-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Diabetes Research
p-ISSN: 2163-1638 e-ISSN: 2163-1646
2020; 9(2): 29-42
doi:10.5923/j.diabetes.20200902.02

Impact of Sensor Networks towards Individuals Augmenting Causes of Diabetes
Md. Rahimullah Miah1, Md. Shahariar Khan2, AAM Shazzadur Rahman3, Alamgir Adil Samdany4, Mohammad Abdul Hannan5, Shahriar Hussain Chowdhury6, Alexander Kiew Sayok7
1Head, Department of Health Information Technology, Northeast Medical College & Hospital Pvt. Limited, Sylhet, Bangladesh
2Md. Shahariar Khan, Department of Paediatrics, Northeast Medical College & Hospital, Sylhet, Bangladesh
3Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Northeast Medical College & Hospital, Sylhet, Bangladesh
4Professor and Head, Department of Orthopedics, Northeast Medical College & Hospital, Sylhet, Bangladesh
5Assistant Professor, Department of Endocrinology, Northeast Medical College & Hospital, Sylhet, Bangladesh
6Professor and Head, Department of Dermatology, Northeast Medical College & Hospital, Sylhet, Bangladesh
7Associate Professor and Associate Researcher, IBEC, Universiti Malaysia Sarawak (UNIMAS), Sarawak, Malaysia
Correspondence to: Md. Rahimullah Miah, Head, Department of Health Information Technology, Northeast Medical College & Hospital Pvt. Limited, Sylhet, Bangladesh.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Diabetes is a complex, chronic illness and progressive non-communicable disease related with remarkably high levels of blood glucose. Yet Medical experts are facing the undesirable augmenting causes of diabetes towards human body as a very important global issue for several years. The study aims to assess the applications of the wireless sensor networks that affect on pancreas within and around the individuals body boundary. Qualitative and quantitative wireless sensor data were obtained from field experiments and secondary data were poised from various sources. The study represents the urinary flow speed fluctuates with association of infection due to misuse of wireless sensor networks towards pancreas at light and dark environment. The research also focuses the more effective augmenting causes of diabetes in dark than light environment. The findings replicate the implication in diabetes through operative prevention and medication that the State provides, which fails to improve due to abusing wireless sensor networks. The study also found the urban hospitals are in risks due to insecure sensor technology. Scientific healthcare awareness is essential for management with modern technological device but such awareness is still below par, which is alarming to individual’s health. Overall, the study contributes to the diabetes society through development of dynamic health care technology framework indicating effective solutions on free from diabetes. The study suggests future research trajectories of a new sophisticated alternative secure treatment approach to promote healthcare and well-being linking with National Policy and Sustainable Development Goals 2030.
Keywords: Diabetes, Wireless sensor, Pancreas, Hospital, Network security and Environment
Cite this paper: Md. Rahimullah Miah, Md. Shahariar Khan, AAM Shazzadur Rahman, Alamgir Adil Samdany, Mohammad Abdul Hannan, Shahriar Hussain Chowdhury, Alexander Kiew Sayok, Impact of Sensor Networks towards Individuals Augmenting Causes of Diabetes, International Journal of Diabetes Research, Vol. 9 No. 2, 2020, pp. 29-42. doi: 10.5923/j.diabetes.20200902.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Diabetes is a serious and long-term condition that happens when there are elevated points of glucose in an individuals’ blood because their body cannot produce any or enough of the hormone insulin, or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces (IDF, 2019). Almost 463 million adults within aged 20 -79 years were living with diabetes and 79% of adults with diabetes were living in low and middle income countries (IDF, 2019). Over four million people aged 20-79 years are assessed to die from diabetes related causes in 2019 (IDF, 2020). Radiation and electromagnetic waves are being identified in health problems due to update sensor (Ozdemir and Kargi, 2011). Further advances in wireless sensor networking have unlocked up new scenarios in healthcare systems (Priya et al., 2013). This network is actually valuable in several medicare applications, which can be inserted into human body for healthcare services (Chaudhary and Waghmare, 2014; Abidi et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2017). Now different aging society involves extensive medical resources, which have triggered a collective capacity of scarcities. Sensor networks are planned to fulfill the scarcities like measurement, tracking, detection and data classification, particularly the field of healthcare. A synchronized amount of medical technologies have been arranged for patients who suffer from severe disease or have urgent prerequisites. Current and traditional medical methods cannot meet the requirements of patient needs in a timely fashion. Flexible and wearable health-monitoring provides a revolutionary technology, which serves as an alternative to traditional diagnosis methods, putting healthcare data on a path that is more remote, portable, and timely (Kim et al., 2011; Gao et al, 2016; Wang et al., 2014; Sheridan, 2014). These healthcare data can be used by a physician to evaluate body condition like diabetes with an artificial intelligence (AI) deep-learning algorithm (Zang et al, 2015; Zhao et al, 2008; Vu and Kim, 2018). Sensor technology has a great advantages on non-communicable diseases to identify the classical symptoms. High blood sugar produces these symptoms of polyuria, polydipsia and polyphagia (Mazid, 2019). Diabetes is a chronic progressive debilitating disease that occurs when the pancreas is not adequately enough able to produce insulin or when the body cannot utilize the insulin that produces inside the human body due to insulin resistance (IDF, 2019; WHO, 2018). This disease is a pancreatic disorder, whose prevalence is increasing day by day (Murray and Lopez, 1996; Mazid, 2019). The effects of the disease have spread rapidly to the human body from the last 20 to 25 years, which has not increased this much in the history of the world in any other decade. The main reason is the misuse of mobile technology with global positioning systems and global navigation satellite systems. The mobile phone is intimately involved with the body, without which we are not. Diabetes is a noninfectious disease. Many people are suffering from this disease, especially as the frequency of radio frequency is increasing. For example, regular painful conditions in the body - unhealthy eating, western lifestyle (Control and Control, 2011; Deedwania and Fonseca, 2005), unhealthy eating system, unhealthy liver function, pancreas not working easily, abnormal bodily obesity and obesity, genetic problems and abnormal blood cholesterol, high blood pressure and physical weakness, Beyond the effects of diabetes, excessive abuse of radio frequency, abnormal thirst and hunger, sudden urinary pressure and urination immediately become cloudy. The causes of diabetes are: (1) radio frequency consumption, (2) obesity, (3) birth, (4) genitalia, (5) pancreatic abnormalities, (6) liver abnormalities, (7) irregular eating and living conditions. Several review papers have summarized the progress of flexible electronic devices and their applications in health-monitoring (Takei et al., 2015; Zang et al., 2015; Lou et al., 2018; Khan et al, 2016; Zhang et al., 2018; Li et al., 2019). Human body with diabetes has an augmented risk of increasing a number of severe health problems (Peiris, 2013; O'Donovan et al., 2009). Moreover, people with diabetes have an increased risk of developing a number of serious health problems (Bilal and Kang, 2017). Diabetes is a condition that impairs the body’s ability to process blood glucose (Nall, 2019). Consistently high blood glucose levels can lead toahigh risk affecting the heart and blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, nerves and teeth (IDF, 2019). According to WHO (2018) that the adults with diabetes have a two to three fold augmented risk of the major cause of heart attack and strokes(Goharimanesh et al., 2015).The study finds out the new innovations with interdisciplinary approaches to solve the core challenges in health sector to enhance the national and global perspectives on non-communicable diseases. The aim of the study is to observe of the applying a sensor network towards the diabetes as an impact within the body boundary to identify the patient’s urinary infection status. This study attempts to make an assessment of the policy and sensor technology towards impact of non-communicable diseases activities with alternative policies and update implications of wireless sensor for Sustainable Development Golas2030, particularly diabetes disease.
2. Research Methods
- This research method was conducted at as PhD research work from October 2014 to October 2017 at the Universiti Malaysia Sarawak (UNIMAS), Malaysia. The method was connected with different parameters to enhance data collection, ISNAH Experiment, Specimens Tracking Process, Data Analysis and interpretation as below:
2.1. Data Collection
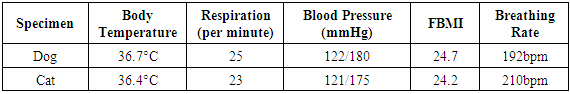
- All specimens were housed in a room with controlled temperature 36.4°C in cat and 36.7°C in dog with breathing rates, respiration, blood pressure and feline body mass index (Sha et al, 2019). The experimental design were randomly divided into three experimental groups with Body Mass Index: obese, normal and thin and observed the impact of wireless sensor networks towards pancreases among them in the light and dark environments. The study necessitates an integration of methods used in wireless sensor networks towards animals’ body and identified its implication. This envisaged the research taking in matter-of-fact research elements to investigate issue hoisted in the study, primarily targeted at SMART devices like telematics’ users towards specimens. Telematics is a smart device, consists of scanner, Global Positioning System (GPS) and Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). The fieldwork conducted in the studied area within January 2015 to January, 2017.
2.2. ISNAH Experiment
- Sensor technology consists with ISNAH Experiment. It implies the experiment on the Impact of Sensor Network on Animals and Human beings (ISNAH). The cyber tracker misuses sensor technology to augment non-communicable diseases among animals and human body (Kays et al., 2011). The study examined into two specimens, one is dog and another one is cat among 14 individuals for identification of this misuse application. These animals are available in the study area and suitable for experiment. The study selected sound health two species with Feline Body Mass Index (FBMI) and other following parameters (Waltham, 2017) as shown in Table 1.
|
2.3. Specimens Tracking Process
- Sensor networks track on animals and human beings, where contains in blood circulation and movement of electron. The ISNAH experiment interlinked electron through tracking process. This process included several steps which enhanced to fulfill the Sensored observation. The study was observed the physical conditions including non-communicable diseases of animals like diabetes affected by the telematics device through misapplication radio frequency through tracking process as shown in Figure 1. Different stages of Tracking Process of Radio Frequency towards animals are listed as below: (i) Selective communication devices, (ii) Searching object and scanning of individuals body organ, (iii) Identify body organ and light and dark environment, (iv) Sensored the specimens with high, normal and low radio frequency, (v) Observed and compared the specimens status, (vi) Feedback meeting and illustrated the consequences at result and discussion.
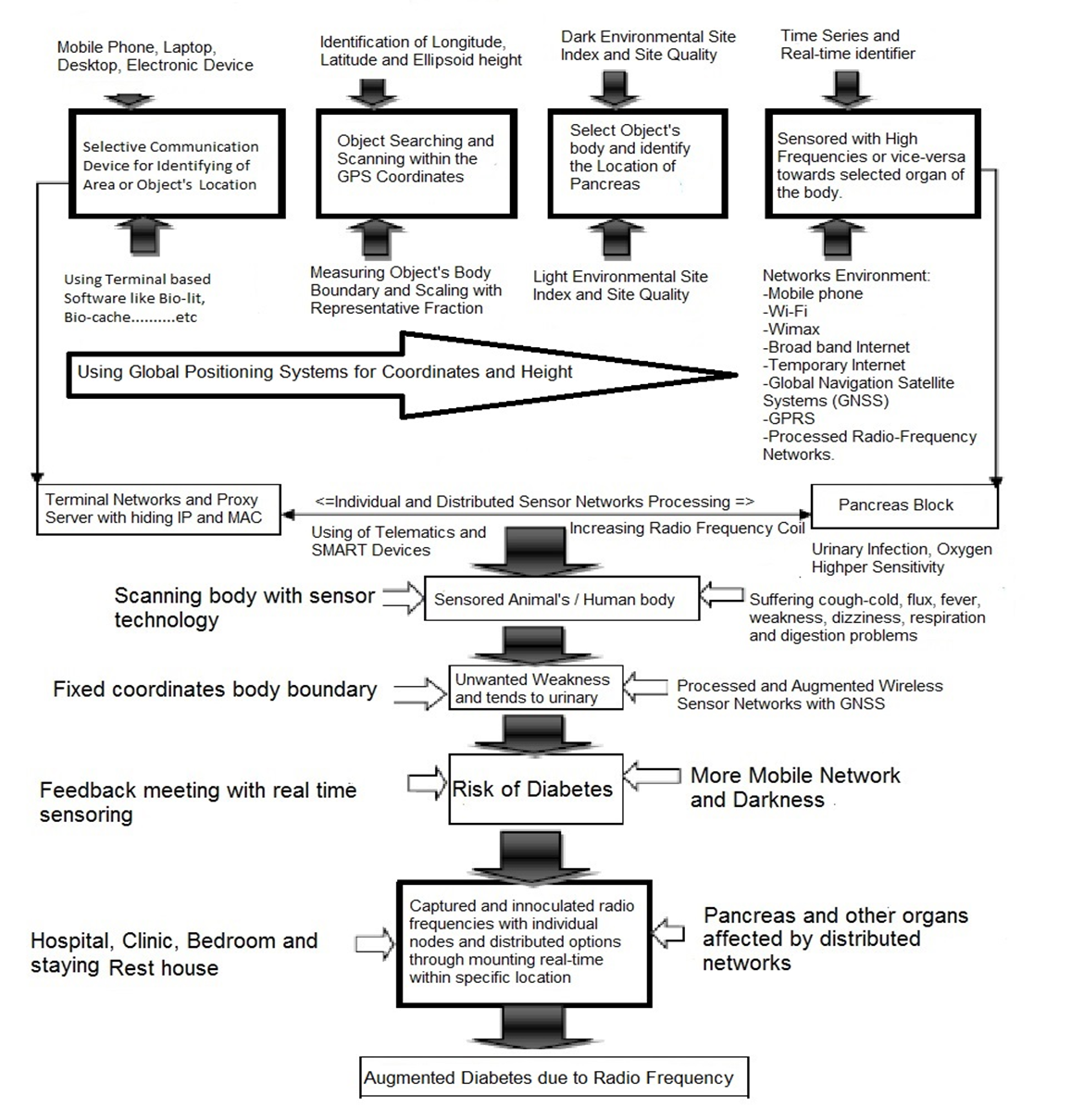 | Figure 1. Tracking Process of Radio Frequency towards Animals |
2.4. Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Quantitative and qualitative related bio-sensor data were obtained through field observation, interviews, field surveys and ISNA experiment while secondary data were obtained from diverse sources. All general information regarding the occurrence of specimens, status and affected condition were checked for accuracy from the different sources and sources of information were also verified. Information regarding the initiatives of the authority towards the geographic locations was collected through relevant secondary information and field survey. The compiled and processed data were involved in the preparation of data master sheet and assimilated into suitable systems used in the results and other segments consecutively. The data were compiled and analyzed for presentation and interpretation using standard data analysis software like MS Office Suite 2016 and SPSS version 26.
3. Results
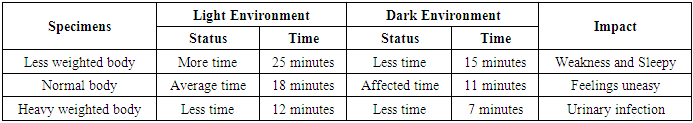
- From the study of misuse of telematics, it observed that the examined species- cat and dog were felt uneasy and after few moments, they sensed urinary infection within the body boundary, as a whole, they were about to throw urinary substances. Immediately cell phone removed and disconnected the wireless sensor network from the study area. During medication time, the study also observed that both animals areweakness and felt pain at scatia and inactive pancreas separately. The study identified that the animals were suffered fromurinary infection and fluctuated body temperature. The radio frequency also affects on tracking effective time to animals, which as shown in Table 2.
|
3.1. Dark Environment
- The wireless sensor network is prone to active in dark environment towards dog and cat. This sensor is more effective towards obese dog within 5 minutes and obese cat within 7 minutes affected to the whole body, particularly pancreas, which as shown in Figure 2.
 | Figure 2. Sensor Affected Time at BMI conditions at Dark Environmental Condition |
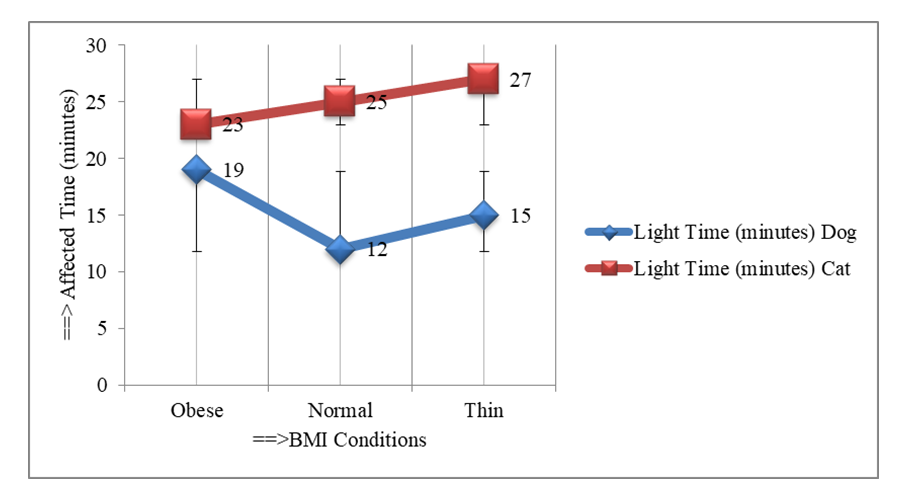
3.2. Light Environment
- Awareness on diabetes at studied specimens on cat and dog within the affected time can be estimated using the equation developed through regression analysis. Here the study expressed the approach through ther following equation,
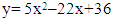 | (1) |
 | (2) |
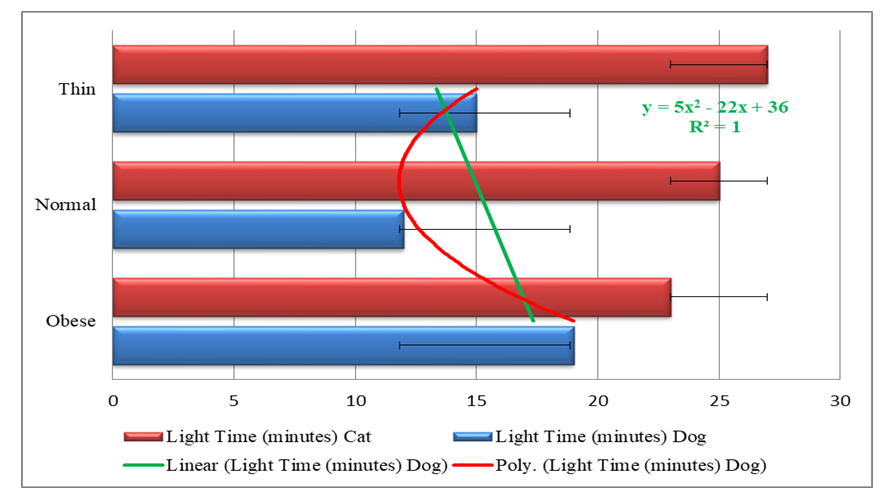 | Figure 3. High Radio Frequency affected on pancreas of different BMI Animals in light conditions |
3.3. Combined Dark and Light Environment
- The study was observed that the examined specimens could not breath properly after 15 minutes and 7 minutes of exposure respectively in the dark environment. They fell asleep within 25 minutes and 12 minutes respectively as they were sensored by RFID as shown in Figure 4.
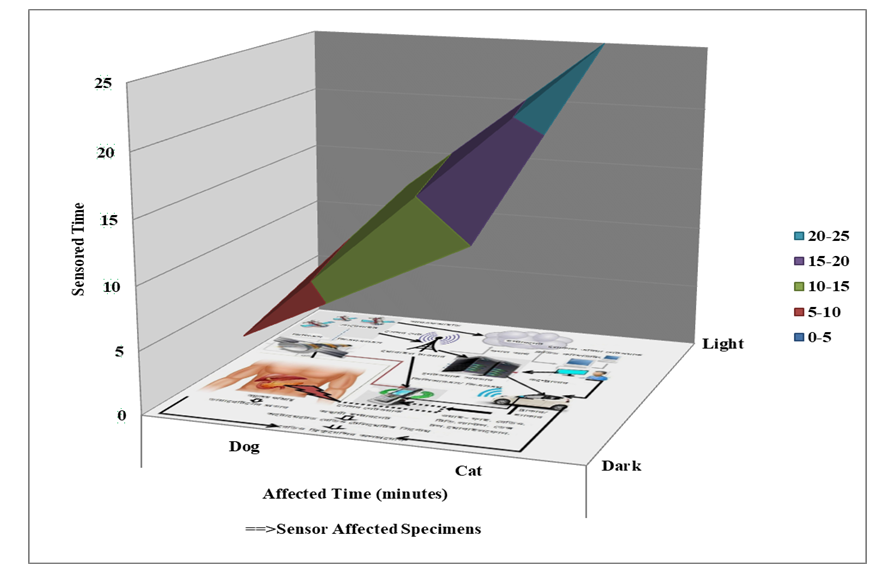 | Figure 4. Tracking Affected Time towards Animals at Dark-Light |
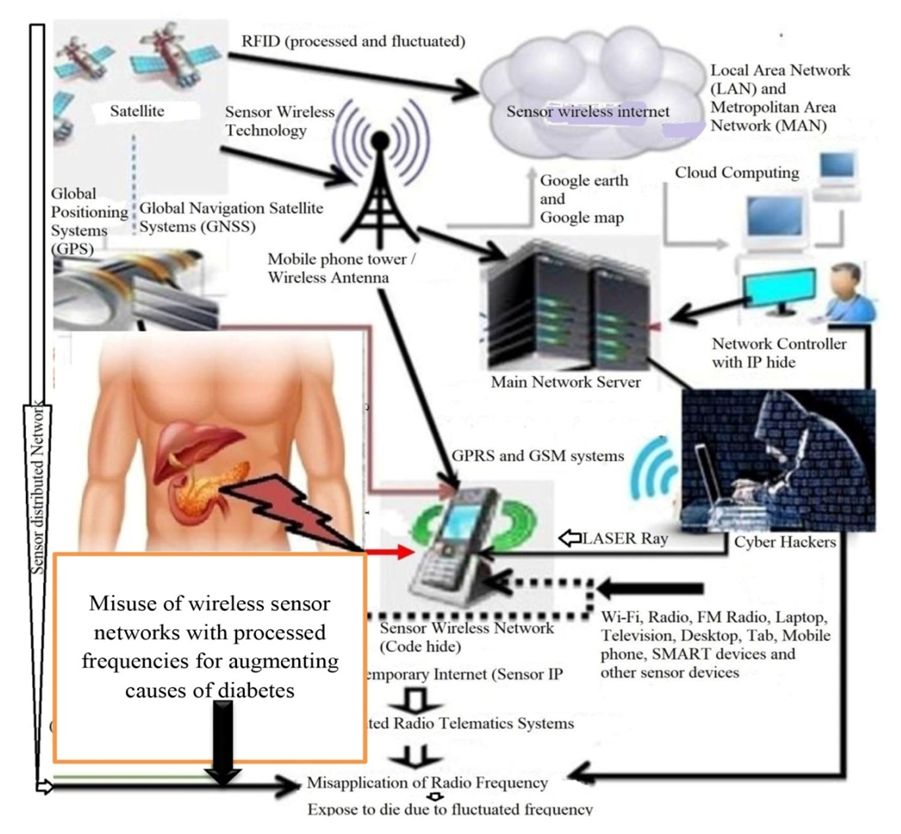 | Figure 5. Radio Frequency Affected on Body Anatomy |
3.4. Radio Frequency Affected on Body Anatomy
- The study also suggested for improvement of biodiversity conservation policy in connection with modern technology, BCHM and further trajectory research. The way of information is processed through the telematics technologies that the study was examined, along with the digitalization and abstraction of observation analysis, reconfigures space and time in National Park Area. Further investigation is required into how telematics track on wildlife through transmitting server data from satellite to captured location within the stipulated distance for conserving of biodiversity require even more attention in misuse technology.
3.5. Participants’ Perception
- From field observation, most of patients have little idea on the security system of sensor technology. The study regarding security systems stated on participant’s perception among three categories including secured security system, restricted location and no comment. The study showed that about 96% opined for secured security systems, 3% restricted location and 1% no comment (Figure 6). The experiment was going on two animals, namely dogs and cats, in different steps. During the experiments, the study used different radio frequencies at different distances and ellipsoid heights through smart phone and telematics devices. Prior to the experiment, the experiment calculated individual body mass index (BMI), body temperature, respiratory rate and blood pressure to confirm the health of each animal and to check for disease-free animals. In this regard doctors, nurses, intern medical students assisted in this examination.
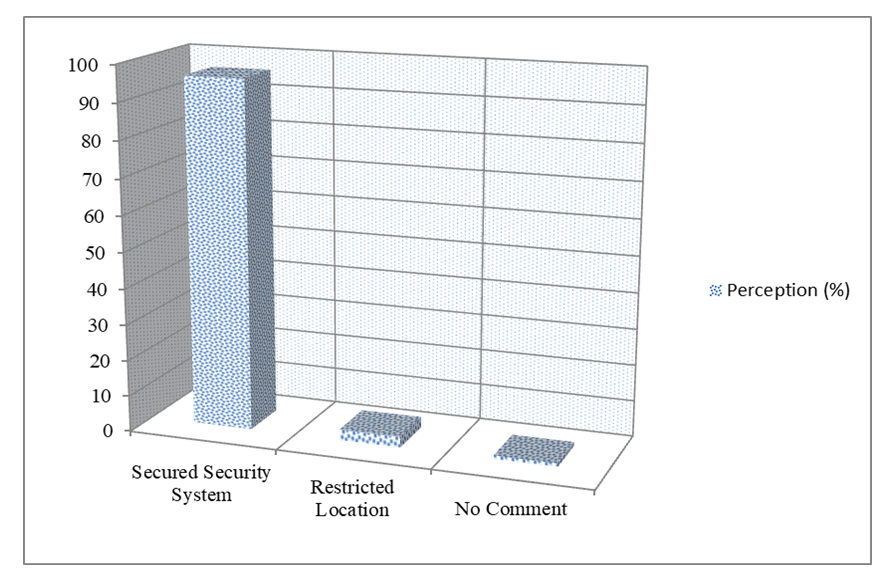 | Figure 6. Security perception of wireless sensor network among participants |
4. Discussion
- The findings of the study on impact of sensor networks towards augmenting causes of diabetes in connection with animals and humans body felt frequent urination with terminal dribbling. The study also represents the urine flow speed fluctuates with infection due to misuse of wireless sensor networks. The findings reflect the importance in diabetes through prevention and treatment that the physicians provide, which fails to recover due to access abusing sensor network’s envirtonments. The study demonstrated the signs of augmenting causes of diabetes in the dark and light environment within BMI status. In the dark environment, the obese people are more vulnerable than normal and thin individuals and vice versa in the light environment. The study illustrates to test the radio frequency of patients’ coordinates by RFID detectors with GPS locations, whether the actual radio frequency pressure was abnormal in the body of those suffering from diabetes due to abuse of radio frequency. This is known through the radio frequency detector with the application of GPS towards pancreas and scartia. The GPS devices recognize body boundary of patients, beside the mobile phone in them. If the patients need to check radio frequency within 6 feet, the lab technicians /specialists should never allow mobile phone, Wi-Fi, wireless device or even internet connectionor any relevant sensor devices. The RFID test can compare to the radio frequency of adjacent space. If the relative frequency of sensored body fluctuates, then the concerned person is suffering from diabetes by abusing the radio frequency, otherwise, the patient is normal either urban or rural hospitals, clinics or dwelling places. The study also found the urban hospitals are in risks due to insecure sensor technology than that of rural due to more mobilephones and SMART devices users. Moreover, due to the above mentioned devices, reports identified by RFID technology may be changed. On the other hand, no words can be indicated when analyzing the tested data; It can be recorded and edited by sensor technology. Where diabetes patients sleep or rest, they need to be in a Personal Area Network Control Unit (PANCU) or non-networked locations using anti-radiation and zammer devices. In the same way, if no higher scale is detected after the urine test, we should keep in mind that we should be more than 7 feet away from our own beds, dining tables, reading tables, office tables, and bathrooms and story telling areas. It should not put mobile phone under the pillow in the bed - as an alarm clock; as well as wireless access to the bedroom should always be prohibited. Many diseases occur in people including heart disease, kidney disease, tuberculosis, eye diseases, complications during pregnancy, oral complications due to misuse of radio frequency. So we need to be careful about using modern wireless sensor technology to prevent diabetes and other diseases. In addition, some changes in eating habits, such as ending dinner within 8 pm and should not sleeping in bed immediately after dinner. Before going to bed, one cup of bitter carrot should be consumed, sleeping on the right shoulder and never using a mobile phone in bed. However, there are some gaps in diabetes control management on the priority of using mobile technology and adopting policy. The cutting-edge and augmented control policy over diabetes was pursued to explore. The considered model is one of the anticipated diabetes models, which cogitated the conditions of diabetic patient. There are uncertainties due to risk factors such as excessive mobilephone using in bedroom, daily late meals and sudden stresses. In addition to different approaches towards the elimination of these uncertainties, distinct diabetes control policies could be conducted to monitor mobilephone using within coordinates location (Goharimanesh et al., 2015). Orthodoxical control policies over insulin infusion rates, were impotent to keep the blood glucose concentration in the anticipated radio frequency range, due to its multifaceted and non-linear environment (Dazzi et al., 2001; Grant, 2007).
4.1. Treatment
- Safeguarding signal is used to augment diabetes treatment emphasizing the imperative connections between diabetes and universal health coverage humanizing access to insulin with a view to strengthening global fighting to reduce the impact of diabetes for individuals, their families and society (IDF, 2019). Diabetes is a debilatating disease that none can treat easily one’s at a time. There are several options for diabetes treatment, such as: psychological treatment, medical treatment, technological treatment, herbal treatment, environmental treatment, ethical treatment, nutrtional treatment and administrative treatment. The physician will assist the patient s in diabetes treatment options that is appropriate for individuals. The patients may also need other health care professionals on his/her diabetes treatment team including foot doctor, nutritionist, eye doctor and an endocrinologist. The improvement of diabetes team management has been still sluggish; observed in different health care facilities. Meanwhile various performances are below par. For this purpose, scientific healthcare sensor knowledge is indispensable for treatment with modern technological arena but such knowledge is poorly identified. The input uniqueness of research findings of health care services should influence the impact of sensor networks within body boundaries used to deal with them. If the assessment of diabetic control services is allowed without due to reflection of technological information implicated, there is a huge jeopardy of distinctive sensor network only in significant impacts near to the pulverized usefulness.Further patients with diabetes live in urban than in rural areas due to global technological urbanisation. This means equates to a prevalence of 11.9% in 2030 and 12.5% in 2045 (IDF, 2020). Earlier diabetes –related mortality almost 4.2 million adults aged 20-79 years are estimated to die as a result of diabetes and its complications, which is equivalent to one death every eight seconds and associated with 11.3% of global deaths from all causes among people in this age group (IDF, 2019). So, designing of efficient biosensors for sensitive and selective measurement of specific biomarkers, is a significant step for the primary disease diagnosis, treatment, and management (Babamiri et al, 2019). However, intensive monitoring can facilitate future research to make better treatment decision-making in the creation of environmentally fundamental and innovative instruments. Lastly, the study suggests future diabetes research trajectories of a new commonancillary approach to effort the methodological agenda and recommendations on ways to further incorporate the challenging the diabetes control instruments towards wireless sensor network management.Self-management for people with diabetes is a significant part of effectively preventing or postponing diabetes complications (IDF, 2019). The psychologists give pleasure the patients uplift on 80% psychological and 20% medical treatment, which enhance diabetes recovery. The endocrinologists treat the diabetes patients according to the diagnosis and chief complaints with peripheral medical supplements. The diabetes patients use mobile technology to treat diabetes on the restricted extreme radio frequency. The ayurvedic doctor can treat the patient with herbal medicine like aloe vera, cinnamon, bitter melon, milk thistle, fenugreek, gymnema, ginger, ivy’s gourd, salaciaoblonga (Moradi et al., 2018). Moreover, all physicians advise them regards with dwelling places are neat and clean with patient-friently environment. The diabetes patients are also satisfied ethically in connection with religious activities to follow regularly. They are taking nutritional elements regularly to fullfil the food stuff supports, which are available in the society and alternative options ((Forouhi et al., 2018). The policy-makers and physicians develop the update national health policy in connection with National Health Policy and Sustainable Development Goals 2030. When any patient affects on diabetes suddenly, that patient should move the existing location quickly towards above 6 feet distances from the self body boundary. The new sensors, alternating arrays of printed light-emitting diodes and photodetectors, can detect blood oxygen levels in any part of the body. The sensor uses light-emitting diodes to emit red and near infrared light, penetrating the skin and detecting the proportion of reflected light (Khan et al., 2018); The sensor made of biodegradable materials utilizes edge-field capacitance technology to monitor arterial blood and then transmits the data wirelessly (Boutry et al., 2019). Moreover, the patients should continue regular monitoring of the risk factors for diabetes complications and early intervention results in reduced hospitalizations and improved clinical outcomes (IDF, 2020) through effective sensor technology.
4.2. Diabetes Control Model
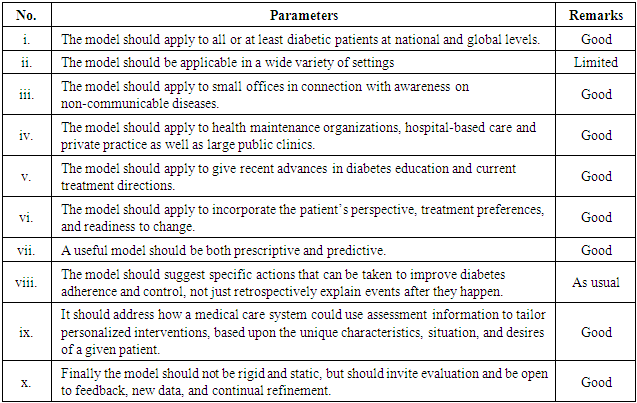
- Sensor network focuses on the analysis and review of the present tools to enhance diabetes control model using status of mobile phone in order to provide justifiable policy optionsby the use of smart advanced technology. Diabetic individual needs tight control of his blood glucose (Ding and Schumacher, 2016). Diabetes treatment consists of diet, exercise, ethical perception and medication (Azizi et al., 2007). Medications and exercises as prescribed by the doctor are a must to control diabetes (Khan and Palma, 2018). Diabetes is a progressive disease, which is very tough to controll through individual treatment. Diabetic affected persons need to securely control their blood glucose concentration according to requirements (Ding and Schumacher, 2016). For dynamic treatment, integrated control model is necessary for the present and upcoming generations. Good control of blood sugar prevents complications of diabetes (Frier, 2014; Burge et al., 2008). Controlling seven places for sustainable non-communicable disease manament, which is to prevent the state-of-the-art of various aspects of wireless body area sensor network (Khan and Pathan, 2018). A good model can be very practical and provide important guidelines for treatment, clinical use and research directions. Jargon-filled and esoteric theoretical models that are not easily understood by most health care professionals will do little to advance the field of diabetes care (Glasgow, 1995). In contrast, a good and practical model of diabetes management and education that is relevant to the above issues should satisfy some or all of the following criteria in Table 3.
|
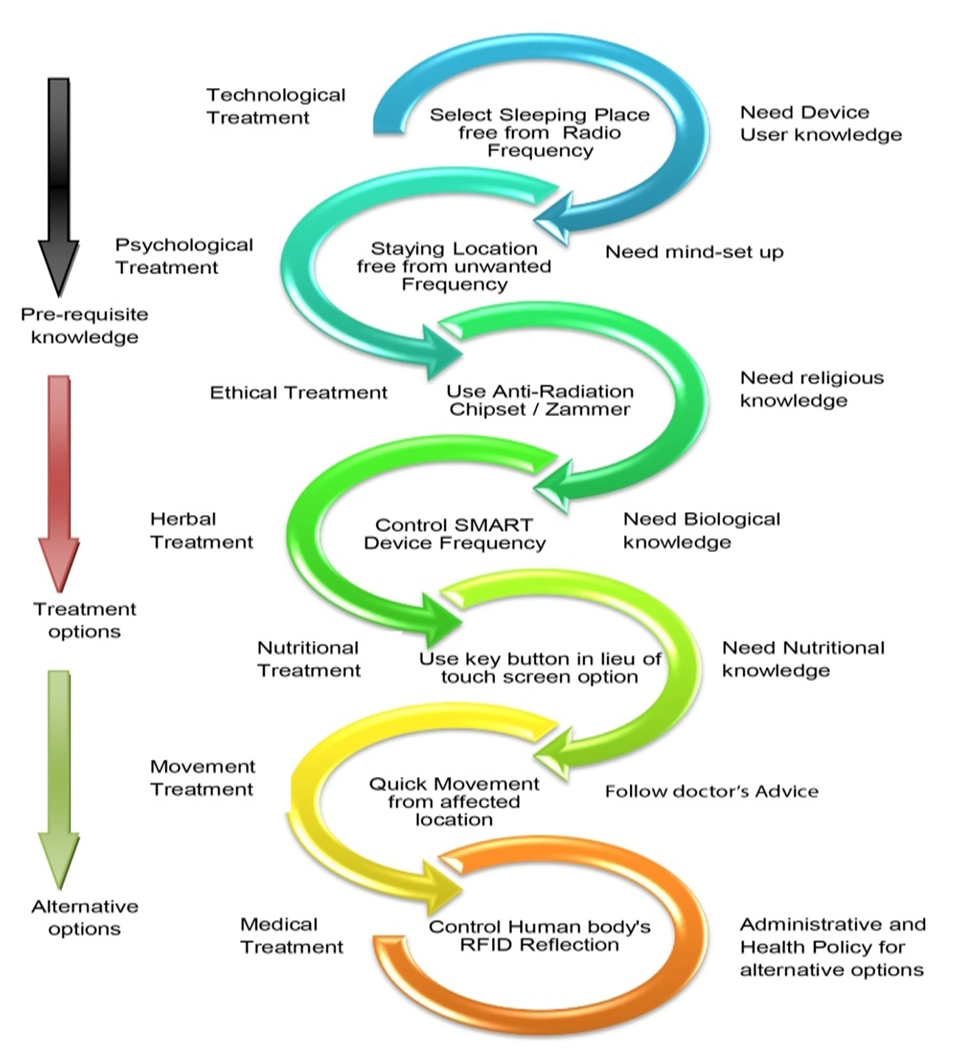 | Figure 7. Diabetes Control Model |
4.3. Economic Impact of Diabetes Due to Over-Exploitation of Technology
- Human body affects with different diseases due to misuse of sensor networks particularly diabetes-related chronic kidney disease. This chronic disease is linked with considerable surplus health expenditure (IDF, 2019). For people with diabetes undergoing dialysis, the mean annual healthcare cost increased 2.8 times compared with End-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients not on dialysis (Li et al., 2013). The health costs of detection and treatment of diabetes-related complications are high. All of the complications of diabetes, both acute and long-term, contribute significantly to the overall economic impact of the condition (IDF, 2020). Despite its impact characterized by premature mortality and lower quality of life due to diabetes related complications, diabetes also imposes a significant economic impact on countries, health systems and, when healthcare needs to be funded ‘out-of-pocket’, for individuals with diabetes and their families (ADA, 2018; Peters et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2012). The economic impact of diabetes is expected to continue to grow due to augmenting of health expenditure in the successive year due to misapplication of sensor technology. It is anticipated that expenditure will reach US $825 billion by 2030 and US $ 845 billion by 2045, which represents an increase of 8.6% and 11.2% respectively (IDF, 2020). Moreover, update technology hikes more prices in the monopoly market to share with psychological lucrative behaviour.
4.4. Security
- The global people are facing the effective sensor security. Sensor Network Security (SNS) is a prime concern according to web threats (Agarwal and Hussain, 2018). Infrastructure-less architecture and integral desires of SNS might pretense some weak points that fascinate diverse stakeholders. Consequently, sensor security is a big apprehension when SNSs are arrayed for special requirements at healthcare. Owing to their unique characteristics, traditional security methods of computer networks would be useless (or less effective) for WSNs. Hence, lack of security mechanisms would cause intrusions towards those networks. These intrusions need to be detected and mitigation methods should be applied. More interested readers would refer to Butun et al.'s paper (Butun et al., 2014), regarding intrusion detection systems devised for SNSs. Furthermore the aggregators can introduce false data into the summative and show the improper situational agreement with false data. Thus, while data aggregation improves energy efficiency of a network, it complicates the existing security challenges (Butun et al., 2015). In this case, with the direct cooperation of the mobile phone companies and government, which will be more viable and significant. The study should demonstrate in harmony with suitable technology and health policy with Sustainable Development Goals 2030 for reconciliation between different cell phone companies and departmental agencies.
4.5. Challenges for Effective Diabetes Treatment
- Adherence to most diets in the longer term is an important challenge (Johnson et al., 2014). Some areas of uncertainty and controversy remain and further research is needed to resolve the diabetes complications (Forouzanfar et al., 2015). The key security challenges in locked data accumulation are privacy and veracity of data. Though encryption is usually recycled to deliver end to end concealment in wireless sensor network, the cyber hackers in a threatened data accretion consequences pre-requisite to decrypt the encoded data to perform aggregation. The current cyber world faces a number of challenges for empirical dynamic technological policies due to unwanted phishing, pharming, scamming, spoofing, false interfacing and misuse tracking. Mainly, the study is alarming that matters such as national policy can be effectively executed at the local government and department levels in cyber world; which would to need sectorial/departmental ICT policies integration. Even if individuals do not have a mobile phone, they may become ill suddenly due to misuse radio frequency. As if they are standing somewhere waiting for a car or bus. Within 5 meters of their locations, mobile phone hackers applied high radio frequencies to their standing place via a remote mobile phone. Individuals must change their locations immediately as their experiences a frequent urination. Otherwise they will suffer due to staying existing coordinates. They need to be more aware of their situations. For examples, (1) the bed in which someone sleeps, will never use a cell phone, laptop devices etc., or (2) the bed someone sleeps in, when they have a sneezing, coughing, or any such facial air movement, then they quickly leave the bed. The study would request to replace the another location, (3) quickly remove the polluted air from their body to the other place without getting into bed; they cannot be done properly. If needed, use a signal or silent mode, (4) if individuals are in bed or in the closet, leave the bed quickly and go somewhere else. After breathing ten / twelve times, if they are in a previous state, go to the bathroom, otherwise stay in same location. These parameters are challenging to fulfill without free from wireless sensor networks.
5. Conclusions
- The study has assessed the impact of wireless sensor networks towards pancreas for causes of diabetes. The obese individuals are affected quickly on diabetes in the dark environment and vice versa to the others. Based on this study, human body is not secured due to misuse of wireless sensor networks with body boundary coordinates in the existing environment. However, the study has attempted to develop a complete scenario of the augmenting causes of diabetes due to reflect high radio frequency. The findings of this research clearly indicate that insecure telematics and excessive misuse of smart devices among rationalized generations, and traditional health policy in connection with national and global perspectives are important sources for the causes of non-communicable diseases. Moreover, everyone uses mobile phone for advanced communication but none can aware of its security systems. The research has also illustrated the dynamic tools that strengthen the potentialities of wireless sensor networks to integrate mobile phone users in decision-making and promote medical jurisprudence. Finally, the impact of radio frequency on the human body should be publicized through social media, print media, electronic media and others to extend consciousness.
Declarations
- FundingThis research work is a part of PhD Thesis, which was funded by the Zamalah Postgraduate Scholarship of UNIMAS, Malaysia and also sponsored by the Information and Communication Technology Division, Ministry of Posts, Telecommunication and Information Technology, Government of People’s Republic of Bangladesh. The funders had no role in the design of the research, in data collection, analyses or final interpretation of data, in the writings of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the findings.Data AvailabilityThe data are being used to support the findings of this research work are available from the corresponding author upon request. Competing InterestsThe authors declare no potential conflict of interests in this research work.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors acknowledged the authority of Universiti of Malaysia Sarawak (UNIMAS), Malaysia for providing the Zamalah Postgraduate Scholarship for the completion of PhD degree. The authors are also grateful to the authority of the Information and Communication Technology Division, Ministry of Posts, Telecommunication and Information Technology, Government of People’s Republic of Bangladesh, for PhD Fellowship during the higher study in Malaysia.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML