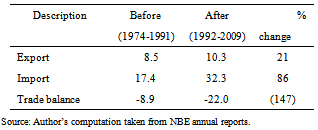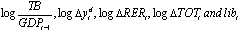-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
2012; 2(5): 75-81
doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20120205.02
The Impact of Trade Liberalization on the Ethiopia's Trade Balance
Hailegiorgis Biramo Allaro
candidate (Agricultural Economics)
Correspondence to: Hailegiorgis Biramo Allaro , candidate (Agricultural Economics).
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This study examines the impact of trade liberalization on the Ethiopia's trade balance using the data over the period 1974 to 2009 from NBE (National Bank of Ethiopia). The country has undertaken serious trade reforms, either as a part of major macroeconomic reforms and commitments with international regulations, or by decisions driven by a process of internal adjustment for the last two decades. One of the anticipated gains from the trade liberalization policies adopted by Ethiopia is improved export performance. In this research, the arguments on which this expectation is based were reviewed and the impact of trade liberalization on Ethiopian trade balance was analyzed. However, when it was examined with the application of export equation of Santos-Paulino and Thilwall [2004], it showed that trade liberalization led to the deterioration of the trade balance or too fast of an increase in imports. Thus, it was deduced the evidence that the trade liberalization worsens trade balance due to more imports than exports [Santos-Pauulino and Thirlwall, 2004].
Keywords: Ethiopia, Export; import, Trade Liberalization, Trade Balance
Article Outline
I. Introduction
- The relationship between trade liberalization and trade balance has been an important area of study in recent years, especially for developing countries. The studies on the impact of trade liberalization on trade balance in developing countries, showed conflicting conclusions. The empirical literature shows that trade openness or liberalization affects trade balance significantly [Santos-Pauulino and Thirlwall, 2004]. Theoretically, the effect of a change in tariff on the trade balance is ambiguous [Thiriwall and Gibson, 1992; Santos-Paulino and Thirlwall, 2004], as the impact will depend on the relative change of import and export growth. The literature survey of Ostry and Rose [1992] on the effect of trade tariff on the economy based on different theoretical frameworks concluded that there is no clear conclusion about the effect. They showed that the effect depends on the behaviour of real wages, exchange rate, a variety of elasticity, the degree of capital mobility, and whether the tariff shocks are perceived as temporary or permanent. Given the ambiguity, the impact of trade liberalization on the trade balance needs to be studied empirically.Empirically, there are only a few cross-countries studies that examined the impact of trade liberalization on the trade balance [Santos-Paulino and Thirlwall, 2004; Wu and Zeng, 2008]. Santos-Paulino and Thirlwall [2004] showed that for the period 1972-1997, trade liberalization worsened the trade balance of developing countries. They also demonstrated that trade liberalization caused both imports and exports to grow faster, but the growth of imports was faster than that of exports for a panel of 22 developing countries. Wu and Zeng [2008] illustrated that both imports and exports increased after trade liberalization, however, the evidence that trade liberalization worsens trade balance was not robust for the trade liberalization dates. Parikh [2006] concluded that trade liberalization promotes growth in most cases, but the growth itself has a negative impact on the trade balance and adverse terms of trade. UNCTAD [1999] studied the effect of trade liberalization on the trade balance for 15 developing countries over the period 1970 to 1995 and found a significant negative relationship. Studies have also examined the impact of trade liberalization on imports and exports separately. Santos-Paulino [2002a]; Melo and Vogt [1984]; and Bertola and Faini [1991] showed that the impact on imports have been positive. However, the findings of empirical studies on the effects of trade liberalization on exports haven been mixed. Santos-Paulino and Thirlwall [2002b] and Thomas and Nash [1991] showed a positive impact but Greenaway and Sapsford [1994] and Jenkins [1996] found little evidence of such a relationship.This manuscript deals with descriptive and econometric analysis on the impact of trade liberalization (open to international trade) on trade balance to confirm the hypothesis that trade liberalization reduces anti-export bias and makes exports more competitive in international markets by reducing exchange rate distortions and export duties, however worsen trade balance.
2. Trade Liberalization and Trade Balance
- According to the World Bank [2001], trade liberalization is defined as (i) the removal of or reduction in the trade practices that thwart a free flow of goods and services from one nation to another. It includes dismantling of tariff (such as duties, surcharges, and export subsidies) as well as non-tariff barriers (such as licensing regulations, quotas, and arbitrary standards); (ii) the removal of government incentives and restrictions from trade between nations; and (iii) any act that would make the trade regime more neutral (nearer to a trade system free of government intervention). The third definition was adopted in this study. Since the 1980s trade liberalization has become an increasingly common feature of economic policy in developing countries. They have liberalized their trading regime with hope of gaining static and dynamic gains from trade, and that the liberalization will increase both the growth of export and imports, and consequently improve welfare [Santos-Paulino and Thirlwall, 2004].Some developing countries have unilaterally liberalized trade in an attempt to integrate into the global economy and promote economic growth. In other cases, countries have had to liberalize trade in order to satisfy the requirements of international lending agencies. At the global level, multilateral trade negotiations under the auspices of the World Trade Organization (WTO) are pushing for freer trade in response to the demands of globalization. It has been strongly supported by the multilateral institutions, both financially through their structural adjustment loans and intellectually through studies of the effects of trade liberalization. An important plank in the advocacy of trade liberalization is the belief that a more liberal regime will lead to increased exports which in turn will have a favourable effect on economic growth and employment generation [World Bank, 2001].The empirical literatures show that trade openness (liberalization) affects output growth in the era of globalization (a phenomenon, whose economic dimension involves increases in the flows of trade, capital, and information, as well as the mobility of people across borders). In view of trade liberalization, Rodrik [2006] recommended the most common policy reform to developing countries. He indicated that trade liberalization must be accompanied by complementary adjustment policies, particularly macroeconomic reform, and must go along with a long list of conditions, in order to be effective and to be ensured to enhance welfare. One of many conditions, which there must be no adverse effects on the fiscal balance, or if there are, there must be alternative and expedient ways of making up for the lost fiscal revenues. Though he believes that trade policy is overemphasized, and that macroeconomic reform and institutional innovations are far more important in fostering economic growth, he agrees that trade liberalization accompanies development and that in long run an economy which fails to integrate with international markets will grow more slowly.A crucial element of the trade liberalization reforms in developing countries is the liberalization of import trade as a means of reducing the anti-export bias of the trade regimes. In that sense, many developing countries have made good progress in the last two decades in liberalizing their trade policies by removing quantitative import restrictions and reducing tariffs [Milner, 1990]. However, most developing countries’ tariffs are still high enough to create significant levels of anti-export bias. Moreover, tariff structures are typically escalated, with higher tariffs on final goods than on intermediate materials and components. Developing countries are also increasingly turning to anti-dumping actions and imposing antidumping duties above normal tariffs (raising both the nominal and effective protection of import substitution production and increasing anti-export bias), and removing quantitative import restrictions of various kinds. Furthermore, the consequent reduction in imports, given these restrictions, leads to less demand for foreign exchange, and enables the country’s exchange rate to be maintained at a higher level than otherwise. This in turn reduces the domestic currency value of the export proceeds.However, several studies have investigated the impact of trade liberalization on export growth in developing countries, and have reached conflicting conclusions. Some studies have looked at individual countries; others have taken a cross-section of countries. The individual case studies which show a positive impact of liberalization on export performance were carried out by Weiss’s [1992] cross-sectional study of Mexican manufactured exports; Jenkins’s [1996] times series and cross section analysis for Bolivia’s manufactured exports; Joshi and Little’s [1996] analysis of India’s economic reforms; and Ahmed’s [2000] cointegration and error correction modelling for Bangladesh and Svedberg [2000]. Multi-country studies for developing countries that confirm the positive relationship between exports and liberalization include; Thomas’s et al [1991] cross-section analysis; Helleiner’s [1994] collection of theoretical and empirical studies; and Bleaney’s [1999] panel data study. Similarly, Santos-Paulino [2000]; [2002]; and [2003] examined the impact of trade liberalization on export performance for a sample of developing economies using the export demand function approach. Results from his study showed that exports react negatively to an increase in relative prices and positively to an increase in world income growth, while export duties have detrimental effect on export performance, although the impact is relatively small. He concluded that trade liberalization emerges as a fundamental determinant of export growth in all the countries in their sample. Multi-country studies that show a non-significant impact comprise UNCTAD’s [1989] analytical assessment of the relationship between trade reform and export performance; Agosín [1991] quantitative and qualitative analysis; Clarke and Kirkpatrick’s [1992] cross-section study; Shafaeddin’s [1994] analytical study; Greenaway and Sapsford’s [1994] times series analysis; Greenaway and Sapsford’s [1997] smooth transitions analysis. The bases of the controversy have been on the importance of complementary reforms, stage of development before opening up to trade, sequence and degree of liberalization as well as methodological and measurement issues among others [Utkulu et al., 2004]; [UNCTAD, 2005]; and [Morrissey and Mold, 2006]. Utkulu et al.; [2004] argued that a traditional model of export supply with explanatory variables such as export prices, home and foreign costs, and productive capacity can be further extended by taking the effects of trade reform, which consists of measures to reduce anti-export bias. They argued that trade liberalization leads to the reduction of anti-export bias and strong supply response. The argument is based on whether trade liberalization has led to positive or negative export performance. However, the assertion of a strong influence of liberalization on export performance has remained largely unresolved in the literature [Utkulu et al., 2004]. The new consensus was adopted by many SSA countries as part of their structural adjustment and reform programmes from the mid-1980s. The SAP (structural adjustment programme) was adopted with the purpose of liberalizing their economies, particularly the external sector. The main purpose of trade liberalization over this period was to promote economic growth by capturing the static (reduced costs from economies of scale, efficiency gains from exploiting comparative advantage, reduction in distortion from imperfect competition and increased product variety) and dynamic (benefits from trade that accumulate over time in addition to static gains from trade) gains from trade through a more efficient allocation of resources; greater competition; an increase in the flow of knowledge and investment and, ultimately, a faster rate of capital accumulation and technical progress. It was the belief that barriers to trade, and anti-export bias would reduce export growth below potential. As a result, the adoption of trade liberalization measures would reduce anti-export bias and make exports (especially non-traditional ones) more competitive in international markets, mainly by reducing trade policy barriers, exchange rate distortions and export duties. Foreign trade was liberalized through the reduction of tariffs and non-tariff barriers and reduction of import duties applied to imports in a large number of SSA countries. In addition, import permits were abolished and duty rates as part of tariff liberalization were also lowered in many SSA countries. Currencies were devalued to encourage exporters, with the aim of boosting exports and growth and fostering the integration of SSA into the global economy. A sizeable number of SSA countries virtually eliminated parallel market premiums, with buying and selling of foreign exchange then becoming market-based, while abolishing previous restrictions on currency transactions [UNCTAD, 2005]. According to the World Bank [2001], Ethiopia has implemented trade liberalization in the late 1990s. It was theoretically designed to increase the efficiency of national industries through competition with the outside world. Instead, such liberalization may lead to the inability of Ethiopian industries to compete at all, thereby further assuring the dominance of the agricultural sector. The potential advantages of trade liberalization for Ethiopia are firmly rooted in the theory of economies of scale. The small size of domestic markets to absorb most of its supply desires expanding markets and increasing participation in the global economy. Therefore, a relaxation of trade restrictions within a given range could reduce internal transport costs, stimulate intra-regional trade, and ultimately increase the growth and productivity of the country. Additionally, liberalization could encourage the country to adopt a more outward-oriented attitude towards trade instead of the protectionist, inward-oriented mentality which frequently exists. Consequently, Ethiopia’s economy has experienced several dramatic events and changes after trade liberalization. The volatile nature of the evolution of the growth rates of Ethiopian economies has been accompanied by a variety of reforms (external and internal real shocks faced), and different responses to them. The theoretical and empirical tools to determine the factors behind the performance of the economy could be broadly categorized in domestic policies and domestic or external shocks (such as domestic supply shocks, terms of trade shocks, international crises, etc.).
3. Model Specification
- The model used for the analysis of impact of trade liberalization on trade balance was based on export equation of Santos-Paulino and Thilwall [2004]. The equation is based on the traditional trade function, where trade is a function of income, price, and a trade liberalization dummy:
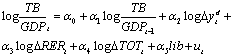 | (1) |
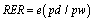 | (2) |
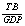 refers to the trade balance over real GDP ratio;
refers to the trade balance over real GDP ratio; 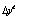 is change in domestic real income in US dollars,
is change in domestic real income in US dollars, 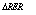 is the change in real exchange rate;
is the change in real exchange rate; 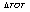 is the change in the terms of trade and
is the change in the terms of trade and  is the trade liberalization dummy;
is the trade liberalization dummy;  ’s are unknown parameters to be estimated, t is time in years (1974-2009) and u is random terms that are independently and identically distributed with mean zero and variance2 (δ2).
’s are unknown parameters to be estimated, t is time in years (1974-2009) and u is random terms that are independently and identically distributed with mean zero and variance2 (δ2).4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Descriptive Statistical Analysis
- Two macroeconomic indicators (real export and real import) were analyzed to describe Ethiopian trade balance. A look at the trends of export performance of Ethiopia before and after trade liberalization reveals that imports did increase as a proportion of GDP following trade liberalization. The comparison of imports and exports performance as the percentage of GDP prior to and following trade liberalization shows that imports increased by 86 percent while exports by 21 percent. By and large, the evaluation shows a high deterioration in the trade balance following trade liberalization. The trade balance following trade liberalization was worsened by 147 percent (Table 1).
|
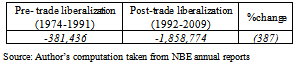
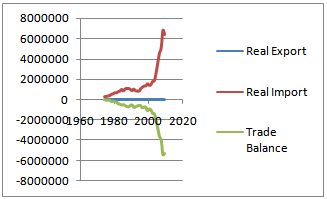 | Figure 2. Trends of Ethiopia's trade balance in million USD (1974-2009) Source: Author’s computation taken from NBE annual reports |
|
4.2. Econometric Analysis
4.2.1. Unit Root Test
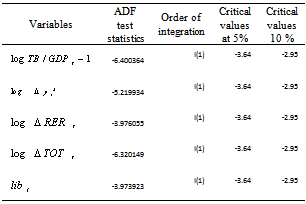
- The preliminary analyses concur with the findings of the previous studies that the trade balance deteriorates after liberalization. Even though the simple statistics were indicative of a change in trade balance, they do not control other factors that may affect trade balance. Hence, regression analyses were used to identify the role of each variable in the model with unit root test (Table 3).Table 3. discloses the results of unit root tests on
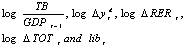
|
4.2.2. Cointegration Test
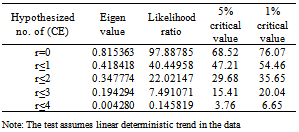
- Having confirmed unit root presence in all data series and the findings of stationarity in the first difference, the next step was a Johansen’s cointegration procedure. It was applied to determine the long-run equilibrium relationship. The second procedure was to specify ECM to account for short-run equilibrium. Johansen’s cointegration multivariate procedure is used to establish whether the variables are cointegrated in the long run. The likelihood ratio indicates one co-integrating equation at 5% significance level. In other words, it accepts the alternative hypothesis of having one co-integrating vector. Since the test statistic (97.89) is greater than the 95% critical value (68.52) of the likelihood ratio test, it is possible to reject the null of more than one co-integrating vector. The maximum Eigen value test also starts with the null hypothesis of at most r co-integrating vector against the alternative of r+1. The result for maximum Eigen value test confirms the rejection of the null hypothesis. Therefore, both maximum Eigen value and likelihood ratio indicate that there is one co-integrating equations at 5% significance levels (Table 4).
|
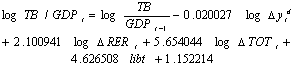 The above cointegration equation shows that there is a direct long- run relationship between trade balance over real GDP ratio and
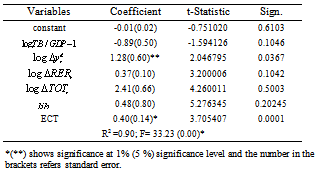
The above cointegration equation shows that there is a direct long- run relationship between trade balance over real GDP ratio and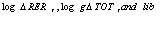 , the coefficient defined that a 1% change in real exchange rate, terms of trade and liberation dummy would change trade balance over real GDP ratio by 2.1, 5.65 and 4.63 percent respectively, while the relationship between trade balance over GDP ratio and lagged value of domestic income was found to be indirect in the long run.The error correction model (ECM) signifies two basic factors: ECT and other variables. The ECT indicates that 40 percent of the short term equilibrium of Ethiopian trade balance will be adjusted in the same year, while 60 percent in the subsequent years (Table 5).
, the coefficient defined that a 1% change in real exchange rate, terms of trade and liberation dummy would change trade balance over real GDP ratio by 2.1, 5.65 and 4.63 percent respectively, while the relationship between trade balance over GDP ratio and lagged value of domestic income was found to be indirect in the long run.The error correction model (ECM) signifies two basic factors: ECT and other variables. The ECT indicates that 40 percent of the short term equilibrium of Ethiopian trade balance will be adjusted in the same year, while 60 percent in the subsequent years (Table 5).
|
5. Conclusions
- This research has put particular emphasis on the impact of trade liberalization on Ethiopia’s trade balance during the sample period, particularly since 1992 when export promotion policies appear to have formed a superior development strategy for the country. The country has undertaken serious trade reforms, either as a part of major macroeconomic reforms and commitments with international regulations, or by decisions driven by a process of internal adjustment for the last five decades. The policy adopted in the pre reform period (during the Derg) was characterized by strongly inward oriented development strategy (ISI) that had a negative impact on export through influencing directly or indirectly the profitability and competitiveness of exports. The current government has undertaken trade policy reforms, which aimed at promoting exports through diversifying the country’s commodity exports. Despite the policy reforms, there is still a bias against exports that calls for active government intervention to create a favorable environment for effective export performance to achieve favorable trade balance [Santos-Paulino and Thirlwall, 2003].The manuscript also disclosed that trade liberalization enhances export and generates two types of gains. It raises static allocative efficiency and average incomes in the medium- run, whereas, it is the source of dynamic gains, mainly in terms of advanced productivity and more rapid growth, in the long-run. As well, it was revealed that in the long-run, a more open economy will achieve higher growth rates because it offers easier access to new technology, provides benefits derived from increased competition and economies of scale. The study further analyzed that trade policies vary from country to country, depending upon a great deal on the level of openness of the external sector. The argument between trade liberalization and exports was examined, which states that the reduction or elimination of trade policy distortions reduces anti-export bias, and therefore, improves export performance and competitiveness. Accordingly, it was divulged that the reduction in tariff and non- tariff measures improved access to international markets to increase exports from Ethiopia. It was further analyzed that trade liberalization seeks to reform a country’s international commercial policies in order to improve economic welfare by achieving a better allocation of resources in the long- run. The results of the estimated model show undoubtedly that in the observed period, 1974-2009, trade liberalization has had a positive and significant impact on the export performance of the country. This implies that policy makers should generate such policies for attracting exports from Ethiopia, which will focus on the utilization of the country’s resource endowments in terms of developing new technologies, and improving national capabilities. As a result, openness has lead Ethiopia to economic growth. This suggests that when countries are more open, they are better able to exploit market opportunities through product diversification and differentiation. These results have important implications for national policies and strategies within the trading system of Ethiopia to open up its foreign trade policies in inter regional and global perspective. Therefore, Ethiopia should further improve its export commodities composition, structure and foreign trade policy instruments (tariffs) based on the expected benefits to stimulate economic efficiency, improve trade balance, and achieve sustained growth in the future. However, when it was examined trade liberalization on the trade balance using Johannes cointegration procedure, it showed that liberalization lead to the deterioration of the trade balance or too fast of an increase in imports. Thus, it was deduced the evidence that the trade liberalization worsen trade balance (Santos-Paulino and Thirlwall, 2004).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We are gratefully acknowledged the anonymous reviewers.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML