-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2012; 2(6): 101-106
doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20120206.02
Public Debt and Economic Growth in Nigeria: Evidence from Granger Causality
Tajudeen Egbetunde
Department of Economics and Financial Studies, Fountain University, Osogbo, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Tajudeen Egbetunde , Department of Economics and Financial Studies, Fountain University, Osogbo, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The paper examined the causal nexus between public debt and economic growth in Nigeria between 1970 and 2010 using a Vector Autoregressive (VAR). The variables used in the study were tested for stationarity using the Augmented Dickey Fuller and Philip Perron test. The result showed that the variables are stationary at first differencing. Co-integration test was also performed and the result revealed the presence of co-integration between public debt and economic growth. The co-integration results show that public debt and economic growth have long run relationship. The findings of the VAR model revealed that there is a bi-directional causality between public debt and economic growth in Nigeria. The paper concluded that public debt and economic growth have long run relationship, and they are positively related if the government is sincere with the loan obtained and use it for the development of the economy rather than channel the funds to their personal benefit.
Keywords: Public Debt, Economic Growth , Nigeria
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Economic theory suggests that reasonable levels of borrowing by a developing country are likely to enhance its economic growth[19]. When economic growth is enhanced (at least more than 5% growth rate) the economy’s poverty situation is likely to be affected positively[3]. In order to encourage growth, countries at early stages of development like Nigeria borrow to augment what they have because of dominance of small stocks of capital hence they are likely to have investment opportunities with rates of return higher than that of their counterparts in developed economies. This becomes effective as long as borrowed funds and some internally ploughed back funds1 are properly utilized for productive investment, and do not suffer from macroeconomic instability, policies that distort economic incentives, or sizable adverse shocks. Growth therefore is likely to increase and allow for timely debt repayments. When this cycle is maintained for a period of time growth will affect per capita income positively which is a prerequisite for poverty reduction[3]. These predictions are known to hold even in theories based on the more realistic assumption that countries may not be able to borrow freely because of the risk of debt denial.Although the debt overhang models do not analyze the effects of debt on growth explicitly, the implication still remains that large debt stocks lower growth by partly reducing investment with a resultant negative effect on poverty. But the incentive effects associated with debt stocks tend to reduce the benefits expected from policy reforms that would enhance efficiency and growth, such as trade liberalization and fiscal adjustment. When this happens the government will be less willing to incur current costs if it perceives that the future benefit in terms of higher output will accrue partly to foreign lenders. Reference[21] contributed that government borrowing can crowd out investment, which will reduce future output and wages. When output and wages are affected the welfare of the citizens will be made vulnerable.Reference[20] opined that countries borrow for two broad categories: macroeconomic reasons[higher investment, higher consumption (education and health)] or to finance transitory balance of payments deficits[to lower nominal interest rates abroad, lack of domestic long-term credit, or to circumvent hard budget constraints]. This implies that economy indulges in debt to boost economic growth and reduce poverty. He is also of the opinion that once an initial stock of debt grows to a certain threshold, servicing them becomes a burden, and countries find themselves on the wrong side of the debt-laffer curve, with debt crowding out investment and growth. This seems to be the position of today because investment, which will accordingly result to high-speed growth with a positive effect on poverty, is moving sporadically in both positive and negative directions. For the past two decades, has borrowed large amounts, often at highly concessional interest rates with the hope to put them on a faster route to development through higher investment, faster growth and poverty reduction but on the contrast economic growth and poverty situations are staggering at the back door amidst excess debt, albeit that was the initial intention. It is then obvious that the Nigerian indebtedness has gone beyond such limits and it is noteworthy if such limit is dictated to help the economy in their pursuit towards debt.The objective of this paper is to examine the direction of causality between public debt and economic growth covering the periods 1970 to 2010. This will assist the policy maker to put the economy at the right direction and regulate investment that is moving sporadically in both positive and negative directions.
2. Theoretical Perspectives
- This section reviews literatures on the relationship between public debt and economic growth in . Reference[6] pinpoints that Nigeria is not the only country faced with this escalating level of government indebtedness, but when compared with other sub-Saharan region, that of Nigeria was seen to be larger than the others by the years. Reference[11] stressed that borrowing from the domestic economy in order to finance its domestic expenditure due to oil price collapse has increased rapidly.Moreover, reference[7] stipulated that the debtor can only share partially in any increase in output and export because a fraction of that increase will be used to service the external debt. His theory therefore implies that debt reduction (internal and external) will lead to increased investment and repayment capacity and as a result, the portion of the debt outstanding becomes more likely to be repaid.Reference[2] posited that the issue of debt and lack of growth are clearly interrelated. In his view, excusive stock of debt retards growth and hamper the socio–economic development of sub-Saharan African countries. The large debt stock and crushing debt service burden have now introduced a vicious circle to the analysis of the development problem of these developing countries because debt servicing in the face of inadequate foreign earning leads to severe import strangulation. Import strangulation hold back export growth thus perpetuating import shortages as observed by[1].Reference[9] in his opinion sees nothing wrong with external debt but that the debt crisis emanates from mismanagement of such funds. To him, borrowing is desirable and also unavoidable because external borrowing is a first order condition for bridging the domestic gap; while the second order is that such funds should be invested in viable project whose rate of return is higher than that of the interest rate on the loan. Put together, he concluded by saying that for external debt to serve as an engine of growth it has to be properly managed and the resources it makes provides need to be prudently and efficiently utilized.Reference[16] is of the view that debts arise from loans and credit procured by the residents of a country from the rest of the world that is meant for bridging the gap between saving and investment. He stipulated that when these resources are productively deployed and utilized, they do not constitute any drain on the future resources. He further buttressed that, to ensure sustainability of debt servicing, borrowing countries like need to adopt efficient external debt management strategies, which entail carefully planned schedules of external debt acquisition, deployment and retirement.According to[17], Nigeria is the largest debtor nation in the Sub-Saharan Africa. They also observe, in a comparative study with Argentina (Latin America’s most severely indebted nation), that Nigeria’s external debt, as a percentage of gross national income, has been continuously higher than that of Argentina since 1985 and continued to follow an upward pattern, unlike that of Argentina. The problem is compounded, according to[13], by inability of the economy to generate the requisite resources to meet repayment obligations, especially since the early 1980s. Reference[10] further shows the severity of the debt burden brought about by the pile-up debt (debt arrears as proportion of total debt stock) as high as 59%. Reference[8] analyzed the African external debt problem with reference to Nigeria and Morocco. He concluded that external debt has affected investment severely. Other findings include the fact that fiscal expenditure, balance of payments, and global interest rates are major factors explaining debt accumulation in the studied countries. He, therefore, suggests measures that could alleviate the above problems (privatization, sustained export promotion program, and restructuring and development of capital markets, among others).Reference[7] also explained the cash flow impacts of debt as the “liquidity constraint” (a reduction in current debt services increases the current level of investments, for any given level of future indebtedness). Another effect identified is the reduction of moral hazard effect. Moral hazard effect implies debt reduction to countries with a record of sound macro policies. According to[5], “inflation tax reduces public investments and uncertainty (option of waiting and misallocation of investments) are likely to occur with a large debt stock. Additionally, large debt stocks lead to capital flights, higher tax rates and continuous over-borrowing, with a negative effect on growth.”The impact of huge foreign debt is recognized by[15]. According to[5], the heavy debt burden and continual reliance on countries of the north for hard currencies has been a major impediment to accelerated integration within and across regional groupings in Africa. There is a growing concern over the amount of borrowing indulged in, the servicing of such foreign debt, and the future strain on regional schemes and general sustainable development. Resources transferred abroad for debt servicing represents a reduction in what can be devoted to regional schemes and economic development. Not only is potential regional integration foregone but, also in many cases, previous development achievements are being eroded. Debt repayments in the form of arrears have grown rapidly giving rise to questions regarding the credit worthiness of many countries. On the other hand, conditionality, associated with debt repayments and trade, has stood in the way of northern creditors at the cost of intra-regional trade. Compounding this situation is the pattern of existing trade. Existing trade patterns reflect strong vertical linkages (developed-developing country) and weak horizontal linkages (between developing countries), which are symptomatic of an unequal global balance of economic power and debt problems.In recent study, reference[4] contends that domestic debt rather than external debt will stimulate economic growth in Nigeria. This is because the repayment of the principal and interest on such internal debt is a reinvestment into the domestic which would usually have a chain investment effect on the domestic economy. But with respect to external debt, more resources will be needed to repay and service the debt and this would impair the positive effect of this debt on economic growth. Thus government should rely more on domestic debt in stimulating growth rather than external debt.Based on the literatures revealed above, most of the studies focused on the relationship between public borrowing and economic growth while studies are yet to emerge from the direction of causality between public borrowing and economic growth in Nigeria. This paper investigates the direction of causality so as to inform the policy makers whether public borrowing promotes economic growth in or not. This will assist the government to channel the resources from public debt appropriately for the development of the economy.
3. Methodology
3.1. Data Description and Sources
- This paper used secondary data (time series data). Empirical investigation was carried out on the basis of the sample covering the period 1970 to 2010. Real Gross Domestic Product (RGDP) was used as an indicator of economic growth, external debt outstanding, domestic debt and debt services were also used as indicators of public borrowing. Data on these variables were sourced for Nigerian economy.Economic growth is measured by real gross domestic product (RGDP). External debt outstanding is measured by total sum of external debts in . Domestic debt is also measured by total sum of domestic borrowing. All these variables were sourced from Central Bank of Nigeria, Statistical Bulletin (2010).
3.2. Specification of Model
- In this study the method of Granger causality2 Vector Autoregressive Model (VAR) is adopted to estimate the effects of public borrowing on economic growth in Nigeria. In order to test the causal relationships, the following model is specified:
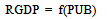 | (1) |
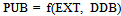 | (2) |
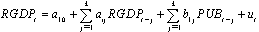 | (3) |
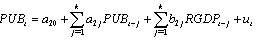 | (4) |
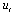 = A zero mean white noise error term For this paper to examine whether domestic or external debt that promotes economic growth, we disaggregate public debt into external debt and domestic debt. This will assist the paper to recommend whether the domestic debt or the external debt helps to promote and enhance economic activities in Nigeria.In order to test the above hypotheses the usual Wald F-statistic test is utilized, which has the following form:
= A zero mean white noise error term For this paper to examine whether domestic or external debt that promotes economic growth, we disaggregate public debt into external debt and domestic debt. This will assist the paper to recommend whether the domestic debt or the external debt helps to promote and enhance economic activities in Nigeria.In order to test the above hypotheses the usual Wald F-statistic test is utilized, which has the following form: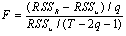 Where:
Where: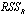 = The sum of squared residuals from the equation under the assumption that a set of variables is redundant, when the restrictions are imposed (restricted equation)
= The sum of squared residuals from the equation under the assumption that a set of variables is redundant, when the restrictions are imposed (restricted equation)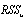 = The sum of squared residuals from the complete (unrestricted) equationT = The sample sizeq = The lag lengthThe hypotheses in this test are:{
= The sum of squared residuals from the complete (unrestricted) equationT = The sample sizeq = The lag lengthThe hypotheses in this test are:{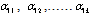 }= 0, if Fc < critical value of FH1 : PUB does Granger cause RGDP, i.e.,{
}= 0, if Fc < critical value of FH1 : PUB does Granger cause RGDP, i.e.,{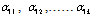 }≠ 0, if Fc > critical value of FandH0: RGDP does not Granger cause PUB, i.e.,{
}≠ 0, if Fc > critical value of FandH0: RGDP does not Granger cause PUB, i.e.,{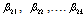 }= 0, if Fc < critical value of FH1 : RGDP does Granger cause PUB, i.e.,{
}= 0, if Fc < critical value of FH1 : RGDP does Granger cause PUB, i.e.,{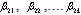 }≠ 0, if Fc > critical value of FThe results related to the existence of Granger causal relationships among economic growth and public debt indicators.
}≠ 0, if Fc > critical value of FThe results related to the existence of Granger causal relationships among economic growth and public debt indicators.3.3. Estimation Technique
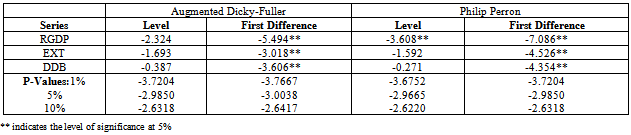
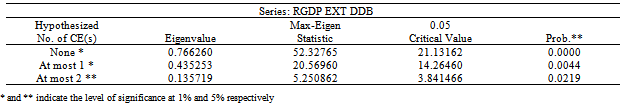
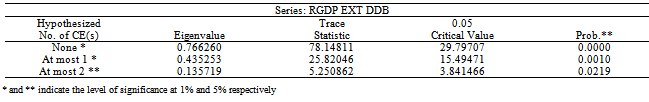
- We perform a unit root test on each variable in our model using the Augmented Dickey-Fuller (ADF) and Phillips Perron (PP) tests. The table 1 below shows the result of the unit root tests for the variables.With evidence of unit roots, the series are said to be integrated of order one – I(1), meaning that they must be modeled in first difference (∆yt = yt – yt -1) to make them stationary. A time series is stationary if it does not change overtime, which implies that its values have constant variability. This enables us to avoid the problems of spurious regressions that are associated with non-stationary time series models.After testing for unit roots, we proceed to test for co-integration (long run relationship between variables). This study uses Johansen and Juselius’s (1991) definition of co-integration. Johansen’s co-integration procedure was used to test for the possibility of at least one co-integrating vector between variables in the models developed for the Nigerian economy in this paper.After the above testing established, the study adopts Granger causality, to know the direction of causality between public borrowing and economic growth in the economy.
4. Empirical Results and Discussion
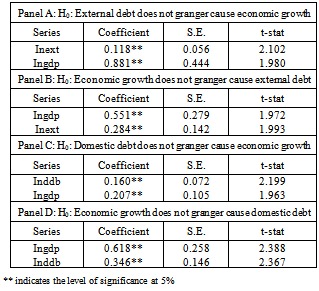
- The results of the co-integration test are reported in table 2 and 3 below and this allows the study to examine the long run relationship among the variables.The result shows that there was at least one co-integration relationship among the variables in the model. The evidence of multivariate co-integration test results suggests that external debt, domestic debt and economic growth are co-integrated. That is, these variables move together in the long run. The table 2 and 3 below also confirm multivariate co-integration test results of Eigenvalue and trace statistic.The table that shows the direction of causality between public borrowing and economic growth is presented in table 4 below.The result in table 4 below shows the direction of causality between public debt and economic growth in Nigeria. The result reveals that there exist bi-directional causality between external debt and economic growth as well as domestic debt and economic growth. This implies that improvement in economic activities call for borrowing to enhance on-going development processes in the economy. Also, borrowing promotes economic growth in . Therefore government should intensify efforts in using the loans obtained (either internally or internationally) judiciously for capital projects that will improve welfare of people in the economy.
|
|
|
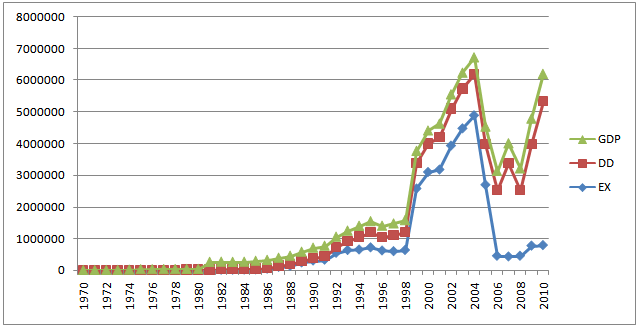 | Figure 1. Trend of Economic Growth, Domestic Debt and External Debt |
|
5. Concluding Remarks
- This paper examines the direction of causality between public debt and economic growth in Nigeria within the context of VAR framework. The paper also examines unit root and co-integration tests among the series.The unit root shows that all the variables are stationary at first difference – I(1). The co-integration test reveals that all the variables are co-integrated, meaning that they have long run relationship. The direction of causality between public debt and economic growth shows bi-directional relationship. The paper concluded that public debt and economic growth have long run relationship, and they are positively related if the government is sincere with the loan obtained and use it for the development of the economy rather than channel the funds to their personal benefit.Therefore, the policy implication of these results is that Nigeria government should source for loans within the economy so that when the principal and interest on the loans are paying back, it will serve as a crowd-in effect which in turn further accelerates economic activities in the country.
Notes
- 1. This involves fund, which were supposed to be remitted to some nationals and multi-nationals account but delayed due to the fund being used for some productive ventures.2. Causality is said to be essential in econometrics analysis in the sense that it makes us to know whether a past change in one variableX has a corresponding impact on current variable Y or whether the relation works in the opposite direction. Granger causality is used for testing the long-run relationship between public borrowing and economic growth. The Granger procedure is selected because it consists the more powerful and simpler way of testing causal relationship [Granger, 1986].
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML