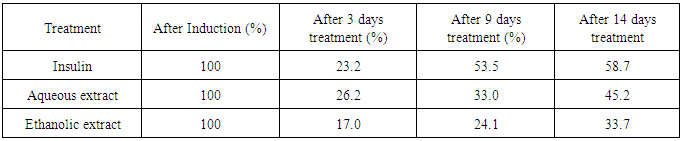-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Diabetes Research
p-ISSN: 2163-1638 e-ISSN: 2163-1646
2016; 5(3): 48-53
doi:10.5923/j.diabetes.20160503.02

Phytochemical Analysis and Antidiabetic Effect of Aqueous and Ethanolic Extracts of Moringa Oleifera Leaves in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Wistar Albino Rats Using Insulin as Reference Drug
Ezeigbo O. R.1, Barrah C. S.1, Ezeigbo I. C.2
1Department of Biology/Microbiology, Abia State Polytechnic, Aba, Nigeria
2Natural and Computational Sciences, Minerva Schools at KGI, San Francisco, California, USA
Correspondence to: Ezeigbo O. R., Department of Biology/Microbiology, Abia State Polytechnic, Aba, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

MoringaoleiferaLam, popularly known as “miracle tree” belongs to the family, Moringaceae. It is a medicinal plant that constitutes an important source of potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of ailments. In this study, the phytochemical screening of M.oleifera Lam and its effect on alloxan-induced diabetes in wistar albino rats was investigated. Hyperglycemia was induced in rats using alloxan (100mg/kg body weight) intraperitoneally for 72 hours resulting in a high glucose level between 340mg/dl and 600mg/dl. Hyperglycemic rats were treated with doses of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of M.oleifera leaves using insulin as a reference drug for 14 days. Fifteen (15) rats were randomly divided into 3 groups (A, B and C) of 5 rats each and feed with standard feed and water. The three groups were induced with alloxan. Group A was treated with insulin while B and C were treated with aqueous and ethanolic leaf extracts of M. oleifera respectively. A glucometer was used to check the blood glucose level of the animals. The analysis showed that Moringaoleifera is rich in bioactive agents that enhanced its use as medicinal plant. The result also showed a significant decrease in blood glucose level of the induced rats at 3, 9 and 14 days for aqueous and ethanolic extracts of M.oleifera respectively. However, the aqueous extract showed more hypoglycemic effect than the ethanolic extract which suggests it to be a better solvent for the extraction of the bioactive agents for this extraction. After 14 days, there was 45.2% and 33.7% reduction of blood glucose for aqueous and ethanolic extracts respectively, while the reference drug (insulin) had 58.7% reduction. The statistical analysis showed no significant difference in blood glucose reduction with insulin and the M.oliefera extracts (p-value > 0.05). However, a significant difference exists between the glucose level after alloxan induction and 14 days treatments (p-value< 0.05). The results from this study confirmed the extensive use of M.oleifera Lam. plant in the treatment of diabetes in ethno-medicinal practice and suggest its use in drug formulation.
Keywords: Moringeroleifera, Alloxan, Wistar albino rats, Anti-Hyperglycemia, Diabetes
Cite this paper: Ezeigbo O. R., Barrah C. S., Ezeigbo I. C., Phytochemical Analysis and Antidiabetic Effect of Aqueous and Ethanolic Extracts of Moringa Oleifera Leaves in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Wistar Albino Rats Using Insulin as Reference Drug, International Journal of Diabetes Research, Vol. 5 No. 3, 2016, pp. 48-53. doi: 10.5923/j.diabetes.20160503.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder of the endocrine system that precipitates disturbance in glucose, lipid and protein homoeostasis [1]. People suffering from diabetes cannot produce or properly use insulin and so persistently have high blood glucose. Diabetes is generally characterized by hyperglycemia, glucosuria, polyuria, loss of body weight, disability, coma and even death. The disease is found in all parts of the world and is increasing rapidly worldwide. According to World Health Organization projection, the prevalence of diabetes is likely to increase by 35% by the year 2020 [2]. Currently, there are 150 million diabetics worldwide and this is likely to increase to 300 million in the year 2025 [2]. Currently, an available therapy for diabetes involves treatment with insulin and other oral anti-diabetic agents such as sulfonylurea and biguanid. Many of these oral anti-diabetic agents have a number of serious adverse effect, thus management of diabetes without side effect is still a challenge [3]. Herbs have become reliable substitutes and have so far played significant role in the management of various disorders and the accompanying oxidative stress. Despite considerable progress in therapies using expensive synthetic drugs, the search for herbal remedies is growing, which can be accounted for its effectiveness, minimal side effects in clinical experience and relatively low cost of the herbal drugs. M. oleifera Lam, popularly called “the miracle tree”, is a monogeneric plant of the family Moringaceae. There is evidence that the cultivation of this tree in India and other parts of the world dates back many thousands of years ago. Many parts of this plant i.e., leaves, immature pods, flowers and fruits are edible and are used as a highly nutritive vegetable in many countries [4]. This plant was well known to the ancient world until recently rediscovered as a multipurpose tree with a tremendous variety of potential uses. It is commonly used in folk medicine as an antidiabetic agent. This is because of its impressive range of nutritional and medicinal qualities [5]. M. oleifera is rich in minerals, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, moisture, crude fiber, and ash contents [6]. Nutritional analysis indicates that the leaves contain wealth of essential disease-preventing nutrients which makes it suitable as supplements in food [7]. The composition of amino acids in the leaf is well balanced [8, 9]. The leaves have been used to combat malnutrition especially among infants and nursing mothers and used to hasten uterine contraction during child birth in pregnant women [6]. M. oleifera has been found to have medicinal and industrial value [10] and has been widely used in alternative medicine. In ethno-medicine, M. oleifera leaves have been used by local traditional healer in treatment of various ailments such as diabetes, gastric discomfort, stomach ulcer, diarrhea, dysentery and skin infections [11-13]. Phytochemical analysis of M. oleifera showed the presence of flavonoid, anthraquinone, alkaloids, saponins, steroids, terpenoids, cardiac glycoside, anthocyanin, tannins and carotenoid in both the aqueous and ethanolic extracts [14, 15]. It has been reported in the literature that M. oleifera extracts has antioxidant potential. Consequently, it has become imperative to investigate the plant for the management of diabetes. Presence of flavonoids and tannins in the extracts is known to possess antidiabetic activity [16]. M. oleifera ameliorates liver fibrosis in rats and reduces liver damage [17]. The leaves have also been found to possess antitumor, antipyretic, antiepileptic, anti-inflammatory, anti-ulcer, anti-hypertensive and anti-oxidant properties [5]. However, it has been reported that climatic factors, stages of maturity and choice of solvent used in extraction could cause variation in distribution of these phytochemicals in M. oleifera leaves [18, 19]. Currently, there is a growing interest in evaluating herbal remedies which are seen to be less toxic and have negligible side effect for the management of diabetes mellitus, especially in countries where access to conventional treatment of the disease is inadequate [20]. This paper evaluates the anti-diabetic effect of the leaf extracts of M. oleifera on alloxan- induced wistar albino rats with a view to providing information on the clinical treatment of diabetes.
2. Materials and Methods
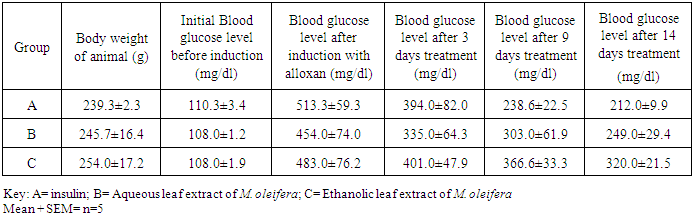
- Collection and Identification of Plant Materials: Fresh leaf samples of M. oleifera Lam leaves were harvested from the Botanical Garden of the Biology Department, Abia State Polytechnic, Aba. A plant taxonomist in the Department identified and authenticated the leaves as M. oleifera.Preparation of Extracts: The fresh leaves of M. oleifera were air-dried and grinded into powder. 50g of the sample was weighed and soaked in 100mL distilled water (aqueous solution) and 98% ethanol respectively and allowed to stand for 48 hours for extraction of active ingredients. After 48 hours, the samples were double filtered using whatman No 1 filter paper and porcelain cloth. The filtrate was evaporated to dryness at reduced temperature of 40°C. Phytochemical Screening: The aqueous extracts of Moringa oleifera were subjected to qualitative screening for chemical constituents using standard procedures [21, 22]. The Experimental Animals: A total of fifteen (15) healthy and pathogen-free albino rats of both sexes, with average body weight of 240g were obtained from the Department of Veterinary Medicine, University of Nigeria, Nsukka. The animals were housed in a cage and kept in the Animal house of the Biology Department, Abia State Polytechnic, Aba and maintained under the standard husbandry condition (between 22°C, 12 hours light and 12 hour dark and 30-35% humidity). The animals were fed with standard feed (animal feed) and clean drinking water to acclimatize for 7 days. Proper sanitation was maintained in the animal house to ensure healthy and clean environment. Handling, management and the use of animals for experiments were maintained. The Animal ethical committee of Biology Department, Abia State Polytechnic approved the animal studies.Induction of Diabetes: The experimental animals were first weighed before the commencement of the experiment. After 7 days, the animals were grouped into 3 (A, B and C). 0.75g of alloxan were dissolved in 10mL of distilled water and were administered to each of the rats in groups A, B and C based on the body weight of each rat and on a dosage of 100mg/kg. Group A served as the control. The administration of alloxan was done intraperitoneally using diabetic syringes [23]. After 72 hours, the rats with sugar level more than 180mg/dl were considered experimentally diabetic [24].Experimental Design: All the animals in each group were fed with standard feed and water. Experimental animals were induced with alloxan until they were confirmed diabetic. Animals in group A were treated with insulin, which served as reference drug; group B were treated with aqueous extract of M. oleifera while group C were treated with ethanolic extract of M. oleifera for 3, 9 and 14 days respectively. Determination of Glucose Level: After 72 hours (3 days) of administering the animals with insulin (for group A) and plant extracts (for B and C respectively), the animals were starved. The blood samples were collected from the vein puncture for the determination of the blood glucose level in the fasting animals using a glucometer. The process was repeated after 9 and 14 days. Statistical Analysis: Data obtained from the study were analyzed by descriptive statistics and presented as mean ± standard error of mean of five (5) determinations (Mean ± SEM). Using the statistical software package (SPSS) for windows version, the difference between means were separated using the analysis of variance (ANOVA) and multiple comparison tests. Values of p< 0.05 were taking as being significant.
3. Results
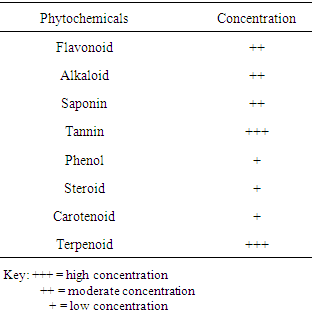
- The phytochemical screening of Moringa oleifera leaf is shown in Table 1. The result showed the presence of flavonoid, alkaloid, saponin, steroid, tannin, carotenoid, terpenoid and phenol. The analysis using the aqueous extract of this leaf revealed that tannin and terpenoid were high in concentration; flavonoids, alkaloid and saponins were moderately concentrated while phenol, steroid and carotenoid were low in concentration.
|
|
|
4. Discussion
- M. oleifera is among the numerous plants adjuvant for the treatment of diabetes. The World health Organization has pointed out that prevention of diabetes and its complications is not only a major challenge for the future but essential if health for all is to be attained [25]. The study had emphasized strongly the need for optimum and rational uses of traditional and natural indigenous systems of medicine in health care systems of any specific country. The present study was therefore designed to investigate the effect of the aqueous and ethanolic leaf extract of M. oleifera on alloxan-induced diabetic wistar albino rats, using insulin as a reference drug. The results revealed that both aqueous and ethanolic leaf extracts of M. oleifera have hypoglycemic effect on the diabetic rats. This result agrees with the findings of other authors who also reported a significant reduction of blood glucose level on rats using M. oleifera leaf extracts [26-28]. The aqueous leaf extract of M. oleifera in this study showed a 45.2% reduction of the glucose level compared with the ethanolic leaf extract with 33.7% reduction at the 14 days treatment period respectively. Sai et al [26] noted that administration of aqueous extract of M. oleifera on diabetic rats for 60 days restored all the alterations to normal/ near normal. The quantitative analysis by some authors revealed that the aqueous extract constituted more phytochemicals than the ethanolic extract [6, 14, 15] and hence exhibited more hypoglycemic activity on the diabetic rats. So far, it has been reported that different solvents had different extraction capabilities and spectrum of solubility for phyto-constituents [29]. Treatment with insulin (which is the reference drug) recorded a non-significant slightly higher hypoglycemic effect (58.7%) with the same period of time when compared with the leaf extracts. The aqueous and ethanolic leaf extracts of M. oleifera have ameliorating effect on the alloxan induced diabetic wistar albino rats comparable to the reference drug (insulin). This finding collaborates with the report of Sai et al [26] which clearly revealed that aqueous extract of M. oleifera leaf possesses potent antihyperglycemic and antihyperlipedemic effect in both insulin resistant and insulin deficient rat models. The comparable effect of M. oleifera with insulin in reducing the blood glucose level of the diabetic rats suggests similar mode of action. Alloxan monohydrate destroys the pancreatic β-cells [30, 31] while M. oleifera leaf extract counteracts alloxan-induced diabetes by the regeneration of β-cells to release insulin [27, 32]. This ameliorates the effect of the alloxan and thereby normalizes the elevated serum level of glucose [27]. This study also revealed the presence of flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, steroids, tannins, carotenoids, terpenoids and phenols. This finding agrees with the findings of Azubuogu [14] and Nwaeze and Nwafor [15]. Numerous epidemiological studies suggest that herbs/diets rich in phytochemicals and antioxidants execute a protective role in health and diseases [33]. Flavonoids, sterols, terpenoids, alkaloids, saponins and phenolics are reported as bioactive antidiabetic principles [34]. The presence of flavonoids, terpenoids, tannins and saponins explains why M. oleifera is used for diabetes treatment [16, 35], because the constituents are used ethno-pharmacologically to treat diabetes and hyperglycemia [7].
5. Conclusions
- This work validated scientifically the widely claimed use of M. oleifera Lam. as ethno-medicinal plant in the treatment of diabetes. Moringa oleifera is rich in phytochemicals and this enhanced its use as medicinal plant. Both aqueous and ethanolic leaf extracts of M. oleifera have hypoglycemic effect on alloxan induced diabetic rats. However, the aqueous extract exhibited more hypoglycemic activity on the diabetic rats than the ethanolic extract. Treatment with insulin (which is the reference drug) recorded a comparable effect suggesting a similar mode of action. Currently, there is a growing interest in evaluating herbal remedies which are seen to be less toxic and have negligible side effect for the management of diabetes mellitus, especially in countries where access to conventional treatment of the disease is inadequate. The use of M. oleifera is therefore recommended as it appears to be generally safe.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors wish to acknowledge the assistance of Mr. D. A. Awomukwu for the identification of the sampled plant.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML