-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Diabetes Research
p-ISSN: 2163-1638 e-ISSN: 2163-1646
2016; 5(5): 92-101
doi:10.5923/j.diabetes.20160505.02

Metabolic Correction in Patients Sample with Diabetes: Clinical Outcomes and Costs Reductions
Jorge R. Miranda-Massari1, 2, 3, José R. Rodríguez-Gómez4, 5, Michael J. González6, Carlos Cidre7, Jorge Duconge8, Heriberto Marín9, Kazuko Grace2, Howard L. McLeod10, 11
1Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, School of Pharmacy, Medical Sciences Campus, UPR, San Juan, PR
2Metabolic Correction Institute, San Juan, PR
3EDP University, San Juan Campus, PR
4University of Puerto Rico, Rio Piedras Campus, Faculty of Social Sciences, Department of General Social Sciences, San Juan, PR
5Carlos Albizu University, San Juan Campus, San Juan, PR
6Dept. of Human Development, School of Public Health, Medical Sciences Campus, UPR, San Juan, PR
7Dr. Carlos Cidre’s Clinical Practice, Manati, PR
8Dept. of Basic Science, School of Pharmacy, Medical Sciences Campus, UPR, San Juan, PR
9Dept. of Administration of Health Services, School of Public Health, Medical Sciences Campus, UPR, San Juan, PR
10Medical Director, The DeBartolo Family Personalized Medicine Institute
11Senior Member, Division of Population Sciences, Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, FL, USA
Correspondence to: Jorge R. Miranda-Massari, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, School of Pharmacy, Medical Sciences Campus, UPR, San Juan, PR.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Diabetes is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide. Diabetes complications produce profound impact on patient’s quality of life and represent very significant economic cost to patients, their family, the government and society as a whole. Metabolic correction has been proposed as an efficient method to improve clinical outcomes and reduce costs in diabetes. Metabolic correction is a concept that supports health maintenance and promotes the healing processes by improving the body’s biochemical-physiological mechanisms. This is done by helping activate the metabolic enzymes necessary to facilitate key physiological pathways. A group of 50 patients followed a simple metabolic correction strategy based on hydration, diet, and magnesium supplementation during a 6 months period. Outcomes measures included laboratory testing, anthropometric measures and medication use including its related costs. Patients had an average weight loss of 9.4 lbs (↓5.0%) from baseline at month 3 and 12 lbs (↓6.4%) at month 6. Waist circumference decreased on average 3.7 inches (↓9.0%) from baseline at month 3 and had further decrease to 5.5 inches (↓13.4%) from baseline at month 6. Laboratory testing of average triglycerides decreased from a baseline of 156.9 to 116.7 (↓25.6%) at month 3 and maintained a reduction of ↓24.2% by month 6. Total cholesterol concentration decreased from a baseline of 181.1 mg/dL to 173.9 (↓4.0%) in month 3 and to 171.1 (↓5.5%) at month 6. Average HgA1c decreased from baseline of 7.17 to 6.52 (↓9.1%) at month 3 and maintained 6.52 at months 6. The atherogenic index decreased from 4.18 at baseline to 3.85 at month 3 (↓7.9%) and then 3.47 (17.0%) at month 6. Medication use and cost was quantified in various ways. The average baseline monthly diabetes medication cost per patient of $124.10 was reduced to $ 78.23 (↓36.7% reduction) at month 3 and to $62.80 (↓49.4% reduction) at month 6. A simple and well structured metabolic correction program that includes a significant educational component, dietary modifications and dietary supplement intake was able to maintain or improve vital signs, anthopometric and laboratory measurements that correlate with improved clinical diabetes and cardiovascular health. This outcome was achieved while decreasing the use medications at month 3 and 6 at significant cost savings.
Keywords: Diabetes, Metabolic Correction, Diet, Magnesium, Diabetes care cost, Cost reduction, Magnesium supplementation
Cite this paper: Jorge R. Miranda-Massari, José R. Rodríguez-Gómez, Michael J. González, Carlos Cidre, Jorge Duconge, Heriberto Marín, Kazuko Grace, Howard L. McLeod, Metabolic Correction in Patients Sample with Diabetes: Clinical Outcomes and Costs Reductions, International Journal of Diabetes Research, Vol. 5 No. 5, 2016, pp. 92-101. doi: 10.5923/j.diabetes.20160505.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The number of patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 (DM2) has continued to grow worldwide steadily making DM2 a serious epidemic of potentially catastrophic proportions. [1-3] Aside from the health implications and inherent life difficulties related to having diabetes the global DM2 epidemic is also skyrocketing the disease management costs. In some developing countries, DM2 threatens to bankrupt the health agencies as pharmaceutical medication prices have continued to outgrow the inflationary trend. [4, 5] Economists at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) of the United States have reported that the cost of having diabetes has doubled in just two decades. [6] Besides the personal suffering, loss of productivity and negative social implications of DM2, the fact appears to be that DM2 together with its closely related companion obesity foretells of a global public health crisis that threatens the economies, the social structure and the public health agencies of all nations. [2, 7-13] The DM2 statistics are alarming and the future projections are gloomy. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) revealed in a press release in 2011 revealed that the number of people living with diabetes was expected to rise from 366 million in 2011 to 552 million by 2030 when one in every ten people was expected to be diabetic, if no urgent action was taken. [14, 15] Attempts at managing DM2’s hyperglycemia with intensive oral or injected hypoglycemic medication have proven dismal as they increased mortality for the diabetic patients aside from being exceedingly costly. [16-19] There is some evidence that achieving a reduction in the DM2 patient’s dosage needs for exogenous insulin can reduce all mortality cause, cardiovascular events and the incidence of cancer. [20-22] Furthermore, the intensive glucose control has been focused on hypoglycemic medication that has been emphasized during the last decades seems to be the main cause of a growing wave of diabetic hypoglycemic events. Hospital admission rates for diabetic hypoglycemia now exceed those for hyperglycemia among older adults adding more financial burdens to an already overtaxed health system. [23] Diabetic patients are now more likely to experience adverse events related to overtreatment of diabetes mellitus. [24] Meanwhile the costs associated with hospitalization for patients with DM2 accounts for half of all health care expenditures for this disease. [25-27].RATIONALE OF METABOLIC CORRECTION THERAPYThe “metabolic correction” concept is a clinical strategy that addresses the root biochemical causes of disease by providing the body with quality nutrition of a low glycemic load (LGL), while also supplying vital hydration and the necessary micronutrients that potentiate metabolism and mitochondrial energy production. The metabolic correction paradigm, postulates that most sickness are related to an energetic deficiency that affects the body’s natural ability to sustain its life systems and its natural homeostatic balance. [28-29]. From this perspective DM2 is just another of the many ways in which the basic energy producing capacity of the body has been compromised, thus creating DM2 which is a metabolic disorder that negatively affects health from metabolic consequences of elevated glucose and many other metabolic disturbances. Within the realm of the metabolic correction concept, any effort made to improve the body’s quantity or quality of energy production is considered valuable. This includes taking into consideration a patient’s individual hereditary differences that could potentially affect his body’s metabolic efficiency and its energy production capacity thus influencing his diabetic control and his obesity propensity. These hereditary differences include metabolic genetic variables like having a body that is either of sympathetic or parasympathetic central nervous system dominance propensities. Some researchers have documented that individual adjustment to the patient’s selection of food according to their individual sympathetic or parasympathetic dominance propensity maintains an adequate metabolic energy production rate. [30, 31] The autonomic nervous system has a substantial influence over DM2 control therefore; it is an important therapeutic consideration. [32, 33] The previous concepts could be provocatively new or even uncomfortably uncommon so the sole proof as to the workability of the “metabolic correction” paradigm or its tenets should rest only in its measurable clinical results. To prove its value any novel clinical protocol concept needs clinical confirmation. This information would ideally result not only in a valid scientific contribution to “evidence based medicine” but also in an even more desirable goal of “result based medicine”.
2. Methods
- An educational metabolic restorative method based on the “metabolic correction” concept and coined as the “Metabolic Restorative Technology Medical Protocol” (MRT-MD) had first been tested on a previous study with 25 DM2 patients for a period for 13 weeks’ as a prospective cohort study under medical supervision. [34] The MRT-MD protocol had evolved out of the practical experiences accumulated with 30,642 weight loss patients at a private weight loss clinic by 2008 and increased to 92,620 by 2015 where many of the obese DM2 patients had reported significant improvements in their diabetic control after utilizing the MRT-MD protocol. [34, 35] The use of this protocol had showed statistically significant benefits in DM2 weight loss (WL), in reducing lipids, in lowering fasting blood glucose (FBG) and in reducing waist circumference (WC) while also improving DM2 control. An interesting finding of the first study was that 21 of the 25 DM2 patients had medication dosage reduction ordered by their physicians in one or more of their chronic medications. This became an important finding because it indicated that any positive outcomes achieved by this protocol were not a result of new medications or dosage increase, but occurred despite a reduction in their medication. [34] The calculation on cost savings by medication reductions were not performed in our previous publication on 25 DM2 patients as it was not part of the scope of the study. However the observation that 21 of the 25 patients had reported medication reductions in both diabetic (insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents) and non-diabetic medications (antihypertensives, antilipidemics, etc.) suggest that MRT-MD protocol has a potential for achieving medical expense reductions. This study provided the basis for larger second longitudinal cohort study with a design that would include per patient medication cost both clinical and biochemical analysis during a 6-month period. EDUCATING THE DM2 PATIENT TO FOSTER PATIENT RESPONSIBILITY:The National Center for Education measured the health literacy in the United States and published the results in their 2003 report. [36] This comprehensive report shows that only 12% (1 in 8) of the American population are proficient at understanding their own health condition and that means that 88% of the population varies from total ignorance to only having a basic understanding of their health condition. This analysis and its statistical data seemed to point out that there is insufficient patient education if we are ever to reverse the DM2 medical complications and the financial burdens they carry. There have been many previous attempts to educate DM2 patients in order to control hyperglycemia and reduce medical complications and medical expenses with some limited or modest success. [37-40]. The MRT-MD protocol seems to be a promising fresh educational approach as it teaches several unique metabolic enhancing strategies that had previously showed statistically significant results including an unusually high patient satisfaction index that translated into weight loss, more energy, better sleep quality and a generally increased adherence to the new DM2 lifestyle. [34] REDUCING DM2 HYPERGLYCEMIA: The MRT-MD protocol is a novel educational approach that specifically teaches DM2 patients how to reduce or avoid hyperglycemic events by educating them on the glycemic effect that each different food type has. This is achieved with the help of the 3x1 Diet ® that simplifies a diabetic patient’s food selection and combining options without a need for counting calories, diabetic food exchange lists, weighting grams or other hard to understand or limiting nutritional plans. [34] It also teaches DM2 patients to monitor their postprandial glucose regularly to allow them to learn from the effects of their own food choices and the resulting glycemic levels. [41-44] As other complementary individualized metabolic correction factors like efficient hydration and autonomic nervous system predominance differentiation are taken into consideration some promising results have been experienced with DM2 patients. [33, 34, 45] Reducing hyperglycemia is a mayor goal of the MRT-MD protocol. The LGL 3x1 Diet® had previously proven effective at achieving lower postprandial glucose averages for DM2 patients and a reduce their A1c Hemoglobin. [34) The MRT-MD protocol utilizes multiple graphical illustrations with suggestions and examples of possible meals, breakfasts and food combinations that would result in lower average glucose level that are conductive to both weight loss and lower glycemic averages. [46] In our estimation, lower postprandial glycemic averages would also translate into better DM2 control and less hypoglycemic medication needs. WEIGHT LOSS (WL), WAIST CIRCUMFERENCE (WC) & BMI REDUCTIONS:An estimated 85% of all DM2 patients are overweight or obese so one of the goals of the MRT-MD protocol is to help diabetic patients reduce their weight. Most DM2 patients are overweight and more than half are obese. [9] Achieving reductions of WC in overweight or obese DM2 patients has been found to have significant cardiovascular risk reduction benefits. [47-49] Meanwhile cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) remain the leading cause of both disability and mortality amongst diabetic patients. [50, 51] Furthermore, approximately 80% of all deaths and most hospitalizations in DM2 patients are attributable to cardiovascular causes [52]. It has been found that even moderate WL will improve DM2 control while reducing medical management and medication costs [53-56] Thus, DM2 patients should do their best to reduce BW, BMI and WC as it could result in not just improved health and energy for the patients but could also conceivably result in reduced total medical expenses for both diabetes and non-diabetic related conditions. MAGNESIUM SUPPLEMENTATION FOR DM2 PATIENTS: Previous clinical experience of the MRT-MD protocol has demonstrated that neither glucose control in patients with DM2, nor its insulin resistance or their related conditions like hypertension can be consistently improved if there is a magnesium deficiency or insufficiency present. Magnesium deficiency appears to be exceptionally common within the DM2, obese and overweight populations probably because of poor dietary habits. The 2005-2006 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) revealed that at least half of the U.S. population had inadequate intakes of magnesium. [57-58] DM2 has been closely associated with magnesium deficiencies that aggravate insulin resistance and its associated metabolic syndrome. [59-61] The MRT-MD protocol practitioners have found it of benefit to supplement DM2 patients with magnesium on a “bowel tolerance” dosage mode. There are abundant references that support magnesium supplementation for a large portion of the population but especially for DM2 patients. [60, 62-64] With DM2 patients, the sympathetic nervous system relaxation effects caused by magnesium also seems to help in improving sleep quality. Since sleep loss and poor sleep quality have both been found to aggravate insulin resistance while also promoting hyperglycemia, obesity and hypertension magnesium supplementation is presumed to improve the DM2 patient outcomes. [62, 65-72] DM2 patients have a high incidence of hypertension and in this respect; magnesium supplementation could be beneficial. [73-75] Finally, magnesium supplementation seems to have some potential in reducing medication needs thereby reducing medical management costs. [59, 63-64, 76-78]
3. Study Design and Scope
- We followed prospectively 50 patients with DM2 in a longitudinal 6 months (26 weeks) cohort study with two cut off points at 3 months (13 weeks) and at 6 months (26 weeks) for comparison purposes. The study recorded anthropometric measurements of BW, WC, BMI as well as each patient’s TG, CH, LDL, HDL, A1c levels at the start and at each of the two cut-off points at 3 months and 6 months’ time. The study calculated the atherogenic index of plasma (AIP= log TG/HDL mmol/l) as it predicts the risk of development of atherosclerosis in diabetic patients. [79] Studies have shown that serum triglyceride level is an independent determinant of cardiovascular risk. [80-81] CALCULATING POSSIBLE MEDICAL COST REDUCTIONS: To asses any possible medication cost reductions that could be achieved as a result of the clinical application of the MRT-MD educational protocol detailed records were kept on each DM2 patient’s medication dosages and their average costs per patient plus the type of medication (diabetic, non-diabetic) that was being consumed each participant. Average medication costs per dosage of all medications being consumed by the participants were calculated at each of the study’s two cut-off points (3 months and 6 months) using the lower price quoted by the GOODRX medicine cost calculating software available at www.goodrx.com provided by Goodrx Inc. in California, USA.A group of patients with DM2 underwent an educational program, with the help of the audio-visual graphics developed by the MRT-MD protocol practitioners. This program is designed to achieve a balance of protein, carbohydrate and fats at each of its three main meals with an emphasis in not exceeding a certain portion of their food plate with a certain amount of HGL carbohydrates. (82-88) Initially, as the patients learned to implement their new lifestyle and their 3x1 Diet® they received follow up every 2 weeks during the first 3 months. Then they were only monitored once a month during the last 4 to 6 months of the study when the anthropometric results of the first 3 months had shown that each participant had settled into the new lifestyle routine and was able to sustain it on his own.
4. Study Results
- Fifty patients with DM2 participated in the study (29 females and 21 males) for a period of 6 months. Data recollection included baseline measurements and cut off points at 3 and 6 months. The study anthropometric and health parameters results are summarized in figures 1 and 2 below:
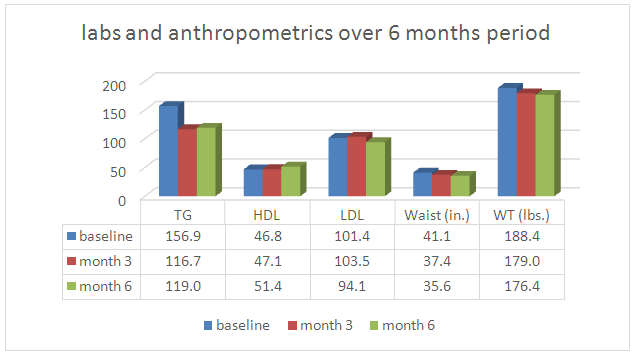 | Figure 1. Labs and anthropometics over 6 months period in MRT-MD protocol |
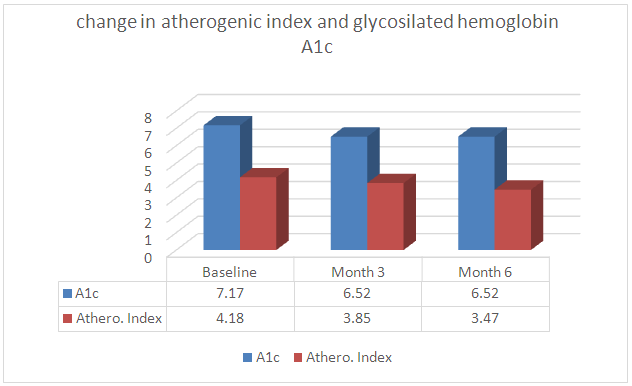 | Figure 2. Atherogenic Index and Glycosilated hemoglobin over 6 months period |
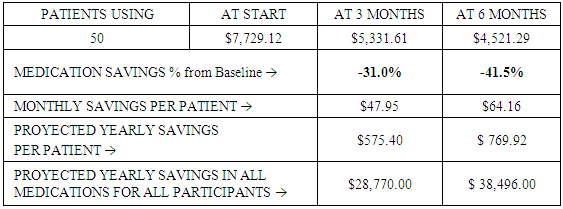
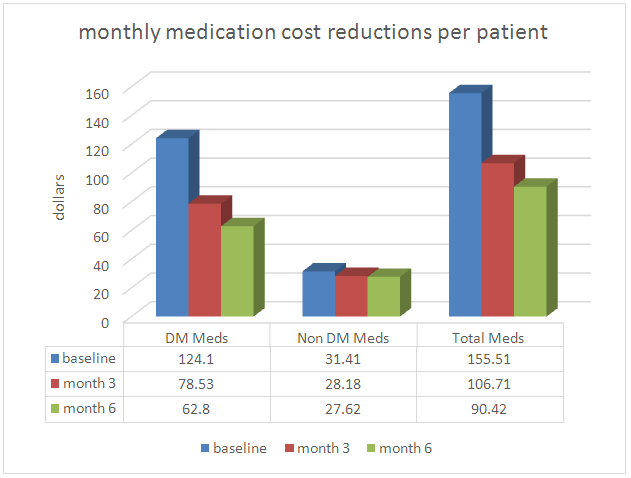 | Figure 3. Monthly Medication Cost Reduction per patient over 6 month |
|
5. Statistical Analysis
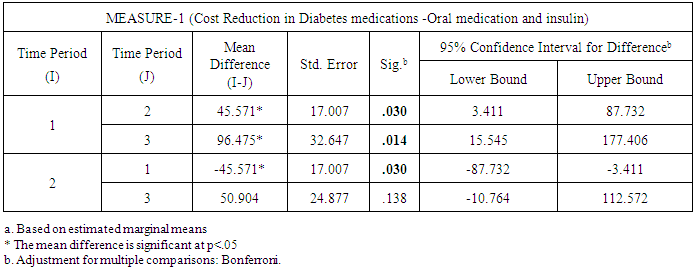
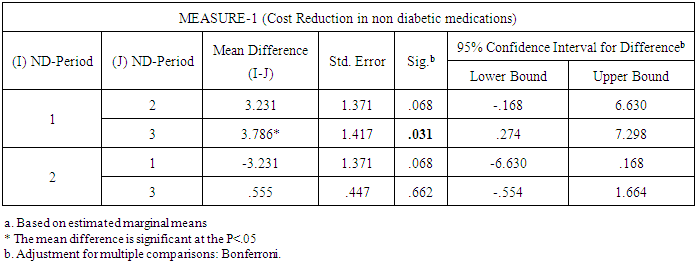
- A 2 tailed paired T test was conducted to determine if there are differences between the parameters values measured at baseline compared to the values measured at 3 and 6 months.We found significant differences between the values of several parameters. Weight, BMI, Waist, A1c and TC all had statistical significant differences between baseline and both, 3 months and between baseline and 6 months. We also found statistically significant difference for HDL when comparing baseline to values at 6 months but not with values at 3 months. Also, found statistically significant difference for atherogenic index when comparing baseline to values at 6 months but not with values at 3 months. With regard to blood pressure, we found that measurements at baseline, were not significantly different than those at month 3; however, values achieved a statistically significant difference at month 6.Another very important observation was a statistically significant reduction in the use of all categories of medications including insulin, oral hypoglycemics and non-diabetes medications. The percentual cost reduction of medication was most dramatic in the oral hypoglycemic agents. Cost reduction in this category at month 3 was 57.9% and it reached 69.7% by month 6. However, since insulin is the most expensive medication the impact of insulin reduction had a greater weight in the total cost reduction. The statistical analysis of cost reductions related to decrease in medication is as follows (see Tables 9 & 10 for diabetic medications and non-diabetic medications respectively).The statistical analysis of cost reductions related to decrease in medication is as follows:From baseline (period 1) to period 2, (3 months) the cost reduction in diabetes medications (Includes Insulin and other oral Hypoglycemic agents), was significant 45.57, (p<.03), First period (baseline) to third period (6 months) cost reduction was significant, 96.48 (P<.01). However, 3 months versus 6 months cost reduction was not significant 50.90 (P<.138). Non-diabetic medications also demonstrate a significant decrease. The statistical analysis of cost reductions related to decrease in non diabetic medications is as follows: From baseline (period 1) to period 2 (3 months) the cost reduction in non diabetes medications was significant 45.57, (p<.03), First period (baseline) to third period (6 months) cost reduction was significant, 96.48 (P<.01). However, 3 months versus 6 months cost reduction was not significant 50.90 (P<.138). The main impact for change in non diabetic medications came from the baseline period to 3 and 6 months period.
|
|
6. Discussion
- Metabolic correction is a concept that can encompass from a very comprehensive set of evaluations and interventions to a relatively simple strategy. The interventions in this study were limited to a simple nutritional/hydration guideline and magnesium supplementation reinforced by a well-structured educational tool. The results from the metabolic correction protocol resulted in statistically significant and beneficial changes in anthropometric measurements and laboratory values (Weight, BMI, Waist, A1c and TC).The benefits obtained by the intervention at month 3 where sustained or improved by month 6. One important consideration is that the implementation of the metabolic correction protocol over a 6 months period lead to significant improvements in several anthropometric and laboratory parameters while reducing the use of medications. The reduction in the use of medication occurred in all medications including insulin, oral hypoglycemics and non-diabetes medications. Non-diabetes medication included antihypertensive, diuretics, hypocholesterolemia agents, neuropathic pain medication, proton pump inhibitor, antidepressants and benzodiazepines. Reducing the dose of medications has the benefit of reducing both the cost of the medication as well as its associated adverse effects.In addition, very significant reductions in the use and cost of medication were documented during the study period. With regard to diabetes medications, the average monthly cost per patient at baseline was $124.10. This cost was reduced to $78.53 (↓36.7%) at month 3 and further decrease to $62.80 (↓49.4%). With regard to non-diabetic medications, the average monthly cost per patient at baseline was $31.41. This cost was reduced to $28.18 (↓10.3%) at month 3 and further decrease to $27.62 (↓12.1%). Implementation of metabolic correction produced conditions that allowed reductions in insulin doses. The monthly cost of insulin at baseline for the 11 patients in the study was $4,536.12. This cost was reduced to $3,219.26 (↓29.0%) at month 3 and further decrease to $2,633.72 (↓41.9%) at month 6. The average monthly cost per patient in all medications at baseline was $155.51. This cost decreased to $106.71 (↓31.4%) at month 3 and further decrease to $90.43 (↓41.9%) at month 6.Achieving good clinical outcomes with less medication not only produces the direct cost savings of decrease medication costs, but decrease medication use will reduce drug related morbidity and mortality. Drug induced morbidity and mortality is due to drug-induced nutrient depletion, mitochondrial dysfunction and other pharmacological and genetic idiosyncrasies. Drug related morbidity and mortality has been shown to have very significant costs (89-90). To understand the impact on the health system and the individual we clarify the distribution of the medication cost coverage. In this population studied the main payer for the medications was Medicare comprising 90% patients followed by private insurance in 10% the patients and none out of pocket.Before this study, we developed a theoretical model explaining how metabolic correction can contribute to not only improve clinical outcomes, but also reduce healthcare costs. In this model, which is being prepared for publication, we proposed that metabolic correction has the potential of reducing complications of the disease by addressing its underlying causes. We also proposed that by using metabolic correction, medication use can be reduced, and therefore, the associated cost. In addition, in that research we also produced estimates of the cost reduction by implementing metabolic correction. It appears that the implementation of metabolic correction has significant potential to produce good clinical results and at the same time produce significant cost savings. More research is needed in order to define the extent of the clinical benefits as well as several important variables decreasing costs and the economic impact of this intervention.
7. Conclusions
- This simple and well-structured metabolic correction program that includes a significant educational component, structured hydration, dietary modifications and dietary supplement intake was able to maintain and/or improve diabetic patient anthropometric measurements and laboratory measurements that correlate with good clinical outcomes in diabetes and cardiovascular health. Therefore, if these benefits can be sustained over a prolonged period, it is expected that patients can experience corresponding decrease in health risks complications accompanied by a reduction in healthcare cost.In addition to the expected decrease in health risks, by achieving improvements in anthropometric and laboratory values, the Metabolic Correction intervention demonstrated significant decrease in costs due to reduction in medication use. Considering the cumulative drug toxicities, its possible that the cost saving of the long term use of metabolic correction could be greater than in the short term. Longer studies are needed to evaluate if the clinical benefits observed at 3-6 months can be sustained over a longer period. In addition, medication use, hospitalizations and overall cost of patient care should be evaluated over a prolonged period.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML