-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Diabetes Research
p-ISSN: 2163-1638 e-ISSN: 2163-1646
2013; 2(2): 21-26
doi:10.5923/j.diabetes.20130202.01
Influence of Preparation Nucleх on the Cytokine Profile of the Patients with Diabetes Type 2 and Neuropathic Form of Diabetic Foot
Tkachuk Z. U.1, Frolov V. M.2, Zelyoniy I. I.2, Afonin D. N.2, Tyutyunnik A. A.2
1Institute of molecular biology and genetics of Ukraine NAS, Kyiv, Ukraine
2Lugansk state medical university, Lugansk, Ukraine
Correspondence to: Tkachuk Z. U., Institute of molecular biology and genetics of Ukraine NAS, Kyiv, Ukraine.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Its objective was to study the effectiveness of the drug Nuclex in the treatment of patients with diabetes and neuropathic form of diabetic foot (NFDF). The studies included 32 patients with DT 2 and NFDF. 16 patients received 2 capsules of Nuclex through 3 times a day for 21 days. To address this goal were used the following methods: general clinical examination, biochemical methods (insulin level in the blood), instrumental methods (Doppler ultrasonography, vascular flowmetery) and ELISA (TNFα, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10). Usage of Nuclex for treatment of patients with diabetes and NFDF is accompanied by a reduction of proinflammatory cytokines on a background of moderate reduction of inflammatory cytokines, which correlates with positive clinical dynamics and tendency of decreasing the insulin daily dose. It is rather prospective to continue to study the distinct mechanisms of Nuclex efficiency in the regulation of expression of genes of insulin system and cytokine cooperation.
Keywords: Diabetes, Diabetic Foot Syndrome, Nuclex, Cytokines, Insulin, Treatment
Cite this paper: Tkachuk Z. U., Frolov V. M., Zelyoniy I. I., Afonin D. N., Tyutyunnik A. A., Influence of Preparation Nucleх on the Cytokine Profile of the Patients with Diabetes Type 2 and Neuropathic Form of Diabetic Foot, International Journal of Diabetes Research, Vol. 2 No. 2, 2013, pp. 21-26. doi: 10.5923/j.diabetes.20130202.01.
1. Introduction
- According to WHO, nowadays over 120 million people are ill with diabetes and every 12-15 years the number doubles[1]. The most frequent complication of diabetes is the development of suppurative – necrotic lesions (SNL) of the lower extremities[2-4]. High susceptibility of diabetic patients to the development of SNL is caused by the symptom complex of the anatomic – functional changes, connected with diabetic micro-, macroangiopathy,neuropathy, and osteoarthropathy, and it is called diabetic foot (DF) syndrome[5-8]. However, it may sound paradoxically, but it is a fact that the correction of metabolism, strict glycemia control and the usage of different means and methods, which influence the normalization of microcirculation, haven’t made a significant impact on the prevention of suppurative – necrotic complications (SNC), which apresented in the category of such patients in general, and especially after amputations of the extremities. The usage of antibiotics to prevent SNC and to stimulate the healing process of postoperative wounds has fallen short of expectations as well [9]. Moreover, many researchers have mentioned the decreasing of general immunological resistance of the organism under the influence of antibiotics, which causes the increasing of percentage of suppuration of postoperative wounds of the patients with diabetes[3]. The problem of choosing the best methods of treatment the patients with diabetes and SNL of feet is rather relevant and not sufficiently studied[11].Terms of treatment the patients with such diseases are 1, 5-2 times longer, then the recovery time of the patients with the same process, but without diabetes, which is caused not only by the abnormalities of all kinds of metabolism, but also by immunological abnormalities[12]. SNL of feet in case diabetes should be based not only on the active drainage of the wound along with the usage of different antibiotics, but also on the usage of the medical preparations, which have a positive influence on the patient’s immune system[13-15]. It helps to renew the absorbing and the bactericidal functions of the neutrophils, the activity of the enzymatic systems of the phagocytes, complement titer and the level of the circulating immune complexes. It also helps to normalize cellular and humoral immunity. The immunoactive drugs is perspective[16, 17]. Our attention was attracted by the modern medicine – Nuclex, which shows cardiovascular and specific antiviral activity, which is based on the mechanism of immunomodulation, anti-inflammatory effect and on the influence on the conformation of surface antigens and receptors of the viruses[18-23]. This medicine is used during the complex therapy of the cardiovascular diseases, chronic viral diseases and secondary immunodeficiencies[24-26].The purpose of this research is to study the effectiveness of the drug Nuclex in the treatment of patients with diabetes type 2 (DT 2) and NFDF and Nuclex influence on the indexes of cytokine profile of blood.
2. Materials and Methods
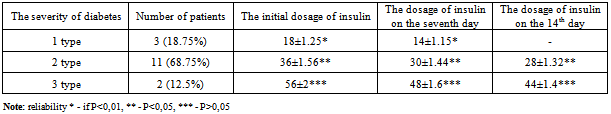
- This clinical study was held as an open, controlled, comparative, randomized, parallel. The study involved 32 patients (men - 8 women - 24) aged from 40 to 65 years (average age 46. 3 ± 1. 2 years) suffering from diabetes and NFDF. The depth of spreading corresponded the II degree, according to the Wagner’s classification[23]. All the patients were undergoing hospital treatment in the surgical department of Lugansk multi – field hospital № 2 (the base of general surgery department of Lugansk state medical university). Patients were divided into 2 groups (basic and comparison) in a ratio of 1:1. Dividing into groups was performed randomly. The scheme of randomized dividing was formed on the basis of random numbers, generated by MS Excel function of random numbers. All the patients had clinical, biochemical and instrumental examination. The state of peripheral arterial blood flow was assessed according to the data received by means of ultrasonic Doppler auscultation (Logidop-2 Kranzbǖhler, Germany) along with the counting of the ankle-brachial index (ABI). The intensity of microcirculation was measured by laser flowmeter BZF-21 Transonic Systems Inc. (USA), using type R sensor - for surface measurements. The patients in both groups were receiving basic therapy during their treatment. Taking into account the presence of purulent wounds, all the patients during their hospital treatment were transferred to the introduction of simple insulin (Aktropid, 5 times a day). The dosage depended on the level of glycemia. In addition, the patients of the basic group additionally received Nuclex (2 capsules 3 times a day for 21 days). Under testing medicine "Nuclex" contains ribonucleic acid – 250 mg, the excipient is mannitol. Manufacturer: LLC «Pharma Start», Ukraine, PLC «Kievmedpreparat», Ukraine[18]. All the supervised patients had special tests, including the study of the concentration of pro-and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the patient’s blood serum, using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) with the help of equipment manufactured by Sanofi Diagnostics Pasteur (France), includingimmunoenzyme analyzer PR 2100. The concentration of cytokines (TNFα, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10)[27-29] in blood was identified by certified reagents produced by LLC "Proteinovyy contour" (ProCon) (Russia - St. Petersburg) [30]. To rate the efficiency during the analysis of this experiment the following criteria were used:• Positive changes of the results according to the clinical examination (disappearance of local and general signs of disease);• Positive changes of the results according to the laboratory testing (includes general clinical laboratory tests and positive changes of the immune status).Statistical analysis of the results of the research was carried out using PC Intel Соге 2 Duo 3, 0 with the help of multivariate dispersive analysis of the licensed software packages Microsoft Office 2007, Microsoft Excel Stadia 6.1/prof і Statistica[31]. The basic principles of the usage of statistical methods during the clinical testing of medical preparations were taken into account too[32].
3. Results and Discussion
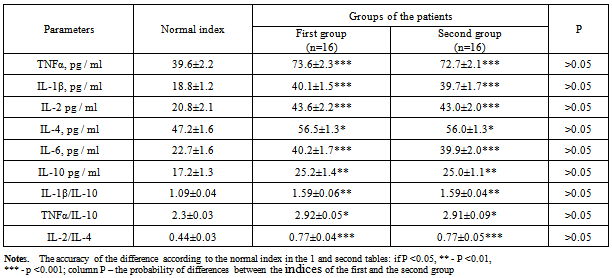
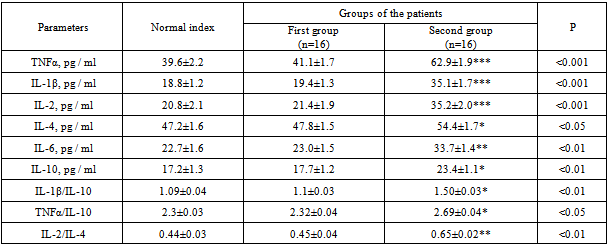
- During the patients’ undergoing of the hospital therapy they were complaining about the swelling of their feet and legs, the presence of SNC on the feet, general weakness, the absence of pronounced pain syndrome, feet’s functions disorders. 15% of the patients were suffering from diabetes less than 5 years, 19% - from 5 to 10 years, 19% from 10 to 20 years, 47% - more than 20 years. Suppurative – necrotic feet’s changes had round or oval shape, different size and were located on the plantar surface (12 cases) and on the dorsal surfaces of toes, very seldom in the place of metatarsal joints. There was an inflammation around the wounds, the width of inflammation was 1.5 - 2 cm, and there were no signs of granulation and epithelialization in the wounds. In 6 cases there were some signs of reactive inflammation of the feet with a pronounced hyperemia of the foot’s tissues and lymphadenitis in the area of the patients’ shin. All the patients were overweight (body mass index, BMI – 31.2 ± 0.8 kg/m2, normal index - 19-25 kg/m2). The level of the compensation of carbohydrate metabolism was assessed by glycosylated hemoglobin content (HbA1c) 8.7 ± 0.2%, normal content - 6.4%. 60% of the patients were diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy. Average systolic blood pressure was 160 ± 4 mm Hg. According to the results of instrumental examinations, 29 patients in both groups had high rates of ankle-brachial index (ABI) (> 1.2); it was the evidence of medial calcification. During the researches of arterial pressure in the posterior tibial artery, in both groups of the patients the average result was 05 ± 10 mmHg and it didn’t change significantly in the end of treatment. Average indexes of microcirculation according to the LDF in the patients’ feet were the following: 0.77±0.07 ml. per min/ 100g. of tissue, the first finger - 0.66 ± 0.07 ml. per min. /100g. of tissue. It should be mentioned that we did not measure the level of microcirculation when the reactive inflammation of the foot and the inflammation of the wounds in the area of the first toe were present. The indexes of the level of microcirculation in the end of the treatment in both groups of the patients did not change significantly and were the following: on the foot – 0.85± 0.09 ml. per min/ 100g. of tissue, on the first toe – 0.72±0.07 ml. per min/ 100g.Assessing the local status, we mentioned that after the start of treatment in the group, where the patients were receiving Nuclex, there was much more rapid improvement in the area of SNC s on the foot. Thus, on the 12-14th day after the start of treatment, we observed the reducing of fibrin in the wound and the formation of the initial granulation in the basic group. At the same time, the patients from the second group had the same improvements on the 15-16th day. The macroscopic data was confirmed by histological studies, which noted a concentration of mast cells with the subsequent decreasing of macrophages and fibroblasts. Moreover, the patients who received basic therapy along with Nuclex had a smaller inflammatory area before the process of the granulation, the width was less than 0.5 cm, while the patient from the second group had the inflammatory area with the width of more than 0, 5 cm. On the 4 – 6th day of the treatment the patients, who received Nuclex had the decreasing or practically had no signs of reactive inflammation of the feet and the manifestations of lymphadenitis in the area of the patients’ shin. As a result of special immunological studies, it was found the presence of some abnormalities in the parameters of cytokine profile which had been of the same type before the starting of the treatment in both groups.
|
|
|
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML