Shazmin Shareena Ab. Azis , Ibrahim Sipan , Maimunah Sapri
Faculty of Geoinfomation and Real Estate, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Skudai, 81200, Malaysia
Correspondence to: Shazmin Shareena Ab. Azis , Faculty of Geoinfomation and Real Estate, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Skudai, 81200, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Abstract
Green building concepts are widely accepted and practiced worldwide. The aim of green building is to reduce building impact on environment and human health and in a meantime conserve natural resources. Many initiatives have been carried out in order to support green building development. Many incentives has been offered and provided as a means to support the development of green buildings in Malaysia. The participation of local authority in supporting green buildings is very sound. As an initiative, the local authority can participate in green building by providing property tax incentives on green building within their jurisdiction area. United Stated has applied and implemented property tax incentives on green buildings earlier since year 1975. There are 3 types of model that have been applied in 44 counties in US which are property tax exemption, property tax reduction and property tax credit. Nevertheless, each of these models was developed according to LEED’s green criteria. Whereby Malaysia are using GBI green criteria as listed in GBI’s Malaysia. Therefore, this paper focus on entitle technology or component on each LEED’S green criteria that been used in property tax incentives in order to establish property tax incentives according to GBI on green buildings in Malaysia. This is essential in order to explore the potential of property tax incentives on green building to be implementing in Malaysia.
Keywords:
Property Tax Incentives, Green Building, Green Building Criteria, Green Component
Cite this paper: Shazmin Shareena Ab. Azis , Ibrahim Sipan , Maimunah Sapri , The Potential of Implementing Property Tax Incentives on Green Building in Malaysia, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 3 No. 2, 2013, pp. 63-67. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20130302.01.
1. Introduction
The growths of technology have developed extremely over decade ago. Consequently, the growth of technology has led to the extreme exploitations of natural resources and cause damage to the environment. Between 2009 and 2030, the global primary energy consumption is expected to increase by 1.6% annually[3]. It also leads to the environmental issues such as pollution which consequently effect human health and well being. In order to address the global environmental issues, real estate development has move towards sustainable development which focuses on three elements which are social, economic and environmental[1]. Green or sustainable buildings are all revolve around the same function[6]. Green building concept has been widely practice around the globe particularly in well developed countries such as United State and Europe. The Urban Land Institutes (2005) defined green building as practice of increasing the efficiency with which the building use resources while reducing building impact on human health and the environment during the building lifecycle, through better sitting, design, construction, operation, maintenance and removal. The definition of green building is in line with it aims to reduce the impact of building on environment and generate a healthier space in which to live and work[10].On April 2009, Malaysia has launched a green building rating tool that was recognized as Green Building Index (GBI)[7]. All level of government institution channelling their support toward green buildings by providing numerous types of incentives and policy enforcement. Unfortunately, to date, there are no records available on incentives provided by the local authority in Malaysia regarding green development. This is reversed from other local governments in developed countries which already have provided various incentives on green development at local level. Local authority has been recognised as the agent to promote sustainable development at local level in Local Agenda 21 (Ministry Of Housing and Local Government Malaysia). Each property including green building which within local authority administration area is imposed with property tax assessment as property tax yield is the main source of income for local authority. Property tax can be referred as rates collected by local authorities to cover expenses for services and development. The imposition of property tax is related to the role of local authorities in developing the area and providing the necessary services and facilities[9]. Reference[2] found from their research which conducted at United State and Europe that in terms of monetary incentives provided at the local level, property tax incentives in terms of reduction was discovered as the most offered and utilized in energy efficiency sector. Based on literature reviews, it showed that there are three types of models that have been formulated for property tax incentives. These models have been adopted widely in United Stated and United Kingdom. These models developed according to green criterion as listed in the country’s green rating tool.Therefore, the aim of this research is to explore the potential of property tax incentives on green building to be implementing in Malaysia. Thus, this paper provides analysis on entitle technology or component on each LEED’S green criteria that been used in property tax incentives in order to establish property tax incentives on green buildings in Malaysia.
2. Green Building Rating Tools
Green building rating tools were believed to be able to assist architects, builders, government bodies, building owners, developers and end users to understand the impact of each design choice and solution to the environment[11]. Each country developed their own green rating tools according to their own climate, environmental and developmental context, cultural and social needs. The aims of green rating tools are to enhance the environmental awareness in building practice and providing direction or guideline for the building industry toward achievement of sustainability in building development. Reference[4] added that the adoption of green building rating tools has lead in creating green market demand and increase public awareness and perception towards the quality of green building.There are several types of green rating tools which are identify as BREEM, LEED, GreenStar, GreenMark,GBI and many more. For the purpose of this research, comparison is highlighted between LEED and GBI rating tools.
2.1. LEED Green Rating Tool
In year 1993, United Stated Green building Council (USBG) developed their own green rating tools called LEED which stands for Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design. There are six criteria listed in LEED rating tools which are sustainable site, water efficiency, energy and atmosphere; material and resources; indoor environment quality, innovation and design/construction process[8].
2.2. Green building Index (GBI) Malaysia
Green Building Index (GBI) is recognized as green building rating tools in Malaysia. It was first launched in 2009 at the Garden Design Forum held at Kuala Lumpur Convention Centre. GBI is developed by the Malaysia Institute of Architect (PAM) and Association of Consulting Engineer of Malaysia (ACEM).There are six (6) key criteria recognized in the GBI namely energy efficiency (EE), water efficiency (WE), sustainable site planning and management (SM), indoor environment quality (EQ), materials and resources (MR), and innovation (IN)[7].Table 1.0 below summarized the green criteria as listed in LEED US and GBI Malaysia.| Table 1. LEED and GBI green criteria |
| | RATING TOOLS | LEED(United State) | GBI(Malaysia) | | GREENCRITERIA | Energy and atmosphere | Energy efficiency | | Water efficiency | Water efficiency | | Sustainable sites | Sustainable site planning and management | | Material and resources | Material and resources | | Indoor environment quality | Indoor environment quality | | Innovation | Innovation | | SOURCE | http://www.usgbc.org/LEED | http://www.greenbuildingindex.org |
|
|
3. Property Tax Incentives Models
Based on data collected from Database of State Incentives for Renewable and Efficiency (DSIRE) by North Carolina State University[5], stated that there are 3 types of property tax incentives that being utilized in the United State namely property tax exemption, property tax reduction and property tax creditFrom the database, it was found that each certified green buildings are eligible for property tax incentives based on the green elements that installed or attached to the property. In other words, property tax incentives were given according to the types of green element found on the building. These green elements that eligible for property tax incentives have to be the same element as listed in the green building criteria in green rating tools. As for in United State, they utilized LEED as green rating tool, it comprises 6 green criteria which are energy and atmosphere, water efficiency, sustainable sites, material and resources, indoor environment quality and innovation. Property tax incentives are provided to all types of green properties such as residential, commercial, industrial, agricultural and utilities. From the database, it can be summarized that there are 44 counties or states in United States that provided property tax incentives on green properties. There are 26 counties/states that provided property tax exemption, 14 counties/states provided property tax reduction, and 8 counties/states provided property tax credit. The database also recorded that there are three bases in calculating formula for property tax incentives models as been practice in US which are:a. Property tax exemptionGreen elements installed or attached to a property are considered to add no value to the property. In other words, the exemption is given on the value of green elements installed or attached to the property but not on the existing property building. A green property is assessed as a conventional property / non green property.b. Property tax reduction:Green elements installed or attached to a property are given several percentages of discounts on value.c. Property tax credit: Property tax credit is cash money given back to green property owner depends on the level of certification of the green building achieved. The amount is varies depending on different percentages allocated for each level of certification achieved. The tax credit is given within a period of time. * Property tax assessed x discount based on green building level achieved.
4. Methodology
4.1. Data Collection and Analysis Method
The data collection for this paper is a combination of qualitative and quantitative study. The secondary data is gathered using literature reviews. The literatures reviews of secondary data have been used to get an overview of the research fields which is on property tax incentives and green buildings. Most of them originate from scientific articles, reports and databases. The collected literatures are limited to the most relevant articles or study on green building incentives and green building rating tools. Content analysis is used as a method to analyse the collected literatures. Then, the collected data being analyse quantitatively using frequency analysis to obtain the result in order to serve the objectives of the research.
4.2. Conceptual Framework
Figure 1.0 below provides the conceptual framework for this paper.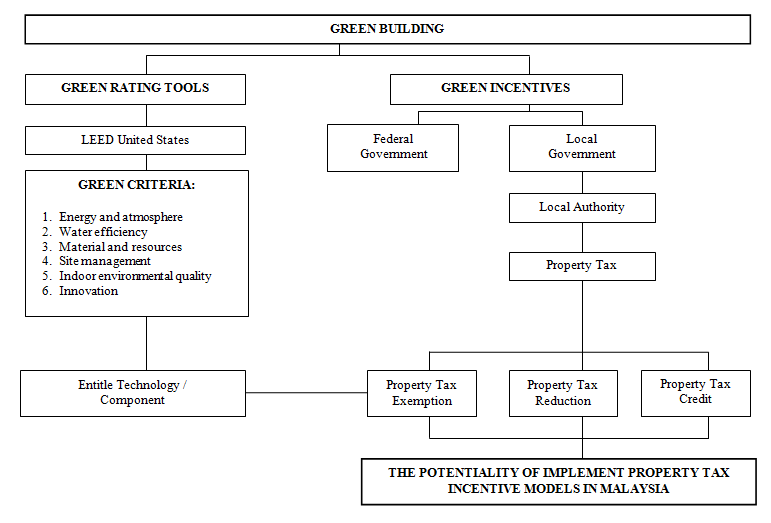 | Figure 1. Conceptual research framework |
5. Result and Discussion
There are 44 counties/ states in US that provide incentives on property tax for green building. There are three types of tax incentives provided for green building which are property tax exemption, property tax reduction and property tax credit. Table 2.0 explains the numbers of counties/states in US that provides types of property tax incentives accordingly.| Table 2. Type of property tax incentives utilized by state in US |
| | TYPES OF PROPERTY TAX INCENTIVE | NO. OF STATES/COUNTIES | | Property Tax Exemption | 26 | | Property Tax Reduction | 14 | | Property Tax Credit | 9 |
|
|
Table 2.0 shows that property tax exemption is the most popular type of property tax incentives that being provided in US on green buildings. It followed by property tax reduction and property tax credit respectively.
5.1. Summarization of LEED Green Criteria according to Types of Property Tax Incentives
Below is the summarization of types of property tax incentives as provided based on each green criteria. These green criteria are based on LEED green rating tool.| Table 3. No. of US counties that provides types of property tax incentives according to LEED green criteria |
| | LEED GREENCRITERIA | Property tax exemption | Property tax reduction | Property tax credit | Total LEED criteria applied by all models | | Energy & Atmosphere | 25 | 14 | 8 | 47 | | Water Efficiency | 24 | 12 | 8 | 44 | | Material & Resources | 15 | 11 | 5 | 31 | | Innovation | 3 | 8 | 4 | 15 | | Indoor Environment Quality | 3 | 6 | 4 | 13 | | Sustainable Sites | 2 | 6 | 4 | 12 |
|
|
Generally, the table 3.0 above ranks that energy and atmosphere, water efficiency, and material and resources are the most popular green element that are given incentives by all three types of property tax incentives models in US. Then, it followed by innovation, indoor environment quality and sustainable sites respectively. There are about 26 counties in US that offered property tax exemption as an incentive for green buildings. The graph explains that energy and atmosphere, and water efficiency are the most popular green criteria that are given property tax exemption incentives by most of the counties in US. Meanwhile the least popular green criteria that are exempted from property tax are material and resources, indoor environment quality, innovation and sustainable site respectively. Furthermore, there are 14 counties in US that offered property tax reduction on green buildings. For incentive as in reduction in property taxation, green criteria that most prevalently given incentives are energy and atmosphere, water efficiency, and material and resources. On the other hand, sustainable sites and indoor environment quality are the least types of green criteria that given incentives. In addition, 9 counties in US are recorded to provide property tax credit as incentives for green buildings. Table 3.0 demonstrates that all the counties provide property tax credit on green building that consists with energy and atmosphere, and water efficiency. For that reason, this result implies that these three types of green criteria which are energy and atmosphere, water efficiency, and material and resources are important and significant with green building concept. For that reason, these three green elements should be taken into consideration in developing property tax incentives model for green building in Malaysia. Nevertheless, other green elements such as sustainable sites, innovation and indoor environment quality also play important part in green buildings since all of the green criteria are listed as incentives for green building. Hence, they also should be taken into consideration in developing property tax incentives in Malaysia.
5.2. Analysis on Types of Entitle Technology/Component for each LEED Green Criteria that Applicable for Property Tax Incentives
This section provides the details on eligible technology/component according to LEED green criteria that are applied to the property tax incentives models in US.Table 4. Entitle technology/component based on Water Efficiency
 |
| |
|
Tables 4.0 until 9.0 have listed types of entitle technology or green component that applied to property tax incentives according to LEED criteria. This result can be applied as strategies to develop property tax incentives models in Malaysia. Therefore, it signify that there are a potential for Malaysia to succeed in developing own property tax incentives model on green building according to GBI green criteria. Furthermore, developing a model for property tax incentives in Malaysia is an advantage since LEED green criteria are identical with GBI green criteria. Thus, it enlightens the potential of property tax incentive to be implementing in Malaysia in order to support the growth of green building development.Table 5. Entitle technology/component based on Energy and Atmosphere
 |
| |
|
Table 6. Entitle technology/component based on Material and Resources
 |
| |
|
| Table 7. Entitle technology/component based on Sustainable Sites |
| | Leed Green Criteria | Entitled Technology/Component | | Sustainable sites | Comprehensive Measures/Whole Building. |
|
|
Table 8. Entitle technology/component based on Indoor Environmental Quality
 |
| |
|
| Table 9. Entitle technology/component based on Innovation |
| | Leed Green Criteria | Entitled Technology/Component | | Innovation | Comprehensive Measures/Whole Building. |
|
|
5. Conclusions
In a nutshell, property tax incentives can become an initiative for the local government to take part in supporting green building development in Malaysia. The successfulness of property tax incentives models in US has given the opportunity for Malaysia to take the same effort. It is an advantage for Malaysia to develop property tax incentives models as been applied in US due to the similarity in the green criteria as listed in both rating tools. Therefore, these incentives should become one of the efforts for encouraging the growth of green building development in Malaysia.
References
| [1] | Campbell S., “Green Cities, Growing Cities, Just Cities: Urban Planning and the Contradictions of Sustainable Development”, Journal of American Planning Association , pp.296-312,1996. |
| [2] | Clement, David et al., “International Tax Incentives for Renewable Energy: Lessons for Public Policy”, Center for Resource Solutions, San Francisco, 2005. |
| [3] | Chua S.C and Oh T.H., “Green Progress and Prospect in Malaysia”, Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy Review, vol.15, pp. 2850-2861, 2011. |
| [4] | Cole, R.J., “Building Environmental Assessment Methods: Redefining Intentions and Roles”, Journal of Building Research & Information, vol. 33, Issue 5, pp. 455-467, 2005. |
| [5] | Database of State Incentives for renewable & Efficiency, DSIRE, North Carolina State University, 2009. |
| [6] | Esa M.R et al., “Obstacles in Implementing Green Building Project in Malaysia”, Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, vol.5, no.12, pp.1806-1812, 2011. |
| [7] | Online Available: http://www.greenbuildingindex.org. Green Building Index. (2011) |
| [8] | Online Available: http://www.usgbc.org/LEED. Homepages of LEED, 2008. |
| [9] | Pawi S., Juanil D. M., Yusoff W. Z., “Property Tax Management Model of Local Authorities in Malaysia”, Proceeding of the International Conference on Social Science, Economics and Art, pp.124-130, 2011. |
| [10] | Pitts J. and Jackson T.O., “Green Building: Valuation Issues and Perspectives”, the Appraisal Journal, vol.76, no.2, pp. 115-118, 2008. |
| [11] | Tan L.M., “The Development Of GBI Malaysia”, Green Building Index, Malaysia, 2009. |


 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML


