-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2014; 4(6): 219-225
doi:10.5923/j.economics.20140406.01
The Analysis of Interaction between Growth and Profitability on the Basis of Growth Persistency: The Case of Turkey
Nesrin Özataç1, K. Batu Tunay2
1Department of Banking and Finance, Eastern Mediterranean University, Famagusta, North Cyprus
2Department of Banking, Marmara University, Institute of Banking and Insurance, Istanbul, Turkey
Correspondence to: K. Batu Tunay, Department of Banking, Marmara University, Institute of Banking and Insurance, Istanbul, Turkey.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
From the beginning of 2000, there have been a growing number of researches on the profitability and the growth of commercial banks, however, there is a paucity of studies done on Turkey. Generally, the studies indicate that the growth rate of companies for a period is independent from their size. However, it is accepted that the volatility in the growth rates can be correlated with their size. On the other hand, it is found that in different periods, companies’ growth rates can be uncorrelated. In regard to these observations, the growth rates of the companies are accepted to show a random walk. It is also possible to apply this analysis to commercial banks. The basic aim of this research is to analyze the correlation of growth and profitability of commercial banks. In regard to this, persistency of growth and profitability of Turkish Banks, as well as, the growth in size and the profitability will be analyzed by using the Dynamic Panel Data model. While growth is not persistent, the profitability of banks is persistent. Finally, it is found out that the banking sector intensity has positive effect on the growth of banks as well as their profitability.
Keywords: Gibrat`s law, Banks growth, Bank profits, Persistence, Dynamic panel data
Cite this paper: Nesrin Özataç, K. Batu Tunay, The Analysis of Interaction between Growth and Profitability on the Basis of Growth Persistency: The Case of Turkey, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 4 No. 6, 2014, pp. 219-225. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20140406.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The law of Gibrat which is also known as “Gibrat’s Proportionate Growth Rule” contributed in an important way in the analysis of Dynamics of firm growth. In recent years, the law is also used in analysis of the correlation of growth and profitability of the banking sector. There are many studies that investigated the profitability of banking in different respects. Levonian [1, 2], Berger et al. [3], Goddard et al. [4, 5], Agostino et al. [6], Bektaş [7], Kaplan and Çelik [8], Shehzad et al. [9], Flamini et al. [10], Goddard et al. [11], Francis [12], Garza-Garcia [13], Aslan et al. [14] are the studies that investigated persistence of bank profitability and Dynamics of profitability. Moreover, the correlation between bank growth and bank profitability are taken into consideration the studies such as Goodard et al. [4, 5]. Although Shehzad et al. [9, 15] and Goodard et al. [4, 5] made progress in their researches; there is still a limited number of studies done on the area.The basic questions that arise in this type of analysis are; if there is a correlation between growth and bank profitability and if the correlation between growth and profitability is persistent or not. However, the results of the existing analysis are not robust and it is difficult to end up with assumptions. The ambiguous results can be due to the methods that are used and also on the differences on the structures of the data. It is inevitable to state the need for more empirical analysis to have answer for the stated questions. The aim of this study is to investigate the persistence of growth and profitability of commercial banks in Turkey. The analysis will be based on alternative dynamic panel data model which are used in previous studies. It is important to note that the results of the models were contradictory. Our analysis will also be based on such empirical studies. This will make it possible for us to make assumptions by using different econometric models. As an emerging country, Turkey has a fast developing economy. The Turkish commercial have recently been investigated in recent years. The factors that influence the profitability of banks are investigated by the studies such as Kaya [16], Tunay and Silpagar [17, 18], Doğru [19] and the persistence of bank profits by Bektaş [7], Kaplan and Çelik [8], Aslan et al. [14]. However, there is no any other study done on the bank growth on the basis of persistence of bank profits. In this study, the aim is to make theoretical evaluations on the persistence on banking growth and bank profits and results will be presented by applying econometrical analysis.
2. Theoretical Background and Method of Analysis
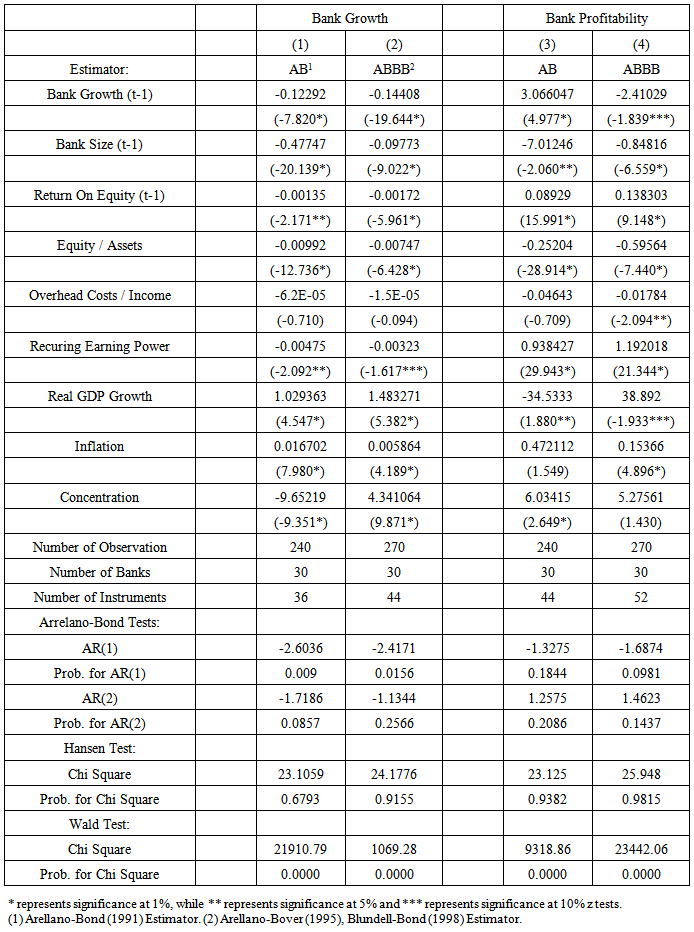
- In 1931, Robert Gibrat set a rule which is known as “Gibrat’s Law of Proportionate Effect”. It contributed a lot to the literature in the dynamics of firm growth, proposing three basic points. The first proposition is that for a specified period, the growth rate of a firm is independent from its size. The second, the variability of a firm’s growth rate is independent from its size. The third one is that for two consequentive periods the size of the firms is independent from each other. Regarding the law of Gibrat, the firms follow random walk process. The studies analysed if the Gibrat law is significant for banks or not, also analysed the correlation between growth and bank profitability. However, the results indicate significant variance according to the data set and the method of estimation.If Gibrat law is valid for bank or not is studied by the works of Goddart et al. [4, 5], Benito [20] (2008), Shehzad et al. [9, 15]. Goddard et al. [4, 5] analyzed the validity of Gibrat’s law as well as the bank growth and profitability. They examined 600 commercial banks in five EU countries for the years between 1992-1998. The results present that the profitability of banks play an important role in the growth of banks in the future. It is also pointe out that the growth makes the banks to perform better. Likewise the growth of banks indicates persistence. The persistence of profit in commercial banks is found to be higher than savings banks, co-operative banks.Benito [20], in his study, examined the commercial, saving banks and cooperatives in regard to the distribution volume of the population for the years between 1970-2006. The data is tested by the panel unit root test if they fit to the Gibrat law or not. According to the results, the size and the growth is not consistent (istikrarli) in time. According to the banking activities, depending on the competitive environmental factors this plays a variance in the relation. As Spanish banking sector is highly regulated, it is observed that small sized banks are growing at a higher speed compared to the large–sized banks. This result supports the law of Proportionate Effect. Shehzad et al. [9, 15], investigate if there is persistence of growth and profitability in the commercial banks and also if the level of growth and profit and the volatility depends on the size of banks and consequently if there is an interaction between growth and profitability. Using dynamic panel GMM model 1500 commercial banks form 65 countries from the years of 1997 to 2000, are examined. Not only growth and profitability but also the level of the firms and the banking sector is investigated by macroeconomic variables. They found no evidence indicating the persistence of growth, however, results indicate persistence of bank profitability. Moreover, they pointed us that the growth in banking as well as the profitability dynamics are found to be different in OECD countries and non-OECD countries. The result of the studies done by Shehzad et al. [9, 15] indicate that there is persistence in bank profits but not on growth which deviate from the findings of completely Goddard et al. [4, 5]. As the studies done by Shehzad et al [9, 15] can be considered more extended and their data set is more recent with more robust results, their studies is considered superior. Instead of using Arellano and Bond [21] dynamic panel data model they used system dynamic panel data model presented by Blundell and Bond [22]. The Arellano and Bond [21] dynamic model type can provide biased results regarding for a data set of short period of many banks. However, the results of the dynamic models of Blundell and Bond [22] provide more reliable results due to different structured data set.This study will use Shehzad et al. [9, 15] model using control variables on the firm, the sector and macroeconomic level. Shehzad et al. [9, 15] primarily investigated if bank growth and its variance is independent from bank growth or not and then their persistence. In regard to this issue they developed the model given below:
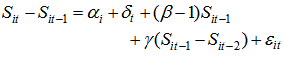 | (1) |
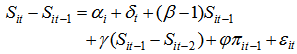 | (2) |
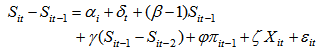 | (3) |
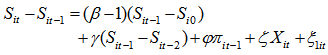 | (4) |
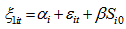 is defined. By such derivation, the model become biased and significant. In the restructuring, take the lagged variables are used by taking their differences.Shehzad et al. [9, 15] applied bank growth model to profitability as equation (4):
is defined. By such derivation, the model become biased and significant. In the restructuring, take the lagged variables are used by taking their differences.Shehzad et al. [9, 15] applied bank growth model to profitability as equation (4):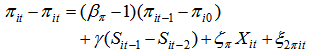 | (5) |
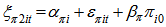 . This model is developed in order to test the propositions of Gibrat in regard to profitability.
. This model is developed in order to test the propositions of Gibrat in regard to profitability.3. Data Set
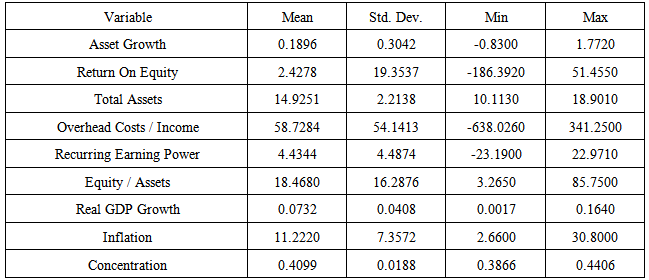
- In the study, the balance sheet of the commercial banks in Turkey and the macroeconomic variables are used for the years 2002-2012. The web sites of Turkish Banking Association and the Turkish Republic of Central Bank are used to compile the data set. For that specific period, 30 commercial bank’s data set is used making it possible to have 300 observations.Bank assets for the bank volume and return on average equity (ROE) and return on average total assets (ROA) are used as bank measures. Equity to total assets ratio is used for the equity structure of the banks. To have a high ratio means that capital adequacy of a bank is high. The overhead costs to net income is the control variable of profitability. When the ratio gets higher the profitability will go down. Recurring earning power ratio is calculated by subtracting unstable earning from net income and tax and then divided by the total assets. As unstable extraordinary income is taken into consideration.In addition, as the reflection of macroeconomic changes, growth rate to real GDP, inflation rate in terms of price index and the concentration in the banking system are used. The concentration ratio is calculated by dividing total assets of five banks into total assets.
4. Empirical Results
- The summary of descriptive statistics is given in Table 1. In Table 2, the correlations are presented that are used in the model. When the correlations of explanatory variables are analyzed, it is observed there is a low multicolinearity problem.
|
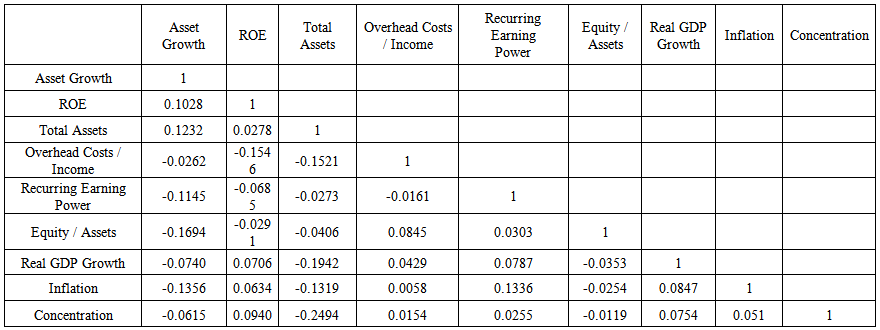 | Table 2. Correlation Matrix |
|
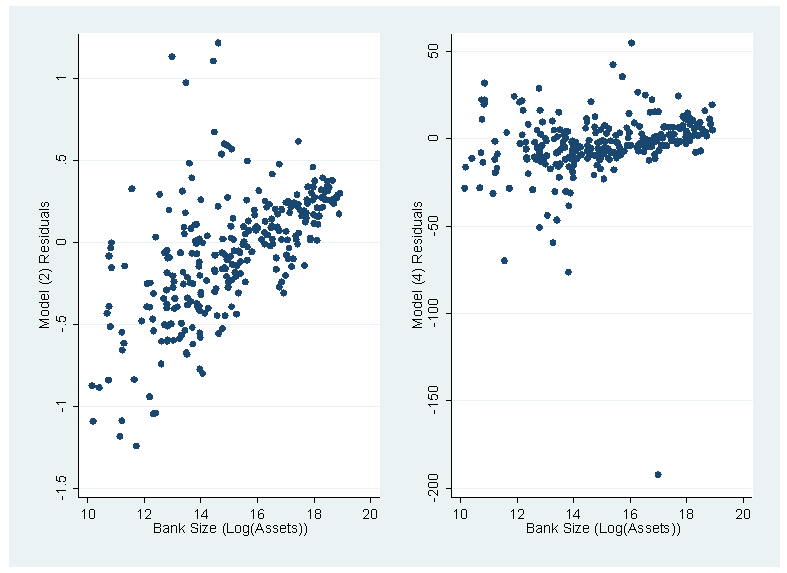 | Figure 1. Residual Plots of Significant Models against Bank Size |
5. Conclusions
- In this study, as an emerging economy, the Turkish Bank`s persistence of growth and profitability is analysed. The models that are developed by Goddard et al [4, 5] and Shehzad et al. [9, 15] are used and two different dynamic panel data models are estimated. Although alternative estimation methods that are used are significant, the model`s significance is different from each other. The models that are developed by Arellano-Bover [23] and Blundell and Bond [22] indicate better results for he dynamic panel data models than Arellano and Bond [21]. The close parameter values are considered to be due to the added new variables to the analysis rather than the methodology used before. There is a need for further analysis for this issue to come up with a judgement.Generally, the results in this study are close to the results of Shehzad et al. [9, 15]. The results of analysis indicate that in Turkey, there is persistence of bank profits thus at a low level. This result is consistent with the results of other empirical studies done on Turkey and on other developing countries. On the other hand, the persistence of growth is found as negative. The reason of this result is seen in the growth trend. That is to say, the banks that had a growing trend in the past may stop their growth in current period indicating that the profitable banks do not have a motive to grow. As there is no other investigation on the persistence of growth of banks and it is not possible to make a comparative analysis. However, the results indicate that large-sized banks compared to small-sized ones are growing at a lower speed supporting our finding that there is a negative persistence of growth.In this study, bank size and growth and also growth and profitability interactions are analysed. It can be said that between bank size and such variables there is no significant correlation. Moreover, the effect of concentration in the banking sector on growth and profitability is analysed and it is found that concentration had a positive effect on both growth and profitability.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML