-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Diabetes Research
p-ISSN: 2163-1638 e-ISSN: 2163-1646
2015; 4(3): 43-48
doi:10.5923/j.diabetes.20150403.01
Common Variants in IGF2BP2 Gene rs4402960 and rs1470579 Polymorphisms Associate with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Egyptians: A Replication Study
Dalia El-Lebedy, Ingy Ashmawy, Alshaymaa A. Ibrahim
Department of Clinical and Chemical Pathology, National Research Center, Cairo, Egypt
Correspondence to: Dalia El-Lebedy, Department of Clinical and Chemical Pathology, National Research Center, Cairo, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Genome-wide association studies identified novel genes associated with T2DM which have been replicated in different ethnic populations and yielded inconsistent results. Our study aimed to replicate in Egyptian population the identified association of insulin growth factor 2 m-RNA binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) genetic variants rs4402960 and rs1470579 with T2DM. Our study included 120 unrelated T2DM patients and 128 control subjects who were genotyped by real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR). For rs1470579, the variant C allele was associated with T2DM (p<0.001). The frequency of (A/C + C/C) genotypes vs. A/A genotype was significantly higher in T2DM patients than in controls (70% vs. 30% and 37.5% vs. 62.5%, respectively) (p=0.00001). For rs440960, the variant T allele was associated with T2DM (p<0.001). Genotype G/G was the most frequent in controls (62.5%). The frequency of (G/T + T/T) genotypes vs. G/G genotype was significantly higher in T2DM patients than in controls (65.5% vs. 34.5% and 37.5% vs. 62.5%, respectively), (p=0.00001). These associations remained significant under all genetic models and after adjustment for covariates: gender, BMI, TGs and HDL-c. Both SNPs were in strong LD (D′ = 0.99 and r2 =0.98). Taking the common GA haplotype as reference, TC was the most frequent haplotype in T2DM patients and strongly associated with the disease (p = 0.004, OR= 3.29, 95%CI = 2.19–10.84), followed by GC haplotype (p = 0.02, OR=1.42, 95% CI=1.08–1.88) then the TA haplotype (P= 0.04, OR=1.14, 95%CI=0.99–1.86). In conclusion, IGF2BP2 susceptibility variants rs4402960 and rs1470579 associate with T2DM in Egyptians.
Keywords: Type 2 diabetes mellitus, Single nucleotide polymorphism, IGF2BP2
Cite this paper: Dalia El-Lebedy, Ingy Ashmawy, Alshaymaa A. Ibrahim, Common Variants in IGF2BP2 Gene rs4402960 and rs1470579 Polymorphisms Associate with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Egyptians: A Replication Study, International Journal of Diabetes Research, Vol. 4 No. 3, 2015, pp. 43-48. doi: 10.5923/j.diabetes.20150403.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Diabetes mellitus is a global health problem with a tremendous impact on morbidity and premature mortality worldwide. It affects 366 million people worldwide (6.4% of the world’s adult population aged between 20–79 years). This number will be increased to 552 million by 2030 [1]. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a complicated heterogeneous metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia as a result of pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction and/or insulin resistance [2]. It is associated with long-term damage, dysfunction, and failure of several organs [3]. Multiple environmental factors and genetic determinants are considered to be involved in the pathogenesis of the disease. Meanwhile diet, physical activity, and other lifestyle factors contribute to the initiation and progression of T2DM [4] yet genetic factors play crucial role in the pathogenesis of the disease [5]. Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) belongs to a family of IGF2 mRNA-binding proteins that is implicated in mRNA localization, turnover and IGF2 translational regulation [6, 7]. IGF-2 plays a role in glucose homeostasis through increasing peripheral glucose uptake in different tissues as well as inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipolysis [8]. Several variants of IGF2BP2 gene located on chromosome 3q27.2 were identified and investigated for association with T2DM. Intron-2 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) rs4402960 and rs1470579 were the most studied and have been considered strong candidate variants for T2DM susceptibility [9]. However, due to the ethnic difference in risk-alleles frequency, the contribution of these common variants to T2DM appears to be race dependent [2] which makes them highly controversial candidates for T2DM. In this study we investigated the association of IGF2BP2 rs4402960 and rs1470579 risk variants in Egyptian T2DM patients.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
- This case-control study included 120 unrelated T2DM patients and 128 controls. The T2DM patients were recruited from the outpatient clinic of the National Diabetes & Endocrinology Institute, based on their medical record and fulfilling the diagnostic criteria of American Diabetes Association [3] that specifies fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 126 mg/dl or 2h plasma glucose (PPG) ≥ 200 mg/dl or random plasma glucose (random blood sugar) (RBG) ≥ 200 mg/dl.Full medical history and clinical examination were applied. Anthropometric measurements (weight and height) were collected and used for BMI calculation according to the standard formula BMI = weight (kg)/ [height (m)]2. Exclusion criteria were other types of diabetes (including T1DM, or maturity onset diabetes of the young [MODY]), renal disease, hepatic disease, endocrinal disease, metabolic disorders and autoimmune diseases.Informed consent was obtained from all subjects and the study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the National Research Center.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Biochemical Markers
- Venous blood samples were collected from all subjects after 12 hours of overnight fast. Fasting plasma glucose, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) were assayed on Cobas c311 clinical chemistry analyzer (Roche Diagnostics, Germany).
2.2.2. Genotyping of IGF2BP2 SNPs
- Genomic DNA was isolated from whole peripheral blood using QIAamp DNA extraction kit (Qiagen Hilden, Germany, Cat no. 51304) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Genotyping of IGF2BP2 rs4402960 and rs1470579 polymorphisms was performed with the Taqman-based allelic discrimination method using ABI 7500 Real Time PCR (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). All primers and probes were designed by Applied Biosystems (Foster City, CA). For rs4402960, the primers sequence were Forward 5'-GGAGCAGTAAGGTAGGATGGACAGTAGATT-3' and reverse 5'-AAGATACTGATTGTGTTTGCAAACATGCCC-3'. VIC/FAM probes were AGTAAGGTAGGATGGACAGTAGATT [G/T]AAGATACTGATTGTGTTTGCAAACA. For rs1470579, the primers sequence were Forward 5-'TATCATCATTAGATAAGATCCATACGAGTT-3' and reverse 5'-ATCCTGCCTATCAAGAAAAGGA CTTTTCCC-3'. VIC/FAM probes were TCATTAGATA AGATCCATACGAGTT[A/C]ATCCTGCCTATCAAGAAAAGGACTT.The genotyping success rate was greater than 98% for all SNPs. For genotyping quality control, 10% of samples were randomly selected and measured in duplicates and the concordance rate was 100%.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
- Data were analyzed using SPSS version 16.0 for Windows (Chicago, IL, USA). Data were expressed as mean± SD for continuous variables and as percentages of total for categorical variables. Intergroup significance was assessed by Student’s t-test for continuous variables and χ2 test for categorical variables. Allele frequencies were calculated by gene-counting method. The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium was estimated by χ2 test using Pypop software. Haploview software was used to obtain estimate of Linkage Disequilibrium. Chi-square was used to test the difference in alleles and genotypes frequency between groups. Bonferroni correction method was applied for multiple testing. Associations of IGF2BP SNPs and haplotypes with T2DM were evaluated by logistic regression adjusted for gender, BMI, TGs and HDL-c. P value less than 0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of Studied Subjects
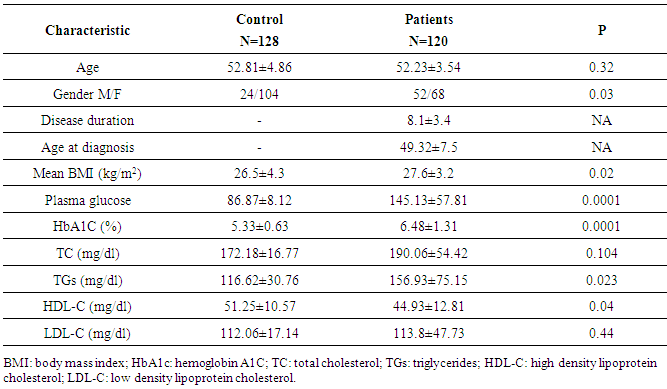
- The clinical and laboratory characteristics of studied subjects are summarized in Table (1). While age, TC and LDL-C were comparable between cases and controls, significant differences between patients and controls were noted in gender distribution (P = 0.03), mean BMI (P = 0.02), serum TGs (P = 0.023) and HDL-C (P = 0.04) which were the potential covariates adjusted for in subsequent analysis.
|
3.2. Association Studies of IGF2BP2 SNPs
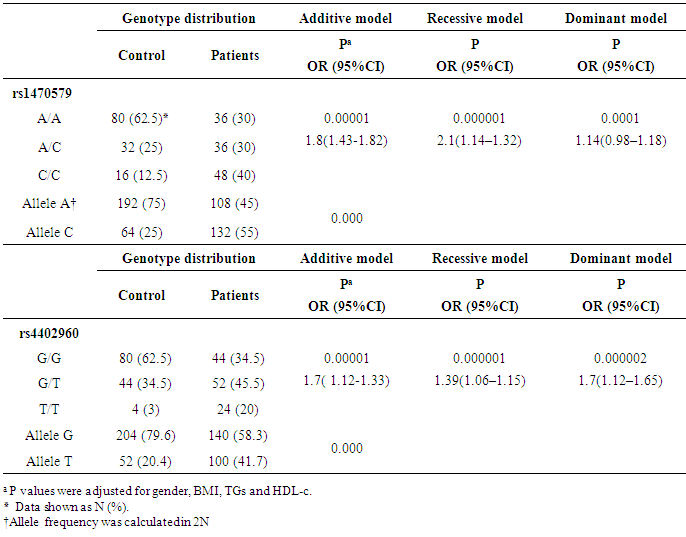
- For rs1470579, the C allele frequency was significantly higher in T2DM patients than in controls (p<0.001). The frequency of (A/C + C/C) genotypes vs. A/A genotype was significantly higher in T2DM patients than in controls (70% vs. 30% in patients and 37.5% vs. 62.5% in controls, respectively) (p = 0.00001).For rs440960, The T allele frequency was significantly higher in T2DM patients than in controls (p<0.001), with G/G genotype was the most frequent in controls (62.5%). The frequency of (G/T + T/T) genotypes vs. G/G genotype was significantly higher in T2DM patients than in controls (65.5% vs. 34.5% in patients and 37.5% vs. 62.5% in controls, respectively) (p=0.00001). Distribution of IGF2BP2 rs4402960 and rs1470579 variant genotypes and alleles in patients and controls and their association analyses under additive (T vs. G for rs4402960 and C vs. A for rs1470579), dominant (GG vs. TT for rs4402960 and AA vs. CC for rs1470579) and recessive (TT vs. GG+GT for rs4402960 and CC vs. AA+AC for rs1470579) genetic models are summarized in Table (2). Both IGF2BP2 SNPs showed a significant association with T2DM under all genetic models and after adjustment for the covariates, gender, BMI, TGs and HDL-c.
|
3.3. Haplotype Analysis
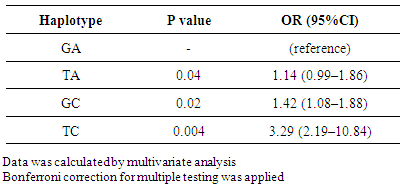
- Both SNPs were in strong LD (D′ = 0.99 and r2 = 0.98). Haplotype analysis was performed and minor alleles were defined based on frequency in controls. TC was the most frequent haplotype in T2DM patients and strongly associated with the disease (p = 0.004), followed by GC (p = 0.02) and TA (P = 0.04) haplotypes. Taking the common IGF2BP2 rs4402960/rs1470579 GA haplotype as reference (OR = 1.00), multivariate analysis confirmed theses associations (Table 3).
|
4. Discussion
- IGF2BP2 is one of the genes identified though GWAS (Genome-Wide Association Studies) to be associated with T2DM, which has been repeatedly confirmed among different ethnic populations [10]. The most extensively studied variants were intron-2 polymorphisms rs4402960 and rs1470579. While many studies confirmed the association [10-20], other studies reported no association [21-24]. Moreover, subsequent replication studies in different populations yielded inconsistent results. Our study is the first replication study of IGF2BP2 risk variants, rs4402960 and rs1470579, in Egyptians. Our results showed a strong association of both SNPs with T2DM. In a previous study in Lebanese Arab population, both IGF2BP2 variants represented common T2DM susceptibility genes with the strongest association at rs4402960 (p = 6.5x 10-6), followed by rs1470579 (p = 5.3x10-4) under additive and recessive models, but, only rs4402960 remained significantly associated with T2DM under the dominant model (p = 002) [18]. For rs4402960 variant, significant association with T2DM was identified in Moroccan population under additive (GG vs. TT; p=0.009) and recessive (TT vs. GG+GT; p=0.003) models [25], and with T2DM and overweight/obesity risk in Tunisian population [26]. Significant increased risk has been also confirmed by several studies in European and non- European populations under additive, dominant and recessive genetic models. But in Africans, no significant association was detected under any genetic model [27]. Interestingly, replication studies in the same population yielded inconsistent results. Controversial association of rs1470579 with T2DM in France was reported by two independent French studies [21, 32]. In Indian population, two studies reported no association between both SNPs and T2DM [22, 33], on the other hand, a north Indian study [34] which included the largest sample from India showed significant association of these two SNPs with T2DM. This conflict of results has been attributed to ethnic/background variations. Moreover, a potential bias in finding and reporting significant associations was recently suggested [35] as some studies have examined several genetic models [18, 19, 24], while other studies have examined only the additive model [20, 23]. Our results showed significant associations of both IGF2BP2 rs4402960 and rs1470579 variants with T2DM in Egyptians under all genetic models. In our patients, haplotype analysis showed that the strongest association of T2DM was with rs4402960/ rs1470579-minor alleles-containing haplotype (TC) (P=0.004) followed by rs1470579- minor (C) allele-containing haplotype (GC) (P=0.02) then the rs4402960- minor (T) allele-containing haplotype (TA) (P=0.04). In a study on Lebanese Arab, Caucasian and non-Caucasian populations, the 2-locus haplotypes identified both rs4402960 minor (T) allele containing haplotypes (TC and TA), to be associated with increased T2DM risk while no association was found with GC haplotype [18].It is becoming evident that single susceptibility locus is not shared among all ethnic groups. In addition, haplotype variation in populations may indicate different SNPs within IGF22BP2 gene that may be associated with T2DM, which might be located at a distance downstream or upstream of the most common variants [42].In conclusion, our replication study identified a significant association of IGF2BP2 rs4402960 and rs1470579 variants with T2DM in Egyptians. Further studies are to be addressed to assess other IGF2BP2 variants that could modify the risk of T2DM in our population.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML