-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
July, 2012;
doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20120001.35
Comparative Study of Philosophical Mentality of Professors and Managers of University and Seminary (Theological School)
Najmeh Soltaninejad 1, Parvin Salari Chine 2
1Department of Education, Khorasgan (Isfahan) branch, Islamic Azad University, Isfahan, Iran Master Teacher Tarbiatmoalem
2Department of Education, Tehran Science & Research branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran - Master Teacher Tarbiatmoalem
Correspondence to: Najmeh Soltaninejad , Department of Education, Khorasgan (Isfahan) branch, Islamic Azad University, Isfahan, Iran Master Teacher Tarbiatmoalem.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The holly Quran is the book of ponder and insight and invites man to contemplate. A human being who thinks and is used to contemplation does not look at the events and phenomena superficially or perfunctorily. It is perceived that there is a need to develop an organize system of thinking that would play the best role in making individuals able to make decisions, to solve problems, to guide themselves or others, as well as organizations, in the direction of goodness and deliberation. The directors and higher education professors need for a creative and dynamic system of thinking with the ability to enrich their performance made the researcher to develop and introduce a kind of pondering called philosophical mindedness suitable for the mentioned subjects. This system analyzed the extent of directors and professors philosophical mindedness, in theological schools (TS) and University, to determine the amount of the effects of individualistic factors on their philosophical mindedness.
Keywords: Faculty, Philosophical Mindedness, Comprehensiveness, Penetration, Flexibility
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- It seems that it is vital and essential to create a cohesive and well-organized system for thinking of people (cogitation) in a way that enables them to play the most critical role in decision making, solving the problems , guiding themselves and others for goodness and reformation (Smith 1998: 23). Also, Philip G. Smith believes that the value of each person depends on well thinking. Therefore, the cogitation and skill of well thinking is one of the most important issues that philosophers have dealt with since many years ago. In order to carefully and basically concentrate concern and observe the issues, it is essential to deeply and generally understand and perceive the issue. This understanding is provided by a philosophical mentality. Whenever a manager or professor studies an issue by considering other affairs and observing the opposite beliefs and affairs, he wouldn’t comment and judge base on superficial culture and perception. The theoretical bases and principles of this research for studying the collectivity characteristics are cogitation and adaptability (flexibility) of the theory of Smith.Smith compared the managers by three features of philosophical mentality in a research. He concluded that the manager who thinks generally, cognitively and flexibly (adaptable), has different effects on his deeds in compare with one whose thought lacks this quality (Zaki 1998).An educated, experienced, clever, supple manager with philosophical mentality who is aware of management and leadership principles and tasks and one who can suit and adapt his knowledge and experiences with every action anytime, certainly can provide the conditions of improvement and excellence for others and can encourage the employees to achieve the ideal purposes and aims. ( Alagheband, 1992, 130)Managers and professors of university and seminary should consider the logical thinking and cogitation and their viewpoints in order to observe fairs and caution in judging and to avoid presuming the beliefs as definite and certain collectivity. When it is declared that having philosophical mentality means to have broad-minded, reasonable doubt, confidence, etc., it means that lack of such qualities in a manager or professor would cause obstacles in his development. Therefore, although collectivity has many difficulties and problems, if they compare what they lack and what they gain with such a mentality, they would easily and appropriately tolerate the difficulties and adversities to reach the ideality.Since Managers and teachers of educational centers are wise and sage, they are known as the guide and leader of students. It is essential for them to realize the several various issues and subjects and found out the necessary solutions and answers. If a person uses the instruments and techniques of logical and reasonable thinking, it can help him to realize issues and find proper solutions for resolving the problems.Mir Kamali (2005) believes that logical thinking is the result of philosophical mentality. In Diyooyi’ opinion, logical thinking is formed by active, continual and carful study of each belief , culture or perception with the reasons which confirm that and more results that caused because of that ( Smith & Holfish 1992,36). Shariatmadari (1985) believes that philosophical spirit is not limited to philosophers. He believes that when scientists theoretically and intellectually analyze, criticize and study an issue in their research, they have used the characteristic of spirit or philosophical mentality. He applied the term “real philosophers” for those who consider some characteristics such as reasonable doubt, so curious, cognitive perception, general viewpoint, broad-minded, willing to develop and progress, modesty, unity of personality, self-confidence and supporting human values in their behaviors.
2. Indexes of Philosophical Mentality
- Collectivity (comprehensiveness): sociological mentality is a mentality that considers world as a living organism that all of its members communicate and have unity and relation with each other. When one limb passes its day in pain, the other limbs can't remain easy and also it is a collectivity mentality and a belief or thought that has such collectivity. Saadi (blessed be his soul) composed the following couplet regarding the collectivity mentality:* Human beings are members of a whole, in creation of one essence and soul* If one member is afflicted with pain, other members uneasy will remainSheykh Mahmoud Shabestri (reported by Jafari, 1980) explained and interpreted this kind of mentality as if any little things’ subject and task change , the whole world would be in disorder. He declared that: If you remove any tiny particle from its real place, all of the world would be in disorder. Paul Latjon‘s idea reported by Jafari (1980) is based on such mentality. He believes that “if I move my luggage on the table, it would affect on all galaxies. Smith (1998) believes that the most obvious characteristic of one who has philosophical thinking is as follows: he always tries to popularize his thought or belief. Philosophy sometimes is considered as the struggle to view life as a whole or continual flow.
3. Collectivity Indexes
3.1. Considering Specific Cases in Relation with Extensive Field
- According to the first indexes of collectivity principle, the manager who looks for effective factors of any phenomenon on creating those conditions and the related factors can be successful.
3.2. Relating the Present Issues to Final Aims
- Smith (1995) believes that an educational manager should not only fluently memorize proper final aims for education, but also he should be able to discipline the daily issues and properly use the opportunities to achieve and verify his aims.
3.3. Applying the Ability of Popularization (Distribution)
- In Smith’s opinion (reported by Shariatmadari, 1968) , if a researcher analyzes one or some case/s instead of observing all cases or samples and theoretically studies what he has observed in the case, he can suggest any hypothesis and temporary accepts.
3.4. Considering Theoretical Aspects
- Smith (1998) believes that one who thinks generally would realize that the only way to make an action effective and purposeful is to work by a proper and suitable theory.
4. Cogitation
- Motahari (1982) explained cogitation as follows: to study something and then observe something else; to realize the origin and hidden facts inside and beyond these impressions by studying the phenomenon; to deduce a fact from a sign, clue; to discover an invisible and hidden thing.
4.1. Cogitation Indexes
4.1.1. To Discuss and Deal with Something Which is Considered Manifest or Certain
- One who has philosophical mentality deals with and discusses what others do not by resisting against the stress of obvious affair. (Smith 1995, 79)
4.1.2. Introduction and Compilation of Basic Ideas, Questions and Hypothesis in Specific Conditions or Circumstances
- In Shariatmedari’s opinion (2000), one who has philosophical attitude (thinking method) not only tries to deal with affairs doubtfully and interrogatively, but also he tries to realize the main points and general imaginations and beliefs which are effective in resolving problems in every conditions.
4.1.3. Considering the Signs and Affairs Related to the Main Aspects of each Circumstance
- Regarding this index, Smith (1995) declared that when the bases of a circumstance have been realized, the person with philosophical mentality would be highly eager to understand the main principles of that base or doctrine.
4.1.4. To judge and Command based on Hypothetical – Comparative Method
- The cogitation factor, like the fourth factor of collectivity shows that the role of theory is incontrovertible and formal in all affairs even in most practical ones (Smith, 1995).
5. Adaptability (Able to be Supple)
- When someone is properly compatible with a specific and immediate action, which is considered in an extensive field and with magnificent and great aims while observing the principles and considering the great and general advisability and assets, he has in fact, observed one of the indexes of philosophical mentality.
5.1. This Action Is Called the Adaptability
5.1.1. To Free from Psychological Strictness or Rigidity
- Shariatmadari (1990) declared about this aspect: when someone encounters new circumstances, conditions and situation, these conditions are so new that he can’t react properly.
5.1.2. To Evaluate the Ideas and Thoughts While not Concerning about their Sources
- People are free either to accept the rightness and philosophy of speech, beliefs and ideas or not. Jesus (peace be upon him) commanded: accept the righteous word even if it is said by wrongdoers and do not accept the wrong or idle words even if it is said by righteous men. According to the above hadith, accept the righteous word even if it is said by one who is not ideologically and rationally compatible with you. At the other hand, never accept the illogical and irrational word even if it is said by someone whom you do approve of.
5.1.3. To Think about Issues from Several Aspects
- Those who have philosophical method of thinking, firstly separate paradoxical and opposite aspects for discussing and studying the affairs and issues. Then, they study opposite affairs carefully.
5.1.4. To be Patient in Temporary and Conditional Judges and to Make Decision in Vague Times
- One who has philosophical mentality would accept the temporary judges instead of looking for stable and absolute concepts and meanings. Therefore, he can resist against vague and unknown conditions.
6. Instruments of Collecting Data
- Two kinds of philosophical mentality questionnaires are used in this research. In the first part, the data were collected regarding field of study (major), managing record, years of working, type of educational center, degree of education, age and sex. In the second part, the rate and level of philosophical mentality of respondent is evaluated by asking 24 questions regarding triple aspects of philosophical mentality ( by presenting 4 assumed conditions in the fields of decision making, planning, communication and organizing ; by considering the triple modes of collectivity, cogitation and adaptability in every conditions in the first questionnaire and 12 distinct questions in the second questionnaire).The rate and level of effect of individual factors on philosophical mentality and its aspects in managers and professors of seminaries (theological schools) and faculty of literature and humanities of Bahonar university were compared by use of rate of determination coefficient (
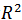 ) .
) .7. Conclusions
- The results of research show that the rate of collectivity, cogitation and adaptability of managers and professors are medium. Also, there is no meaningful difference between rates of effects of sex, age, degree of education, service record and managing record on collectivity, cogitation and adaptability of managers and professors of seminaries (theological schools) and Shahid Bahonar University. Therefore, it is suggested to consider the relation between a specific affair and a general and extensive field while observing specific affairs and always relate final and longtime aims to the present issues.Profoundly study the issues and never judge base on experimental and visible affairs. Also, don’t limit your thoughts to only two direction of this way or another. Recognize the different aspects for studying the issues. Then, present and introduce different hypotheses for resolving problems and issues.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML