-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2012; 2(6): 122-127
doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20120206.05
Defense Spending and Poverty Reduction in Nigeria
Olabode Philip Olofin
Department of Economics, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Osun-state, Nigeria., 220005, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Olabode Philip Olofin , Department of Economics, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Osun-state, Nigeria., 220005, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This study examines the relationship between the components of defense spending and poverty reduction in Nigeria for the period 1990-2010. While most studies on defense spending and poverty rely on monetary measure of poverty, this study constructed poverty index from human development indicators using principal component analysis. Four models were estimated using Dynamic Ordinary Least Square (DOLS) method, two in which poverty index constructed from human development indicators serves as dependent variable and the others in which infant mortality rate serves as dependent variable. The results show that military expenditure per soldier, military participation rate, trade, population and output per capita square were positively related to poverty indicator. They were all found to be statistically significant except trade and output per capita square. Population that was not significant in model four was found to be significant in model two. Military expenditure, secondary school enrolment and output per capita were negatively related to poverty level. However, only total military expenditure was found to be statistically significant in model one and three, while output per capita in model three was found to be statistically significant. Others were statistically insignificant. The findings confirm the trade off between the well-being and capital intensiveness of the military in Nigeria, pointing to the vulnerability of the poor among the Nigerians.
Keywords: Internal Security Threat, Defense Spending, Poverty, Principal Component Analysis, Nigeria
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Recent increase in defense spending in Nigeria due to increase in internal resistance and threat is an issue of concern to many Nigerians and other stakeholders in the Nigerian economy. Presently, internal resistance and threat especially that of the increasingly violent Islamist sect, known as Boko Haram is forcing increasing financial cost on government’s expenditure towards defense sector. According to[1], the military expenditure (% of GDP) in Nigeria in 2008 was 0.78, in 2009, it was 0.89 and in 2010, it stood at 1.00. Nigeria’s security bills have risen to 20 percent of spending in the budget from 16 percent in 2010. This has led to diversion of the money needed for infrastructure projects and work on reforms of social and industrial sectors (see[2]). Spending on power infrastructure, education and healthcare combined receive smaller allocation compared to security in the 2012 budget allocation. Also, the direct cost of security is at least 2 percent of Nigeria’s $250 billion economy, measured by the share of spending-to-Gross Domestic Product in 2012 ([2]). This diversion of funds has economic implication since some social sectors are likely to suffer in Nigeria especially at this crucial moment of striving to achieve povertyreduction, and minimum levels of per capita income. Increased spending on military has been associated with reduction in well-being ([3]). This view has been expressed by the UN Committee for Development Planning, which states that: “The single and most massive obstacle to development is the worldwide expenditure on national defense activity” ([4]). A joint study analysis of the research departments of the World Bank and International Monetary Fund (IMF) also noted that, for an average country, doubling military expenditure caused reduction in growth rate for a period, and later reduced the level of income of 20 percent (see[5]). These adverse effects of increased defense spending in a developing country like Nigeria is likely to exacerbate the existed poverty since almost all the military hardwares are imported.While a number of studies focus on the relation between defense spending and economic growth, few studies the impact of defense spending on poverty especially in developing countries. Exception to this is[6], who use a cross-national panel models to examine the impact of disaggregated components of defense spending on the well-being of 82 developed and less developed countries. Also, most of the studies that examine the relation between defense spending and poverty are either cross countries or panel data analysis. Majority of the studies that examine individual countries focus on United States military (see[6]). However, the importance of country-specific analysis on the relation between defense spending and well-being has been advocated (see[7]). To the best of my knowledge, no study has empirically examined the impact of the component of defense spending on poverty level in Nigeria. More so, with the exception of[6], most studies that examine the impact of military spending on well-being failed to consider the disaggregated impact of military spending on poverty and this aspect has been pointed out to be essential when analyzing the impact of military spending on poverty (see[8]). Besides, most studies on defense-poverty relation, including[6] who use household income inequality rely on monetary measure of poverty. In recent time, it has been argued that poverty is multifaceted and using multiple index to capture it complements the income-based poverty measures by reflecting the multiple deprivations that people face at the same time[9]. Thus, this study intends to fill these gaps by examining the impact of disaggregating military expenditure (i.e. military expenditure per soldier, military expenditure as a percentage of GDP and military participation rate) and some other explanatory variables on poverty level (proxied by human development indicators and mortality rate) in Nigeria. The economic impact of defense expenditure in less developed countries (LDCs) has being a subject of extensive debate since the seminar work of[10]. A large number of studies have examined the impact of defense spending on economic growth and results have been inconclusive or mixed. Some studies argued that defense spending may hinder economic growth through its investment “crowding-out” effect([11]);[12];[13];[14];[15];[16]), or displacement of an equal amount of civilian resource use. They explained that during economic down-turns where unemployment increases, more people join the armed forces and this increases military personnel spending but reducing poverty. However, it has been noted that procurement and research and development will probably have marginal labor impacts on the poor if they are channelled to high skilled, high tech labor sectors. Therefore, spending on these components should tend to increase inequality[15]. Other studies also claimed that defense spending may spur growth through Keynesian-type aggregate demand effects. They argue that, increased defense spending can create increased employment and this is likely to reduce poverty through higher investment, which will further accelerate short-run multiplier effects ([17];[18];[19]). In addition, economic growth may stimulate spin-off effect such as the creation of some socio-economic structures that are germane to economic growth[20];[21]. Many studies have also found no consistent, statistically significant connection between military spending and economic growth ([22];[23]). In the study of[24], negative relationship between military expenditure and under-five child mortality was found in countries without armed conflict in contrast with those in active conflicts. The study also noted positive relationship between military participation and child mortality in countries without conflicts and negative relationship in countries with armed conflicts. Recently, the study by[9] has noted that states with high levels of defense spending have lower poverty rates, less income inequality, lower unemployment and higher median family income. This study also showed that the U.S. economy is increasingly dependent on military spending. Thus, the issue of defense spending and poverty level is still empty of empirical generality. The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 discusses the computation of principal component analysis (PCA), ordinary least square models, sources of data and measurement of variables. Section 3 discusses the results and also presents the results of PCA and ordinary least square; while section 4 concludes with some recommendations.
2. Methodology
2.1. Computation of a Poverty Index using Principal Components Analysis
- To measure poverty among Nigerians, I create a poverty index by applying PCA to human development indicators (i.e. longevity, measured by life expectancy at birth which captures the capability of leading a long and healthy life; rural development measured by per worker agricultural value added; real per capita income; and consumption per capita which represents access to resources needed for a decent standard of living) (see[26];[27] and[28]). These human development indicators were obtained from United Nations Statistical Millennium Development Indicators. I also use infant mortality rate that captures the aspect of material hardship of poverty as a dependent variable.The PCA is a multivariate statistical method used to reduce the number of variables without losing too much information. It is efficient in generating fewer numbers of variables that explain most of the variation in the original variables. While the new variables generated are linear combinations of the original variables, the first new variables will account for as much as possible of the variation in the original data.Suppose
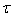 variables
variables 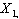 . . . ,
. . . , 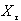 , measured in n human development indicators, the
, measured in n human development indicators, the 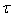 principal components
principal components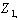 . . .
. . . 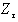 are uncorrelated linear combinations of the original variables,
are uncorrelated linear combinations of the original variables, 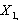 . . . ,
. . . , 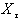 , given as :
, given as :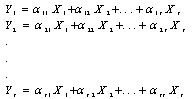 This system of equation can be written as z = A×, where
This system of equation can be written as z = A×, where 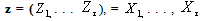 and A is the matrix of coefficients.The coefficient of the first PCA,
and A is the matrix of coefficients.The coefficient of the first PCA, 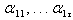 are chosen in such a way that the variance of
are chosen in such a way that the variance of 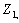 is maximized subject to the constraint that
is maximized subject to the constraint that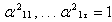 . The variance of the component is equal to
. The variance of the component is equal to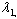 which is the largest eigenvalue of A. The second principal component is totally uncorrelated with the first component and its variance is equal to
which is the largest eigenvalue of A. The second principal component is totally uncorrelated with the first component and its variance is equal to 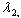 which is also the largest value of A. This component explains additional but less variation in the original variable than the first component given the same constraint. Other principal components (up to
which is also the largest value of A. This component explains additional but less variation in the original variable than the first component given the same constraint. Other principal components (up to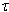 ) are explained in the same manner. The squares of the coefficients of principal components sum to one and each is uncorrelated with one another.
) are explained in the same manner. The squares of the coefficients of principal components sum to one and each is uncorrelated with one another. 2.2. Dynamic Ordinary Least Square Models
- Four models were estimated in the study, two in which poverty index created from principal component analysis serves as dependent variable and the others in which infant mortality rate serves as dependent variable. I include military expenditure in the first model without its square and the square of military expenditure without military expenditure in the second model. This was also done for the other two models to avoid multi-collinearity. Following[29] specification of poverty model, I try to answer the following question: does spending on defense components reduce infant mortality and poverty? I examine this question by estimating variants of the following models:
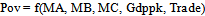 | (1) |
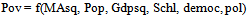 | (2) |
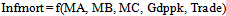 | (3) |
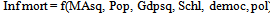 | (4) |
2.3. Data Sources
- Since military personnel’s spending can be the strongest candidate for poverty reduction because its impact is felt disproportionately on the less skilled sectors of the labor force; and coupled with the recent literatures that support disaggregating military expenditure into materials and personnel expenditures (see[29];[30];[6]). I follow[6] and use annual data on military expenditure per soldier to capture the capital-intensiveness of the military, (this was calculated by dividing total military expenditure by total military personnel), military expenditures as percentage of GDP and military participation rate calculated as the ratio of the number of military personnel per 1000 population. These data were obtained from[31]. Data on other variables were obtained from[1]. To measure the level of economic development, I use output per capita in constant 2000 US dollars. All these variables were logged to ensure their coefficients are constant elasticity measures. Following the study of[32], in which a panel data was used to search for the existence of Environmental Kuznet curve (EKC) in the environmental efficiency of human well-being and that of[6] which account for a potential Kuznets distribution in his study on military spending and human well-being, I include the centered quadratic[33];[7];[34] for GDP per capita and military expenditure per soldier in my models. To control for world-economic integration, I include trade as a percentage of GDP. The data was calculated as the sum of exports and imports of goods and services measured as a share of GDP. I also include annual data on political terrorism and democracy as collected from[35], a newly available and extensive dataset on civil war, terrorism, and trafficking, as well as socio-economic, demographic and political matter.
|
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Poverty Index Results
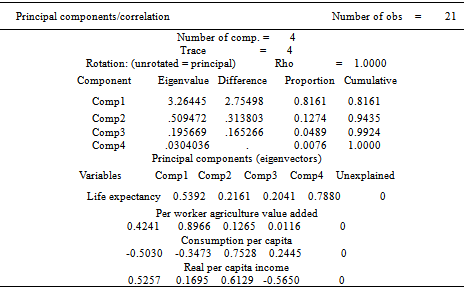
- Table 1 shows all the variables used in the construction of poverty index and the result of the PCA.The results of PCA indicate that each of the first principal components explains 81% of the variation in the original variables and each subsequent component explains a decreasing proportion of variance. The screeplot in figure 1 shows the proportion of variance explained by eachprincipal component and indicates that the first two components would sufficiently explain the original variables.
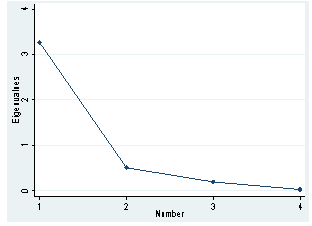 | Figure 1. Scree plot of eigenv alues after pca |
3.2. Results of Dynamic Ordinary Least Square (DOLS) Regression
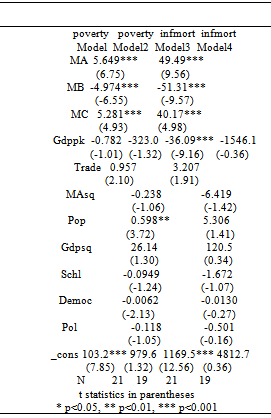
- In estimating my DOLS model, I examine the summary statistics of the data used when each of the generated poverty index and infant mortality is used as dependent variable. This is shown in Table 3 and Table 4 respectively. The results of the correlation coefficients (not presented because of space) do not seem to show any serious problem in terms of the relationship to be estimated. The DOLS results are presented in table 2 below. The findings show that, capital intensiveness of the military, that is, military expenditure per soldier, military participation rate, trade, output per capita square and increase in population were found to be positively related to poverty indicators. However, trade and output per capita square were found not to be statistically significant, while increase in population was only found to be statistically significant in model 2. This result confirms the hypothesis that increasing spending especially on capital-intensive military may not reduce poverty in Nigeria. Although, I find a positive relationship between the square of output per capita and poverty indicator in model 2 and 4; and negative relationship between the square of military expenditure per soldier and poverty indicator in model 2 and 4, but they were not statistically significant. This suggests that we cannot affirm the existence of inverted U-shape in defense spending-poverty relation in Nigeria. Total military expenditure, output per capita, secondary school enrolment, democracy and political terror were found to be negatively related to poverty indicators. They were all found to be statistically insignificant except total military expenditure. Output per capita was also found to be statistically significant in model 3. We can see this in table 2. The fact that total military expenditure is inversely related to poverty suggests that, partially, the Keynesian hypothesis of negative relation between poverty and defense spending holds. However, caution should be made when interpreting this result. For school enrolment, democracy and political terror, one would expect their relationship with poverty to be significant; nevertheless, their statistical insignificance could be due to gradual process of development.
|
|
4. Conclusions
- The objective of this article is to verify the Keynesian hypothesis of negative relation between defense spending and poverty level. For this purpose, recent studies have noted that using monetary measure such as headcount index to proxy poverty may not really capture the deficiency of the poor especially in developing countries and therefore result to spurious findings. It has been argued that possessing an increased income does not necessarily mean an improvement in the well-being of people especially if this increased income does not translate to accessibility of basic necessities of life. It was also noted that since poverty is multi-faceted, multiple indicators are necessary, including measures of distribution of real expenditure per adult, access to non market goods like health and education, distribution within households and the personalcharacteristics of the poor. On this note, the study considered the poverty among Nigerians and uses principal component analysis to create a poverty index as a dependent variable and also use infant mortality rate as second dependent variable and regressed them on some other explanatory variables. The study finds that capital intensiveness of the military and the participation rate have important implication on poverty level in Nigeria. The results show that the poor is likely to be worse off if resources are diverted to military hardwares. The study provides insight into how the components of defense spending in Nigeria impacts on poverty level. These findings rebut the Keynesian argument that defense spending is positively related to well-being. The results inform the policy makers on the necessity of weighing the cost of the so-called “classic choice of spending between guns and butter”.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- I am very grateful to Dr. Olayeni, O.R. of the Department of Economics, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife for his valuable comments to shape this work. I would also like to extend my profound appreciation to my wife for her support. My appreciation goes to the anonymous referees and the editor for time spent on this work.
References
| [1] | World Development Indicators. World Bank, Washington, DC, 2010. |
| [2] | Nigeria Politico. Boko insurgency beginning to take toll on economy; security threat dominates government’s attention, 2012. Available athttp://www.nigeriapolitico.com/tolloneconomy%20.html. |
| [3] | Collier, P. The Economics of Peace and Security Journal, ISSN 1749-852X P. Collier, War and military expenditure in developing countries p.13 © www.epsjournal.org.uk – Vol. 1, No 1, 2006. |
| [4] | Jolly, R. Disarmament and World Development. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1978. |
| [5] | Knight, M., N. Loayaza, and D. Villanueava. “Military Spending Cuts and Economic Growth.” World Bank Policy Research Working Paper 1577, 1996. Available at http://econ.worldbank.org/files/629_wps1577.pdf. |
| [6] | Kentor, J., Jorgenson, K.A., and Kick, E. The “new” military income inequality: A cross national analysis, Journal of Social Science Research, 41, 514-526, 2012. |
| [7] | Chan, S. "The Impact of Defense Spending on Economic Performance: A Survey of Evidence and Problems." Orbis 29 (2): 403-34, 1985. |
| [8] | Kentor, J., and Kick, E.L. Bringing the military back in: military expenditures and economic growth 1990-2003. Journal of World Systems Research 14, 2, 2008. |
| [9] | Alkire, S. Roche, J.M. Santos, M.E. and Seth, S. Multidimensional Poverty Index: 2011 Data. Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative, November Available at: www.ophi.org.uk/policy/multidimensional-poverty-index/, 2011. |
| [10] | Benoit, E. Defense spending and economic growth in developing countries. Lexington: Lexington Books, 1973. |
| [11] | Kaldor, M. The military in development. World Development 6, 459-482, 1976. |
| [12] | Eide, A. Arms transfer and third world militarization. Bulletin of Peace Proposals 8, 99–102, 1976. |
| [13] | Lock, P. and Wulf, H. Consequences of transfers of military-oriented technology on development in the third world. Bulletin of Peace Proposals 8 (2), 127-136, 1977. |
| [14] | Senghaas, D. Militarism dynamics in the contemporary context of peripheral capitalism. Bulletin of Peace Proposals 8, 103-109, 1977. |
| [15] | Deger, S. Economic development and defense expenditure. Economic Development and Cultural Change, 35 (1), 179–196, 1986. |
| [16] | Levy, Y. Militarizing inequality: a conceptual framework. Theory and Society. 27, 873–904, 1998. |
| [17] | Baran, P. and Sweezy, P. Monopoly Capital: An Essay on the American Economic and Social Order. Penguin, Harmondsworth, 1968. |
| [18] | Kidron, M. Western capitalism since the war. Harmondsworth: Penguin. Kleykamp, 1970. |
| [19] | Bluestone, B., Havens, J. Reducing the federal deficit fair and square. In: Paper for the Symposium of the Joint Economic Committee. The American Economy in Transition: From the Second World War to the 21st Century. US Congress, Washington, DC, 1986. |
| [20] | Deger, S. Economic development and defense expenditure. Economic Development and Cultural Change, 35 (1), 179–196, 1986. |
| [21] | Chowdhury, A. A causal analysis of defense spending and economic growth. The Journal of Conflict Resolution 35 (1), 80–97, 1991. |
| [22] | Rothschild, K. Military expenditure, export and growth. Kyklos, 26, 804–813, 1977. |
| [23] | Biswas, B. and Ram, R. Military expenditures and economic growth in less developed countries: An augmented model and further evidence. Economic Development and Cultural Change, 34(2), 361–372, 1986. |
| [24] | Carlton-Ford, S. Major armed conflicts, militarization, and life chances: a Pooled time-series analysis. Armed Forces and Society 36(5), 864-889, 2010. |
| [25] | Casey, B. and Wallace, M. Military Spending and Economic Well-Being in the American States: The Post-Vietnam War Era. Oxford journal of Social Science, Social Forces vol. 88, 4, pp. 1727-1752, 2010. |
| [26] | Masud, N. and Yontcheva, B. “Does Foreign Aid Reduce Poverty? Empirical Evidence from Nongovernmental and Bilateral Aid,” IMF Working Paper 05/100, 2005. |
| [27] | Chirino, J.B. and J.M.B. Melian. Analysis of the effectiveness of official Development Assistance”, International Research Journal of Finance and Economics, no. 3, June, 2006. |
| [28] | Morrissey, O. “Conditionality and Aid Effectiveness Reevaluated, “World Economy 27(2), 2004. |
| [29] | Clark, Brett., Jorgenson, K.A., Kentor, J. Militarisation and energy consumption: a test of treadmill of destruction theory in comparative perspective, International Journal of Sociology, 40, 23-43, 2010. |
| [30] | Jorgenson, K.A., Clark, B., Kentor, J. Militarisation and the environment: a panel study of carbon dioxide emissions and the ecological footprints of nations, 1970-2000. Global Environmental Politics 10, 7-29, 2010. |
| [31] | SIPRI – Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) Military Expenditure Database. Sweden: SIPRI, 2010. |
| [32] | Dietz, T., Rosa, E.A. and York, R. Environmentally efficient well-being: Is there a Kuznets Curve? Journal of Applied Geography, 32(2012), 21-28, 2012. |
| [33] | Neter, J, Wasserman, William, Kutner, Michael H. Applied Statistical Models, thirded. Irwin, Boston, MA, 1990. |
| [34] | Errol, A.H. Military Spending and Poverty. The Journal of Politics, Vol. 60, No 2, pp. 503-520, 1998. |
| [35] | World Development Report on Conflict, Security and Development (2011). |
| [36] | Lee, Cheol-Sung, Nielsen, Francois, Alderson, Arthur S. Income inequality, global economy and the state. Social Forces 86, 77–111, 2007. |
| [37] | Alderson, A. and Nielsen, F. Income inequality, development, and dependence: a reconsideration. American Sociological Review 64, 606–631, 1999. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML