-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Diabetes Research
p-ISSN: 2163-1638 e-ISSN: 2163-1646
2013; 2(3): 39-44
doi:10.5923/j.diabetes.20130203.01
The Effect of Some Biochemical Parameters in Brain Tissue of Rats Pine Oil Streptozotocin with Experimental Diabetes in Rats
Ersin Demir1, Okkes Yilmaz1, Ayse Dilek Ozsahin2
1FiratUniversity, Faculty of Science, Biology Department, Elazig, 23169, Turkey
2Bitlis Eren University, Faculty of Science, Biology Department, Bitlis, 13000, Turkey
Correspondence to: Ayse Dilek Ozsahin, Bitlis Eren University, Faculty of Science, Biology Department, Bitlis, 13000, Turkey.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
The aim of this study pine oil Type-2 diabetes created the rats in the brain tissue of some biochemical parameters on the investigation of the effect of the purposes. To create diabetes in male rats,a 40mg/kg STZ (streptozotocin)intraperitoneal injection was given. These rats (n=20) were divided into two groups. The diabetes control group was given a 1mg/kg dose of intraperitoneal injection DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide) two days a week. The diabetes treatment group was given pine oil DMSO with a 1/1 dilutionratio and this mixture was given to the diabetes+pine oil group two days a week, and also 0.5 ml of pure pine oil was added to 500 ml of water and given to the rats.This practice lasted for 8 weeks.Diabetes control group, compared to the diabetes+pine oil group of MDA (malondialdehyde) and total protein levels significantly decreased, the GSH (glutathione) level significant level was found to increase.Diabetes group, compared to the diabetes+pine oil group applied to the pine oil in the brain tissue, fatty acid composition, cholesterol, stigmasterol and β-sitosterol with vitamin K outside the lipophilic vitamin at the level of the resulting change to prevent were determined.Experimental diabetes is created in rats’ brain tissue, examined, the parameters obtained positive, according to the data of the pine oil diabetes during brain tissue occurring metabolic abnormalities correction would be useful to us suggests.
Keywords: Diabetes, Pine Oil, Brain, Lipid Peroxidation, Fatty Acid, Cholesterol
Cite this paper: Ersin Demir, Okkes Yilmaz, Ayse Dilek Ozsahin, The Effect of Some Biochemical Parameters in Brain Tissue of Rats Pine Oil Streptozotocin with Experimental Diabetes in Rats, International Journal of Diabetes Research, Vol. 2 No. 3, 2013, pp. 39-44. doi: 10.5923/j.diabetes.20130203.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Diabetes mellitus (DM) is the most significant chronic diseaseand cause of death in modern society. Diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defective insulin secretion, resistance to insulin action or both. DM involves high level ofblood glucose, which contributes to an increase in free radical production[1,2]. It is a global healthcare problem that affects 5–7% of the world population[3]. This disease is divided into two broad categories, including type 1 and type 2. Type1 diabetes or insulin- dependent diabetes mellitus occurs due to immunological destruction of pancreatic β cells and consequent insulin deficiency. Type 2 diabetesornon-insulin-dependentdiabetes mellitus is characterized by impaired insulin secretionor insulin resistance[4].The neurological consequences of diabetes mellitus in the Central Nervous System (CNS) are now receiving greater attention. Cognitive deficits, along with morphological and neurochemical alterations illustrate that the neurological complications of diabetes are not limited to peripheral neuropathies[5]. The central complications ofhyperglycemia also include the potentiation of neuronal damage observed following hypoxic/ischemic events, aswell as stroke[6,7]. Experimental diabetes hyperglycemia revealed significant changes in neuronal and glial cells; damage is caused by causing transient ischemia[8]. Glucose utilization is decreased in the brain during diabetes[2,5], providing a potential mechanism for increased vulnerability to acute pathological events.An increased level of lipid peroxidation in diabetes[9] similar to the result of experimentally induced hypoglycemia was reported with an increase in oxidative damage in the brain tissue of rats[10].Streptozotocin (STZ) is preferred by many researchers in the creation of experimental diabetes. The induction of experimental diabetes in the rat using chemicals which selectively destroy pancreatic B cells is very convenient and simple to use. The most usual substances to induce diabetes in the rat isstreptozotocin. Streptozotocin action in B cells is accompanied by characteristic alterations in blood insulin and glucose concentrations[11].Ethnopharmacological surveys indicate that more than 1200 plants are used in traditional medicine for their alleged hypoglycemic activity[12-14]. Literature has shown specific chemical constituents of these plants, such as phytochemicals to be the active hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic principle in many medicinal plants with blood glucose and lipid-lowering attributes[15]. Since antiquity, diabetes mellitus has been treated with plant medicines. Recent scientific investigation has confirmed the efficacy of many of these preparations, some of which are remarkably effective[15]. The aim of this study pine oil Type-2 diabetes created the rats in the brain tissue of some biochemical parameters on the investigation of the effect of the purposes.
2. Materials and Methods
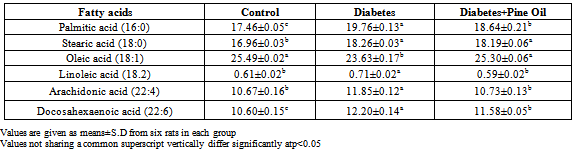
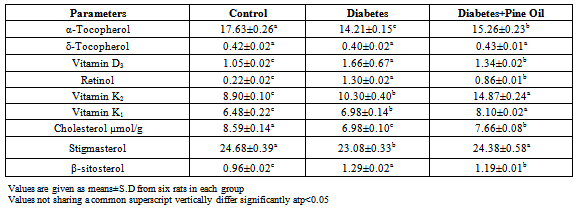
- Animals Animals, experimental design the experimental protocols were approved by the local Animal Use Committees of Firat University (Elazig, Turkey). Animal care and experimental protocols complied with the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH publication no. 05.05.2011/81). Thirty healthy adult male Wistar albino rats, aged 8–10 weeks were obtained and maintained from Firat University Experimental Research Centre (Elazig, Turkey). The animals were housed in polycarbonate cages in a room with a 12 h day-night cycle, temperature of 24 ± 3℃, and humidity of 45% to 65%. During the whole experimental period, animals were fed with a balanced commercial diet (Elazig Food Company, Elazig, Turkey) ad libitum and fresh distilled drinking water was given ad libitum.Experimental DesignThe animals were randomly divided into three groups with ten animals in each group. The first group was taken as:1. Control group: Normal control received 10% DMSO (pure DMSO) intraperitoneallyonly two days a week for a period of 2 months.2. Diabetes group (D): Streptozotocin (STZ) was dissolved in sodium citrate buffer (pH 4.5) and injected two days a week for a period of 2 months at a dose of 40mg/kg body weight. Blood glucose levels were determined 3 days after STZ injection. Rats with a blood glucose concentration above 140-200mg/dl were declared diabetic[16-17].3. Diabetes+Pine Oil group (D+PO): Rats received pine oil dissolved in DMSO (1:1 v/v) intraperitoneally for two days a week for a period of 2 months at a dose of 1mg/kg body weight. Also the addition of 0.5 ml of pure pine oil added to 500 ml drinking water was given to the rats.All protocols described were reviewed and approved by the local institutional committee for the ethical use of animals. Eight weeks STZ diabetic rats and age-matched controls were killed by decapitation. The brain tissues were removed and samples were used fresh or kept at –70°C.Homogenate PreparationTissue samples were homogenized in Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.5) and centrifuged at 9000xgfor 20 min at 4°C. Supernatants were collected, aliquoted, and stored at –70°C until use. The supernatant obtained from the TBARS, reduced glutathione and total protein analysis, the pellets ADEK vitamins, cholesterol, and fatty acid analysis was performed.Biochemical DeterminationsDetermination of MDA-TBA levelLipid peroxides (TBARS) in tissue homogenate were estimated using thiobarbituric acid reactive substances by the method of Okhawa et al.[18]. To 1,0 ml tissue homogenate, 0,5 ml of 8,1% SDS, 1,0 ml of (20% acetic acid/NaOH pH 3,5), 1,0 ml of 10% TCA,50 µl of 2% BHT and 1,0 ml of 0,8% TBA were added. The mixture was heated in a water bath at 95℃ for 60 min. After cooling, 4 ml of n-butanol / pyridine mixture were added and shaken vigorously. After centrifugation at 4250 rpm for 15 min, the organic layer was taken and its absorbance at 532 nm was measured. 1.1.3.3-tetramethoxypropane was used as standard. The resulting nmol MDA/g tissue was calculated.Determination of GSH level in tissue samplesReduced glutathione (GSH)was determined by the method of Ellman[19]. Briefly, 1 mL tissue homogenate was treated with 1 mL of 5 trichloroacetic acid (% 10) (Sigma, St. Louis, MO), the mixtures were centrifuged at 5000 rpm and the supernatant was taken. After deproteinization, the supernatant was allowed to react with 1 mL of Ellman’sreagent (30 mM 5, 5’-dithiobisnitro benzoic acid in 100 mL of 0.1% sodium citrate). The absorbance of the yellow product was read at 412 nm in spectrophotometer. Pure GSH was used as standard for establishing the calibration curve[20].Lipid extractionLipid extraction of tissue samples were extracted with hexane-isopropanol (3:2 v/v) by the method of Hara and Radin[21]. A tissue sample measuring 1 g was homogenized with 10 mL hexane-isopropanol mixture. Fatty acids in the lipid extracts were converted into methyl esters including 2% sulphuric acid (v/v) in methanol[22]. The fatty acidmethyl esters were extracted with 5 mL n-hexane. Analysis of fatty acid methyl ester was performed in a Shimadzu GC-17A instrument gas chromatograph equipped with a flame ionization detector (FID) and a 25m, 0.25 mm i.d.permabond fused-silica capillary column (Macherey- Nagel, Germany). The oven temperature was programmed between 145–215℃, 4℃ / min. Injector and FID temperatures were 240 and 280℃, respectively. The rate of nitrogen carrier gas was at 1 mL / min. The methyl esters of fatty acids were identified by comparison with authentic external standard mixtures analyzed under the same conditions. Class GC 10 software version 2.01 was used to process the data. The results were expressed as (%) tissue.Saponification and extractionAlpha-tocopherol and cholesterol were extracted from the lipid extracts by the method of Sanchez-Machado et al.[23] with minor modifications. Five milliliters n-hexane / isopropyl alcohol mixture was treated with 5 mL of KOH solution (0.5 M in methanol), which was immediately vortexedfor 20 s. The tubes were placed in a water bath at 80℃ for 15 min. Then after cooling in iced water, 1 mL of distilled water and 5 mL of hexane was added, and the mixture was rapidly vortexed for 1 min, then centrifuged for 5 min at 5000 rpm. The supernatant phase was transferred to another test tube and dried under nitrogen. The residue was re-dissolved in 1 mL of the HPLC mobile phase (68:28:4 (v/v/v) methanol:acetonitrile:water). Finally, an aliquot of 20 μL was injected into the HPLC column. Before injection, the extracts were maintained at −20℃ away from light.Total Protein AssayTotal protein contents of brain tissue were determined as Lowry’s method described. The procedure for measuring protein was followed according to Lowry et al.[24]using BSA (Bovin serum albumin) as standard. The absorbance was read at 750nm using aspectrophotometer. Statistical analysisValues were given as means±S.D for ten rats in each group. Data were analyzed by one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Duncan's Multiple Range Test (DMRT) using SPSS-15. The limit of statistical significance was set at p<0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
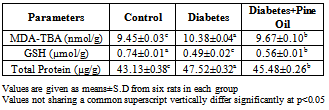
- Lipid Peroxidation and GlutathioneThe levels of TBARS, GSH and total protein in the brain of control and diabetic rats are presented in the Tables 1. The TBARS and total protein levels was found to be significantly high in the diabetes group (p<0.001) when compared to the control group.The GSH level in the diabetes groups was found to decrease significantly compared to the control group (p<0.001). When the TBARS and total protein amounts was compared with the diabetes group, significant decreases were observed in diabetes+pineoil group (p<0.001) and GSH levels was determined to increase significantly.
|
|
|
4. Conclusions
- In conclusion, experimental diabetes created in rats brain tissue, examined, the parameters obtained positive, according to the data of the pine oil diabetes during brain tissue occurring metabolic abnormalities correction would be useful to us suggests.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- This work has been supported by the Firat University Research Fund (FÜBAP Project number 1652 and 1670)
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML