-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Diabetes Research
p-ISSN: 2163-1638 e-ISSN: 2163-1646
2012; 1(5): 73-80
doi: 10.5923/j.diabetes.20120105.01
Health Intervention Impact Assessment on Glycemic Status of Diabetic patients
Hemant Mahajan1, Tejashri Kambali2, Manish Chokhandre3, Amod Borle1, Maya Padvi2
1Department of Community Medicine, RCSM GMC Kolhapur, Maharashtra, India
2Department of Community Medicine, TN Medical College, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
3Department of Pediatrics, TN Medical College, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
Correspondence to: Hemant Mahajan, Department of Community Medicine, RCSM GMC Kolhapur, Maharashtra, India.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2012 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Diabetes has been proved to be the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in developed countries, and is gradually emerging as an important health problem in developing countries as well. Diabetes, an iceberg disease could be described as the ‘sleeping snake’- which bites when it wakes up. Diabetics, who are joyfully moving in and around us in the society, who are really not aware of the possible catastrophic end results of harbouring this ‘sleeping snake’. This study was carried out to assess the impact of health intervention on life style, self care practices and Glycemic status of Diabetic patients. A cross-sectional study was conducted at Shivaji Nagar urban slum which is a field practice area of Department of Preventive and Social Medicine; of TN Medical College Mumbai, India. Diabetic patients above 40 years of age were included in this study. The information was gathered by personal interview using semi-structured questionnaire. The collected data was numerically coded and entered in Microsoft Excel 2007 and then transferred to SPSS version 15.0 Added data was analysed with appropriate test and results were obtained. Out of 300 subjects183 (61%) were males, 146 (48.7%) patients were in the age group of 51-60. Before intervention 178 (59.3%) patients’ had Body mass index (BMI) > 25 kg/m2 and they had poor control over blood sugar. Significant improvement in life style, self care practices; illness perception and Glycemic status of patients were seen after health intervention. People have to be educated through mass media about Diabetes and its risk factors like consumption of food having high Glycemic index, alcohol etc. People have to be educated on the importance of regular physical exercises and should be encouraged to do the same.
Keywords: Type 2 Diabetes, Glycemic Status, Health Intervention, Urban Slum
Cite this paper: Hemant Mahajan, Tejashri Kambali, Manish Chokhandre, Amod Borle, Maya Padvi, "Health Intervention Impact Assessment on Glycemic Status of Diabetic patients", International Journal of Diabetes Research, Vol. 1 No. 5, 2012, pp. 73-80. doi: 10.5923/j.diabetes.20120105.01.
1. Introduction
- After combating gigantic problem of communicable diseases, like many developing nations India is also facing the new problem of chronic non communicable diseases such as diabetes because of rapid urbanization and adaptation of modern life styles. After hypertension, Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the most daunting challenges posed by chronic non-communicable disease. Although many preventive and control measures are available, prevalence of Diabetes is rising and it has become a global problem causing enormous morbidity and mortality in all developed as well as developing countries. In 2000, according to the World Health Organization, at least 171 million people worldwide suffer from diabetes, or 2.8% of the total population. The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus is steadily increasing worldwide with an estimated 366 million patients in 2030[1]. Type 2 DM is the commonest form of diabetes globally as well as in India. The prevalence ofdiabetes has shown increasing trend in the last three decades in India. The number of people with diabetes in India currently around 40.9 million is expected to rise to 69.9 million by 2025 unless urgent preventive steps are taken[2]. The present study was carried out keeping in view the illness perceptions, lifestyle and self care adopted by the patients after diagnosis and to identify the area that needs urgent attention to modify the life style and promote self care practices among them. Objective of the study was to improve the health and blood sugar control in type 2 diabetes patients by giving health education, dietary advice and encouraging them for regular blood sugar monitoring and physical exercise.
2. Material and Methodology
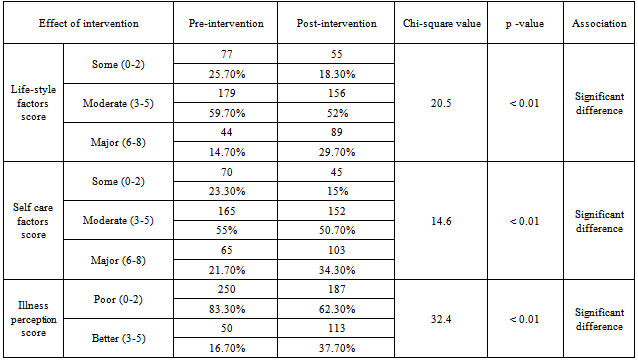
- The study was conducted at Shivaji Nagar urban slum which is a field practice area of Department of Preventive and Social Medicine, of TN Medical College,Mumbai,India. This is situated at an eastern suburb of Mumbai which comes under the jurisdiction of M East Ward of Municipal Corporation of Greater Mumbai, India. The population of Shivaji Nagar consists of people who have migrated from different parts of India, mainly from Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu. They have migrated to Mumbai in search of job. Study population was selected from type 2 diabetic patients of age 40 years & above.Total Population of Study Area = 1, 22,000.According to National Family Health Survey data 2005 -06 the population of more than 40 years is around 25.8%.Population of more than 40 years would be around 31476.Prevalence of Diabetes > 40 years in an urban slum of Mumbai is 9.3%[3].Expected number of diabetic patients in study population = 2928Taking 10 % of expected patients = 292.8 Sample size (n) = / > 293. By taking, inclusion and exclusion criteria into consideration, total 300 known Diabetic patients were selected by employing simple random sampling method.This study was conducted in the following 6 phases-1) Preparatory Phase: October 2009 to December 2009 (3 months)2) Phase of rapid survey: January 2010 to March 2010 (3 Months)2) Phase of Pre Intervention Data Collection: April 2010 to June 2010 (3 months)3) Intervention Phase: July 2010 to June 2011 (1 year)4) phase of Post Intervention Data Collection: July 11 to September 2011 (3 months)5) Phase of Data Analysis: October2011 (1 month)6) Documentation Phase: November 2011 to December 2011(1 month)Semi structured interview schedule was constructed relevant to the study. This interview schedule was tested by pilot study on 25 diabetic patients attending geriatric clinic in Urban Health Center (UHC). Appropriate changes were done based on pilot study and the interview schedule was finalized. Voluntary consent form was prepared in English, Hindi and Marathi. Home visits were done between 10.00 am to 4.00 pm on working days. The information was collected about various socioeconomic factors, illness perceptions, family history, addiction, duration of disease, exercise, complications, associated disorders, life style, self care etc. on preformed, pre tested interview schedule by investigator himself. Height, Weight and Blood pressure, Blood sugar were measured by using appropriate technique. Participants were followed up for 12 months from July 2010 to June 2011 for intervention. Each diabetic patient had been given one individual number like 1/2010 to 300/2010. Regular follow up and monitoring of weight, blood pressure, blood sugar and medical history was maintained in that register.Formation of batches and fixing of timing: Total 300 patients were grouped in to 10 batches of 30-35 patients. All the participants were told and motivated to attend the health education session on a particular day depending on the feasibility of all the patients of a particular batch. Such health education sessions were headed by two doctors and conducted every week in morning hour from 10:15 am to 11:00 am. The health education was given in local language by the doctor.Intervention measures included:1) Medical treatment: Participants were followed up fortnightly in Urban Health Center. In follow up visits complete physical examination including weight, blood pressure, and blood sugar were done and treated accordingly. Patients having complications were referred to higher centers for expert’s opinion.2) Health Education: Health education was given monthly during follow up visits at Urban Health Centre (UHC). Health education was given in group and in single. In health education patients were given basic information about diabetes and its complications and how to control blood sugar and prevent its complications. Patients were also given information about hypoglycaemia, how to prevent it and what to do in hypoglycaemic episode.3) Dietary Advice: Dietary Advice was done during follow up visits at UHC with the help of dietician. In dietary advice patients were given information about different types of foods which are harmful or beneficial in diabetes and spacing of meals.4) Blood Sugar examination: Blood sugar (fasting and post prandial) were monitored once in a 3 months in the laboratory of Urban Health Center.5) Eye check up: Each patient motivated to come for their eye check-up which was done by Ophthalmologist.Appropriate scoring was done for illness perception, life style factors and self care factors in both pre intervention and post intervention phases. The collected data was numerically coded and entered in Microsoft Excel 2007 and then transferred to SPSS version 15.0 Added data was analyzed with appropriate test like Chi-square test, ‘t’ test to see the association between various parameter, with p value 0.05 considered as significant.
3. Results
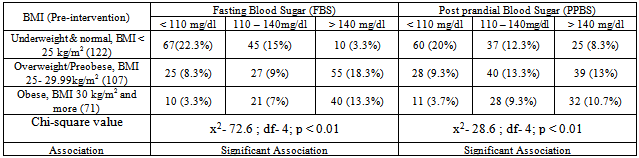
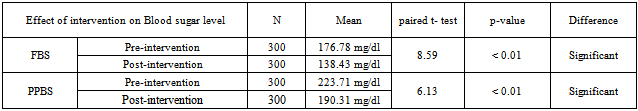
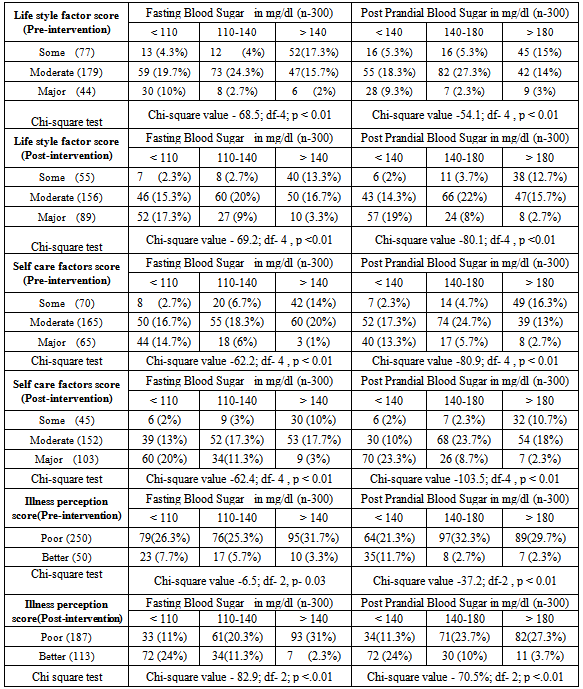
- Total 300 diabetic subjects were examined consisting of 183 (61%) males and 117(39%) females. Majority of patients 146 (48.7%) were in the age group of 51-60 years with mean age of patients was 51.6 years. 188 (62.7%) subjects were from Socio-economic class III, IV, V (according to Modified Prasad classification). Most of the patients 135 (45%) were either unemployed or unskilled, 162 (54%) were illiterate or just completed primary education and 34.3% patients had family history of diabetes.Table 1 shows, total 178 (59.3%) had Body mass index (BMI) more than or equal to 25 kg/m2 and had poor control over fasting and post-prandial blood sugar.
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. Discussion
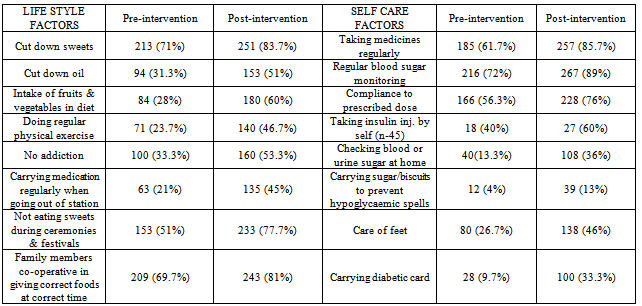
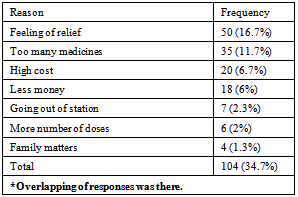
- The present community based descriptive epidemiological interventional study was conducted at an urban slum in Mumbai, India which is a field practice area of Department of Preventive and Social Medicine, TN Medical College, Mumbai, India. It was conducted during the period of October 2009 to September 2011, selecting 300 known cases of type 2 diabetes by employing simple random sampling method.Total 300 diabetic subjects were examined with mean age of 51.6years. In present study 155 (64.5%) of the subjects had BMI more than 25. Mean BMI was 25.64 (SD=4.03) which is above the normal BMI. In a study conducted by Kapur et al[4], the multivariate-adjusted hazard ratios were 1.15 for normal-weight inactive, 3.68 for overweight active, 4.16 for overweight inactive, 11.5 for obese active, and 11.8 for obese inactive participants.In this study both fasting and post-prandial (PP) blood sugar were high (Fasting >140 mg/dl, PP > 200 mg/dl) in 145 (48.3%) and 161(53.7%) of subjects respectively. Obesity was found to be significantly associated with both high fasting & Post-Prandial blood sugar levels. Though patients’ had diabetes for more than a year still the blood sugar was not under control. R Gupta et al in his study[5] had similar results that BMI correlate significantly with fasting blood sugar, and negatively with physical activities. There was a significant increase in fasting blood sugar with increasing BMI. Any physical activity was inversely related to BMI. A steep increase in the prevalence of diabetes was observed in patients having BMI > 25kg/m2.In this study it was found that only 28% subjects had increased consumption of vegetables and fruits in diet, 23.7% were doing regular exercises and 33.3% had no addictions. Only 13.3% of subjects used to check urine and blood sugar at home, 26.7% used to take care of their feet and 4% used to carry the sugar or biscuit and water during the travelling to avoid hypoglycaemic spells. For most of them, the main concerns were only their curative treatment. Similar findings were observed in many studies. In the cross-sectional study[6] conducted at Chandigarh of the 60 diabetic individuals 48 subjects knew that sweets and fatty foods should be avoided but only 18.3% were avoiding them, monitoring of blood sugar was poor (46.7%), and none of the patients knew about self therapy.In the study[7] conducted in 150 diabetic residents of Pondicherry most of the patients were aware of the need for dietary care or medication, but only 50% modified their diet. Of the 97% using anti-diabetic agents, some were using them wrongly and only 10.6% of the subjects tested their urine, although 71% were aware of the need. None of the patients had any formal education regarding diabetes and only 34% consulted the physician regularly. Cross sectional study[8] done in Egypt in 2003 showed attitude of patients regarding different self care behaviours – nearly half of them paid frequent attention towards testing blood sugar (45.5%), compliance to medications (51.3%), diet (41.5%) and exercise (10.5%).This study shows that, 104 (34.7%) were taking treatment irregularly. Similar result was seen in a study conducted by Puria et al[9] at Urban Health Centre (UHC) of GMCH Medical College, Chandigarh in 273 known cases of type 2 diabetes where 28% patients were taking treatment irregularly. Reasons for irregular treatment in 28% were mainly failure to understand the importance of adhering to the treatment, lack of family support and expensive medicine. In a study[10] only seven respondents out of 611 (1.1%) undertook home monitoring of blood glucose. Similar findings were noted in the CODI study[11] where only 6% of patients monitored their diabetes more than once a month. The rest monitored their diabetes once every two months or more (48%), or once every three months or more (47%).Diabetic patients should examine their blood sugar once in three months, but this study shows that only 55 (18.3%) subjects used to check their blood sugar once a month while 161 (53.7%) subjects used to check sugar once in 3 months. Similar result was seen in study by Kapur et al[12] that showed only 6 per cent of patients monitored their diabetes more than once a month. The rest monitored their diabetes once every 2 months or more or once every 3 months or more (47%). Both life style and self care were improved after interventions which are important parameters to control diabetes. Present study shows that regular health education about diabetes can help to control blood sugar within normal range. Significant decrease in mean fasting and post-prandial blood sugar was there from pre intervention to post intervention phase. Similar results were seen in a study[13] carried out in Iran to assess the effectiveness of dietary education in reducing plasma glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. It was found that, the intervention group lost 1.5 ± 2.2 kg as against a weight gain in the control group of 0.5 ± 2.3 kg. Fasting plasma glucose decreased 21 ± 55 mg/dl in the intervention group and increased 19 ± 78 mg/dl in the control group. Glycosylated haemoglobin decreased 1.9 ± 2.1% in the intervention group and 0.2 ± 2.2% in the control group. In a study[14] of 165 diabetic patients who received outpatient diabetes education for one week showed a significant increase in the knowledge score, which was associated with a significant fall in HbA1c at 6 months. Hawthorne et al in his eleven trials[15] in 2008 involving 1603 people, showed an improvement in Glycemic control (HbA1c), following health education at three months[weight mean difference (WMD) - 0.3%, 95% CI -0.6 to -0.01], and at six months (WMD -0.6%, 95% CI -0.9 to -0.4), compared with control groups who received ‘usual care’. This effect was not significant at 12 months post intervention (WMD -0.1%, 95% CI -0.4 to 0.2). Knowledge scores also improved in the intervention groups at three months (standardized mean difference (SMD) 0.6, 95% CI 0.4 to 0.7), six months (SMD 0.5, 95% CI 0.3 to 0.7) and twelve months (SMD 0.4, 95% CI 0.1 to 0.6) post intervention. Similarly the six-year prospective study[16] showed that after two years of intervention 59% of the patients proved well controlled. In “Modena Diabetes Project"[17] after four years follow-up, the individual before/after match-paired outcomes revealed an improvement in Glycemic control: HbA1c levels significantly decreased to 7.39+/-1.31%, and the percentage of patients with HbA1c level of < 6.5% significantly increased from 15.7% to 22.1%. There was also a significant decrease in body weight (from 78.3+/-14.8 to 77.6+/- 14.6kg) and BMI (from 28.8+/-4.8 to 28.5+/-4.9 kg/m2).In a large US-based cohort study[18] by Karter et al which included 24,312 patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, HbA1c was lower in patients who regularly did SMBG. Satpute et al in their study[19] assessed the impact of patient counselling, Nutrition and Exercise in 35 patients with Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus. Glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c), Fasting plasma glucose, PPG (Post-prandial Glucose), total cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL (High Density Lipoproteins), LDL (Low Density Lipoproteins) and BMI were measured at baseline and the end of the study. It was shown that glycemic control of type-2 diabetic patients can be improved through patient counselling regarding disease, medication, diet and exercise. In a study[20] done to determine the effects of a culturally competent diabetes self-management intervention in Mexican Americans with type 2 diabetes, experimental groups showed significantly lower levels of HbA1c and fasting blood glucose at 6 and 12 months and higher diabetes knowledge scores. At 6 months, the mean HbA1c of the experimental subjects was 1.4% below the mean of the control group. This study confirms the effectiveness of culturally competent diabetes self-management education on improving health outcomes.One of the routine in-house studies[21] conducted to assess the quality and benefits of education at M.V Diabetes Specialties Center, The study revealed that awareness of glucometer was significantly higher among those who attended the education programme. 38.6% changed their exercise pattern after attending the education programme. When the patients were assessed regarding their knowledge of diabetes and its actual practice (dietary practice, compliance, home monitoring) the intervention group showed a significant and greater improvement in the knowledge of the disease and self-care and in the dietary practice.The results of another study[22] conducted in Netherland in which follow up was done after 12 months, indicated that primary care programs which integrated education into structured care were able to improve both the type 2 diabetic patient's knowledge about the disease and their self care behaviour. In a study[11] done in Gujarat Refinery Hospital, Vadodara, it was found that quarterly health and nutrition education program for diabetics decrease blood sugar, weight and total fat intake.Chandalia et al[23] assessed the nutritional knowledge and control of diabetes in 43 non-ketosis-prone diabetic subjects. The patients were exposed to a 1-h nutritional counselling program in groups of three to five. It was observed that the patients' nutritional knowledge and the control of diabetes improved significantly after counselling in those patients in whom control had been inadequate.In this study mean blood sugar of patients doing regular physical exercise was less than others. Meta analysis[24] of effects of different modes of exercise training on glucose control done by Snowling and Hopkins, concluded that aerobic, resistance and combined exercise have small to moderate beneficial effect on glucose control in type 2 diabetic patients. Study[25] done by Nield et al to assess the effects of different types of dietary advice through weight change in people with type 2 diabetes, and the effects of dietary advice plus other lifestyle interventions (i.e. exercise, behavioural approaches) through weight change in people, appears to improve glycated haemoglobin at six and twelve months in people with type 2 diabetes. In a study conducted in Copenhagen[26-28] showed the group-based diabetes rehabilitation programme consisting of empowerment-based education, supervised exercise and dietary intervention had better short- and long-term glycaemic outcomes than the traditional best practice for individual lifestyle counselling in a diabetes outpatient clinic setting. Jie Hu in his study[29] found that age, BMI, Nutritional health and physical exercise significantly predict the quality of life in Diabetic patients.From the above observations we found that Health & Nutrition Education are important intervention measure to control blood sugar, modify the diet and life style and improve the self care practices.
5. Conclusions
- People have to be educated through mass media on Diabetes and its risk factors. The health workers have to play part by educating the people and also themselves being an example in avoiding the risk factors for diabetes like consumption of food having high glycemic index, alcohol etc. People have to be educated on the importance of regular physical exercises and have to be encouraged to do the same.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-Text HTML
Full-Text HTML