaysia in September 1998, just after the Asian crisis. In order to prevent the destructive effects of international capital flows; firstly, strong domestic precautionary measures were put into force and by this way, it was aimed to restrain uncontrolled inflow or outflow of capital into the country or out of the country, respectively [36]. In particular, after the global financial crisis of 2008-2009, free mobility of international capital has caused an increasing amount of concerns regarding not only countries drawing foreign capital but also the developed economies, and this situation has urged countries to take more intense measures in the subject of the capital controls [39].Capital controls are considered as a tool for both preventing panic attacks caused by international capital flows and removing destabilized actions, which countries may experience in practice [20]. Basically, it is aimed to interfere to free international exchange in financial assets [14]. In Table 2, the control methods, which were implemented on capital processes of domestic and foreign residents, are displayed. The mentioned control methods are classified as direct and indirect methods [40].
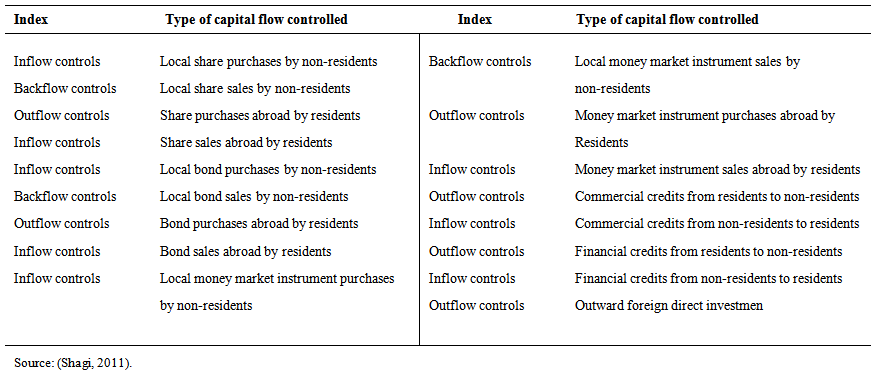 | Table 2. Types of capital controls |
4. Practices for Control of Capital Mobility and New IMF Policies
- In parallel with the development in the volume of world trade, private capital movements have gained considerable speed. Especially the increase in capital mobility, which is seen at emerging market economies, is significant. There have been two great fluctuations of private capital flows in this time period. The first one of these flows has begun in the early 1990s and ended all of a sudden with Asian crisis, which took place in 1997-98. The second or the last fluctuation have started in 2002 and peaked in the late 2006. The first global fluctuation was dominant in Emerging Asian and Latin American countries (Figure 3), whereas the last fluctuation emerged in Emerging European countries and other emerging market countries and later in the USA, and its effects are still believed to be continued [12, 4]. While the first fluctuation caused Mexican, Asian, Turkey, Venezuela, Russia crises [20], the second big fluctuation caused mortgage crisis in the USA in 2008 and then, contagion effects caused a global economic crisis spreading all over the world initially in European countries [17].
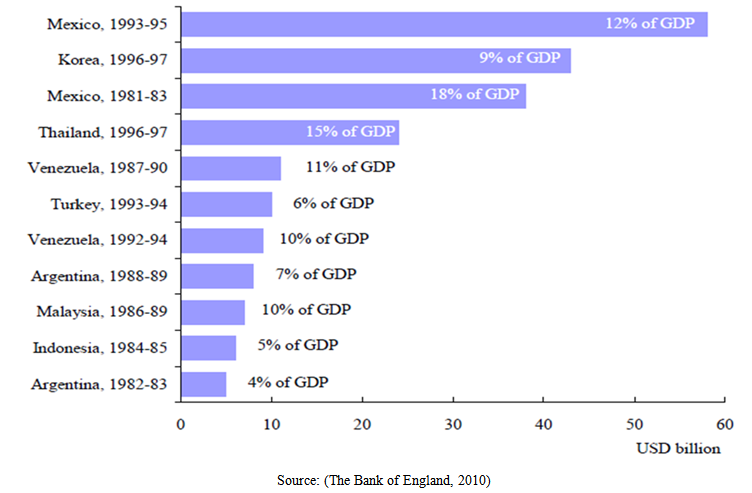 | Figure 3. Large reversals in capital flows |
5. Practice Process in Turkey for Capital Controls
- Since the idea of Bretton Woods has been disappeared, international financial markets have encountered financial crises for many times within the last 30 years. It was emphasized that financial liberalization could be helpful in many areas from reducing the savings gap to moderating burden of debt and then GDP growth especially in the developing countries; however, the negative consequences based on aforesaid capital flows have been almost ignored [17].For example, during the free capital period since mid-1970s, while capital mobility has been rapidly mobilizing, GDP growth in OECD countries has reduced by nearly half. The growth rate has reached 2.8% after 1970s, which was 4.8% during the Bretton Woods period. Moreover, interestingly, further data show that the high rates of growth of investment in OECD countries in the Bretton Woods period were replaced by much lower figures in the free capital period. Thus, in the developing countries, intense capital flows can cause some side effects such as overvaluation of national money, increase in loan volume-leverage ratios and foreign deposit accounts, growth in asset prices and imports, negative effects on domestic industry, deficit in payment balance, increase in debt and interest rates. Considered in general terms, financial fragility is rising [25] and this situation shows similar consequences in the practices of Turkey. Considering the financial liberalization period in Turkey; with Law Regarding the Protection of the Value of Turkish Currency dated back to 1930, there was a transition to exchange controls and financial markets, which were isolated from the outside world. In 1954, Law on Encouraging Foreign Investments, which was one of the most liberal regimes, was prepared and put into force in order to get more benefit from foreign resources. However, due to extremely rigid exchange rate regime, capital inflows didn’t reach the level desired. In 1962, with the decision No. 17, restrictions and controls on the exchange and capital movement were concentrated in extreme ways [26]. Therefore, there were closed economy model practices in Turkey before 1980. During this time, import substitution industrialization policies were followed. Domestic production of imported goods was encouraged and the domestic industry was protected. It was necessary to import the industrial goods to sustain the domestic industry based on assembly. However, the depressions and especially oil crises, experienced in the 1970s, have increased the cost of exported goods and made the process more difficult. External debts have reached the limit, and due to scarce foreign exchange resources, economy of the country almost reached to a standstill level. In order to eliminate such problems and provide financial sustainability, the state has formed additional measures. For this purpose, "24th of January, 1980 Economic Stabilization Decisions" were put into force, and it has targeted the liberalization of foreign trade and opening of Turkish economy to foreign countries [26]. Within the decisions made, it was aimed to bring inflation under control, close foreign financial gap, and reach a more extraverted and market-oriented economic system. Significant subsidies were obtained by encouraging export oriented growth, and depreciation of Turkish Lira was allowed in real terms. These moves were important in re-gaining trust of international credit institutions. IMF stand-by and World Bank adjustment loans were scheduled rapidly and the payments were made. As a result, (i) loans, which are obtained from foreign countries, have increased the importation of intermediate goods and pressures on public finance were lessened; strong encouragements, which are given to the firms, carried exportation to significant levels (ii), although the depreciation of Turkish Lira was high, sustainability was maintained (iii) by reducing domestic demand significantly, a financial environment was prepared for strengthening exportation [43, 14]. The Capital Market Board was founded in 1982; the banks and other finance institutions have become subject to the supervision of the Board about their activities since the establishment day of the institution. In the same year, commercial banks were allowed to have foreign exchange position. In 1983, Saving Deposit Insurance Fund was formed. Exchange rate regime was liberalized to a large extent with the Decree No. 30 dated July 7th in 1984. In 1986, Istanbul Securities Exchange has begun its operations as second hand government debt securities market. In August 1988, Foreign Currency and Effective Markets were established within the body of Central Bank and daily sessions determining the rates have begun. Liberalization practices of capital mobility in Turkey were completed by Decree No. 32 in conjunction with economic and financial reforms carried out in 1980 [43].With the decision no.32, entry to the country and exit from the country of securities and other capital market instruments, their export to abroad and their sale to foreign countries were liberalized. With this decree, it was legalized for residents in Turkey to get a loan from foreign banks and to invest in any country or a free zone. Turkey has applied to IMF in the year of 1990 and asked them to register Turkish Lira as a convertible sort of money [26].Thus, Turkey’s economy has started a period of integration with the world after 1980 and during this period, the routing of economy was left to the market mechanism. At market economy, prices route the economy. In order to reach the desired economic targets, there should be a balance among “goods prices”, “exchange rates”, “interests” and “wages”. The financial crises emerge in the failure of delivering these balances [26].
5.1. The Effects of Capital Movements in Turkey
- After the liberalization of capital movements in 1989, (except the Gulf Crisis of 1991, the Financial Crisis of 1994 and the Russian Crisis of 1998) Turkey has provided more foreign capital inflow than its need for financing current account transactions during 1990s. Although the purpose, expected from financial liberalization, was stated as integration with international capital markets, the determinative points was reducing financial constraints based on increasing public expenditure in practice. After liberalization, there have been important changes in the structure of capital flows, which work for financing balance of payments, short term loans that have taken the place of medium and long term loans. Along with the Gulf War in 1991, economy of Turkey has experienced an important constriction resulted from external shocks. Then, Turkey has faced a serious financial crisis in 1994. A combination of uneven liberalization, large fiscal deficits, and a reliance on short-term, unhedged foreign currency loans sparked the initial 1994 crisis. While Turkish Lira was losing half of its value during the first three months, the reserves of Central Bank regressed from 7 billion dollars to 3 billion dollars. GDP was reduced at the rate of 6%, and the inflation numbers have reached three digits. The full blown crises, experienced once again in 2000-2001, have shown that how inadequate the measures taken were; and Turkey has failed to address the underlying problems with both its economy and its banking system [5, 7]. After the period of 2000-2001, structural reforms, which provided the removal of volatility towards banking sector that played an important role in the emergence of crises, have become the engine of the economic growth and the key to exit from the crisis [6]. After the crisis of 2008, Turkey’s post-crisis adjustment under the AKP administration traces the steps of many developing countries, which are dependent upon foreign capital and conditioned to adopt or maintain contractionary policies in order to secure “investor confidence” and “international credit worthiness” [2].There is an analogy between the outflow of capital from the country and financial crises shown in Figure 4 at below. In the early 1990s, capital flows, which began with the Gulf Crisis, have caused the emergence of many crises at important levels parallel to the ones happened in Turkey in 1994 and 2001, in Russia in 1998and global crisis in 2008 at a later time. This situation is important in terms of seeing the effects of internal and external shocks. Considering the case in terms of direct investments, investments were considerably low in the period between 1990 and 2001. In 2000 and in the following years, improvements provided by political stability and structural reforms, development provided by legal arrangements (taxational-judicial), the distance covered in privatization practices have been significant. In terms of portfolio investments, they saw the lowest points in their history after Russian crisis in 1998 and they experienced the second biggest break as a result of the crisis happened in 2001. Portfolio flows, which entered the country in parallel to the expansion, have experienced in global liquidity circumstances after 2002 and they have reached significant levels. Thereafter, short-term funds (stocks-bonds), which exit as a result of 2008 global crisis that caused narrowing in our country as it had done around the globe, have developed increasingly in the following years (Table 3).
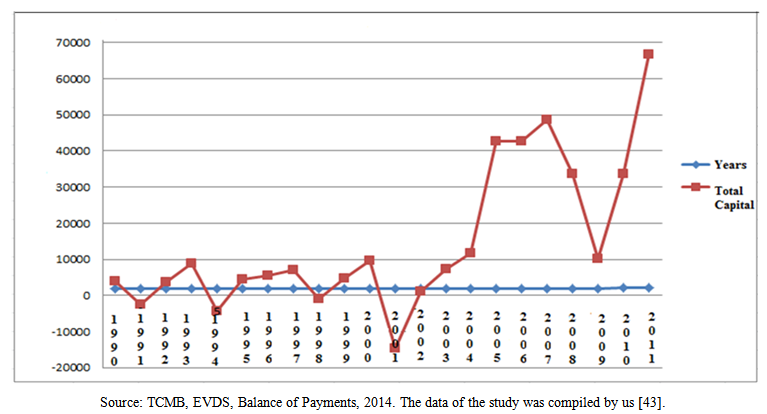 | Figure 4. Total Capital Flow for Turkey (1990-2011) |
|
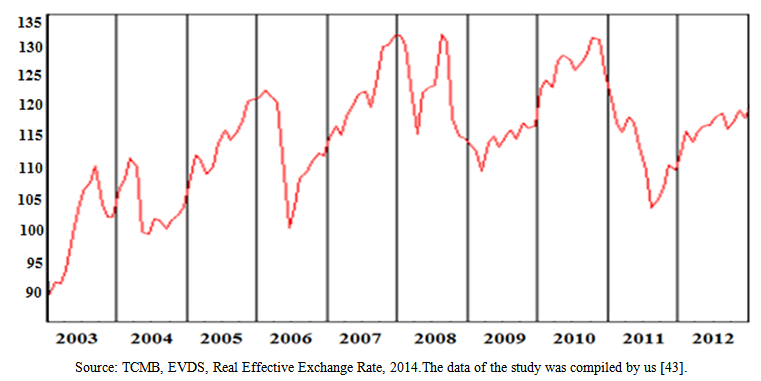 | Figure 5. Real Effective Exchange Rate (Consumer Price Index-based /2003=100/monthly) |
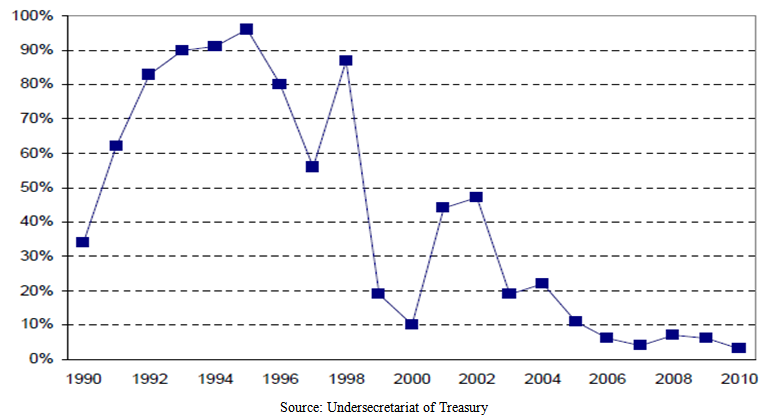 | Figure 6. Short-Term Domestic Debt / Total Domestic Debt |
6. Conclusions
- After the crisis happened in 2008, in many countries like Korea, Indonesia, Brazil, Colombia, Thailand, Iceland and India, capital controls are implemented on short term capital movements; and it is understood that similar policies are also discussed in EU countries as well as in most of the developed countries. However, it seems that the control practices implemented in EU are some arrangements aiming to realize macro-economic targets in EU, which are in the content of directives instead of controlling capital flows. In Turkey’s economy, where there are significant savings gap, capital control practices contain difficulties, and this situation brings along economical volatilities caused by short term capital flows. Capital flows in the developing countries have played an important role in the growth of economies in addition to the contributions they make in the finance of domestic investments. For example, telecom systems in Mexico, the roads in Thailand and similar services in many other countries are considered as a return of foreign capital and the added-value; because these services create jobs for human capital. However, hot money flows, which create positive effects while entering into the country but leave it abruptly at any speculative attack, can cause social, economic and political destructions as in the case of Latin America. While this one and similar examples highlight the views that full liberalization doesn’t always result in positive consequences, they also bring along the arrangements towards the control of capital movements. First of all, according to Rajan (2011), there is a need for practicing “market-friendly” capital controls. Furthermore, according to a limited number of the studies conducted in the literature, capital controls are more effective in moderating capital inflow surges than capital outflows, and they can be considered as more useful in lengthening the maturity of capital inflows instead of reducing the actual volume of the flows. Any dampening effects would be transitory on the volume of inflows at best as people find ways to circumvent the controls. The empirical evidence that show the influence of capital controls on currency swings suggests that they are depending on manner and type of the controls introduced. In the literature, most of the empirical studies were conducted on Chilean and Colombian experiences so far, which imposed unremunerated reserve requirements (URR) to manage capital inflow surges and price booms. If they are applied appropriately, URR seems to be effective prudential and counter-cyclical tools that may generate much interest with one caveat, may also result in negative unintended consequence, while it can disproportionately raise the cost of credit for small and medium sized enterprises. It is extremely important to convert short-term financial flows into long-term or institutional investments in the speculative capital. In terms of providing the functioning in the practice of capital controls, taxational arrangements like transaction tax are among the precautionary methods in practice. In order to be protected from negative effects of capital movements, it is important that governments should put inspection, criminal sanction and effective design of financial sector especially banking system into force in a way that doesn’t contain any moral danger as IMF stated earlier. According to Moschella (2010), the efforts spent for creating an early warning system under IMF supervision are remarkable. By this way, it is aimed to send detailed warnings about capital inflows and outflows in a country by creating an effective data network regarding market structures in addition to the economic and financial circumstances of the member countries. Meanwhile, it is considered to block the use of funds coming from IMF resources by countries, which are imposed to continuous fund flows and do not discharge their responsibilities properly. Thus, while member countries are encouraged to act more cautiously about capital inflows and out flows, it is also possible to consider this system as an indirect capital control method. In this context, it is stated that a reform, which can be realized for arranging international financial flows, will be beneficial for global welfare. However, the reasons such as the presence of countries, firms or stakeholders, which generate a high income by this way, restrict the practices for capital controls and the possibility to govern aforesaid flows considerably. Nevertheless, as Keynes has stated earlier that “the functioning of the markets is such a sharp area that it can’t be left to the initiatives of private capital owners, who run after their personal benefits”. Thus, it is highly necessary to provide a multilateral international cooperation in this area. Otherwise, no country will be able to benefit from international liquidity, which is growing rapidly and very changeable; and the current controls will not be able to go beyond having only a limited effect.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML