-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Diabetes Research
p-ISSN: 2163-1638 e-ISSN: 2163-1646
2016; 5(6): 129-134
doi:10.5923/j.diabetes.20160506.02

The Potential of Apple Cider Vinegar in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
Joanna Morgan1, 2, Sapha Mosawy1, 2
1School of Medical Science, Griffith University, Gold Cost Campus, Queensland, Australia
2Menzies Health Institute Queensland, Griffith University, Gold Cost Campus, Queensland, Australia
Correspondence to: Sapha Mosawy, School of Medical Science, Griffith University, Gold Cost Campus, Queensland, Australia.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Type 2 Diabetes represents a large burden on public health systems worldwide. The chronic metabolic condition is characterised by hyperglycaemia and insulin resistance and is frequently associated with obesity, hypertension and dyslipidaemia. There is a growing need for effective management techniques of these conditions that patients can utilise complementary to conventional therapy. Apple cider vinegar (ACV) has been the subject of growing interest in this field. The main component of ACV, acetic acid, has demonstrated effectiveness in reducing hyperglycaemia, correcting dyslipidaemia and assisting weight loss. The dominant polyphenol compound in ACV, chlorogenic acid may also be useful in managing the condition.
Keywords: Apple cider, Diabetes, Vinegar, Hyperglycaemia, Dyslipidaemia
Cite this paper: Joanna Morgan, Sapha Mosawy, The Potential of Apple Cider Vinegar in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes, International Journal of Diabetes Research, Vol. 5 No. 6, 2016, pp. 129-134. doi: 10.5923/j.diabetes.20160506.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- In Australia 280 people develop type 2 diabetes each day which currently affects 1.7 million Australians. The burden on the public health system is estimated at $14.6 billion [1]. Type 2 diabetes, accounting for 85% of all diabetes, is a complicated chronic metabolic condition characterised by insulin resistance and eventually insufficient insulin production resulting in abnormal glucose metabolism. The condition is generally associated with obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, hypertension and dyslipidaemia. Type 2 diabetes significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. Management of the condition involves managing the risks of cardiovascular disease as well as managing blood glucose levels [2, 3]. Apple cider vinegar (ACV) may be able to play a role in the day-to-day management of type 2 diabetes as growing research has demonstrated that certain aspects of the beverage assist in controlling hyperglycaemia, as well as reducing cardiovascular disease risks through weight loss, lowering blood pressure and lowering blood lipids [4, 5]. Not all ACV, however, is made alike. There are several techniques utilised in commercial vinegar production, from slower more traditional methods to techniques that can produce ACV within a day. There are many other factors in production, from apple cultivar, yeast and bacterial cultures used, to whether the product was filtered and pasteurised [4, 6, 7]. Few studies have examined the effect different production methods have on the final product and the presence and quantity of organic components. Commercial varieties also give limited information on package labelling regarding production methods. The present review focuses on ACV and its beneficial effects on type 2 diabetes.
2. Production of Apple Cider Vinegar
2.1. Two-Step Fermentation Process
- ACV can be produced by a two-step fermentation process, and this process is characterised by the presence of acetic acid at a concentration equal to or above 4% [8]. Cider vinegars are typically 5-6% acetic acid [9]. The pH of vinegar will depend on acetic acid concentration and is typically between 2 – 3.5 [10].Yeasts initially ferment the sugars or starch in raw materials to form ethanol, which is further fermented by acetic acid bacteria (AAB) to produce acetic acid. This can be accomplished with juices/mashes from apples, grapes, coconuts, rice, potato and others. If a starch is the initial raw material, it will first need to be hydrolysed into a sugar. Depending on the method used for the second fermentation, vinegar can be produced as quickly as within 24 hours or may be left for months to years to ferment [4]. Figure 1 shows the chemical equations for the 2-step fermentation process. The final product may be filtered and pasteurised prior to consumption. This process removes and destroys AAB, preventing formation of 'mother of vinegar'. Mother of vinegar develops when unpasteurised vinegar is allowed to remain in the product, forming an extracellular cellulose layer which can be seen as a layer on the surface of the liquid, or as a cloudy cobweb-like substance, making the fluid appear murky. It is not unique to ACV. Production of ACV can occur spontaneously via the naturally occurring yeasts and bacteria on the surface of the fruit, allowing the beverage to be easily made in the home [11]. The product produced in the home will likely differ in microbiota, acetic acid content and other molecules given that the spontaneous process is not standardised. Filtering and pasteurisation may not be done and the 'mother' may be consumed or used to inoculate subsequent batches of vinegar.
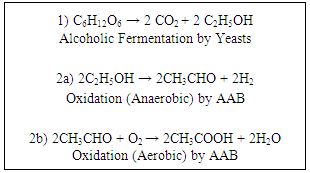 | Figure 1. Chemical equations for 2-step fermentation process |
2.2. Other Vinegar Production Techniques
2.2.1. Orleans Process (Traditional)
- Orleans process is an early traditional process, in which wine covered in a film (mother) of AAB, oxidises slowly in a barrel. The barrel has holes, allowing for air flow and wine is added beneath the mother. The mother causes the apparatus to become slimy and slows the rate of vinegar production and vinegar is removed through the bottom of the barrel [10].
2.2.2. Generator Process (Surface Culture/Quick Process)
- The generator process is believed to date back to the 17th century. AAB are grown in a thick layer on a non-compacting material, such as beech wood shavings. A pump circulates the liquid, allowing a slow trickle over the bacterial culture while air is permitted to circulate through the apparatus. While generator fermentation is used commercially, it is considered to be slow and expensive [10, 12].
2.2.3. Submerged-Culture
- In the submerged-culture generator, a mechanical system keeps the AAB submerged within the liquid in close contact with aeration. The Frings acetator is a popular submerged-culture generator. Submerged culture method was designed for efficient commercial use [10].
2.2.4. Maceration
- Maceration is a process already utilised in wine-making in which the remaining pulp from extracted juice is left to soak in the juice for a period of time. The phenolic and flavour compounds within the skin and pulp are extracted via this process. It has been shown that maceration in combination with the surface production method yielded the ACV with the highest phenolic content [6].
3. Production Methods, Apple Cultivar and End Product
- The production method utilised may affect the final properties and composition of ACV. Different production techniques have been demonstrated to affect pH, acidity and phenolic content [6, 13]. Budak et al. [4] concluded that production method affected the ability of ACV to alter triglyceride levels in rats with some methods more effective than others. The total content of phenolic compounds in ACV and hence, production method, may also be relevant to the ability of the beverage to promote good health. The variety of apple (cultivar) used may affect the phenolic content of the juice product [14] which, not surprisingly, will also carry over to the cider vinegar [7]. The level of ripeness that the apples achieved may also affect the final product. A study that examined the ripening stage of apples on phenolic compounds in apple cider (non-alcoholic) found that unripe apples yielded a product with a lower phenolic content compared to ripened apples. The apples used in production can also affect the microbial content of the end product, with organic apples found to produce a more heterogeneous product compared with conventional apples [15]. The variations in microbiota may in turn influence the organic components of ACV which may affect the health promoting properties.
4. Organic Components of ACV
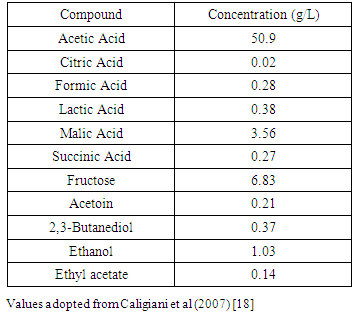
- Acetic acid is the most abundant compound. Organic acids from an analysis of a commercially produced ACV using high resolution H NMR spectroscopy are found in Table 1. ACV is well established that various types of phenolic compounds are found in cider apples, particularly the hydroycinnamic acid derivatives, oligomeric flavan-3-ols, dihydrochalcones, and flavonols [16]. The phenolic content of ACV will vary with cultivar and processing [17]. Phenolic content of ACV was determined to consist of gallic acid, catechin, epicatechin, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid and p-coumaric acid. Chlorogenic acid is the dominant phenolic substance in ACV [6]. The total phenol content and chlorogenic acid content appear to vary significantly between different studies, possibly attributed to the different ACVs being used.Dietary polyphenols are natural phytochemical compounds and include the phenolic acid chlorogenic acid, a hydroxycinnamic acid derivative. Studies demonstrate rapid absorption of the polyphenolic compounds from the intestine. Many healthful benefits are attributed to polyphenols, such as antioxidant, antiallergic, anti-inflammatory, anti-viral and anti-microbial, anti-proliferative, anti-mutagenic, anti-carcinogenic, free radical scavenging, and induction of antioxidant enzymes [19, 20]. There is also some evidence of modulation of signalling pathways such as nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) [16].
|
5. Management of Hyperglycaemia Using ACV
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level measures the glycation of hemoglobin, accurately identifies the average plasma glucose concentration over the previous three months. A study which investigated the effect acetic acid had on HbA1c in type 2 diabetics, found that Hb1Ac values fell by 0.16% units over the course of the 12-week trial, compared with controls who did not ingest any vinegar, where HbA1c levels rose by 0.06% [21]. HbA1c in diabetic rats was also significantly lowered with ACV consumption [22].Several mechanisms may explain the ways in which acetic acid lowers plasma glucose have been suggested. These include inhibition of disaccharidase activity [23-25] and/or decrease in the hydrolytic enzyme α-amylase [26], delayed gastric emptying [27, 28] and an enhanced glucose uptake and conversion to glycogen in the periphery [23, 29, 30]. Delayed gastric emptying was noted in healthy subjects who consumed white bread along with a white vinegar dressing which contained olive oil (18mmol acetic acid in 20g vinegar). White vinegar is an aqueous solution containing approximaetly 6% acetic acid. Gastric emptying rate was indirectly measured through consumption of paracetamol baked into white bread; the blood paracetamol level was lower in the vinegar group compared with the control group. During the postprandial phase subjects who had consumed vinegar had significantly lower blood glucose levels and the insulin response in these subjects was also noted to be significantly lower compared with the reference meal [28]. Paracetamol however, may be absorbed and metabolised at different rates. Other research has also found a link to acetic acid consumption with delayed gastric emptying [27].Recent investigation found that ACV had a stronger ability to lower plasma glucose levels than acetic acid alone [26]. This study found that it was not until day 7 that ACV significantly reduced plasma glucose levels in diabetic mice. ACV had comparable antiglycemic effects to the positive control group treated with the anti-diabetic agent sulfonylurea Glibenclamide. It was found that ACV treated groups had a significant decrease in α-amylase. The ability of ACV to have a stronger effect than acetic acid alone suggests a role for other components of ACV in controling hyperglycemia. Another study found that consuming two tablespoons of ACV prior to sleeping was found to reduce fasting glucose the following morning [25]. Furthermore, acetic acid was demonstrated to significantly decrease the activites of the diasscharides sucrase, maltase, trehalase and lactase in Caco-2 cells, but did not affect the enzymes at transcriptional or translational levels. It was suggested that suppression of the disacharrides may occur in the post-translational processes, such as trafficking of the enzymes to the cell membrane [24]. Consumption of 100mL ACV (5% acetic acid) in diabetic rats demonstated a significant decrease in the activity of maltase, sucrase and lactase [23]. In addition, vinegar ingestion (10g) was found to have no effect on postprandial glycemia (PPG) when only monosaccharides were ingested while a meal of complex carbohydrates consumed with vinegar did result in decreased PPG, further indicating that a acetic acid may inhibit disaccharidase activity [31].Glycogen uptake by the liver and skeletal muscle was found to be enhanced in mice fed a diet containing 2g acetic acid/kg, a contentration that corrosponds to foods prepared with vinegar. Acetic acid ingestion may inhibit glycolysis through accumulation of glucose-6-phosphate and a corrosponding increase in glycogen synthesis, which was seen in liver and skeletal muscle of rats supplemented with acetic acid [29, 32, 33], causing an anti-hyperglycemic effect. Modulation of GK, G6PD and PFK in the liver of rats consuming ACV has been associated with decreased plasma glucose levels [23].The quantity of acetic acid needed to exert effects has been investigated and a significant dose-response relationship was found in a study that examined the effects of ingestion of 18, 23 or 28g of white vinegar (6% acetic acid; equivalent to 18, 23, 28 mmol acetic acid, respectively) [34]. Compared with the control, the highest concentration of acetic acid caused a significant decrease in plasma glucose and insulin response postprandially while the lower acetic acid concentrations did lower blood glucose and insulin response, it was not signifiant [34]. Chlorogenic acid has been demonstrated to have some antiglycemic effects that may be useful in the management of type 2 diabetes. 1mM of chlorogenic acid was found to significantly inhibit glucose-6-phosphatase (G-6-Pase) activity in rat hepatocytes. G-6-Pase promotes glucose production through catalyzing steps in both gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis and inhition of this step can decrease plasma glucose concentration [35]. Synthetic derivatives of chlorogenic acid also have been shown to inhibit G-6-Pase [36]. Liver perfusion experiments, however, did not find a decrease in glucose production at various chlorogenic acid concentrations, perhaps due to insufficent uptake of chlorogenic acid by hepatocytes. However, 1mM chlorogenic acid was able to significantly reduce the plasma glucose peak during the oral glucose tolerance test in rats and this is thought to be due to reduced activity of Na+-dependant D-glucose transporters in brush-border membrane vesicles, as administration of chlorogenic acid intravenously was unable to achieve the same result [35, 37]. Insulin sensitivity was improved in human subjects with both insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes when 20g of ACV was consumed with a high-carbohydrate meal [38]. Animal studies also demonstrated results suggesting improved insulin sensitivity with chlorogenic acid infusion [39]. Improved insulin sensitivity results in increased glucose uptake and hence lowered plasma glucose levels. A diet supplemented with chlorogenic acid has also been shown to significantly lower insulin levels in mice [40].
6. Management of Hypertension and Obesity
- Diabetes may affect the autonomic nervous system and endothelium which results in microvascular complication, which in turn impairs the autoregulation of blood flow. Diabetic subjects have been shown to have lower levels of the vasodilator nitric oxide and increased levels of the vasoconstrictor endothelin-1 which results in a state of vasoconstriction [41]. A consequence of elevated blood pressure is vascular damage which leads to cardiovascular disease. Acetic acid combined with vinegar were found to significantly decrease blood pressure (21-30mmHg lower than the control) and renin activity compared with controls and subjects consuming only vinegar. A decrease in renin and the subsequent release in angiotension II may be the reason for lowered blood pressure. A decrease in aldosterone was also seen. Both rice vinegar and acetic acid were given at a concentration of 46.2g/L [42]. Rice vinegar is generally 4% acetic acid [43], therefore the acetic acid given alone would be more potent then the vinegar solution. It was suggested that acetic acid may cause an increase in calcium absorption, which in turn may cause an calcium influx into renin secretory cells, inhibiting renin secretion [42]. A combination of red wine vinegar and grape juice was also found to decrease activity of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) [44].Type 2 diabetes is commonly associated with obesity and weight loss is considered to be an important component in the management of diabetes [2]. Acetic acid has been proposed to have a role in reducing food intake. This may occur as a result of the taste of acetic acid in vinegar and the nausea it may induce from ingestion [45]. A study found that supplementation of a meal with white vinegar increased the subjective rating of satiety compared with a control group. Improved satiety may result in lowered food consumption and hence, weight loss [34]. A 12 week study found that ingestion of both 75g and 150g of acetic acid significantly reduced the bodyweight, body mass index (BMI), visceral fat and waist circumference in comparison with a control group [46]. Chlorogenic acid has been demonstrated to halt the cell cycle of mouse embryo 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and arrest the G1 phase, hence preventing proliferation. Preadipocytes were inhibited in this study in both time- and dose-dependant manner at a concentration of 100μM. Decreased preadipocyte differentiation is just one proposed method to reverse obesity [47]. Another recent study supplementing the diet of mice on a high fat diet with 0.02% (w/w) chlorogenic acid resulted in a significant 16% weight loss compared with the control group and increased adiponectin levels [40].
7. Management of Dyslipidaemia
- Type 2 diabetes is frequently associated with dyslipidaemia. Part of management of the condition involves attempting to achieve normal blood levels of total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein (LDL), high density lipoprotein (HDL) and triglycerides. Dyslipidaemia is highly correlated with atherosclerosis.
7.1. Dyslipidaemia and ACV
- Ingestion of ACV improved lipid profiles in both normal and diabetic rats, decreasing triglycerides, total cholesterol and LDL while increasing HDL. These effects became pronounced after 4 weeks of treatment [23]. Further animal studies found similar effects on plasma total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL and LDL levels [22, 48]. Other research focused on healthy humans has found the same improvement in lipid profile with ingestion of 30ml of ACV (4% acetic acid) [49].
7.2. Dyslipidemia and Acetic Acid
- Research studies examining the effect acetic acid has on blood lipids found that rats fed a diet supplemented with 1% (w/w) cholesterol combined with acetic acid had significantly lowered total cholestrol and triglycaride levels compared with controls. Acetic acid was found to lower liver ATP citrate lyase (ATP-CL) activity, liver 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA content, all of which are involved in lipid synthesis. Liver mRNA levels of sterol regulatory element binding protein-1, ATP-CL and fatty acid synthase were also found to be decreased. Faceal bile content was found to be higher in the group fed acetic acid. Blood lipids in rats fed acetic acid were decreased by both the inhibition of lipogenesis in the liver and the increased increment of cholesterol in faecal bile acid [50].
7.3. Dyslipidemia and Chlorogenic Acid
- Supplementation of mice on a high fat diet with chlorogenic acid significantly lowered plasma triglyceride and total cholesterol concetrations compared with the control group on a high fat diet. Adipose tissue triglycerides were also found to be significantly lowered. Hepatic activity of HMG-CoA reductase was lowered and fatty acid β-oxidation levels increased with chlorogenic acid intake [40]. Studies using obese, hyperlipidemic and insulin resistant (fa/fa) Zucker rats which were infused with chlorogenic acid (5mg/Kg body weight/day) found significant decreases in fasting plasma cholesterol and triglycerides [39].
8. Conclusions
- The ACV is a readily available product that is easily able to be incorporated into meals. Large body of research has demonstrated its beneficial properties as an entire product, as well as the abilities of the individual components acetic acid and chlorogenic acid. ACV may assist in controlling blood glucose and lipids, weight loss and hypertension and therefore may be helpful in the management of type 2 diabetes. ACV as a whole may be more effective than acetic acid alone, although there is little research directly comparing acetic acid and ACV. Consumption of the ‘mother of vinegar’ may also increase beneficial effects compared with ACV lacking this component. Production method of ACV has been shown to alter the components of ACV, which may in turn affect the beneficial qualities. Further investigation may be beneficial here to determine the extent of the effect of production method. Consumption of ACV may indeed be beneficial in the management of type 2 diabetes.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML