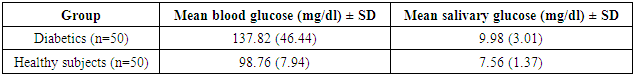-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Diabetes Research
p-ISSN: 2163-1638 e-ISSN: 2163-1646
2017; 6(3): 63-67
doi:10.5923/j.diabetes.20170603.03

A Comparative Study of Glucose Levels in Blood and Saliva of Type 2 Diabetic Patients of Balkot
Karki Prabin Kumar1, Maharjan Niroj2, Shrestha Saroj3, Silwal Sanzee4
1Department of Physiology, Kathmandu Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal
2Department of Physiology, KIST Medical College, Lalitpur, Nepal
3Gorakh Medical & Diagnostic Center Pvt. Ltd., Bhaktapur, Nepal
4Balkot Dental Clinic, Bhaktapur, Nepal
Correspondence to: Karki Prabin Kumar, Department of Physiology, Kathmandu Medical College and Teaching Hospital, Kathmandu, Nepal.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2017 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

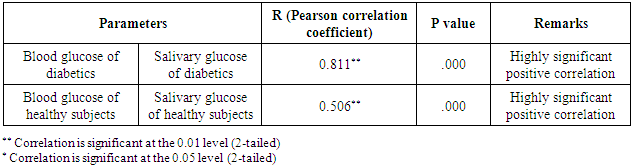
Background and objective: The increasing trend in prevalence of diabetes mellitus around the world is alarming. Glucose levels in diabetic patients should be regularly monitored to minimize the diabetic complications. The purpose of the present study was to study the correlation between salivary and blood glucose levels. Awareness and knowledge about diabetes and perception on blood glucose maintenance among study population was also assessed. If a close correlation were to exist, diabetic control could be monitoed by the noninvasive method of measuring salivary glucose. Methods: Age matched 50 diabetic and 50 healthy non-diabetic individuals were included in the study. Structured questionnaire was used to know the educational status and knowledge about diabetes mellitus. Estimation of serum and salivary glucose levels in fasting state were carried out by Glucose Oxidase Peroxidase (GOD-POD) method, using semi-automated machine. Results: Higher percentage of diabetic patients had good knowledge and perception about diabetes and blood glucose maintenance than healthy subjects. Among diabetics mean salivary glucose level was 9.98±3.01 mg/dl. This was much higher as compared to non-diabetic individuals (7.56±1.37 mg/dl). Mean salivary glucose levels were found to be significantly correlated with mean blood glucose levels of diabetics (r= 0.811) and non diabetics (r= 0.506). Conclusion: This study suggested that saliva may become an alternative to blood for lab diagnostic procedures if further extensive studies are done in future.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus, Salivary glucose, Non-invasive
Cite this paper: Karki Prabin Kumar, Maharjan Niroj, Shrestha Saroj, Silwal Sanzee, A Comparative Study of Glucose Levels in Blood and Saliva of Type 2 Diabetic Patients of Balkot, International Journal of Diabetes Research, Vol. 6 No. 3, 2017, pp. 63-67. doi: 10.5923/j.diabetes.20170603.03.
1. Introduction
- With the increasing incidence of diabetes mellitus it is very important for the patients to have good knowledge about diabetes and its management. It is also important to know about patients’ perception about blood glucose maintenance. This will help to limit the complications related to diabetes mellitus.Saliva is a clear fluid secreted into the oral cavity by major and minor salivary glands. It is very important body fluid with large range of body functions. Nowadays saliva is used regularly to diagnose various endocrine disorders as well as autoimmune and infectious diseases [1]. Saliva consists of 99.5% water and 0.5% electrolytes, amylase, lipase, mucin, glycoproteins, glucose and antimicrobial enzymes [2-4].High risk of transmission of diseases like AIDS and Hepatitis to health care professionals has increased the demand of diagnostic tests that doesn’t require blood. These factors have encouraged scientists and researchers in developing new diagnostic methods which can be done easily at home with less risk. Lab diagnostic procedures which are done today regularly use blood and urine and hardly other body fluids like saliva. [5]. Saliva used as a diagnostic fluid can determine both local and systemic alterations [6].Salivary sample collection is an easy process that can be done with short training period. Sophisticated and costly equipments are not needed for collection of the fluid. Analysis of saliva has potential to become a cost-effective tool for the screening of large populations in future [7]. Various studies in the past have shown correlations between serum and saliva levels. We can collect multiple salivary samples from the same person at required time of period with ease [8].Regular monitoring of glucose levels in diabetic patients is an important aspect of diabetes management. Use of noninvasive and simple methods offers various advantages. There will be no fear of needle puncture which can increase the frequency of glucose estimation helping in good glycemic control [9, 10].The purpose of the present study was to investigate the relationship between salivary and blood glucose. If a close correlation were to exist, diabetic control could be monitored by the noninvasive method of measuring salivary glucose.
2. Methods
- This cross sectional study was done in confirmed type 2 diabetic patients and healthy non diabetic subjects attending Gorakh Medical & Diagnostic Centre Pvt. Ltd. Balkot, Bhaktapur. The study period was of 6 months, starting from October 2016 till March 2017. For this study total 100 subjects were selected randomly (50 type 2 Diabetics and 50 age matched healthy subjects). Individuals with past history of salivary gland surgeries, receiving radiotherapy around head & neck region, and taking medicines for long duration except for diabetes mellitus were excluded from study. All subjects were thoroughly informed about the study and written consent was taken. Helsinki guidelines were followed. Structured questionnaire was used to know the educational status, knowledge about diabetes mellitus and blood glucose maintenance.Collection of samples: Samples were collected in the morning after overnight fasting. Diabetic patients were advised to take their regular medicine.1) Saliva: - Approximately 2 ml of unstimulated whole saliva was collected in a sterile tube by spitting over a period of 5 minutes. Subjects were asked to rinse their mouth with clean water before saliva collection. Obtained salivary sample was analyzed immediately or stored in refrigerator, for no more than 2 hours. It was then centrifuged at 3000 RPM for 10 minutes. Obtained supernatant solution was analyzed for salivary glucose concentration.2) Serum: - Aseptic conditions were maintained. 2 ml of intravenous blood was obtained from median cubital vein of forearm, centrifuged at 3000 RPM for 10 minutes. Obtained serum was then analyzed.3) Serum Glucose and Salivary Glucose determination: - Serum and salivary glucose were assayed by use of Glucose Oxidase Peroxidase (GOD-POD) method. Semiautoanalyzer was used for assaying procedure.Methods of Statistical AnalysisStatistical analysis was performed by using the program SPSS 20. The results were evaluated by using Pearson correlation test to assess correlation between blood glucose and salivary glucose. Statistical significance was considered at P values <0.05.
3. Results
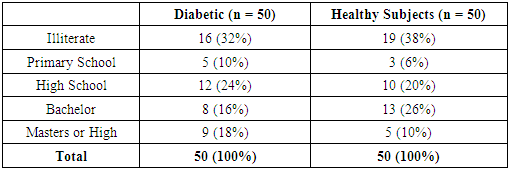
- The mean and standard deviation of age was 58.18 (10.13) years in diabetics and 54.08 (14.53) years in healthy subjects. There were 32 males and 18 females among diabetics and 26 males and 24 females among healthy subjects. 68% among diabetics were literate compared to 62% in healthy subjects. Based on the questionnaire diabetic patients were more aware about diabetes mellitus than healthy subjects. The mean blood glucose in diabetics was 137.82 (46.44) mg/dl and in non-diabetics 98.76 (7.94) mg/dl. Similarly mean salivary glucose & standard deviation of diabetics was 9.98 (3.01) mg/dl and that of non-diabetics was 7.56 (1.37) mg/dl. Mean salivary glucose level was higher in diabetics.
|
|
|
|
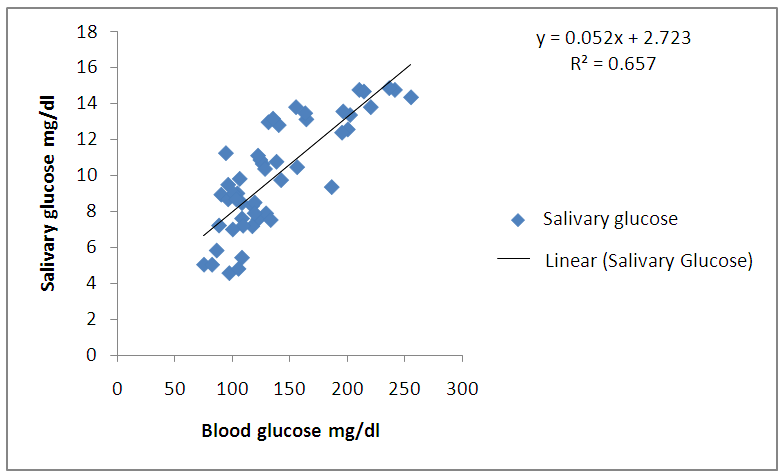 | Graph 1. Correlation between blood glucose and salivary glucose in diabetics |
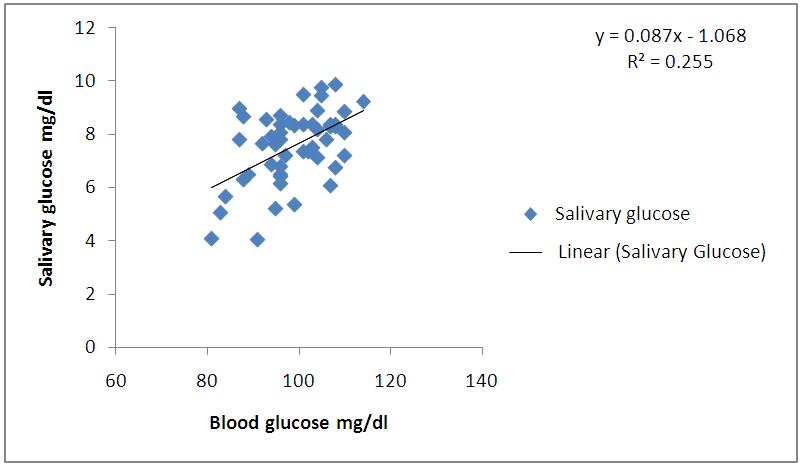 | Graph 2. Correlation between blood glucose and salivary glucose in healthy subjects |
4. Discussion
- A good knowledge and awareness of diabetes is a major determinant for control of diabetes mellitus. Patients should have positive attitude towards regular glucose monitoring so that future complications can be minimized. In Nepal only few studies have been done on knowledge about diabetes mellitus among subjects [11, 12]. In our study higher percentage of diabetic patients had good knowledge about diabetes mellitus. They were more positive towards monitoring of blood glucose than healthy subjects. The salivary glucose level in diabetic patients (9.98±3.01 mg/dl) was much higher as compared to healthy non- diabetic individuals (7.56±1.37 mg/dl). These results are in agreement with reports of other researchers who found the same increased levels of glucose in the saliva of diabetics [13-15]. Iqbal S et al and Vasconcelos ACU et al found significantly higher mean salivary glucose level in diabetic patients than that of control in a similar study [16, 17].Glucose is a small molecule which can easily pass through the blood vessels membranes to the fluid present in gingiva, and mixing in the saliva [18]. In the diabetic patients, glucose metabolic end products cause microvascular damages in blood vessels and basal membranes of salivary gland cells causing higher levels of glucose in saliva [19, 20]. However, in studies done by done by Vaziri PB et al and Hegde A et al no significant difference in salivary glucose concentration was found between diabetics and non -diabetics [21, 22].In the present study mean salivary glucose levels were found to be significantly correlated with mean blood glucose levels of diabetics (r=0.811) and healthy non diabetics (r=0.50). Consistent with this study, a significant correlation was found between salivary and blood glucose concentrations by Amer S et al in Karachi [13]. This finding is similar to other studies done by Jurysta C et al, Hedge A et al and Panda A et al [14, 22, 23]. These results have indicated that the concentration of glucose in saliva may depend on its concentration in serum.In contrast, some of the studies have contradicted the correlation between blood glucose and salivary glucose [17, 24, 25]. It was suggested that saliva may not be used to indicate blood glucose level in diabetics.The analysis of glucose level in saliva is an attempt to find a noninvasive and painless method for frequent monitoring of blood glucose in diabetic patients. Considering the high correlation obtained between blood glucose and salivary glucose, further research is required to establish it as a reliable diagnostic tool in future.
5. Conclusions
- On the basis of obtained results, we may conclude that there is a high correlation between blood glucose and salivary glucose. Saliva may be a potential diagnostic fluid in future. However, there are few issues that need consideration for further extensive research by increasingly sophisticated techniques.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML