-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Diabetes Research
p-ISSN: 2163-1638 e-ISSN: 2163-1646
2013; 2(2): 27-32
doi:10.5923/j.diabetes.20130202.02
Improvement of Insulin Sensitivity by Rosiglitazone Decreased the Visfatin Level in Obese Rats Induced by High Fat Diet
Husam M. Edrees, Enas N. Morgan
College of Medicine-Department of Physiology- Zagazig-University
Correspondence to: Husam M. Edrees, College of Medicine-Department of Physiology- Zagazig-University.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Despite the insulin-mimic effect of visfatin, controversy exists over its relation to insulin resistance associated with obesity. Rosiglitazone maleate (RSG) is used as insulin sensitizers in the treatment of type2 diabetes. Aim: the present study had been carried out in a trial to identify the relation of serum visfatin to glucose and insulin homeostasis in fatty albino rats and the effect of RSG treatment in regulation of visfatin level. Materials and Methods: A total number of 30 adult male albino rats were divided into 3 equal groups: Group I, rats were served as control. Group II, rats received only high fat diet (HFD). Group III: rats received HFD and treated with RSG for 7 days. In all groups, HOMA-IR and serum levels of glucose, insulin and visfatin were measured. The correlation between visfatin levels and insulin resistance in treated and non treated groups was investigated. Results: There was a significant increase in serum visfatin, insulin, glucose levels and HOMA-IR value (p<0.001for all) in high fat diet fed group in comparison with control group. However, all these values were significantly decrease (p<0.001for all) in HFD fed group treated with RSG in comparison with Group II. There was a significant positive correlation between serum visfatin and HOMA-IR in group II (r=0.935; P<0.001) and group III (r=0.951; p<0.001). Conclusion: Rosiglitazone caused improvement of insulin sensitivity and decrease in the visfatin level in the HFD-fed treated rats. The decreased level of visfatin may be a consequent effect for the improvement of insulin resistance.
Keywords: Visfatin, Rosiglitazone, High Fat, Diabetes, Insulin Resistance
Cite this paper: Husam M. Edrees, Enas N. Morgan, Improvement of Insulin Sensitivity by Rosiglitazone Decreased the Visfatin Level in Obese Rats Induced by High Fat Diet, International Journal of Diabetes Research, Vol. 2 No. 2, 2013, pp. 27-32. doi: 10.5923/j.diabetes.20130202.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Obesity is highly associated with insulin resistance, increased risk to type2 diabetes and cardiovasculardiseases[1-3]. The accumulation of adipose tissue in the abdominal visceral depot is especially correlated with insulinresistance[4,5]. Adipose tissue is a known endocrine organ secreting several soluble factors, known as adipocytokines oradipokines, like adiponectin, leptin, resistin and, visfatin[6]. In addition there are other products of adipocytes like free fatty acids, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-1, Monocyte chemo-attractant protein-1 (MCP-1), coagulation mediators such as platelet activatorinhibitor-1 (PAI-1), and complement components[7]. These adipokines have essential roles in energy homeostasis, glucose and lipid metabolism, insulin resistance, inflammation, andatherosclerosis[8].Visfatin is one of these adipokines that is secreted by visceral and subcutaneous fat[9], human bone marrow, liver, and muscle, it is also called pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor 1 (PBEF-1)[10]. PBEF-1 was primarily considered a factor related to the pre-B cell colony formation activity of stem cells and was therefore defined as a cytokine which acts on early B linkage precursor cells, now known asvisfatin[11]. Visfatin was found to be released predominantly from macrophages infiltrating the adipose tissue rather than from adipocytes in visceral adipose tissue. In this regard, there is sufficient evidence to consider that visfatin is produced in response to inflammatory signals[12]. It is now believed that visfatin actions can be endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine as well. These autocrine effects of visfatin may play an important role in regulating insulin sensitivity in the liver [13,14].Despite the insulin-mimic effect of visfatin[10],controversy exists over its role in insulin resistance. Several studies failed to show an association of circulating visfatin with insulin sensitivity[15-17] while others indicated that visfatin was shown to be involved in the development ofobesity-associated insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus in human and animal models[15,18]. In vitro studies showed an insulin-like effect of visfatin on regulation of glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and L6 myocytes, and also in adipocyte differentiation[10].Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)[Rosiglitazone], an insulin sensitizer which act via stimulation of peroxisomeproliferator activated receptor-γ (PPAR-γ)[19], it enhances the flux of free fatty acids (FFAs) into the tissue and facilitates their enzymatic degradation[20]. TZDs have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and insulin resistance. FFAs directly impair insulin sensitivity and are critically involved in the pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus[21]. Rosiglitazone (RSG), an insulin sensitizer, is widely used clinically as an anti-hyperglycemic agent in type 2 diabetes because of its effects on glucose and lipid metabolism[22]. Besides its insulin sensitizing property, RSG also has benefits on cardiovascular functions, including improvement in endothelial function and lowering of blood pressure[23]. Interestingly, these cardiovascular actions of RSG have also been found in type 1 diabetic animals.[24] In the current study, the relation of visfatin to insulin resistance in obese rats induced by HFD was examined. Furthermore, the effect of improvement of insulin sensitivity by Rosiglitazone maleate administration on the visfatin level was investigated.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animal
- The current study was carried on 30 male adult albino rats (body weight, 180-200 gm) rats were housed under hygienic conditions, in the animal house of the College of Medicine, Zagazig University at 21°C–24°C in a 12 hr/12 hr light/dark cycle[25] for 7 weeks[26]. They were given free access to water and food. The animals were classified into three equal groups:Group I: (Control group): rats were served as a control group; rats were fed standard rat chow that consisted of 25.8% protein, 62.8% carbohydrates and 11.4% fat (total 12.6 kJ/g)[27].Group II: (High fat diet fed non treated group): rats were received high fat diet (HFD) for 7 weeks; (HFD; is consisted of 16.4% protein, 25.6% carbohydrate, and 58.0% fat in the form of cotton seed oil added to the laboratory chow diet[27,28]) (a total Cal.=23.4 kJ/g) The diet was provided from the college of Veterinary Medicine-Zagazig University.Group III (High fat diet fed treated group): rats were received high fat diet (HFD) and treated with Rosiglitazone maleate (ESG) (Glaxo-Egypt) at a dose of 3mg/kg/day via oral gavages for 7 days.[29]For all groups, body weight was recorded per week and at the end of the study period (7 weeks for the non treated group and 8 weeks for the treated group).
2.2. Sampling of Blood
- At the end of the experimental period and after overnight fasting, at 8:00a.m, blood samples were obtained from sinus orbitus vein of each rat after ether inhalation. The blood samples were allowed to clot at room temperature before centrifuging at approximately 3000rpm for 15 minutes. The serum was stored at -20°C.
2.3. Laboratory Analysis
2.3.1. Estimation of Serum Visfatin Level
- Rat visfatin ELISA kits: which is an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitative measurement of visfatin concentration in rat blood plasma and other biological body fluid (BioVendor-Laboratorni medicina, U.S.A.).
2.3.2. Estimation of Serum Glucose Level
- According to Trinder using glucose enzymatic (GODPAP) - liquizyme Kits (Biotechnology, Egypt).
2.3.3. Estimation of Serum Insulin Level
- By a solid phase enzyme amplified sensitivity immunoassay according to Starr et al. usingKAP1251-INSEASIA (Enzyme Amplified Sensitivity Immunoassay) Kits (BioSource Europe S.A., Belgium).
2.3.4. Determination of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR)
- It was assessed by homeostasis model assessment (where HOMA-IR=(fasting insulin (μU/ml) x fasting plasma glucose (mg/dl) /405.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
- Results are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. Statistical analysis was performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS), version 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, United States). Repeated measures of analysis of variance (ANOVA) statistical analysis were applied followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test. P value <0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Pearson's correlation analyses were performed to screen potential factors related to fasting serumconcentrations of visfatin.
3. Results
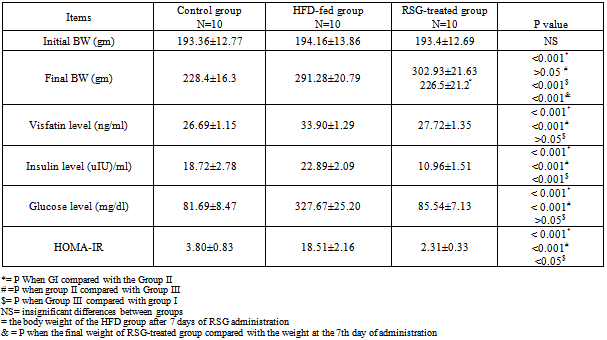
- The results of the laboratory analysis were represented in table (1).In group II there were significant increases in the body weight (291.28±20.79), visfatin level (33.90±1.29), insulin level (22.89±2.09), fasting blood glucose level (327.67±25.20) and HOMA-IR (18.51±2.16) in comparison with the control[228.4±16.3; 26.69±1.15; 18.72±2.78; 81.69±8.47; 3.80±0.83 respectively] (p<0.001 for all). Moreover, there was a significant positive correlation was recorded between the visfatin level and HOMA-IR (r=0.935; p<0.001); Fig. (1).
|
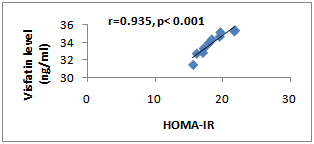 | Figure (1). Correlation Between Visfatin Level and HOMA-IR in Group II Rats |
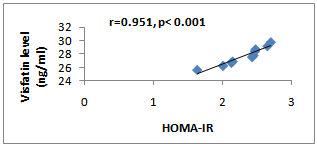 | Figure (2). Correlation Between Visfatin Level and HOMA-IR in Group III Rats |
4. Discussion
- The results of the present study revealed that there was a significant increase in serum insulin and glucose level in HFD fed-rats. Consequently, the HOMA-IR value was also significantly increased indicated a development of insulin resistance. These findings are in good accordance with other published works in which high fat/high sucrose diets have been shown to enlarge adiposity and to impair whole body insulin action[32, 33]. Moreover, HFD-fed rats showed a significant higher serum visfatin level. This finding is in line with the finding of Naz et al.[34] that indicated an increase in the visfatin levels in obese mice fed on a high fat diet for 4 months. Moreover, Taşkesen et al.[35] demonstrated higher visfatin level in obese adolescents than non obese adolescents. Many studies revealed that T2DM patients showed significantly higher serum visfatin levels than non diabetic subjects[15,36,37]. However, the relation between the level of visfatin and insulin resistance still shows controversial results, some studies found positive correlations of circulating visfatin with HOMA-IR and insulin levels[38], Taşkesen et al.[37] indicated positive correlation between visfatin level and HOMA-IR and negative correlation of it with glucose and insulin levels in combined control and obese group of adolescents, while other failed to found any association of circulating visfatin with HOMA-IR[39]. In the current study there was positive correlation indicated between the HOMA-IR and visfatin levels. However, it is yet to be proven whether visfatin production is a compensatory response to tissue specific insulin resistance or it is a marker for insulin resistance development.Naz et al.[34] showed that the administration ofexogenous recombinant-histidine soluble (mice) visfatin in obese and diabetic groups of mice resulted in significant reduction in their fasting blood glucose levels but it remained higher than the glucose levels of normoglycaemic mice. These results are congruent with the results of Fukuhara et al.[10], who demonstrated an insulin mimetic effect of visfatin. They further established that visfatin used the system of tyrosine phosphorylation - dependent signaling for its actioncomparable to that of the insulin receptor. Although visfatin levels had been increased in the HFD received group, the blood glucose also was high. This may be due to the development of visfatin resistance similar to that of insulin resistance as visfatin uses the same receptors used by the insulin for its action[17]. Moreover, in insulin resistant diabetes mellitus, various adipocytokines have been documented to be released such as resistin, which have been proposed to oppose the action of insulin[1]. Naz et al.[34] suggested that increased levels of visfatin in obesity and insulin resistant diabetes mellitus might have beenneutralized by other adipocytokines and have resulted in visfatin resistance and hyperglycaemia because visfatin acts on the same receptor as that for the insulin.In the current study, it was found that treatment of HFD received rats with RSG significantly decreased the serum visfatin, insulin and glucose levels. These findings are in agreement with[40] who revealed that RSG causessignificant down-regulation of circulating visfatin concentrations and this effect were normalized by lipid infusion. In contrast Hammarstedt et al.[17] findings indicated that treatment with pioglitazone (one drug belongs the TZDs) unaffected the visfatin levels. This controversial result may be due to several factors including the duration of treatment, the characteristics of the diabetic cohort and the properties of the various TZDs.In contrast to the findings of this study,[41] demonstrated that RSG treatment increases circulating visfatinconcentrations in healthy humans and induces a release of visfatin from isolated adipocytes into the supernatant medium. This effect is counteracted by FFA and can be influenced in vitro by antioxidant strategies. Furthermore, visfatin secretion from adipocytes by rosiglitazone involves activation of PI 3-kinase and Akt. They concluded that the systemic effect of rosiglitazone on plasma visfatin concentrations is not likely the result of altered insulin sensitivity, and the changes observed occurred in the absence of altered circulating insulin concentrations in healthy subjects.The current study revealed improvement of the insulin resistance and decrease in the HOMA-IR in the RSG treated group. In addition the visfatin levels are significantly and positively correlated with the HOMA-IR in this group.
5. Conclusions
- The present study revealed higher visfatin production at obese HFD received rats which correlated with HOMA-IR. Moreover, improvement of insulin resistance afterRosiglitazone administration led to down regulation of serum visfatin. However, visfatin's role in the pathogenesis of obesity, T2DM and insulin resistance still shows somewhat of contrivers. Its function and effect may be depending on the metabolic state of the body. Additional researches are needed to clarify the role of visfatin, visfatin receptors and their mechanisms of action in pathogenesis of insulin resistance and obesity.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- The authors would like to acknowledge the supporting team of technicians in the Department of MedicalBiochemistry, Zagazig University for their assistance in the laboratory analysis.This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML