-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Economics
p-ISSN: 2166-4951 e-ISSN: 2166-496X
July, 2012;
doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20120001.03
Studying the Trends of Policy Research in Policymaking Environment
Rahmatollah Gholipour , Gholamrea Jandaghi
University of Tehran, Iran
Correspondence to: Rahmatollah Gholipour , University of Tehran, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The aim of this research is to study the trends of policy research in policymaking environment. In this line, a model by Dukeshire and Thurlow is utilized. Their model consists of four aspects including identifying the problems and difficulties, understanding main problems, supporting selected actions and the impacts of assessment and control process. In a descriptive survey among policy research agencies in Iran, Research Center in Iranian Parliament was selected as statistical community. Among 120 members of the community, 40 subjects were selected randomly. Needed data were gathered and analyzed by SPSS software. According to findings on each four aspects, there is significant difference between quo status and ideal status. It means that policy research activities in statistical community lack necessary effectiveness in policymaking environment.
Keywords: Policy Research, Policymaking, The Trends Of Policy Research
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Policy research is a way to make policies scientific. However, it is not a new knowledge and has been already existed. Since policymaking and lawmaking should be performed by scientific tools and techniques due to the complicated nature of public problems; so, it needs a research approach. Today, public problems and difficulties have complicated and multidimensional nature so that one can not find a proper way (law or policy) to resolve them without a scientific study. Therefore, while establishing a relationship between knowledge and policies, various ways should be utilized to make policies scientific. To create a proper relation between policymaking arena and knowledge/science field and making policies scientific, three methods are suggested: 1. Involving scientific elites in the positions of policymakers and lawmakers. 2. Involving scientific elites as the counselors of policymakers and lawmakers.3. Utilizing policy research method to make policies scientific. The first two suggestions have no practical or scientific possibility since it is not possible to involve only scientific elites in the positions of policymakers and policymaking bodies consist of trustees of people not necessarily community scientific elites. On the other hand, it is unlikely to use scientific counselors regularly in all fields and all times. However, third suggestion is more feasible. In this method, policies are investigated by research bodies before selection. Policy research is a bridge between policymakers and thinkers of various sciences to optimize devised policies in order to accelerate social development. Policy research is a scientific (rather than political) method to study policymaking procedure. It can provide policymakers with scientific recommendations by its profound looking.
2. What is Policy Research?
- Policy research is the process of studying an important social problem or analyzing it in order to provide policymakers with scientific recommendation to resolve the problem (Levine, 2004: 3). Policy research is to apply scientific researches in policymaking by which one can identify social problems, collect sensitive data, devise concepts and assumptions and, more importantly, cause the credit of research before policymakers (Oreszcyn & Carr, 2004: 480). Policy research is to use research in politics by which researches are applied and the relationship between academic disciplines and public policymaking sectors are expanded (Wilhelm, 2009: 5- 6).
3. The Type of Research in Policy Research
- The research has various categories. Albert Cherns identified four types of research:1. Pure basic research.2. Basic objective research, oriented toward a problem which arises in some field of application of the discipline, but is not aimed at prescribing a solution to a practical problem. 3. Operational research, aimed at tackling an ongoing problem within some organizational framework but which does not include or involve experimental action.4. Action research (Thomas, 1985: 8).
4. Policy Research Characteristics
- Policy research is multidimensional. Typically, public policies are looking for complicated social problems consist of some aspects, factors, effects and causes. Policy research uses inductive – empirical approach. Policy research starts with social problems and looks for conceptual experiences and scientific theories during social problem study. Policy research focuses on flexible variables. Policy research should concentrate on affectability and intervention in order to provide practical and executable recommendations. Policy research responds the users of the study. An important trait of policy research is to recognize such users as an initial step in policy research process. These various users have different expectations, agendas, values, assumptions and needs. Policy research involves values. It has many values by which the origins of decisions in study are various and even contradictory values (Majchrzak, 1984: 15 – 17)
5. The Policy Research Process
- Like policymaking, policy research goes on during different stages. by considering, one can define research policy process in a final conclusion. Preparing: in this stage, preliminary information should be gathered and the methods of data collection and decision making on problems of policy research are defined (Majchrzak, 2000: 18). Conceptualization: it means to select a theoretical base in studying social problems. It includes three fundamental initiatives: • Building social problems initial model• Devising research-based questions• Selecting the researchersTechnical analysis: in a technical analysis, policy researcher studies the factors which may be the origin of a public or social problem. Recommendation analysis: this stage addresses the way of providing and executing suggestions obtained in technical analysis sector. Results Shift. Devising final recommendations does not mean policy approval necessarily. While policy researcher can not establish a dynamic and trusting relation with policymaker, the best recommendations will not change to politics. (Gholipour, 2008: 268).
6. Research Conceptual Model
- In this study, the model provided by Dukeshire & Thurlow is applied to review the trends of policy research in policymaking environment. It consists of four aspects: identifying problems and difficulties, understanding main problems, supporting selected action plans and the impacts of assessment and control process.
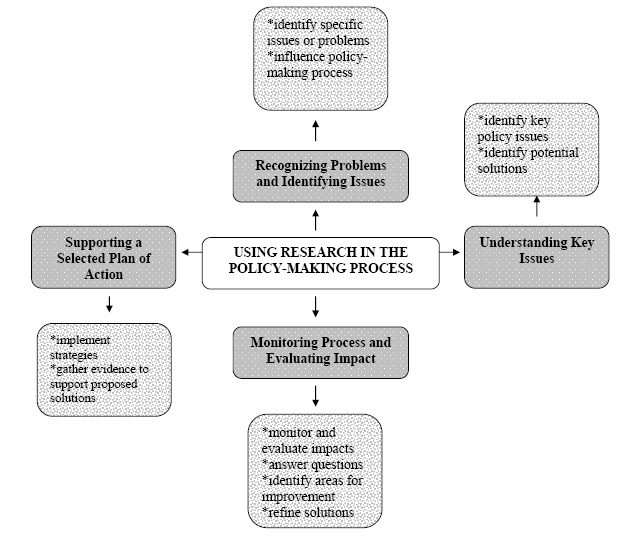 | Figure 1. Research conceptual model |
6.1. Major Hypothesis
- There is significant difference between status quo and ideal status of research trends in policymaking environment.
6.2. Main Hypotheses
- 1. There is significant difference between status quo and ideal status in recognizing the problems and difficulties. 2. There is significant difference between status quo and ideal status in understanding main problems.3. There is significant difference between status quo and ideal status in supporting selected initiatives.4. There is significant difference between status quo and ideal status in assessment and control process.
6.3. Methodology
- Regarding applied aim and the method of data collection, it is a descriptive-survey research. It is descriptive since it represents a picture of status quo and it is survey since it collects data via sampling to study the distribution of statistical population characteristics. As mentioned in literature, policy research bodies in Iran include Research Center in Iranian Parliament, Research Center in Guidance Council and the Secretariat of Expediency Council. Since the research is performed in just on organization, it is a case study. Used tool to collect data was questionnaire. A twelve-item questionnaire was obtained from Dukeshire & Thurlow model. Since it was going to compare status quo and ideal status, a bilateral questionnaire with Likert five-item scale was considered. The validity and reliability of the questionnaire was examined in mentioned organization. According to academic and organizational connoisseurs, the validity of the questionnaire was ideal. Its reliability (chronbach alpha) was calculated 0.896 which was acceptable.
6.4. Statistical Population and Sample
- The statistical population of the research consists of 120 of managers, experts and researchers in Parliament Research Center. Randomly, 40 individuals were selected as statistical sample.
7.Findings
- The findings were studied in the format of a descriptive and inductive statistics. Since demographical variables were used as categorization measure in variance analysis test, these variables are described here summarily. The first variable was organizational position. Our sample included 15 managers, 20 researchers and 5 experts. 12 respondents have Ph. D., 24 have M.A and the rest have M.A. in terms of service years, 24 respondents have more than 5 years working experiences, 11 respondents have between 2 – 5 years of working experiences and the working experiences of four persons are less than 2 years. Finally, 18 respondents have regularly attended in Parliament commissions, 4 persons have no experience in this regard and 18 respondents have sometimes attended in such commissions. The descriptive statistics regarding the status quo and ideal status on research trends in policymaking environment is shown in table 2.
7.1. Hypothetical Test
- H0: There is not a significant difference between status quo and ideal status of research trends in policymaking environment.H1: There is significant difference between status quo and ideal status of research trends in policymaking environment.To review research hypotheses, the mean test of two depended groups are utilized. The results of testing major hypothesis are indicated in table 3.
|
|
|
8. Discussion and Conclusions
- Policy research is a new knowledge to make policies scientific which ties science and political actions arenas by using research scientific methods. The scope of policy research is the arenas where decisions are made to resolve public problems. Regarding the diversity of fields, the methodology of policy research also differs. So, the research is useful when a proper method to make the recommendations functional. In this line, some characteristics are represented by Weiss (1980), Grember (2005) and Dukeshire (2002). According to Levine, the existence of some elements in researches to make them profitable is vital. These elements include research application, agents and research product. Dukeshire & Thurlow believe that a research is effective if performed in a four-stage procedure. They include identifying the problems and difficulties, understanding main problems, supporting selected initiatives and control and assessment process. By testing this model in research statistical population (Iranian Parliament Research Center), it was concluded that there is a significant difference between ideal status (research effectiveness in policymaking environment by using above procedures) and status quo. It means that policy research in statistical population is not effective in policymaking environment. By reviewing the reasons of status quo, one can point out following factors: 1. Lack of experience (about one decade) of policy research in Iranian Parliament Research Center2. Low experiences of researches and experts on policy research 3. Inadequate attention to research scientific procedures in policy research environment4. Weak interactive relationship between policy research and policymaking bodies5. Emergency difficulties and public problems by which there is no enough time for research in policymaking environment.The results of this research and other similar ones show that the role and positions of policy research in policymaking environment is moderate. It has resulted into devising policies that are mainly ineffective and inefficient. So, it is recommended in this research to utilize the mentioned model in policy research process.
Notes
1A research in the format of graduate thesis by Mr. Ghasemi in Qom Pardis Management College, Tehran University. Its results show that thinking locus has the lowest role in policymaking process.
References
| [1] | Morss, R. E.2005.” Problem definition in science public policy”, American Politics Research.Vol.2, pp. 181-191. |
| [2] | Grebmer, K.V.2005. “Converting policy research into policy decisions: the role of communication and the media”. Available atwww.ifpri.org/divs/cd/dp/vonGrebmer200401.pdf |
| [3] | Levine, B.2003.” Improving Research-Policy Relationships: Lessons from the Case of Literacy”. University of Mainitoba Winnipeg. pp. 1-29 |
| [4] | Levine, B.2004.” Bridging research and policy in international development”. Available at publications@odi.org.uk |
| [5] | Brown, L. D., & Bammer, G., & Batliwala. S., & Kunreuther., F.2003.” Framing practice-research engagement for democratizing knowledge”. Action Research.Vol.1.pp.81-102. |
| [6] | Dukeshire, S and Thurlow, J.2002. “Understanding the Link between Research and Policy”, Rural Communities Impacting Policy project, Vol.18, pp. 1-18. |
| [7] | Majchrzak, A.1984.” Technical analysis. In Methods for Policy Research”. Sage: Beverly Hills. |
| [8] | Majchrzak, A.1984. “Methods for policy research”, published by sage. |
| [9] | Thomas, p. p.1985.” The aims and outcome of social policy research”. Published Taylor & Francis. Vol.114 |
| [10] | May, H. 2004. “Making statistics more meaningful for policy research and program evaluation “. American evaluation association. Vol. 25. pp. 525- 540. |
| [11] | Saunder, & Fine, M.1995.” Evaluation and research in social policy”. Social policy research center. Vol.62.pp. 1-31. |
| [12] | Wilhelm, T. 2009.” Strange Bedfellows: The Policy Consequences of Legislative Judicial Relations in the American States)”. American Politics Research Vol. 37. pp. 3- 29. |
| [13] | Majchrzak, A., 2000, “the methods of policy research (research to policymaking)” translated by Hooshang Naeini, Tehran, Tabian Publications. |
| [14] | Gholipour, Rahmatollah, 2008, “organizational decision-making and public policymaking”, Tehran, Samt Publications. |
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML