-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Computer Science and Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1484 e-ISSN: 2163-1492
2025; 15(3): 67-74
doi:10.5923/j.computer.20251503.01
Received: May 16, 2025; Accepted: Jun. 10, 2025; Published: Jun. 13, 2025

SAP S/4HANA Conversion or New Implementation?
Harendra Singh Gangwar
Manager Global IT Transportation, TopGolf Callaway Brands, Fort Worth, USA (TopGolf Callaway Brands)
Correspondence to: Harendra Singh Gangwar, Manager Global IT Transportation, TopGolf Callaway Brands, Fort Worth, USA (TopGolf Callaway Brands).
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Many IT leaders today find themselves facing a difficult decision: should they migrate their current SAP ECC system to S/4HANA through a system conversion, or embark on a fresh, Greenfield S/4HANA implementation? This decision isn’t straightforward, as it depends on a variety of technical and business factors. Both paths offer their own set of advantages, drawbacks, and implementation challenges. Determining the optimal approach requires a methodical evaluation, as recommended by SAP, and should involve input from seasoned SAP S/4HANA conversion specialists. In my opinion, the ideal route is the one that brings the lowest deployment cost, minimal complexity, the least amount of user disruption, limited system downtime, and preserves existing valuable functionality—while also ensuring business processes can be carried out efficiently on the digital core and across the digital value chain. It’s important to consider that if your existing SAP ECC environment is not technically eligible for a direct system conversion—perhaps due to outdated release levels, lack of Unicode support, dual-stack configuration, or being out of maintenance—then the cost and effort involved in conversion can approach that of a Greenfield deployment. Moreover, unforeseen technical issues during conversion could drive up costs even further. Whether you opt for a system conversion (Brownfield) or a complete re-implementation (Greenfield), you’re likely to spend more than initially budgeted. Still, the goal should be to avoid significant budget overruns. Your decision should be informed by expert consultation, utilize SAP’s recommended methodologies, and leverage SAP-provided tools to assess system readiness. Engaging a knowledgeable SAP S/4HANA Solution Architect or a Conversion Specialist can provide insights into conversion strategies you might not have considered and help maximize the potential of your existing landscape. In this article, I’ll be sharing insights from my own experiences with SAP S/4HANA implementation and conversion/upgrade projects, which may guide your decision-making process between a Greenfield or Brownfield approach.
Keywords: SAP - Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing, Enhancement Package (EHP), XML- Extensible Markup Language, DVM- Data Volume Management, UPL-Usage and Procedure Logging
Cite this paper: Harendra Singh Gangwar, SAP S/4HANA Conversion or New Implementation?, Computer Science and Engineering, Vol. 15 No. 3, 2025, pp. 67-74. doi: 10.5923/j.computer.20251503.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Although SAP’s ERP system ECC6.0 is designed to integrate a vast array of core business processes across the enterprise, it is not uncommon for customers to encounter gaps wherein certain critical functionalities are either underdeveloped or entirely absent. In light of these limitations, both SAP and its global clientele have increasingly acknowledged the strategic value of co-innovation and collaborative enhancement to extend the platform's capabilities. In this context, the evolution toward SAP S/4HANA represents a deliberate response to such functional shortcomings, offering a modernized architecture and enriched feature set.SAP S/4HANA empowers decision-makers by delivering real-time visibility into financial and operational data through a unified view, facilitating rapid, data-driven insights and enabling dynamic business process automation. Its integrated suite—particularly the S/4HANA Finance solution—provides a comprehensive framework encompassing planning, analytics, core accounting, and financial close activities, all underpinned by the high-performance in-memory computing capabilities of SAP S/4HANA. Furthermore, the system is designed with agility at its core, offering the ability to respond autonomously to external disruptions while maintaining operational continuity. With deployment options spanning both cloud-based and on-premise editions, S/4HANA affords enterprises the flexibility to adopt innovation at a pace aligned with their strategic roadmap.Amidst a rapidly accelerating wave of digital transformation, a growing number of SAP ECC customers are re-evaluating their operating models, core business processes, and customer engagement strategies to remain competitive in an increasingly volatile landscape. As traditional paradigms are being disrupted—wherein once-stable business models face obsolescence, industry lines blur, emerging competitors redefine market dynamics, and smart technologies redefine product capabilities—organizations are compelled to adapt or risk irrelevance. In such a context, SAP S/4HANA emerges not merely as an upgrade, but as a pivotal enabler of enterprise-wide reinvention, offering the digital foundation necessary to thrive in a fluid, interconnected global economy.Consequently, a significant number of SAP ECC customers have been undertaking careful evaluations to determine whether a system conversion to SAP S/4HANA or a complete re-implementation represents the most appropriate strategic path forward for their organizations. This decision, inherently multifaceted and often fraught with uncertainty, becomes particularly challenging in the absence of a structured, methodical approach—an approach that SAP itself has sought to provide through a combination of general guidelines, evaluative frameworks, and diagnostic tools designed to support such critical transitions. In the course of this discussion, I will not only underscore the utility of these SAP-provided instruments and methodologies but will also integrate insights gleaned from my own professional experience with system conversions and upgrades, with the aim of helping stakeholders gain clarity on which path may be better aligned with their long-term business objectives.During numerous client engagements, one recurring theme that has surfaced pertains to the financial implications—specifically, the comparative cost of executing a technical conversion versus undertaking a full-scale re-implementation. While it is broadly acknowledged that re-implementation tends to incur significantly higher expenditure than conversion, it is imperative to recognize that cost considerations, though important, should not singularly dictate the decision-making process. A comprehensive evaluation must extend beyond financial metrics to include factors such as the current system’s complexity, the degree of customization, alignment with future business strategy, and the opportunity for process redesign—each of which may profoundly influence the ultimate recommendation.
2. Conversion vs. Re-Implementation: Navigating Your Journey to SAP S/4HANA
- Among the three available transition paths to SAP S/4HANA, this article concentrates on two primary approaches: a fresh implementation of SAP S/4HANA (commonly known as the Greenfield approach) and a system conversion from SAP ECC to SAP S/4HANA. The third pathway—SAP Landscape Transformation (SLT)—is particularly well-suited for large-scale enterprises operating multiple SAP or non-SAP ERP instances. This route supports organizations aiming to consolidate disparate systems into a unified global SAP S/4HANA environment or perform targeted, selective data migrations. For further details on the Landscape Transformation approach, please refer to the linked resources. Our focus here remains on the first two methods:Approach 1: Greenfield Implementation of SAP S/4HANAThis method involves initiating a completely new deployment of SAP S/4HANA—either on-premise or via a cloud-first approach. It's especially suitable for customers transitioning from non-SAP systems or those wanting a clean break from legacy ECC environments. Cloud adoption typically involves subscribing to SAP S/4HANA and migrating legacy data using SAP-provided migration utilities and tools.Approach 2: System Conversion to SAP S/4HANAThe second option entails converting your current SAP ECC environment to SAP S/4HANA. This process applies to systems running SAP ECC 6.0, whether on traditional databases or already on SAP HANA. Customers on HANA 1.0 must first upgrade to HANA 2.0 before commencing the S/4HANA conversion project.Many SAP ECC users are currently evaluating how best to proceed with this transition and are raising questions regarding the technical feasibility and readiness of their existing systems for conversion.A system conversion to SAP S/4HANA is inherently complex and must account for various factors within the current ECC landscape—ranging from infrastructure considerations to business process alignment. Drawing on my experience from previous transformation projects, I’ve utilized several diagnostic tools and methodologies to assess system convertibility and readiness. I’ll share those practical insights and lessons learned in the sections below.
3. Tool 1: In-Depth Analysis of Business Operations and System Landscape for Strategic Planning
- To determine whether a system conversion or a fresh SAP S/4HANA implementation is the right fit, a detailed assessment of the organization’s current SAP environment is essential. This process begins with a SAP S/4HANA Solution Architect conducting a comprehensive review of the client’s business processes and technical architecture.The objective is to answer key questions:• Which SAP modules are currently active?• What degree of customization exists, and how complex is the custom code?• How well does the existing SAP ECC system support current business operations?• What reporting capabilities are in place, and what additional insights are desired in the future?• What enhancements or new functionalities are needed?• Are there planned expansions, new business models, or application needs (cloud or on-premise)?• What is the current SAP release version?• How large is the data footprint that would need to be migrated?• Is the system configured for Unicode, and is it based on a single-stack (AS ABAP) or dual-stack setup?These and other strategic questions form the foundation for building a business justification—weighing the pros and cons of a system conversion versus a clean slate re-implementation. This helps identify whether a single-step transition is viable or if a phased migration approach would better suit the organization’s complexity and roadmap.Aligning Business Goals with Transition StrategyEqually important is a clear understanding of the organization’s strategic objectives for moving to SAP S/4HANA. The architect must assess whether these goals can be met through a technical system conversion or if a re-implementation would provide a more flexible and future-ready platform. Once this is clarified, a dual-path business case is prepared, outlining the expected benefits, potential risks, and cost estimates for both the conversion and re-implementation scenarios.Technical Readiness and System AssessmentIf initial analysis suggests that a system conversion is the preferred approach, the next step involves conducting a technical readiness assessment. This ensures that the ECC environment is not only aligned with SAP S/4HANA’s architecture but is also capable of supporting the new platform's functional enhancements.This includes evaluating:• Current database and operating system compatibility,• System performance and scalability,• Integration touchpoints,• Custom code impact analysis,• Unicode compliance and dual-stack status.SAP specialists use a variety of SAP-provided tools and proprietary techniques to conduct this evaluation, which ultimately guides the decision-making process on whether the system can transition smoothly to SAP S/4HANA or requires remediation first.Feasibility of ECC to S/4HANA System ConversionNot every SAP ECC system is designed to seamlessly support a direct conversion to SAP S/4HANA. Many legacy systems lack the structural flexibility needed to take advantage of S/4HANA's advanced innovations. Therefore, customers are advised to undergo a formal SAP S/4HANA Readiness Assessment, which serves to:• Gauge the current system’s alignment with S/4HANA requirements,• Identify necessary technical and functional upgrades,• Highlight gaps in compatibility,• Offer recommendations for either conversion or re-implementation based on business impact.To facilitate this, SAP provides tools like the SAP Readiness Check for S/4HANA (e.g., version 1709 FPS2 and above), which enables SAP professionals to perform a structured evaluation based on system usage, custom developments, data volumes, and compatibility.Final Conversion Feasibility DecisionBy analyzing the system across the above dimensions, an SAP S/4HANA Conversion Specialist determines the convertibility status of the ECC environment. This final assessment provides leadership with the confidence to move forward with a well-informed transformation strategy—whether via a conversion or a re-implementation track.
4. Tool 2: Technical Requirements Study
- Business Case1: SAP ERP Versions Prior to ECC 6.0If your current SAP ERP system is running on a release older than ECC 6.0, a preliminary upgrade is mandatory before considering a transition to SAP S/4HANA. The system must first be updated to ECC 6.0 with a supported Enhancement Package (EHP) version, as this is a fundamental requirement for initiating any readiness assessment for conversion. It is recommended that this upgrade project be handled independently from the S/4HANA migration to ensure a stable baseline.Business Case2: SAP ERP on ECC 6.0 with EHP 0–8Organizations already operating on SAP ECC 6.0—regardless of whether they are using Enhancement Package 0 through 8—are generally considered eligible candidates for a system conversion. These versions fall within SAP's supported paths for transitioning to S/4HANA, subject to a successful readiness check and compatibility analysis. Such systems offer a strong foundation for direct conversion with relatively lower technical overhead compared to older versions.Business Case3: SAP ECC Installations Outside SAP MaintenanceIf your SAP ECC system is currently out of mainstream SAP support, you are operating in a high-risk environment for conversion. SAP does not extend support or tooling for S/4HANA conversion activities on outdated platforms. In such cases, attempting a system conversion may introduce critical issues and unsupported scenarios. For customers in this situation, a Greenfield Implementation (starting anew with SAP S/4HANA) is often the preferred and more sustainable option. Upgrading to a supported ECC version just to enable conversion may not be cost-effective or technically viable.Business Case4: Non-Unicode and Dual-Stack ArchitecturesAn essential prerequisite for S/4HANA system conversion is that your SAP system must be based on a Unicode architecture. If your system is still non-Unicode, you must perform a Unicode migration in advance. This process should be treated as a standalone technical project, separate from the S/4HANA conversion itself. Attempting to combine Unicode migration with the conversion process can significantly increase project risk and complexity.Additionally, dual-stack systems (those running both ABAP and Java stacks) are not eligible for conversion. Your ECC system must be a pure AS ABAP instance to proceed. For detailed guidance and technical limitations, please consult SAP Notes 1655335, which outline the specific conditions and constraints associated with these scenarios.
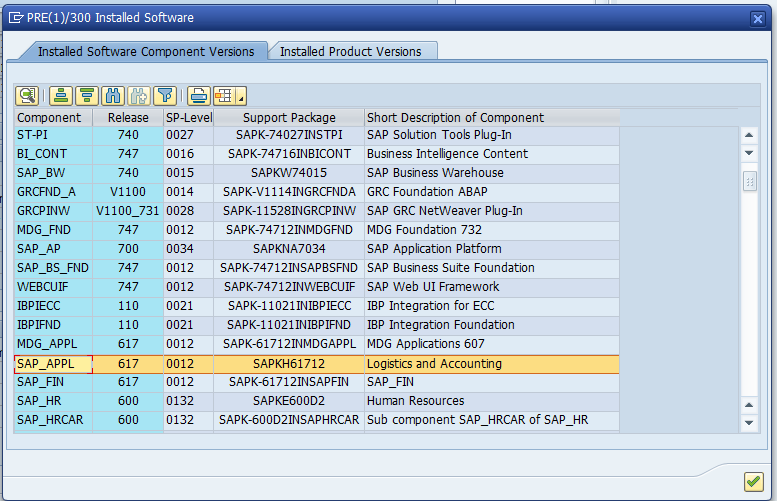 | Figure 1. Installed Software’s |
5. Tool 3: Maintenance Planner Utility
- The Maintenance Planner plays a pivotal role in managing both SAP S/4HANA system conversions and upgrades from lower to higher versions within the S/4HANA landscape. Whether you’re transitioning from ECC to S/4HANA or moving between S/4HANA releases, this tool is an indispensable part of the preparation phase.Before utilizing Maintenance Planner, it is critical to ensure that SAP Solution Manager is properly configured. This tool is responsible for generating a stack XML file, which is later consumed by the Software Update Manager (SUM) during the actual conversion or upgrade procedure.One of the core functions of Maintenance Planner is to perform a compatibility check across the system’s landscape. It evaluates:• Installed add-ons,• Activated business functions, and• Utilized industry solutions (IS).If any of these components are found to be incompatible with S/4HANA, or if there is no supported upgrade or conversion path for them, the conversion process cannot proceed. Hence, Maintenance Planner is a gatekeeper that determines whether the system is eligible for S/4HANA transformation.Hosted on SAP’s infrastructure, Maintenance Planner is accessible using the customer’s S-User ID. It serves as the next-generation replacement for the older Maintenance Optimizer tool, offering a more integrated and streamlined approach to system maintenance, upgrade planning, and transformation readiness.By consolidating crucial validation steps and providing a structured output (such as the XML stack file), Maintenance Planner ensures that your upgrade or conversion path is technically sound and aligned with SAP's guidelines. Refer screenshot as given below:-
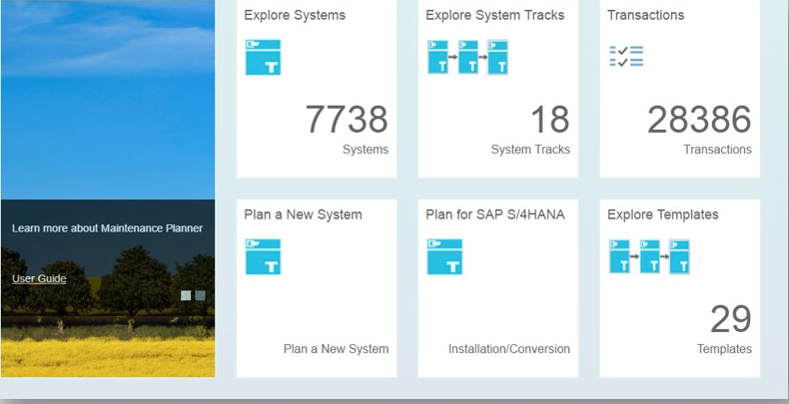 | Figure 2. Maintenance Planner |
 | Figure 3. SAP S/4HANA -Plan Overview |
6. Tool 4: Enabling the Simplification Item-Check
6.1. Note Implementation
- Depending on the target software level of your system conversion or release upgrade, specific minimum versions of this SAP Note (2399707) and SAP Note 2502552 are required. Otherwise, the check may be incomplete or inaccurate.The minimum versions are (If the Support Package Stack is not specifically listed, then its version requirement defaults to match that of the closest Support Package Stack.):• SAP S/4HANA 2021 Initial Shipmentο 2399707: Minimum recommended version 147 (Minimum technical version 82)ο 2502552: version 97• SAP S/4HANA 2022 Initial Shipmentο 2399707: Minimum recommended version 154 (Minimum technical version 82)ο 2502552: version 97• SAP S/4HANA 2022 Feature Package 1ο 2399707: Minimum recommended version 155 (Minimum technical version 82)ο 2502552: version 97• SAP S/4HANA 2023 Initial Shipmentο 2399707: Minimum recommended version 161 (Minimum technical version 82)ο 2502552: version 105While the minimum technical version of SAP Note 2399707 enables the conversion process to proceed, the minimum version may not reveal all application-level issues. As a result, we advise using at least the recommended version referenced above.Regardless of the minimum note version, when starting your project, it is recommended to use the most recent version of SAP Notes 2399707 and 2502552. When you reach the hard-freeze phase in your project, you should also freeze the version of these notes.
6.2. Simplification Item Catalog Maintenance
- The simplification item catalog contains a list of generally available target product versions and documented simplification items. A local replica is imported into the system to support the execution of the simplification item checks.The initial implementation of the check report (/SDF/RC_START_CHECK) includes the most recent version of the simplification item catalog. While continuing to scope and plan the project, we recommend using an up-to-date version of the simplification item catalog. Since conversion projects can take some time, you should consider and plan catalog updates during the project.While we advise you to use the most recent simplification item catalog content in early project phases, you should freeze and synchronize this content as part of the hard-freeze phase in your project. As you prepare to enter the hard-freeze phase of your project, download the local replica of the simplification item catalog from the system where you plan to perform your final test conversion. You can download the catalog using the corresponding button on the /SDF/RC_START_CHECK selection screen. We recommend downloading the content before converting the system. Similarly, you can then upload this content using report /SDF/RC_START_CHECK to synchronize the version before performing checks in any subsequent systems.The SAP hosted version of the simplification item catalog is updated periodically to accommodate new product versions, introduce new simplification items, and integrate lessons learned from project experience. By default, the report /SDF/RC_START_CHECK does not automatically update the local replica of the simplification item catalog from SAP servers. If you want to update the content from the SAP servers, you explicitly need to trigger this via the Update catalog with latest version from SAP button in /SDF/RC_START_CHECK.If no connection exists between the system and the SAP support backbone, you could download the content as an archive directly from the simplification item catalog site. Once you download the archive to your local machine, you can manually upload it in /SDF/RC_START_CHECK. The Local Version will be marked with a watch icon when the local replica is over 30 days old.
6.3. Executing the Simplification Item Checks
- 1. Start report /SDF/RC_START_CHECK in transaction SA38.
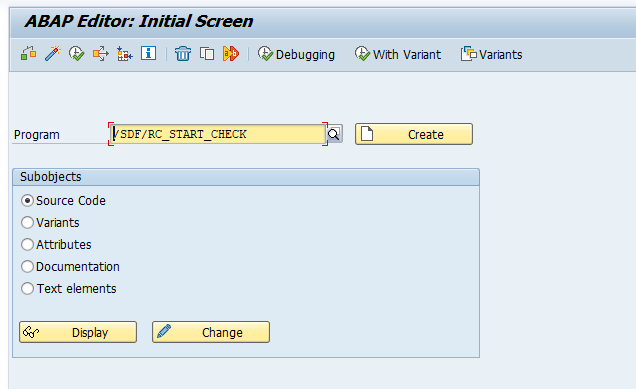 | Figure 4. SA38 Transaction Code |
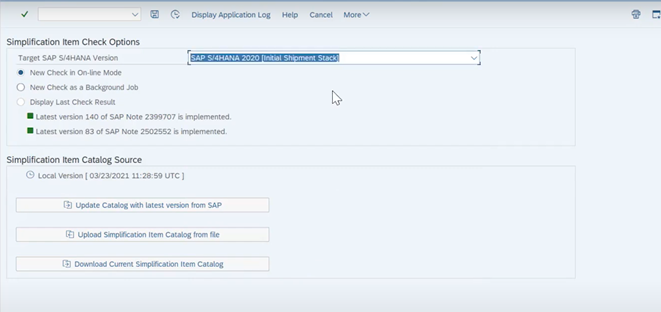 | Figure 5. Simplifications Item Check Options |
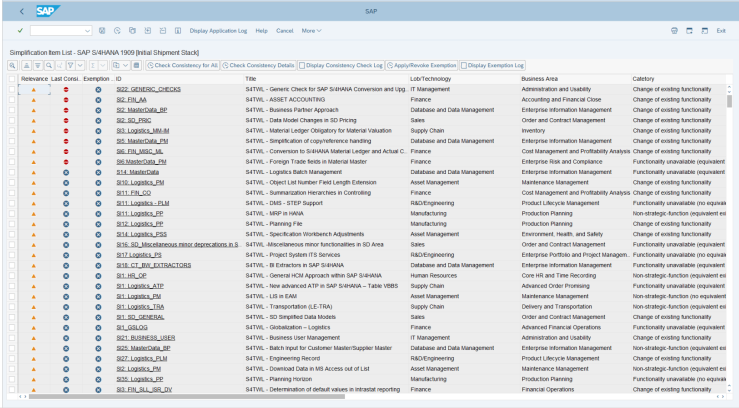 | Figure 6. Simplifications Report Output |
7. Tool 5: SAP Readiness Check 2.0
- If dependent SAP Note 2310438 has been implemented previously, de-implement before implementing notes below1) In the Production System, Implement SAP Note 2185390 & SAP Note 2758146. SAP Note 2185390 has some manual configuration steps that need to be completed.2) The below SAP Notes are required for the execution of report RC_COLLECT_ANALYSIS_DATA for the Readiness Check Dashboard and should be implemented in the Production System using transaction SNOTE: o SAP Note 1872170 (HANA Sizing) – Please implement the most recent version o SAP Note 2399707 (Simplification Items) – Please implement the most recent version o SAP Note 2745851 (for business process analysis) – Please implement the most recent version o SAP Note 2769657 (for IDOC analysis) – Please implement the most recent version o SAP Note 2612179 (for Data Volume Management) – Please implement the most recent version o SAP Note 2758146 (for Readiness Check 2.0) – Please implement the most recent version Note: As part of Detailed Planning Phase: Note 2502552 is recommended as per SAP Note 2758146 but is not necessary if you do not want to have a deep analysis on data consistency (Not required as a pre-requisite for Adoption Starter). 3) Run report SAPRSEUC in background mode using transaction SE38 in the Development System (This job is a long running job that can take a number of days to complete). 4) Once SAPRSEUC report has completed, run report SYCM_DOWNLOAD_REPOSITORY_INFO using transaction SE38 in background mode in the Development System.5) Execute program RC_COLLECT_ANALYSIS_DATA in Production system to download all checks except the consistency check in the zip file, by ensuring the “Simplification Item Consistency" checkbox is NOT selected and click the button “Schedule Analysis” to schedule a job to collect data.RC_COLLECT_ANALYSIS_DATA will trigger several different background jobs based on options selected. You must check the job logs to ensure data was collected properly. o RC_COLLECT_ANALYSIS_DATA Main Job from RC_COLLECT_ANALYSIS_DATA o TMW_RC_BPA_DATA_COLL for BPA data collection o TMW_RC_HANAS_DATA_COLL for HANA Sizing data collection o TMW_RC_DVM_DATA_COLL for DVM data collection o TMW_RC_SITEM_DATA_COLL for Simplification Item Check data collectionUpload: 6) The zip file output from report RC_COLLECT_ANALYSIS_DATA would then need to be uploaded to the SAP Launchpad to generate the Readiness Check Dashboard. To finalize the analysis, the zip file output of report SYCM_DOWNLOAD_REPOSITORY_INFO would need to be attached to the existing Readiness Check Analysis.SAP Launchpad: 7) Logon to the dashboard with your s-user https://rc.cfapps.eu10.hana.ondemand.com.8) Share the link with your project colleagues so that they access thus with their s-user. 9) Interpret the results of the Readiness Check based on the slides shared.
8. How do I Generate the Readiness Check Report
- 1) Upload Readiness Check Results here: https://rc.cfapps.eu10.hana.ondemand.com.2) Fill out the relevant information and submit for processing. 3) Receive results in less than 15 minutes.
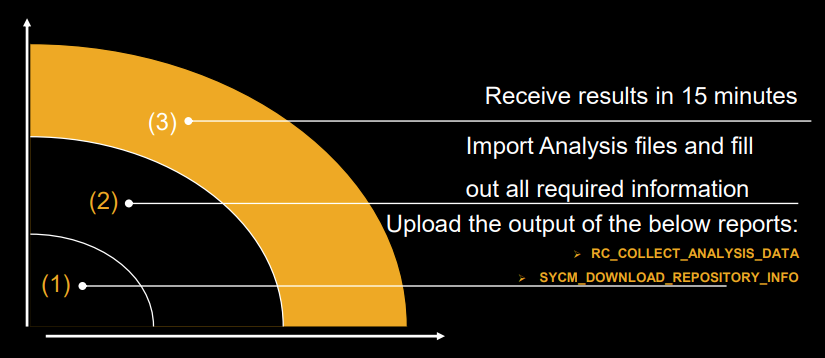 | Figure 7. Readiness check report -process steps |
9. Conclusions
- Are you facing critical issues within your current SAP ECC environment, perhaps underwhelming reporting capabilities, poor configuration in modules such as Controlling (CO), or an outdated Chart of Accounts that no longer aligns with your business growth trajectory? Maybe your system suffers from technical or functional rigidity, making it difficult to embrace new innovations, particularly if it’s heavily customized or has fallen out of mainstream maintenance.For many IT leaders, such constraints lead them to consider a complete re-implementation as the only viable path forward—often motivated by the desire for:• Enhanced analytical reporting,• Improved master data structures (e.g., cost centers, profit center hierarchies),• Cleaner financial design frameworks.However, a thoughtfully designed system conversion strategy executed by an experienced SAP S/4HANA conversion specialist can offer an alternative path—one that avoids the upheaval of a full re-implementation.An expert consultant can evaluate whether strategic reconfiguration—rather than starting from scratch—might enable your existing system to evolve into a streamlined, high-performing digital core. In many cases, this route proves to be far more cost-effective, less disruptive, and quicker to realize.Optimize Before You Rebuild: Clean Up for Performance and AgilityBefore committing to a full transformation, it’s worth exploring how much value you can unlock simply by performing targeted clean-up within your current landscape. Redundant or obsolete configurations, inactive custom developments, outdated reports, and unused programs all contribute to system bloat and inefficiency.Leveraging tools such as Data Volume Management (DVM) or Usage and Procedure Logging (UPL) can help identify what's no longer in use—and what can safely be removed or optimized.In many cases, dormant configurations or activated features—enabled unintentionally or long forgotten—can significantly hinder performance and increase system complexity. Eliminating these pain points through effective SAP housekeeping could revitalize your ECC system, creating room for innovation and reducing overall system noise without necessitating a full rebuild.Engaging the expertise of a seasoned SAP S/4HANA Conversion Consultant can prove to be an exceptionally cost-efficient approach to acquiring the strategic insight required to evaluate, with precision, whether a system conversion or a complete re-implementation would better serve the long-term goals and operational realities of your organization.Contrary to common assumptions, a re-implementation does not inherently entail greater financial investment, nor is a system conversion invariably the more technically arduous route; in practice, the relative cost and complexity of each path are highly contingent upon the unique configuration, customization footprint, and strategic aspirations of the enterprise in question.In many scenarios, both options—conversion and re-implementation—may emerge as technically feasible and functionally sound. Therefore, it is strongly advisable to seek the counsel of an experienced SAP S/4HANA Solution Architect prior to reaching any definitive conclusion. Leveraging their specialized knowledge and prior transformation experience can safeguard your project from avoidable missteps and ensure that critical decisions are grounded in informed analysis rather than post-facto realization.Disclaimer: I cannot give any guarantee about the usage of the tools specified in the article. I have shared my personal experience and opinions with the intention of helping the SAP Consulting community.
10. Key Citations
- 1. Readiness Check: Analyze your SAP ERP 6.0 system and highlights important aspects of the conversion to SAP S/4HANA.2. Simplification Item Check: Identifies relevant simplification items for your conversion.3. Maintenance Planner: Helps plan the conversion project.4. Custom Code Analysis: Analyzes custom code behavior.5. Software Update Manager (SUM): Used for Software updates during conversion.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML