-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
July, 2012;
doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20120001.11
Customer Retention Structural Model of Direct Selling Employees
Lee Wen Chiat , Nik Kamariah Nik Mat , Nooraini Saidin , Nur Hazirah Md Ludin , Hafnida
Othman Yeop Abdullah Graduate School of Business, Universiti Utara Malaysia, Sintok, 06010, Malaysia
Correspondence to: Nik Kamariah Nik Mat , Othman Yeop Abdullah Graduate School of Business, Universiti Utara Malaysia, Sintok, 06010, Malaysia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
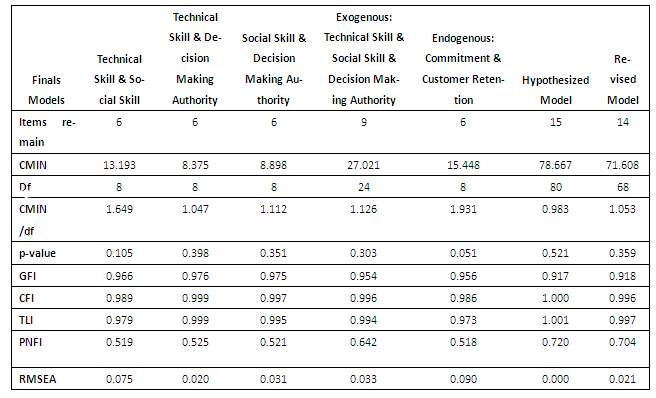
Customer orientation of service employees is seen as important success factor for gaining customer retention in Gano Excel, a direct selling company in Malaysia. The objective of this study is to understand how customer orientation (CO) of service employee (SE) can affect the commitment (COM) and customer retention (CR). A structural model of all the variables was developed for the study. Each variable is measured using 7-point interval scale which is grouped into 3 exogenous latent variables: technical skills (3 items), social skills (3 items), and decision making authority (3 items); and two endogenous latent variables: commitment (3 items) and customer retention (3 items). The responses collected were 119 completed questionnaires whereby, 2 respondents were deleted due to outliers problem (D2). The data was analyzed using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) through AMOS7. Confirmatory factor analysis of measurement models indicates adequate goodness of fit when 1 item was eliminated through modification indices verifications. Goodness of fit for the revised structural model shows adequate fit a[GFI=0.918, P-VALUE=0.359, RMSEA=0.021 and ratio (cmin/df) =1.053]. This study has established four direct significant and positive causal effects: (1) technical skill and commitment; (2) social skill and commitment; (3) technical skill and customer retention and (4) commitment and customer retention. The findings are discussed in details.
Keywords: Customer Retention, Direct Selling Employees, Commitment, Customer Orientation , Service Employee
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Direct selling companies or direct retailing companies in Malaysia is a diversified business with sizeable product categories. The direct selling companies have become a significant distribution channel within the country’s total retailing system. According to World Federation of Direct Selling (WFDSA) Statistics published in 2011, direct selling business in Malaysia has retail sales about RM6.8 billion (approximately 0.89% of GDP in Malaysia) and has a population of about 4.25 million direct sales distributors or sales people in Malaysia (more than 10% of Malaysian total population) in 2010. This shows that the direct selling business has a bright prospect. Customer loyalty or customer retention towards a product or service is critical to the world of relationship marketing especially in direct selling business. Hennig-Thurau[1] explains that there is a positive relationship between customer relationship and customer orientation approaches. This means if the company emphasized more on customer orientation approaches or treats the customers well, the customer relationship will be better and companies can retained customers. However, some companies neglect the customer orientation approach in doing business. This leads to reduction of customer retention towards businesses or organizations. Furthermore, limited studies have focused on the effect of customer orientation model on customer retention in direct selling business. Thus, the objective of this study is to examine the effect of customer orientation model on the customer retention in direct selling business.
2. Literature Review
- In the customer orientation service employee’s model developed by Hennig-Thurau[1], there are three exogenous variables inside the orientation service employee namely technical skills, social skills and decision making authority which affect the commitment and also customer retention.
2.1. Technical Skill and Commitment
- Technical skill is referred to knowledge or technical skill which the firm needs to fulfill during the process of providing good services to the customers[2]. Commitment is defined as customer’s enduring desire to continue and willingness to make efforts at maintaining a relationship with a service provider[3]. Past studies showed that technical skill has a significant positive relationship with commitment[1], [4]. Hence, this study proposes the first hypothesis as:Hypothesis 1: Technical skills have a positive effect on commitment.
2.2. Social Skills and Commitment
- Social skill is the ability to interact in three types of dimensions which are visually, cognitively and emotionally [1]. Past studies showed that social skill has a significant positive relationships with commitment[1],[4]. Thus, the following hypothesis is proposed:Hypothesis 2: Social skills have a positive effect on commitment.
2.3. Decision Making Authority and Commitment
- Bowen & Lawler[5] and Spreitzer[6] stated thatdecision-making authority is related to the empowerment concept intensively discussed in services literature. Past studies showed that decision making authority has a significant positive relationship with commitment[1],[4]. Hence,hypothesis three is developed as:Hypothesis 3: Decision making authority has a positive effect on commitment.
2.4. Commitment and Customer Retention
- Past studies showed that commitment has a significant positive relationship with customer retention[1],[4]. We thus hypothesized:Hypothesis 4: Commitment has a positive effect in customer retention.
2.5. Technical Skills and Customer Retention
- Customer retention is defined as the rate of customer retention can be measured by the percentage of customers who continuously buying the services or products over a finite period of time[7]. Past studies showed that technical skills have a significant positive relationship with customer retention in online travel agencies and media retail services [1].Hypothesis 5: Technical skills have a positive effect on customer retention.
2.6. Social Skills and Customer Retention
- Past studies showed that social skill has a significant positive relationship with customer retention[1].Hypothesis 6: Social skills have a positive effect on customer retention.
2.7. Decision Making Authority and Customer Retention
- Past studies showed that decision making authority has a significant positive relationship with customer retention[1].Hypothesis 7: Decision making authority has a positive effect on customer retention.
3. Methodology
- A conceptual framework is formed based on the three variables in customer orientation service employees’ model and the effects of them towards commitment and customer retention. This model was derived from Hennig-Thurau[1] model. A total of 200 questionnaires were distributed to the Gano Excel direct selling company’s staff. Only 119 questionnaires were collected back from the respondents. The 3 items scale for technical skills, social skills, decision making authority, commitment and customer retention in the questionnaire were adapted from Hennig-Thurau[1], whereas the data was analyzed using AMOS and the results of structural Equation Modeling (SEM) and goodness of fit are obtained.
|
4. Results
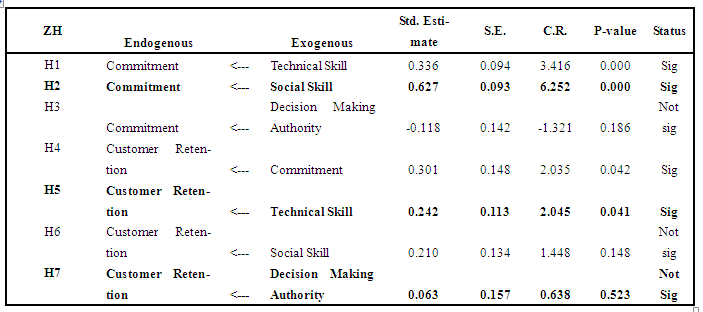
- In Table 1, the goodness of fit indices of all exogenous, endogenous variables and revised structural model achieved good fit (according to these benchmarks of GFI>0.90, cmindf ratio < 2, rmsea <0.08, p >0.05) (Hair et al. 2010). There are four (4) significant relationships found in the customer retention structural model. The first hypothesis (H1) is supported when technical skill has a positive significant relationship with commitment (β=.336, critical ratio=3.416, p=.000). Hypothesis 2 (H2), is also supported when social skill has a significant effect on commitment (β=.627, critical ratio=6.252, p=.000). Hypothesis 4 (H4) betweencommitment and customer retention is also accepted (β=.301, critical ratio is 2.035, p < 0.05). It explains that commitment has a significant positive effect on customer retention. Technical skill has a significant positive relationship with customer retention in hypothesis 5 (β=.242, critical ratio is 2.045, p-value is 0.041). However, the third hypothesis (H3) is rejected. The p-value is 0.186; more than 0.05 and critical ratio is -1.321. Decision making authority has insignificant negative effect (the beta value (β) is -0.118) on commitment. Meanwhile, hypothesis 6 is rejected which implies that social skill does not have significant effect on customer retention (p-value is > 0.05 and critical ratio is 1.448). The beta value is 0.210 which shows social skill has positive relationship with customer retention though it is not significant. Finally, there is also no significant effect between decision making authority and customer retention in hypothesis 7 (p-value > 0.05) and critical ratio is 0.638. The beta value, 0.063 in hypothesis 7 shows that decision making authority has positive effect on customer retention though it is also not significant.
|
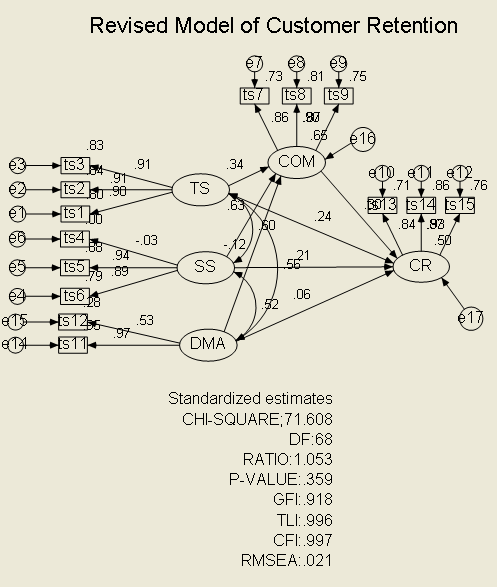 | Figure 1. Revised Model of Customer Retention |
5. Discussion
- The main findings of this study indicate that technical skill and social skill both are important ingredients forsalesperson’s commitment. Previous studies had found similar results[1-4]. It seems that for sales staff to be committed with their challenging task as salespeople, they need to be knowledgeable and friendly. It confirms the marketing theory that relationship marketing is a vital factor in buying the share of the hearts of the customers. Consequently, commitment and technical skill are significant predictors of customer retention. Several past authors support this notion[1],[4],[7]. Apparently, salespeople can be retained when they are highly committed and knowledgeable. Customers will be more trusting when the salespeople can explain the products and services with conviction and devotion. However, decision making authority has no significant effect on both commitment and customer retention. This could imply that salespeople mostly work independently, thus making decision making authority unnecessary. Most salespeople nowadays is not monitored like in olden days due to modern electronic communication such as internet, emails, mobile/internet i-phones, computers, on-lineordering, purchasing and reporting. Place and time become insignificant as long as targets are achieved and immediate feedback could be done daily.
6. Conclusions
- This study has established four significant direct causal effects: (1) technical skills and commitment; (2) social skills and commitment; (3) commitment and customer retention and (4) technical skills and customer retention. This study is without its limitation. For instance, salespeople from only one direct selling company was taken as the samples for the study. The research model also is limited to five factors only, small sample size and small number of items measuring each latent variable. Future research should increase the sampling frame to include more direct selling companies from various regions and to include other factors as well as increasing the number of items to measure each latent variable.Underpinning theory such as technology acceptance model (TAM) could be utilized since salespeople are independent staff depending mostly to new technology knowhow for effective communication. Furthermore, direct salespeople are performance based on commissions rather than permanent employees based on salary. Hence, these factors could contribute to new gap for future research.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The heading of the Acknowledgment section must not be numbered.SAP Productions wishes to acknowledge all thecontributors for developing and maintaining this template.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML