-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
July, 2012;
doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20120001.15
The Influence of Trust, Advertising, Family on Intention and Actual Purchase of Local Brand in Yemen
Jamal Mohammed Esmail Al-Ekam 1, Nik Kamariah Nik Mat 1, Salniza Md. Salleh 2, Norashikin Binti Baharom 1, Tuan Rohasnida Binti Tuan Teh 1, Noor Aida Binti Noh 1, Nor Ermawati Binti Hussain 1
1Othman Yeop Abdullah Graduate School of Business, Universiti Utara Malaysia, Sintok, 06010, Malaysia
2College of Business, Universiti Utara Malaysia, Sintok, 06010, Malaysia
Correspondence to: Jamal Mohammed Esmail Al-Ekam , Othman Yeop Abdullah Graduate School of Business, Universiti Utara Malaysia, Sintok, 06010, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This empirical research investigates the influence of four predictors of actual purchase of local brand in Yemen. The exogenous variables examined are trust, advertising, family and purchase intention against actual purchase as the endogenous variable. Past validated instruments are used to measure the variables specified namely, trust (7 items), advertising (8 items), family (7 items), purchase intention (8 items) and actual purchase (6 items). The study employs quantitative research design by administering primary data collection via questionnaire. A total of 1000 questionnaires were distributed to school staff who represents local respondents in Yemen whereby 711 responses were returned representing 71 percent response rate. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was employed to analyze the relationships among the variables. The goodness of fit indices of the revised model indicate adequate fit (GFI=.989, RMSEA=.017, RATIO CMIN/DF=1.158, P-VALUE=.264). The regression parameter estimates show four significant relationships between trust & actual purchase (β=.322, CR=4.474, P<.001); advertising & actual purchase (β=.240 CR=3.339, P<.001); purchase intention & actual purchase (β=..442,CR=7.828, P<.001); as well as family & purchase intention (β=.537, CR=8.735, P<.001). These findings are discussed in the context of actual and intend purchase of local brands in Yemen.
Keywords: Actual Purchase, Purchase Intention, Trust, Attitude Towards Advertising, Family, Local Brands, Yemen
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- This study empirically investigates the influence of trust, advertising, family on intention and actual purchase of local brand in Yemen. The main issue that triggers this study is that there is a low actual purchase behavior for local product/brand in Yemen as evidence by the increase in the imported products. "The imported products inside the country increased by 14.1 % from 2006 to 2007 and 12.3 %from 2007 to 2008"[1]. Similarly, according to Al-Smeh[2], "the Yemeni government is spending $2 billion to import foreign products while local products are available". In addition, some Yemeni companies 4.5% (50) went bankrupt in 2007 and 2008. According to[1], "ever since Yemen opened its market to foreign products, they faced great competition and local production became non-progressive and local industries needed rehabilitation which consequently led to the incapability of these industries to compete with foreign product and some institutions went into bankruptcy" Yemen Annual Economic Report[1].In advanced countries, consumers are inclined to purchase their local products but in the developing and the less developed countries like Yemen, consumers usually prefer imported products, believing that local products are not as good as their counterpart imported ones[3],[4]. In line with this, Zafar et al.,[5] confirmed that consumers in a developed economy country have a tendency to purchase domestic product first, followed by products from similar level of developed economy, and then goods from less developed economy countries.
2. Problem Statement
- From the research issues discussed above, several problem statements can be derived.The first problem is that there are several fragmented model and inconsistent finding revealed by the previous studies that investigate the actual purchase and purchase intention of local product. As evidenced in some of prior studies, some authors have considered four factor model[6],[7]; ten factor model[8],[9]. Thus, this problem leads to disagreement on what are the significant predictors that affect intention and actual purchase of local product. In addition, research problem rests on lack of study examining predictor of actual purchase of local products or brand in Yemen[10],[11]. Past studies in actual purchase were conducted in other countries such as in Slovenia[12] and Malaysia[9].Moreover, there are lack of studies that used underpinning theory such as TPB in local product/brand setting[13],[14]. Most use TPB in other setting like internet banking[15],[10]; technology[16]. Hence, this study attempts to seal these gaps.
3. Research Objectives
- The main objective of this study is to investigate the influence of trust, advertising, family on intention and actual purchase of local product brand in Yemen. Basically, the specific objectives are: 1. To examine the direct effects of purchase intention, trust, advertisement, family on actual purchase behaviour toward local product/brand in Yemen.2. To examine the direct effects of trust, advertisement, family on purchase intention.
4. Literature Review
4.1. Purchase Intention and Actual Purchase
- Actual purchase is linked to the real purchase of the local product/ brand, Purchase intention is defined as an“individual`s readiness and willingness to purchase a certain product or service”[17]. Similarly, purchase behavior is defined by the dictionary of business management(http://www.businessdictionary.com) as, “decision processes and consumer involvement in purchasing and using product” or simply as purchasing goods and services for personal consumption[18]. According to Kotler and Armstrong[19], actual purchase behavior is evident when a consumer goes through all the relevant steps of a purchase. Actual purchase behavior of local product/brand is defined as consumers in different parts of the world having different abilities in terms of actual purchase to select between local and foreign products brands. Along the same line, local product/brand has been defined by Kotler and Armstrong [19], as a local brand that belongs to local, international, or global firms. The term local brands are defined as a group that belongs to one country or in a restricted geographic location. Local brands provide a link between the national economy and individual well-being.
4.2. Trust and Actual Purchase
- Various researches have revealed trust as the highly contributing variable for purchase behavior when it comes to local or foreign products[20],[21]. Trust is a factor that cannot be created overnight and entirely depends on the relation between the two parties[22]. According to Rousseau [23], consumer trust relies on the willingness of the consumer to be emotionally tied and belief is the variable found to have a role in increasing the level of trust.
4.3. Advertisement and Actual Purchase
- According to Kotler and Armstrong[19], advertising can directly influence the purchase behavior decision. It does this by creating awareness, providing product information and helping consumer determine the worth and quality of the product, thus helping them to decide on the best purchase option.In addition, findings of previous studies regarding purchase intention as antecedent of actual purchase reveal significant positive relationships[7],[8],[24],[13].However several past studies found that trust has a direct positive relationship with purchase intention and significant negatively relationship[25] and an insignificant relationship [26]. Thus, inconsistent findings were found in the literature opting for the necessity of this study to help clarify these equivocal results.
4.4. Family and Actual Purchase
- According to past studies in social factors/subjective norm: family and advertisement, a positive relationship exists between subjective norm and purchase behavior[27], [7], [13],[28] as well as negative[29].Therefore, hypotheses of this study are as follows: H1 purchase intention has a significant and positive influence to actual purchase, H2 Trust has a significant and positive influence to purchase intention, H3 Advertisement is related significantly and positively to purchase intention, H4 Family has significantly and positively relationship with purchase intention, H5 Trust has a significant and positive influence to actual purchase, H6 Advertisement is related significantly and positively to actual purchase.
5. Underpinning Theory: Theory Of Planned Behavior (TPB)
- The Theory of Planned Behavior confirms that actual behavior is a direct function of behavior intention and perceived behavior control and that behavior intention is a function of attitude toward behavior, where attitude is defined as the individual’s negative or positive feelings towards performing a behavior. Subjective norm is considered as the perception of an individual on whether people who matter to him should expect the behavior to be done or not. The contribution of the opinion of important people in his life is weighed against the motivation of his complying to do according to the opinion. Therefore, subjective norm can be wholly expressed as the total sum of the individual’s perception of his motivation assessments of all the important people.
6. Methodology
- The study employs quantitative research design by administering primary data collection via a questionnaire. This study is conducted in Yemen. The Republic of Yemen is a country located on the Arabian Peninsula in Southwest Asia with an estimated population of more than 26 million people. A total of 1000 questionnaires were distributed to school staff who represents local respondents in Yemen whereby 711 responses were returned representing 71 percent response rate. Past validated instruments are used to measure the variables specified namely, trust (7 items), advertising (8 items), family (7 items), purchase intention (8 items) and actual purchase (6 items).Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was employed to analyze the relationships among the variables.
7. Finding
- The goodness of fit indices of the revised model indicate adequate fit (GFI=.989, RMSEA=.017, RATIOCMIN/DF=1.158, P-VALUE=.264). The regression parameter estimates show four significant relationships between trust & actual purchase (β=.322, CR=4.474, P<.001); advertising & actual purchase (β=.240 CR=3.339, P<.001); purchase intention & actual purchase (β=..442,CR=7.828, P<.001); as well as family & purchase intention (β=.537, CR=8.735, P<.001). These findings are discussed in the context of actual and intend purchase of local brands in Yemen. However, the regression parameter estimates shown two insignificant relationships between advertisement and purchase intention (β=-.042, CR= -.605, P<. =.545), also the result show that trust has insignificant relationship with purchase intention (β=-.043, CR= .653, P =.514).
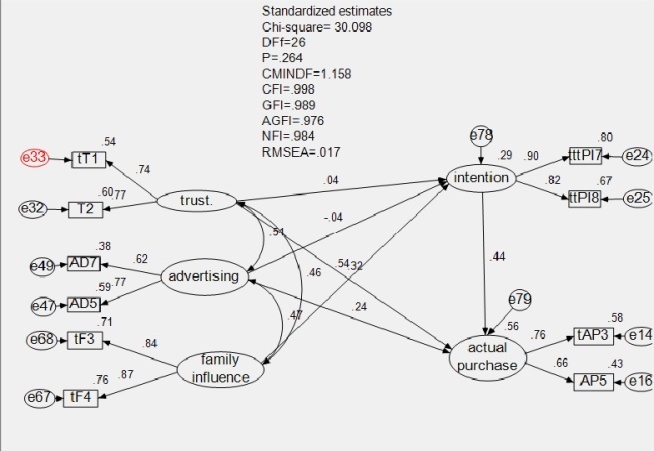 | Figure 1. Direct Hypotheses Testing Results of Revised Model |
8. Discussion
- The present study reveals that the influence of four predictors of actual purchase of local brand on Yemeni consumers trust, advertisement, family and intention are the significant positive antecedents of actual purchase towards local brands. The significant influence and local product brand of intention, trust, advertisement and family indicates that the Yemeni consumers consider their concept and need for trust and advertisement to be in local product brand then like to prefer and purchase local product if local product has good in quality. This replicates and support the finding by the past studies[7],[8],[24].The significant impact of local product brand on perceived intention and family emotional value on local brands reveals that Yemeni consumers prefer local brand because of patriotism and emotional among the consumers, higher of Yemen, supported the findings by a number of previous studies[8],[7]. Significant impact of family and intention on actual purchase of local brands indicates that the Yemeni consumers are more emotional oriented rather than functional value for shopping. The significant positive impact of local product brand on purchase intention of global and local brands reveals that the Yemeni consumers may buy global or local brands regardless of how they perceive the brand.
9. Conclusions and Implication
- The present study concludes that the factors namely trust, advertisement and purchase intention directly influence actual purchase of local product brand in Yemen. And also trust, advertisement and family directly influence the purchase intention in the case of local brands. Intention, trust and advertisement are the other important predictors of the actual purchase. Family is other important predictor of purchase intention. The study provides valuable implication for the existing Yemenis brand. The local and foreign companies are advised to focus on trust, advertisement and family in order to make a great appeal on their product. The advertising campaigns could impact emotionally appealing messages stressing the trust of local brands. While projecting the products features they are advised to focus on improving the self concept of the consumers. Yemeni companies are advised to go for aggressive strategies to improve the customer’s perception on local brands in terms of quality and trust value like “Be Yemeni; buy Yemen”, “proud to be a Yemeni”. The strategic alliances, licensing agreements or joint ventures are the important strategies to sell the local brand under global brand name with higher status and quality.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We would like to thank Prof Dr. Nik Kamariah Nik Mat, Dr Abdullah Swidi and Sukma Pea for their helpful comments and assistance on an earlier version of this paper.
References
| [1] | Yemen Economic Report 2008 www.comtrade.un.org, Central Bank of Yemen annual report, 2008. |
| [2] | Al-Smeh,Abdul Hafiz, Cabinet Secretary–General, Monday 29–March-2010, Alomtamer net. |
| [3] | Batra R, Ramaswamy V. Alden DL, Steenkamp J-BEM, &Ramachander S. Effects of brand local and nonlocal origin on consumer attitudes in developing countries. Journal of Consumer Psychology 9(2): 83-95, 2000. |
| [4] | Wang CL Chen TX, “Consumer ethnocentrism and willingness to buy domestic products in a developing country are setting testing moderating effects “Journal of Consumer Marketing 21(6): 391-400, 2004. |
| [5] | Zafar U. A, Johnson P. J, & Boon, L. C. Does country of origin matter for low-involvement products? International Marketing Review. Vol. 21 No. 1, 2004.pp. 102-120. Emerald Group Publishing Limited, 2004. |
| [6] | Dmitrovic, T, Vida, I, Reardon, J, “Purchase behavior in favor of domestic products in the West Balkans ”, International Business Review 18 (2009) 523–535, 2009. |
| [7] | De Cannière, M. H, De Pelsmacker, P, & Geuens, M. “ Relationship Quality and the Theory of Planned Behavior models of behavioral intentions and purchase behavior” Journal of Business Research 62 (2009) 82–92, 2009. |
| [8] | Rawwas, M.Y.A., Rajendran, K.N. and Wuehrer, G.A. “The influence of worldmindedness and nationalism on consumer evaluation of domestic and foreign products”, International Marketing Review, Vol. 13 No. 2, pp. 20-38, 1996. |
| [9] | Nazlida, M. H & Razli, C. R. “ Consumer Ethnocentrism: The Relationship With Domestic Products Evaluation And Buying Preferences ”.IJMS 11(SPECIAL ISSUE), 29-44(2004). |
| [10] | Zolait, A. H. S , Mattila, M & Sulaiman, A,“The effect of User’s Informational-Based Readiness on innovation acceptance” International Journal of Bank Marketing Vol. 27 No. 1, 2009 pp. 76-1, 2009. |
| [11] | Al-Motwakl and Al-Laozi, “In conference under the industry calling program (made in Yemen)”19-11-2008.almotamer.net/news/61260.htm, 2008. |
| [12] | LrenaVida and James Reardon. “Domestic consumption: rational, affective or Normative choice?”, Journal of Consumer Marketing 25/1 (2008) 34–44 q Emerald Group Publishing Limited[ISSN 0736-3761, 2008. |
| [13] | McEachern, M. G, Schroder, M.J.A, Willock, J, Whitelock, J and Mason, R. “Exploring ethical brand extensions and consumer buying behavior: the RSPCA and the “Freedom Food” brand” Journal of Product & Brand Management 168–177, 2007. |
| [14] | Farah, F. Maya, Andrew J, and Newman. “Exploring consumer boycott intelligence using a socio-cognitive approach”. Journal of Business Research.xxx (2009). |
| [15] | Al-Majali, M, M, & Nik. Kamariah Nik Mat, “ Application of planned behaviour theory on internet banking services adoption in Jordan: Structural equation modelling approach”, China-USA Business Review, V 9, No 12, December 2010ISSN 1537-1514,USA, 2010. |
| [16] | Lee, J, Cerreto, F. A., & Lee, J. Theory of Planned Behavior and Teachers' Decisions Regarding Use of Educational Technology. Educational Technology & Society, 13 (1), 152–164, 2010. |
| [17] | Ajzen I &Fishbein M. Understanding attitudes and predicting social behavior. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall; 1980. |
| [18] | Ajzen,I. & Fishbein, M. Attitude-behavior relations: a theoretical analysis and review of empirical research & psychological Bulletin, 84(5), 888-918, 1975. |
| [19] | Kotler, P., and Armstrong, G. Marketing Essentials, New York: Prentice Hall, 2009. |
| [20] | Sirdeshmukh, D., Singh, J., Sabol, B. "Consumer trust, value, and loyalty in relational exchanges", Journal of Marketing, 66:1, pp. 15-37, 2002. |
| [21] | Harris, L.C. and Goode, M.M.H. "The four levels of loyalty and the pivotal role of trust: a study of online service dynamics", Journal of Retailing, 80:2, pp. 139-158, 2004. |
| [22] | Ganesan. "Determinants of long-term orientation in buyer-seller relationships", Journal of Marketing; 58, 2, pp. 1-19, 1994. |
| [23] | Rousseau, D.M., Sitkin, S.B., Burt,R.S., Camerer, C. "Not so different after all: A cross-discipline view of trust", The Academy of Management Review, 23:3, pp. 393-404, 1998. |
| [24] | Chen, Yen-Hao H and Corkindale, D, “Towards an understanding of the behavioral intention to use online news services An exploratory study ”, Internet ResearchVol. 18 No. 3, pp. 286-312, 2008. |
| [25] | Gwo-Guang Lee and Hsiu-Fen Lin, “Customer perceptions of e-servicequality in online shopping”, International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management. Vol. 33 No. 2, 2005 pp. 161-176, 2005. |
| [26] | Jiming Wu and De Liu, “The Effects of Trust and Enjoyment on Intention to Play Online Games”, Journal of Electronic Commerce Research, VOL 8, NO 2, 2007. |
| [27] | Granzin, K, Janeen E. and Olsen, “Americans’ Choice of Domestic over Foreign Products: A Matter of Helping Behavior?” Journal of Business Research 43, 39–54 ã 1998 Elsevier Science Inc, 1998. |
| [28] | Bhardwaj, S, and i Palaparth, I. “An Empirical Study on the Factors influencing the Buying Behavior of the Consumers: LCD Televisions.2008 The Icfai University Press, 2008. |
| [29] | Safiek Mokhlis, Ab Razak Kamaruddin and Md. Nor Othman, “Understanding How Malaysian Consumers Formulate Their Ethnocentrism Orientation: Do We Love Our Products?” Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Management Conference, 2001, 491-504, 2001. |
| [30] | Erdener Kaynak, Orsay Kucukemiroglu, Akmal S. Hyder. “Consumers' country-of-origin (COO) perceptions of imported products in a homogenous less-developed country”, European Journal of Marketing,Vol. 34 No. 9/10, 2000, pp. 1221-1241, 2000. |
| [31] | Nadia Huitzilin Jiménez Torres & Sonia San Martín Gutiérrez. “The purchase of foreign products: The role of firm’s country-of-origin reputation, consumer ethnocentrism, animosity and trust". Burgos (Spain). Documento de taboo. Vol: 13. Issue: 07. Dated October 2007. http://www3.uva.es/empresa/documentos.php. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML