-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Computer Science and Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1484 e-ISSN: 2163-1492
2025; 15(3): 79-82
doi:10.5923/j.computer.20251503.03
Received: May 20, 2025; Accepted: Jun. 7, 2025; Published: Jun. 13, 2025

Liquidity Synergy: Redefining Financial Integration Through SAP S/4HANA Cash Management
Narinder Pal Verma
Capgemini America Inc, Valencia, California, USA
Correspondence to: Narinder Pal Verma, Capgemini America Inc, Valencia, California, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Cash and Liquidity Management relates to the strategies employed to maximize the effective use of funds. Effective cash management is a cornerstone for guaranteeing financial stability and helping operational efficiency in modern-day businesses. SAP S/4HANA Cash Management is an integrated, real-time solution for managing liquidity, processing bank transactions, and enhancing cash flow forecasting. This paper covers the core components, seamless integration with other SAP Modules and third-party systems, and the strategic role of cash application in enhancing cash management processes. In doing so, it provides information on best practices and emerging trends that allow organizations to achieve enhanced financial control and responsiveness in operations.
Keywords: S4hana Cash Management, SAP Cash Management, Liquidity Management, Cash Application, Automated Payment processing, Real-time cash positioning, Bank Reconciliation, Treasury & Risk Management, Financial forecasting, Digital transformation, Predictive Analytics, Predictive cash flow
Cite this paper: Narinder Pal Verma, Liquidity Synergy: Redefining Financial Integration Through SAP S/4HANA Cash Management, Computer Science and Engineering, Vol. 15 No. 3, 2025, pp. 79-82. doi: 10.5923/j.computer.20251503.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The rapid evolution of international markets has compelled organizations to embrace nimble financial operations with real-time information and congruent processes as the catalyst for success.Traditional systems, with their disintegrated cash management, hamper prompt decisions and trigger operational inefficiency. SAP S/4HANA Cash Management meets such challenges squarely by presenting an integrated solution that combines financial accounting, liquidity planning, integrated with Material Management, Sales & Distribution, and connectivity to banks under one comprehensive platform. Not only is this integration easy to perform for daily cash activities, but it also makes strategic views available with the possibility of instigating transformational change in companies. [1]
2. Literature Review
- The evolution from independent financial systems to coupled enterprise resource planning (ERP) has been the subject of a wide array of academic and professional texts.Early studies explained the negative impacts of isolated financial processes on transparency and decision-making. Later research highlights that today's ERP systems—especially those developed on in-memory platforms like SAP S/4HANA—significantly enhance real-time data processing and cross-functional integration. These innovations are of utmost significance for effective liquidity management and risk management in the competitive business environment of the contemporary age. [2]
3. Overview and Key Features
- SAP S/4HANA Cash Management is a multi-faceted solution that enables responding to the diverse needs of contemporary financial operations. Its key features are:
3.1. Real-Time Cash Positioning and Liquidity Forecast
- This module Integrates with other modules like A/P, A/R, Procurement, Sales, FICA, General ledgers, and bank feeds, bringing together data to provide a current picture of cash balances and liquidity trends. The real-time analysis helps quick response to daily variations in cash flow, allowing active financial planning. [1]Integrates with payment systems to automate cash transactions, reducing manual errors and improving efficiency. [4]
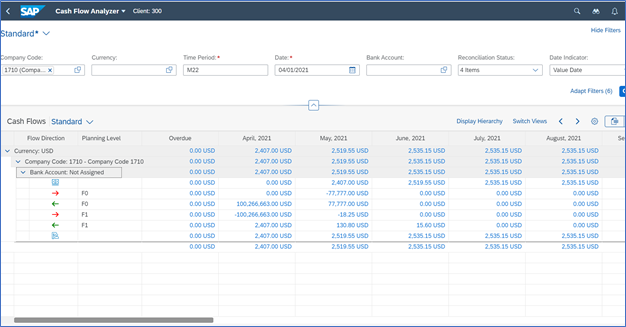 | Caption 1. The above picture is the output of the Cash Flow Analyzer report in S/4 Hana Cash Management |
3.2. Bank Account Management
- The solution integrates bank account data, reconciling processes, and tracking transactions for different banking relationships. The centralization reduces manual interventions while improving the accuracy of cash postings. Bank Account Management is a centralized place to manage the keep lifecycle of a Bank account, starting with the request to open a bank account ends with the closure of the bank account. Integrates with Bank Communication Management for the payment approvers. Compliance & legal reporting relate to Bank Accounts like FBAR.
3.3. Cash Flow Forecasting and Analysis
- Through the application of historical performance information and forecasting methodologies, the system provides estimations of future cash flows. Scenario planning functionality allows organizations to plan for future liquidity needs, so that they are prepared for shortages or can take advantage of surplus cash.
3.4. Automated Payment Processing
- Integrated payment modules ease receivable and disbursement matching. Automation reduces cycle times and improves the overall efficiency of cash operations, with transactions accurately reflected in financial statements.
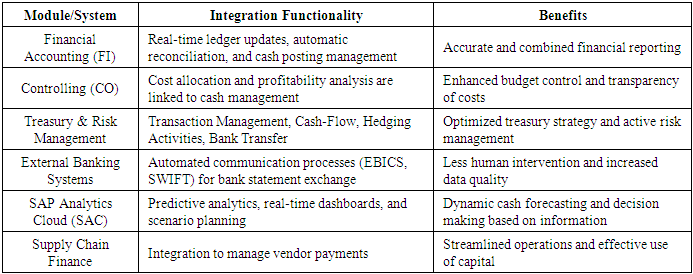
4. Integration with Other Products and Systems
- The other important strength of SAP S/4HANA Cash Management is its integration with a diverse ecosystem of financial and non-financial applications based on transparency and operational efficiency.
4.1. Core Financial Module Interfacing
- Through interaction with Financial Accounting (FI) and Controlling (CO), the solution enables the proper recording and reconciliation of all cash flows in one integrated ledger. This harmony allows for consistent financial reporting and helps effortless budgeting.
4.2. Treasury and Risk Management Interfacing
- High connectivity to SAP Treasury and Risk Management makes it easier for organizations to manage transaction cash flow with due dates, Calculation of Interest income/expense without manual intervention, monitoring market risks, perform exposure analysis, and construct hedging strategies based on cash positions. This allows for the integrated approach between cash management and overall risk management.
4.3. Integration with External Banking Systems
- Direct connection to non-member bank systems using standard protocols (e.g., SWIFT, EBICS) allows automated exchange of bank statements and real-time reconciliation. These improvements reduce manual reconciliation work and enhance the reliability of cash data. Automation of the electronic bank statement, including cash application & GL clearing with auto posting.
4.4. Integration with Analytics and Business Intelligence Tools
- Analysis tools such as SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC) and SAP Business Warehouse (BW) apply real-time information from cash management activities to offer actionable insights. Predictive models and dashboards enable decision-makers to find trends and manage liquidity better.
4.5. Integration with Neighbouring Business Processes
- Apart from usual finance processes, SAP S/4HANA Cash Management supports integration with modules like supply chain finance and customer relationship management (CRM). This ensures alignment of vendor payment, procurement financing, and receivables management with the overall liquidity strategy of the company.
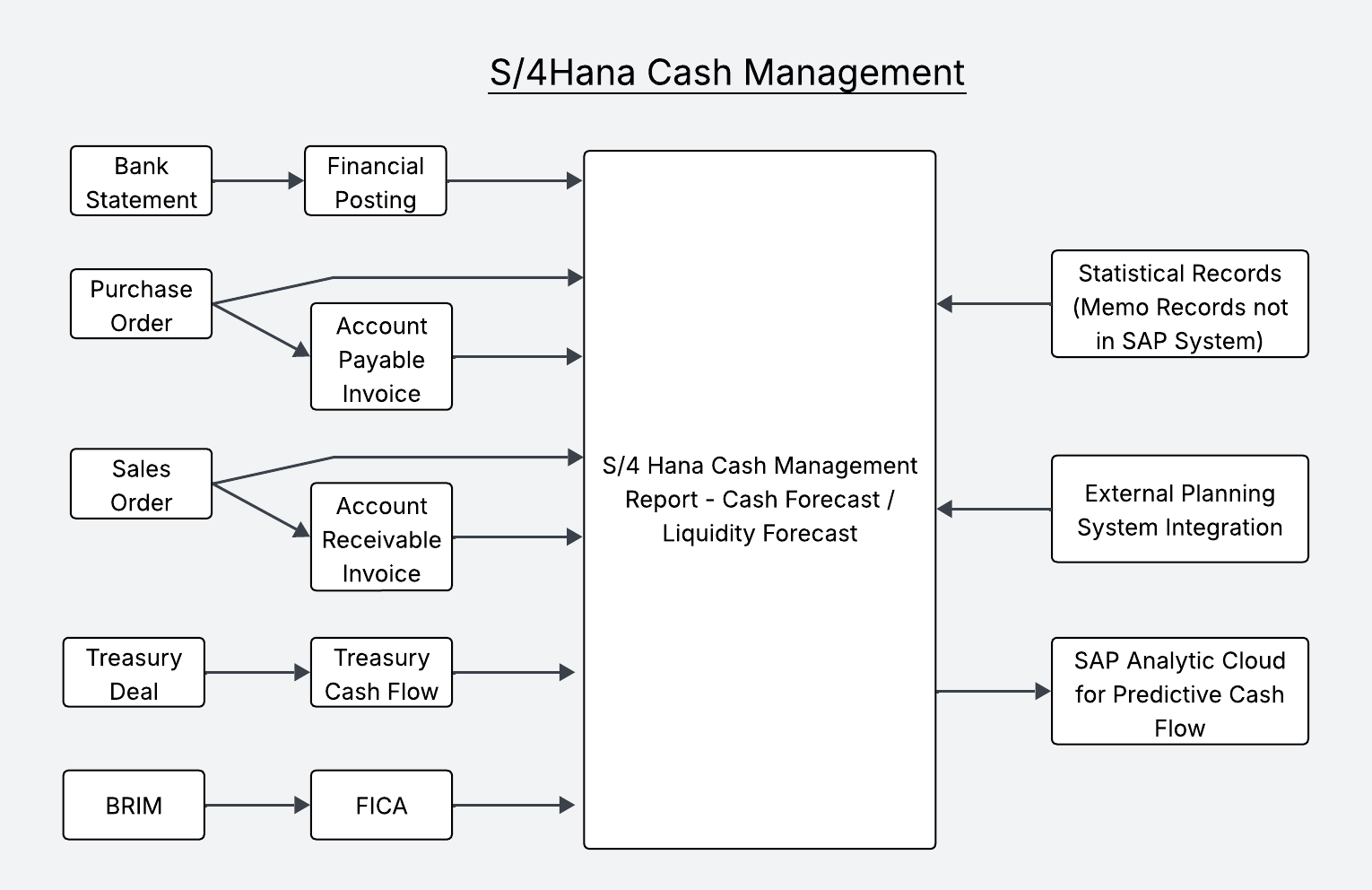 | Caption 2. The Above diagram depicts the Integration of Cash management with other modules for data flow. Cash management is the data representation of cash flow, recorded in other applications |
|
5. Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
- Even highly functional, SAP S/4HANA Cash Management can present a series of challenges:• Data Synchronization: Legacy system integration with S/4HANA requires harmonization of data so that there is a uniform and correct financial narrative across platforms.• Compliance and Security: Greater connectivity needs more robust data security practices and compliance with evolving regulatory requirements.• Training and Change Management for Users: Seamless adoption and proper use of system capabilities need large-scale training programs and effective change management to introduce.Best Practices: Organizations must conduct a pre-implementation analysis, have primary stakeholders involved from the beginning, apply rigorous testing policies, and follow an implementation in phases to reduce risks on deployment. [3]
6. Case Study: Integration within a Multinational Enterprise
- A multinational company with businesses across different geographies and currencies recently implemented SAP S/4HANA Cash Management along with SAP Treasury and SAP Analytics Cloud modules. This combined solution achieved:• Real-Time Global Cash Visibility: Aggregated data from various sources provided a correct and real-time global cash position.• Centralized Bank Reconciliation: Bank statement reconciliation was done automatically in no time.• Enhanced Liquidity Forecasting: Advanced predictive analytics enabled cash shortages and surpluses to be predicted in advance.The result was a substantial reduction in operational spend, increased process efficiency, and superior strategic decision-making within regional markets.
7. Future Directions and Innovations
- In the coming days, SAP S/4HANA Cash Management will integrate more with newer technologies such as machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI). The future breakthroughs are:• Predictive Analytics: AI models can provide further improvement in liquidity forecasting with higher accuracy.• Anomaly Detection: ML algorithms will recognize unusual cash flow patterns, and such discrepancies can be settled faster.• API-Driven Ecosystems: Larger API architectures will accommodate wider integrations with third-party finance technologies to provide greater flexibility and real-time data sharing.
8. In-depth Analysis: Cash Application in SAP S/4HANA Cash Management
- Cash application—the reconciliation of cash receipts on receipt with the matching invoices—is an important process with a direct impact on liquidity management and financial accuracy. With SAP S/4HANA Cash Management, cash application is the key driver that turns unprocessed payment inflows into actionable financial data.
8.1. Cash Application Introduction
- Cash application lies at the core of operational cash management. It refers to the automated reconciliation of incoming payments against outstanding invoices to support reconciliations, current and account statuses aligned. It is paramount not only to support correct financial records but also to support real-time cash visibility to ease liquidity management.
8.2. Mechanisms and Functionalities
- • Automated Matching Process: Advanced matching procedures in SAP S/4HANA leverage preconfigured rules—based on invoice numbers, customer references, payment amounts, and dates—to match incoming payments directly to the correct receivables automatically. Automation minimizes manual effort and results in fewer errors. [1]• Real-Time Updates: Because payments are processed in real time, finance teams have instant visibility into cash positions. Real-time updates enable reconciliation and cash forecasting to be faster and more precise, essential in rapidly evolving financial environments.• Exception Handling: Not all payments are the same with pre-determined criteria. The system throws exceptions and sometimes employs AI/ML algorithms to suggest matches based on historical trends. This method enhances the accuracy of matching over time.• Timely Compliance with Billing and AR Processes: With tight integration with Accounts Receivable (AR) and billing modules, automated cash application reduces Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) and ensures correct customer accounts that show payment status.
8.3. Business and Operational Benefits
- • Improved Liquidity Forecasting: Accurate payment matching has the direct impact of offering improved visibility in cash flow, allowing for better liquidity management and planning for short-term obligations or investment options.• Reduction in Cost: Minimizing manual involvement in payment processing lowers Labor costs and mitigates risks resulting from human mistakes.• Improved Customer Relations: Prompt and correct delivery of payments reduces customer account discrepancies, leading to enhanced trust and effective financial relationships.• Risk Reduction and Compliance: Accurate and frequent payment processing ensures compliance with financial regulations and minimizes risks of misstatements or audit findings.
8.4. Effective Cash Application Best Practices
- • Sustain High-Quality Master Data: Keep up-to-date and correct customer, invoice, and bank information to support best matching rules.• Set up Strong Matching Rules: Create brief, often audited rules to match incoming payments with invoices, updating them as business processes evolve.• Watch Key Performance Indicators: Track metrics such as matching accuracy and error rates to decide on areas for improvement.• Use Advanced Technologies: Implement AI/ML functionality to process exceptions and continually optimize matching algorithms.
8.5. Conclusion on Cash Application
- In an era where financial agility defines business success, SAP S/4HANA Cash Management is a powerful enabler of liquidity management and seamless financial integration by providing real-time cash visibility, enhanced bank reconciliation, and predictive analytics (on SAP Analytics Clouds). It transforms cash and liquidity management from a reactive process to a strategic advantage. Its native integrations with other SAP modules and third-party systems ensure unified financial control, minimizing risk while maximizing operational efficiency and visibility in currency exposure to make effective decisions of Hedging, Transfers, Investment & borrowings. Organizations using S/4HANA Cash Management can expect improved financial forecasting, automated payment processes, and an integrated approach to liquidity management that aligns with modern business demands. As digital transformation accelerates, the ability to predict cash flow fluctuations and perfect fund use becomes a key differentiator in financial strategy. By adopting best practices and emerging trends within this framework, enterprises position themselves for sustainable financial resilience and operational excellence in an increasingly dynamic economic environment.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML