-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2013; 3(1): 27-31
doi:10.5923/j.economics.20130301.06
Factors that Affect Accounting Information System Implementation and Accounting Information Quality: A Survey in University Utara Malaysia
Ahmad Al-Hiyari 1, Mohammed Hamood Hamood AL-Mashre 1, Nik Kamariah Nik Mat 2, Jamal Mohammedesmail alekam 1, 3
1Othman Yeop Abdullah Graduate School of College of Business, Universiti Utara Malaysia
2Othman Yeop Abdullah Graduate School of Business University Utara Malaysia
3GTA graduate teaching assistance, Scholl of business management
Correspondence to: Jamal Mohammedesmail alekam , Othman Yeop Abdullah Graduate School of College of Business, Universiti Utara Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The purpose of this study is to investigate factors that affect accounting information system implementation and accounting information quality from Universiti Utara Malaysia student’s points of view. It examines the effect of human resources, data quality and management commitment on accounting information system and information quality. A survey of 119 respondents is selected to gather information’s to test the study hypotheses. The main findings indicate that there is significant relationship between management commitments, data quality and accounting information system. However, the relation is not significantly related to human resources. Furthermore, the relation between management commitment and data quality are not significantly related to accounting information quality but significantly related to accounting information system and human resources. The study recommends that comprehensive training programmes to get the sufficient knowledge in accounting information system implementation and the importance of data quality, furthermore, top management should support AIS implementation to get full benefit of accounting information system.
Keywords: Accounting Information System (AIS), data quality (DQ), information quality, management commitment, human resources
Cite this paper: Ahmad Al-Hiyari , Mohammed Hamood Hamood AL-Mashre , Nik Kamariah Nik Mat , Jamal Mohammedesmail alekam , Factors that Affect Accounting Information System Implementation and Accounting Information Quality: A Survey in University Utara Malaysia, American Journal of Economics, Vol. 3 No. 1, 2013, pp. 27-31. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20130301.06.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In recent years, accounting information system received a lot of attention, it facilities managers to take appropriate actions related to issues in organization, if AIS output is not accurate management will take wrong decisions, moreover, it considered competitive advantage for organization with well design accounting information system. Failure to implement well accounting information system will have adverse affects on organization success (Salehi and Abdipour, 2011). This study has focused on the perception of students about the factors that contributes to implementation of accounting information system and information quality.The structure of this article is as follows: Section 2 reviews the relevant literature and hypothesis development. Section 3 describes the study methodology. Section 4 present results from the statistical analyses of hypotheses. Finally, section 5 presents the discussion and conclusion of this study, provides the limitations of the current study, and points out some directions for further research.
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
2.1. Human Resources
- (Barney and Wright, 1998) indicate that human resources are most likely to be sources of sustained competitive advantage of originations, also according to (Luna-Arocas and Camps, 2012) human resources affect organization performance. However, they are also main part of accounting information system as they are involved in data entry, processing, and output. Recent research provide evidence that human resources consider important part in success of accounting information system, for instance, (ALshbiel and Al-Awaqleh, 2011) point out that there is a positive relation between human resource, and implementation of the accounting information system in the hospitals in Jordan, they suggest that Training employees to use the accounting information system is an important issue to implement successful accounting information system. furthermore, (Zhou, 2010) indicates that the quality of accounting personals are important in implementing AIS. (Teo. Wong, 1998) found that there is positive relation between information quality and perceptions of the work environment.The above discussion results in the following hypothesis:H1: there is significant relationship between Human recourses and Accounting information system.H2: there is significant relationship between human recourse and accounting information quality.
2.2. Management Commitment
- According to (Cooper, 2006) management commitment is “engaging in and maintaining behaviors that others achieve the goals.” As the management commitment increase accounting information system effectiveness improve, Thong, et al. (1996) argue that if there is low level of top management support then top management may not involved in aspects of IS implementation such as (re- view of consultant's recommendations, participate indecision-making, or monitor the project) except approving the purchase of computer system, they found that management commitment increase the effectiveness of information system because they provide the resources needed for IS projects. (Rahayu, 2012) examined the influence of management commitment on data quality and AIS, he find that management commitment and quality of data together have adequate effects on the Accounting Information System, although the contribution of management commitment to data quality need to be improved, also he find lack of top management adequacy for training and funding for resources development. The above discussion results in the following hypothesis: H3: there is significant relationship between management commitment and accounting information system.H4: there is significant relationship between management commitment and accounting information quality.
2.3. Accounting Information System
- According to Grande, et al. (2011) AIS is defined as “tool which, when incorporated into the field of Information and Technology systems (IT), were designed to help in the management and control of topics related to firms’ economic-financial area”. The resulting statistical reports can be used internally by management or externally by other interested parties including investors, creditors and tax authorities. (Sajady et al. (2008) states that effective accounting information system will enhance financial statement quality. The above discussion results in the following hypothesis: H5: there is significant relationship between accounting information system and quality of accounting information
2.4. Data Quality
- All data production process (data collection, data storage, and data utilization) must work properly in order to achieve high data quality (Lee and Strong, 2003). (Xu, 2009) investigate the factors that influence DQ, they found that input control and competent employees are important to DQ of accounting information system. Inaccurate and incomplete data may damage competitiveness of firms (Redman 1992), IAS output depends on the quality of data, garbage in garbage out is result of poor data quality, and therefore, data quality is important to AIS (Xu. 2003)H6: there is significant relationship between Data quality and accounting information systemH7: there is significant relationship between Data quality and accounting information quality
2.5. Accounting Information Quality
- Poor information quality may have adverse effects on decision making (Huang, Lee and Wang 1999), for example, (Bowen, 1993) indicate that error in inventory database may cause to take wrong decision by managers, resulting in over-tock or under-stock which had severe impact on company profitability and customer satisfaction. Quality of accounting information can be evaluated by four attribute Accuracy, timeliness, completeness and consistency (Xu, 2003), they examined critical success factors for accounting information quality, they identified and interviewed four groups namely (information producers, information custodians, information consumers and information managers), they suggest that organization issue, system and human issue is important to accounting information quality.
3. The Study Methodology
- This part explains and evaluates the research methods which are employed in this study. In addition, it describes the population of the study and its main contents, the sample of the study and its data sources, procedures that will be adopted to gather and analysis of data, and testing of the study hypotheses. Universiti Utara Malaysia (UUM) has been selected as the study population for its importance in the society and its role to disseminate knowledge; therefore, it is important to understand the opinion of students in factors that affect accounting information system and information quality. Questionnaires are sent to different levels of students (Diploma, Bachelor, Master and PHD students). The questionnaire questions have been developed based upon literature review. Five Likert scale was used to score the responses.
4. Data Analysis and Hypothesis Testing
- The questionnaire is used as data collection instrument. two hundred questionnaires are distributed to students in Universiti Utara Malaysia. Only 119 questionnaires are retuned and four questionnaires deleted due to outliers. The response rate is 59.5%.To ensure the questionnaire reliability, Cronbach’s alpha is used as a measure of internal consistency of the questionnaire. A widely cited minimum threshold for the Crobanch Alpha is 0.70 . However, Cronbach’s Alpha was calculated for this study which was 97.1%.
4.1. Social Demography
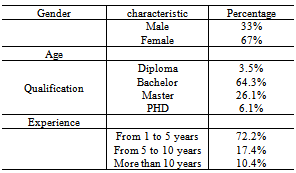
- As shown in Table 1, the major characteristics of the questionnaire respondents are presented in terms of gender, educational level and years of experience. In term of gender, the study respondents can be classified into 33 % as male and 67% as female. The majority of participants are a bachelor degree (64.3%). Finally, regarding to experience years, most of respondents have 1 – 5 years experience (72.2%).
|
4.2. Hypothesis Results
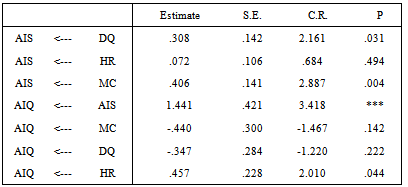
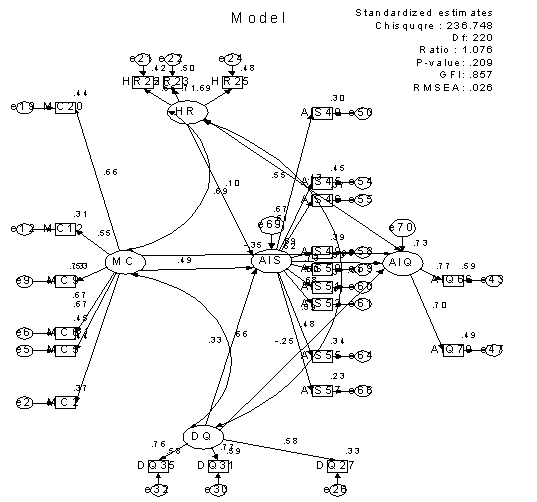
- As a final point, the revised model was achieved and gathering all requirements and possessed adequate goodness of fit with values for ratio as 1.076, P-Value as .209, GFI as .857 and RMSEA as .026, as you see in revise model. Although seven hypotheses were proposed, the estimated model supported only four. Significant support was found for hypotheses H2 (B=.457, P=.044, CR=2.010), H3 (B=.406, P=.004, CR=2.887), H5 (B=.1.441, P=.0, CR=3.418), H6 (B=.308, P=.031, CR=2.161). See (Table 2) and revise model in appendix
5. Discussion and Conclusion and Future Research
- The study focus on the perception of Utara Universiti Malaysia students about factors that affect Accounting information system implementation and information quality, the results indicate that there is significant relationship between management commitment, data quality and accounting information system implementation. However, the relation is not significantly related to human resources, also the study found that there is significant relationship between human resources, accounting information system and accounting information quality. Moreover, the relationship between management commitment, data quality are not significantly related to accounting information quality, consistent with (Rahaya, 2012) and (ALshbiel and Al-Awaqleh, 2011). The study surprising result is the non significant relation between data quality and accounting information quality, perhaps they perceived that even highly quality accounting data may manipulated by management consistent with prior studies about earning management (Eng and Lin , 2012).The study recommends that management commitment should support accounting information system implementation and ensuring adequate resources and comprehensive training to accountants. Moreover, effective corporate governance could increase the quality of accounting information. however, the study was limited to students at University Utara Malaysia. Future research can extend the proposed factors. Moreover, the qualitative evidence can be used to improve the quantitative approach in the real context.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML