-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Computer Science and Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1484 e-ISSN: 2163-1492
2025; 15(2): 58-65
doi:10.5923/j.computer.20251502.03
Received: Apr. 20, 2025; Accepted: May 3, 2025; Published: May 16, 2025

SAP and Big Data Analytics: Enhancing Decision-Making with Real-Time Insights
Alok Chakraborty
Independent Researcher, Coppell, USA
Correspondence to: Alok Chakraborty, Independent Researcher, Coppell, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In today's business environment, organizations are increasingly relying on data-driven decision-making to stay competitive. SAP, a leading enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, has evolved to integrate with Big Data analytics, providing businesses with real-time insights that enhance operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and profitability. This paper explores the integration of SAP with Big Data technologies, examining how it can facilitate real-time data processing, improve business intelligence, and enable better decision-making. Through case studies and practical examples, the paper highlights the benefits, challenges, and future prospects of leveraging SAP and Big Data analytics in organizations across various industries.
Keywords: SAP, Big Data, Big Data Analytics, Integration of SAP with Big data, Business Improvement, Advance Business decision making
Cite this paper: Alok Chakraborty, SAP and Big Data Analytics: Enhancing Decision-Making with Real-Time Insights, Computer Science and Engineering, Vol. 15 No. 2, 2025, pp. 58-65. doi: 10.5923/j.computer.20251502.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
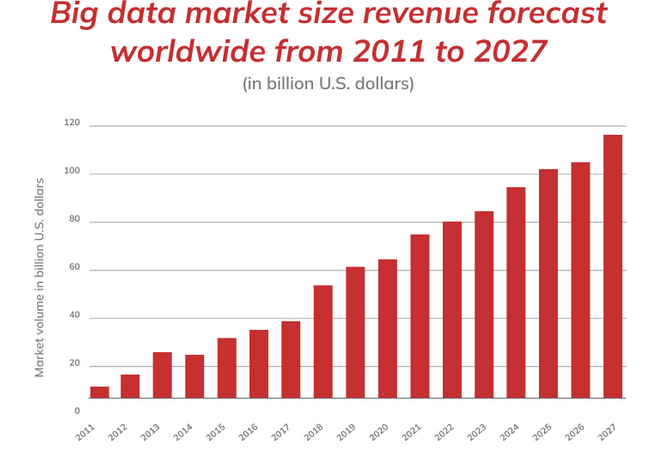
- In an era of information overload, businesses face the challenge of converting massive amounts of data into actionable insights. SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing) has emerged as one of the leading enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms, helping organizations manage and automate various business functions. SAP's core strength is its ability to deliver a centralized, real-time overview of business data across various departments, fostering improved decision-making, operational efficiency, and collaboration. By consolidating disparate business processes, SAP reduces data redundancy, enhances collaboration, and provides accurate, real-time insights that help businesses make more informed decisions However, with the explosion of data, traditional ERP systems have struggled to keep up.Big Data refers to the vast and growing volumes of data that are generated continuously in today’s digital world. This data is often characterized by the three Vs: Volume, Variety, and Velocity. The term "Volume" refers to the enormous amounts of data being created every second, from social media, transactional records, sensors, and more. Variety emphasizes the different types of data, including structured (such as databases), semi-structured (like XML files), and unstructured data (including videos, images, and text). Velocity refers to the speed at which data is generated and needs to be processed in real-time to derive value. In recent years, the rise of technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), social media platforms, and digital transactions has resulted in an explosion of data that companies need to manage. Big Data analytics refers to the use of advanced analytical techniques to process and extract valuable insights from these large and complex datasets. These insights can uncover patterns, trends, and associations that were previously hidden or difficult to identify using traditional data analysis methods.
 | Figure 1 |
2. Understanding Big Data and SAP's Role in Data Management
2.1. What is Big Data?
- Big Data refers to extremely large and complex datasets that cannot be managed, processed, or analyzed using traditional data processing tools and techniques. It encompasses a variety of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, which is generated in vast quantities and at high speed. The term "Big Data" is not just about the size of the data, but also its complexity and the ability to derive valuable insights from it.The key characteristics that define Big Data:2.1.1. Volume: This refers to the sheer amount of data being generated every second. Big Data is typically measured in petabytes (1 petabyte = 1 million gigabytes) or even exabytes. Sources of this data include social media posts, transaction records, sensor data, customer interactions, website logs, and much more.Example: Social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter generate petabytes of data daily in the form of text, images, videos, likes, comments, and shares.2.1.2. Velocity: This is the speed at which data is generated and needs to be processed. Big Data is often created in real-time, requiring rapid data capture, storage, and analysis to provide timely insights. Businesses need to process this information as it is generated in order to make informed decisions quickly.Example: Stock market data or traffic flow data from sensors are generated in real-time, and analyzing them immediately can give businesses or governments critical information to respond to changes on the fly.2.1.3. Variety: Big Data comes in many forms. While traditional data is typically structured (like data in a relational database), Big Data includes unstructured and semi-structured data as well. Unstructured data includes things like emails, social media posts, video content, and images, while semi-structured data might include XML files or JSON objects that are easier to analyze than completely unstructured data.Example: The data generated from customer feedback on social media or the information from an IoT (Internet of Things) device is highly unstructured and needs specialized tools to extract useful information.2.1.4. Veracity (sometimes added to the 3 Vs): This refers to the trustworthiness and quality of the data. Given the variety and volume of Big Data, it is often important to ensure the data is accurate and reliable. Inconsistent or erroneous data can lead to incorrect insights or decisions.Example: If sensor data from a factory floor is inaccurate or inconsistent, any analysis made based on that data would be flawed, leading to poor decision-making.
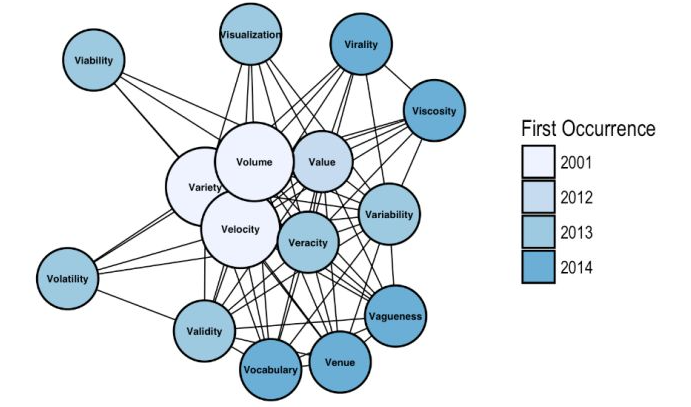
2.2. Addition of Vs
- Big data was initially characterised with 3 V's: volume, velocity, variety, to which IBM added veracity, The Four V's of Big Data, then we had the 5 Vs Everyone Must Know, The evolution of big data – the ‘6 Vs’, the Seven V’s of Big Data, the 10 Vs of Big Data and SAP even went up-to-eleven by adding the V of Vora.
 | Figure 2 |
2.3. SAP's Data Processing Abilities, Including SAP HANA
- SAP BW plays a significant role in enterprise data management by organizing, storing, and analyzing data efficiently. However, with the increasing volume, variety, and velocity of data (commonly referred to as Big Data), businesses are facing the challenge of integrating new sources of unstructured and semi-structured data. To address this, SAP BW has evolved to integrate seamlessly with Big Data sources, enabling organizations to perform analytics on large and diverse datasets.SAP BW has evolved to support integration with Big Data sources by adding the capability to handle larger, more complex, and diverse datasets. This enables businesses to access both structured and unstructured data, integrate it into their analytics workflows, and gain more meaningful insights.Here are the key ways SAP BW integrates with Big Data:2.3.1. Integration with SAP HANASAP BW has been optimized for integration with SAP HANA, an in-memory computing platform. HANA provides the capability to process large datasets quickly and efficiently, allowing SAP BW to analyze Big Data in real-time.2.3.1.1. SAP BW on HANA: When SAP BW is deployed on the SAP HANA platform, it benefits from HANA’s in-memory processing capabilities, which significantly improves the performance of querying and reporting large datasets. This allows businesses to process and analyze Big Data from multiple sources quickly.2.3.1.2. Real-time Data Processing: With HANA’s ability to process data in real-time, SAP BW can integrate with Big Data sources that provide streaming data. This is crucial for industries that need to make real-time decisions, such as finance, telecommunications, and manufacturing.2.3.1.3. Data Storage and Modelling: SAP BW on HANA can handle structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, providing a unified model for managing both traditional data and Big Data in the same system.2.3.2. SAP BW/4HANASAP BW/4HANA is the next-generation version of SAP BW, specifically built to work in cloud and hybrid environments. It integrates seamlessly with Big Data technologies and is optimized to handle the modern data needs of organizations.2.3.2.1. Flexible Data Modelling: BW/4HANA uses flexible data modeling that supports both traditional structured data and modern unstructured Big Data. This allows businesses to easily integrate new sources of data and make the most out of their analytics.2.3.2.2. Enhanced Scalability: BW/4HANA is designed to scale easily, making it capable of handling very large volumes of data generated from Big Data sources. It enables businesses to manage vast datasets without compromising performance.2.3.2.3. Integration with Hadoop: SAP BW/4HANA integrates with Hadoop, one of the most popular Big Data frameworks for storing and processing large-scale data. Through this integration, businesses can bring together data from the Hadoop ecosystem (such as HDFS and HBase) with traditional SAP BW data for unified analytics.2.3.3. SAP Data HubSAP Data Hub is a comprehensive data management platform that facilitates the integration of Big Data sources with traditional data systems like SAP BW. It enables businesses to manage, govern, and analyze data from multiple sources, including cloud, on-premise, and Big Data environments.2.3.3.1. Data Orchestration: SAP Data Hub allows businesses to orchestrate and integrate data pipelines that combine both traditional SAP data and Big Data from sources like Hadoop, Spark, and NoSQL databases.2.3.3.2. Data Governance: SAP Data Hub includes data governance capabilities to ensure that data from Big Data sources is consistent, accurate, and compliant. This is especially important when working with large and diverse datasets that come from various sources.2.3.3.3. Metadata Management: It helps organizations manage and track the metadata associated with Big Data, ensuring that data integration processes are transparent and auditable.2.3.4. SAP HANA Smart Data Integration (SDI)SAP HANA Smart Data Integration (SDI) is a real-time data integration tool that supports the movement and transformation of Big Data into SAP BW and SAP HANA environments.2.3.4.1. Real-time Data Replication: SDI provides real-time replication of Big Data from sources like Apache Kafka, Hadoop, and NoSQL databases into SAP BW or SAP HANA.2.3.4.2. Data Transformation: SDI supports the transformation of data as it moves from source systems into SAP BW, enabling businesses to cleanse and enrich Big Data for use in reporting and analysis.2.3.5. SAP Vora Integration with Big Data PlatformsSAP Vora is an in-memory computing engine designed to work with Big Data platforms, including Apache Hadoop and Spark. Vora enables SAP BW to process data from Big Data environments and integrate it with traditional SAP data.2.3.5.1. Distributed Data Processing: Vora supports distributed processing across multiple nodes, which allows businesses to process and analyze large volumes of Big Data from sources like Hadoop and Spark efficiently.2.3.5.2. Unified Analytics: Vora allows businesses to create a unified analytics environment that blends data from traditional SAP systems with data stored in Big Data platforms, giving users the ability to derive insights from all their data sources.2.3.6. Integration with Cloud-Based Big Data SolutionsSAP also integrates with cloud-based Big Data solutions, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, to bring cloud-based data into the SAP BW environment.2.3.6.1. Data Migration to Cloud: SAP BW supports the migration of on-premise data to the cloud, enabling businesses to take advantage of the scalability and flexibility of cloud-based Big Data solutions.2.3.6.2. Hybrid Data Integration: SAP BW can be deployed in hybrid environments, where some data is stored on-premise and other data is stored in the cloud. This allows organizations to integrate cloud-based Big Data solutions (e.g., AWS S3 or Azure Blob Storage) with their traditional SAP data.
2.4. SAP S/4HANA Real-Time Data Processing
- One of the core capabilities that sets SAP S/4HANA apart from traditional ERP systems is its support for real-time data processing. This capability is essential for businesses that need to make immediate, data-driven decisions and react quickly to changing market conditions.
3. Data-Driven Decision-Making
- In today’s fast-paced business environment, the ability to make timely and informed decisions is essential for staying competitive. Accurate, real-time data plays a pivotal role in enabling businesses to make decisions that drive operational efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and optimize financial performance. Real-time data refers to information that is immediately available for analysis and decision-making as it is created or collected, while accurate data ensures that the insights derived are reliable and actionable.
4. SAP Integration with Big Data Analytics: Technologies and Tools
- The integration of SAP with Big Data analytics requires the use of advanced technologies and tools that enable seamless data flow between SAP systems and Big Data platforms. These technologies provide the foundation for combining real-time operational data with large-scale analytics capabilities. In this section, we will discuss key technologies that facilitate the integration of SAP with Big Data, focusing on tools and platforms that bridge the gap between SAP’s enterprise systems and Big Data frameworks.
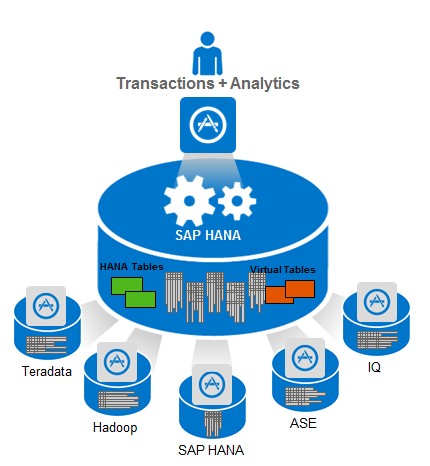
4.1. SAP HANA
- SAP HANA is a high-performance, in-memory database platform that serves as the core engine for running SAP applications in real time. One of its standout features is its ability to process vast amounts of transactional and analytical data in parallel, enabling organizations to perform real-time analytics on their operational data.
 | Figure 3 |
4.2. SAP Data Intelligence
- SAP Data Intelligence is a data integration and orchestration platform that connects various data systems, enabling organizations to combine and analyze data from SAP applications, Big Data sources, cloud platforms, and on-premise systems. This tool allows for the seamless flow of data between SAP and Big Data environments and supports both structured and unstructured data processing.4.2.1. Key Features4.2.1.1. Data Orchestration: SAP Data Intelligence integrates data pipelines across diverse systems, ensuring the flow of data from SAP systems to Big Data platforms like Hadoop and Spark. It allows for data cleansing, transformation, and preparation before it is analyzed.4.2.1.2. Data Connectivity: SAP Data Intelligence supports connectivity with numerous data sources and technologies, including SAP HANA, cloud storage solutions, Hadoop, and data lakes.4.2.1.3. Advanced Data Governance: The platform ensures data quality and consistency across the integration process, which is essential when dealing with large and complex datasets.4.2.2. Benefits4.2.2.1. Real-time Data Integration: By integrating SAP with Big Data platforms, organizations can perform real-time analytics on a unified data model, gaining insights into both operational and external data.4.2.2.2. Data Lineage and Monitoring: SAP Data Intelligence provides tools for monitoring data workflows, ensuring visibility into the entire data pipeline, and tracking changes in data over time.4.2.2.3. Flexibility and Scalability: The platform’s modular architecture supports the dynamic nature of Big Data, enabling businesses to scale and adapt as their data needs evolve.
4.3. SAP Business Warehouse (SAP BW)
- SAP Business Warehouse (SAP BW) is an enterprise data warehouse solution that allows businesses to store, manage, and analyze large amounts of data from various sources. It is one of SAP’s core technologies for integrating data from different enterprise systems and is capable of handling structured and unstructured data.4.3.1. SAP BW on HANA: The integration of SAP BW with SAP HANA enhances the capabilities of the data warehouse by providing in-memory processing for faster analytics. With SAP BW on HANA, organizations can perform real-time analytics on their data warehouse, combining it with Big Data sources to create a unified view of their business operations.4.3.2. Integration with Big Data: SAP BW can integrate with external Big Data systems through Smart Data Integration (SDI), Hadoop, and Apache Spark. It allows data from Big Data sources to be stored and processed in SAP BW for further analysis and reporting.4.3.3. Benefits4.3.3.1. Unified Data View: By integrating Big Data with SAP BW, organizations can consolidate data from various sources (both SAP and external) to provide a comprehensive view for reporting and analysis.4.3.3.2. Real-time Analytics: SAP BW on HANA supports real-time data processing, allowing businesses to analyze data as it arrives from Big Data platforms.4.3.3.3. Data Quality and Governance: SAP BW ensures that data is cleansed, transformed, and stored in a structured manner, providing consistency and reliability for downstream analytics.
4.4. SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC)
- SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC) is a cloud-based business intelligence (BI) platform that integrates various data sources, including SAP and non-SAP data, into a single platform for analysis, reporting, and visualization. SAC combines BI, predictive analytics, and planning capabilities in a unified environment.4.4.1. Integration with Big Data: SAC can connect to both SAP and external data sources, including Big Data platforms like Hadoop and Spark. It allows users to analyze and visualize data from various systems, providing a comprehensive view of business performance.4.4.2. Benefits4.4.2.1. Unified Analytics Platform: SAC consolidates data from multiple sources, enabling organizations to perform advanced analytics on Big Data alongside traditional business data from SAP systems.4.4.2.2. Cloud Flexibility: Being cloud-based, SAC offers scalability and flexibility, enabling organizations to expand their data analytics capabilities as they grow.4.4.2.3. Collaborative Decision-Making: SAC’s integration with SAP systems fosters a collaborative decision-making environment by allowing teams to share insights and collaborate on reports and dashboards.
5. The Benefits of SAP and Big Data Analytics for Decision-Making
- The integration of SAP systems with Big Data analytics platforms has revolutionized the way organizations make decisions. By combining SAP’s comprehensive enterprise resource planning (ERP) capabilities with the immense power of Big Data, businesses can now make faster, more informed and data-driven decisions. This synergy enhances decision-making at all levels of an organization and provides a clear competitive advantage. Below are some of the key benefits that the integration of SAP and Big Data analytics brings to decision-making processes.
5.1. Enhanced Real-Time Decision-Making
- One of the most significant benefits of integrating SAP with Big Data analytics is the ability to make real-time decisions. In today’s fast-paced business environment, the need for immediate action is critical. Traditional systems often rely on historical data and batch processing, which can delay decision-making. However, with Big Data technologies like SAP HANA and Apache Spark, businesses can process large volumes of data in real time, enabling them to act on the most up-to-date information available.For example, an e-commerce business can use real-time data to adjust its inventory levels, optimize pricing, and personalize marketing campaigns based on customer behavior. By integrating this capability with SAP's supply chain and financial management tools, businesses can improve operational efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and reduce costs. Real-time insights help businesses anticipate issues and adapt quickly to market changes, making them more agile and competitive.
5.2. Comprehensive Data Insights and Business Intelligence
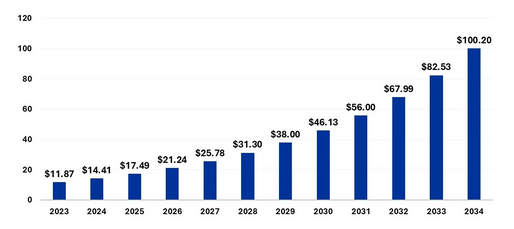
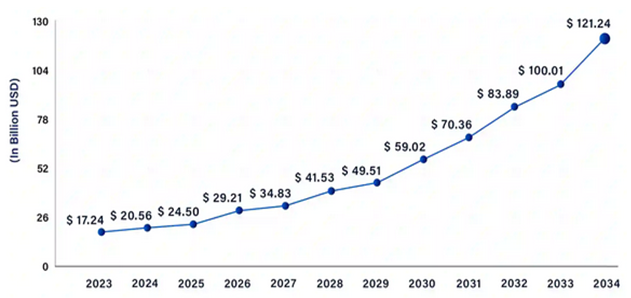
- SAP’s ERP systems are rich in structured business data, covering areas like finance, procurement, human resources, and sales. When combined with the massive unstructured data processed by Big Data analytics tools, companies gain a holistic view of their operations. This integration helps decision-makers obtain comprehensive insights that may not be visible when analyzing isolated datasets. By merging structured SAP data with external data sources such as customer reviews, social media interactions, and IoT device data, organizations can uncover new opportunities, trends, and patterns.For instance, integrating SAP data with Big Data sources can help a manufacturer predict when equipment is likely to fail based on sensor data, historical maintenance logs, and operational performance indicators. This predictive capability allows businesses to make proactive decisions, reduce downtime, and optimize the lifecycle of assets. This depth of insight is especially valuable for executives and managers when making strategic decisions based on a broader, more informed perspective.Predictive Analytics Market Size 2023 to 2034 (USD Billion)
 | Figure 4 |
5.3. Improved Forecasting and Predictive Analytics
- Big Data analytics paired with SAP systems enhances forecasting accuracy and predictive capabilities. Using advanced algorithms and machine learning models, organizations can analyze historical data and current trends to predict future outcomes with greater precision. For example, in finance, predictive models can help businesses forecast cash flows, detect anomalies, and optimize budgeting. In sales, predictive analytics can help identify customer purchasing trends, enabling companies to tailor their offerings to specific customer needs.Moreover, SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC) provides a platform where users can integrate predictive analytics with financial, operational, and external data. This empowers organizations to anticipate market fluctuations, customer demands, and supply chain disruptions before they occur. By enabling proactive decision-making, SAP and Big Data analytics support better resource allocation and risk management, ultimately improving the company’s bottom line.
5.4. Enhanced Collaboration and Cross-Departmental Insights
- The integration of Big Data with SAP systems breaks down data silos and fosters collaboration across different departments. With a centralized data hub, decision-makers from various functional areas (such as finance, sales, operations, and marketing) can access the same unified data set. This enables teams to collaborate more effectively and make decisions based on a common understanding of the data.For example, the integration of SAP with Big Data analytics in a retail organization can allow the marketing team to analyze customer purchasing behavior while the sales team can track inventory levels, and the finance team can monitor profit margins. With these insights readily available across departments, businesses can align their strategies and objectives, resulting in more cohesive decision-making that drives overall business success.
5.5. Increased Operational Efficiency
- Integrating SAP with Big Data analytics significantly improves operational efficiency. By leveraging Big Data’s ability to process large amounts of unstructured data in real-time, businesses can optimize their operations, identify inefficiencies, and automate routine tasks. For example, in supply chain management, SAP’s ERP tools can be used to manage procurement, inventory, and vendor relationships, while Big Data analytics can be used to predict demand fluctuations, optimize delivery schedules, and reduce stockouts.This combination allows businesses to make more informed decisions about resource allocation, scheduling, and logistics. In turn, these improvements lead to cost savings, increased productivity, and better customer satisfaction. Real-time analytics and Big Data also enable businesses to identify bottlenecks in the production process or operational workflows, allowing for immediate corrective action to streamline operations.
5.6. Better Risk Management and Compliance
- Big Data analytics provides the tools needed for better risk management by enabling businesses to detect anomalies and risks earlier. By combining historical data from SAP systems with external data sources (such as market trends, news, and social media), organizations can identify emerging risks that may not be immediately apparent.Global Big Data and Business Analytics Market Size and Forecast
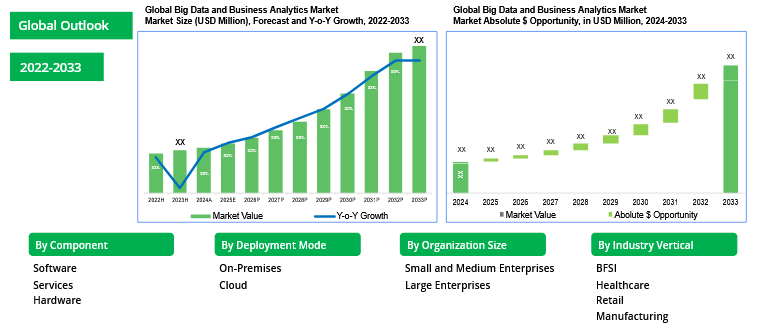 | Figure 5 |
5.7. Data-Driven Culture and Innovation
- The integration of SAP and Big Data analytics fosters a data-driven culture within organizations. By empowering employees across all levels to make decisions based on data insights, businesses promote innovation and creative problem-solving. Decision-makers have access to accurate, up-to-date data at their fingertips, which not only leads to better day-to-day decisions but also helps identify new growth opportunities and potential product innovations.For example, in product development, teams can use SAP’s historical data combined with customer feedback, social media interactions, and market trends to better understand customer needs and tailor new products accordingly. This combination of internal and external data supports continuous improvement and enables businesses to stay ahead of competitors.
6. Real-World Applications of SAP and BigData Analytics
- This section explores several real-world case studies that demonstrate the impact of integrating Big Data with SAP systems across different industries.
6.1. Case Study 1: Coca-Cola - Enhancing Consumer Insights
- 6.1.1. Challenge: Coca-Cola, a leading global beverage company, wanted to gain deeper insights into consumer behavior and preferences across multiple regions and retail channels. The challenge was to collect and analyze data from various sources, including social media, sales, and operational data, to understand customer demand patterns and make better supply chain decisions.6.1.2. SAP and Big Data IntegrationCoca-Cola implemented SAP S/4HANA and SAP Leonardo IoT to collect data from various sources, including sensors in their production plants and social media platforms. With SAP’s Big Data analytics capabilities, Coca-Cola was able to aggregate data from diverse sources and apply predictive analytics to forecast customer demand in real-time. The company also used SAP Data Hub to manage and govern its data across the organization.6.1.3. OutcomeBy integrating SAP with Big Data, Coca-Cola improved its supply chain operations and better aligned its production schedules with actual consumer demand, resulting in reduced waste, improved inventory management, and increased customer satisfaction.
6.2. Case Study 2: Volkswagen - Optimizing Manufacturing Operations
- 6.2.1. Challenge: Volkswagen (VW), one of the world's largest automobile manufacturers, sought to optimize its production process by leveraging data from its manufacturing plants, machinery, and supply chains. The goal was to improve operational efficiency, reduce downtime, and streamline production cycles.6.2.2. SAP and Big Data IntegrationVW adopted SAP S/4HANA and SAP Leonardo to integrate data from sensors embedded in their production lines, such as temperature, pressure, and speed readings from machinery. The data was processed through SAP’s in-memory platform for real-time analytics and machine learning algorithms were applied to predict equipment failures and optimize maintenance schedules.6.2.3. OutcomeWith the integration of SAP and Big Data, Volkswagen achieved significant improvements in its production lines. The company minimized unplanned downtime, enhanced predictive maintenance, and improved overall manufacturing efficiency, leading to cost savings and higher production output.
6.3. Case Study 3: Johnson & Johnson - Advanced Healthcare Insights
- 6.3.1. Challenge: Johnson & Johnson (J&J), a multinational medical devices and pharmaceutical company, aimed to improve its research and development (R&D) capabilities by integrating Big Data to accelerate drug discovery, patient outcomes, and clinical trials. The company faced challenges in aggregating clinical data, genomics, and patient medical records for better insights.6.3.2. SAP and Big Data IntegrationJ&J implemented SAP Cloud Platform and SAP HANA to manage and analyze massive datasets related to clinical trials, genomics, and patient records. They used SAP Data Hub to integrate diverse datasets and leverage machine learning algorithms to accelerate the discovery of drug candidates and predict patient responses to various treatments.6.3.3. OutcomeThe integration of SAP with Big Data enabled J&J to reduce the time it takes to move drugs from the lab to clinical trials. The insights gained from Big Data analytics also helped the company develop personalized medicine solutions, improving patient outcomes and boosting R&D efficiency.USA Big Data Analytics in Healthcare Market size 2023 to 2034
 | Figure 6 |
6.4. Case Study 4: Unilever - Real-Time Supply Chain Monitoring
- 6.4.1. Challenge: Unilever, a global consumer goods company, sought to improve the efficiency of its supply chain by gaining real-time visibility into its logistics operations, including inventory levels, production schedules, and order fulfillment. The company wanted to reduce inefficiencies and ensure timely deliveries.6.4.2. SAP and Big Data IntegrationUnilever integrated SAP S/4HANA, SAP Ariba, and SAP Data Hub to track and analyze data across its global supply chain network. The company deployed sensors and IoT devices to monitor inventory levels, product movements, and equipment status in real-time. Big Data analytics was used to predict supply chain disruptions and optimize delivery routes.6.4.3. OutcomeWith Big Data integrated into SAP, Unilever was able to achieve better real-time visibility into its supply chain, reducing costs associated with overstocking and stockouts. The company improved its inventory management, delivery times, and overall operational efficiency.
7. Challenges and Considerations
- While the integration of SAP with Big Data offers substantial benefits, several challenges must be considered:
7.1. Data Security and Privacy
- Protecting sensitive data while complying with regulations such as GDPR is a critical concern in Big Data projects.
7.2. Data Governance
- Managing data quality, consistency, and integrity across multiple systems and sources can be complex.
7.3. Change Management
- Implementing SAP with Big Data requires organizational buy-in and may require significant changes to existing business processes and workflows.
7.4. Skills and Expertise
- Organizations need skilled data scientists, SAP consultants, and IT professionals to manage Big Data analytics effectively.
8. Conclusions
- The integration of SAP with Big Data has brought transformative benefits to various industries, enabling organizations to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and make more informed decisions. By using Big Data technologies within SAP’s framework, businesses can enhance their operations in areas such as supply chain management, manufacturing optimization, and consumer insights. Real-world case studies from companies like Coca-Cola, Volkswagen, Johnson & Johnson, and Unilever demonstrate the immense potential of combining ERP systems with Big Data analytics. However, businesses must be mindful of the challenges involved in data governance, security, and expertise when embarking on such integrations.
9. Future Outlook
- As technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing continue to evolve, the integration of SAP with Big Data will become even more sophisticated. Businesses that successfully harness these technologies will gain a competitive edge, driving innovation and growth in the digital era.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML