-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Computer Science and Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1484 e-ISSN: 2163-1492
2024; 14(6): 135-141
doi:10.5923/j.computer.20241406.03
Received: Sep. 16, 2024; Accepted: Sep. 28, 2024; Published: Oct. 14, 2024

Transformative Effects of Artificial Intelligence on Cloud Computing
Alekya Jonnala
Senior Software Engineering Manager in Amazon, Mentor for Society of Women Engineers, Expert in Implementing AI & ML Solutions at Scale, Bothell, USA
Correspondence to: Alekya Jonnala, Senior Software Engineering Manager in Amazon, Mentor for Society of Women Engineers, Expert in Implementing AI & ML Solutions at Scale, Bothell, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) with Cloud Computing is driving significant transformations across industries. AI's abilities to analyze vast amounts of data and generate insights is revolutionizing how cloud computing resources are managed and utilized. This synergy enables dynamic scaling, optimized resource allocation, and improved operational efficiency, making cloud environments more adaptive and responsive to user needs. AI-driven tools and algorithms enhance cloud computing by automating routine tasks, such as system monitoring and maintenance, thus reducing operational costs and human error. Additionally, advanced AI models improve data analytics and processing, enabling businesses to extract valuable insights from large datasets and make informed decisions in real-time. Predictive analytics and machine learning further enhance cloud-based applications by enabling more accurate forecasts and personalized user experiences. The transformative effects of AI on cloud computing can also extend to enhanced security measures, where AI can detect and mitigate threats more effectively. Furthermore, the combination of AI with cloud computing leads to increased innovations in services such as intelligent data storage and management. Together, AI and cloud computing are shaping the future of digital infrastructure, offering scalable, efficient, and intelligent solutions that drive growth and innovation.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Cloud Computing, Data analytics, Machine learning, Resource optimization
Cite this paper: Alekya Jonnala, Transformative Effects of Artificial Intelligence on Cloud Computing, Computer Science and Engineering, Vol. 14 No. 6, 2024, pp. 135-141. doi: 10.5923/j.computer.20241406.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Cloud Computing are technology Game Changers in the 21st century when it comes to the rapidly evolving digital landscape. With the capability to mimic human intelligence procedures, AI has empowered varied sectors like healthcare, finance and so on with the AI capabilities. At the same time, Cloud Computing has changed how businesses and consumers implement and access computing resources, providing ready-to-use virtual machines, containers or serverless functions that can be quickly scaled.The shift that AI and Cloud Computing is about to bring together, the dynamics involved in it have substantial opportunities tied around them as well as significant challenges. The Increasing Role of Cloud Infrastructure combined with prowess of AI Organizations rely on the advantage provided by algorithms and models in tasks related to data analysis, automation, and predictive analytics leading to a complex interplay among cloud infrastructure making an important foundation for all these advanced functions. AI with cloud provides scalability of computing, broad storage power and robust tools for data management which helps to improve operational efficiency as well as enabling innovative transformation.The contributions are summarized from three main perspectives: (1) How to further refine cloud AI service (2) the effect on the cloud-service providers and the end-users and (3) How AI-powered improvements are enhancing cloud environments and creating new business models.In the contemporary society Cloud computing and artificial intelligence (AI) are extremely pertinent. These technologies are enhancing various growth possibilities for companies, not only the effectiveness of work but also new ideas are developed every day. Most enterprises are incorporating these technologies because these enhance computing capabilities and reduce expenses. Cloud computing equips artificial intelligence (AI) with tremendous power and considered to be one of the most important catalyst for developing innovative smart applications. With its potential to change the way data used to get stored and processed across various geographies, the scope and impact of AI have reached larger market. With all the cloud models, AI developers and consumers started to create an ecosystem that improve the lives of millions, [1], [2]. Incorporation of AI in cloud platforms allows for functionalities like smart resource utilization, automatic system management and security improvements. Not only is it helping streamline cloud operations, but also allowing for more advanced and reactive cloud-based applications to be built.
2. Next Gen Cloud Computing
- The future of the Cloud Computing Age with the power of AI, what is changing in this New Age. At its core, AI powered automation from machine learning to data analytics and intelligent process automation and it is getting embedded with cloud platforms to form a digital operating model that brings dynamicity, intelligence, agility & efficiency in the way computing resources work together. This goes beyond the range of traditional cloud services to be a redefinition of all computing architecture, where AI is embedded from now on as part of the nature realized by cloud.A key innovation in this next generation computing is the autonomous cloud operations developments. AI algorithms are being used more and more to automate simple management tasks, resource planning optimization, and failure prediction for systems. These self-managed clouds mean dramatically lower operations cost, and that outcome in the end brings far higher availability of your system at significant performance.Furthermore, AI-based Cloud services are making highly personalized and intelligent applications a reality and at a faster pace. With AI services available in the cloud, developers can now create and deploy apps that will learn and adapt on-the-go to furnish their customers with more intuitive and immediate services. This change not only enriches cloud software capabilities but also speeds up innovation cycles by allowing quick iteration and experimentation.In addition, Artificial Intelligence with Cloud computing platforms are to take the lead in providing improved security and data privacy helpful in reconciliation. Utilizing state-of-the-art AI approaches to develop advanced, effective threat detection and response systems that have the ability to detect actual or even potential security breaches up to an effectiveness level, well above their predecessors. The services around security are especially important in today's climate of rampant breaches and cyber threats.With the new dawn of cloud computing, comes issues that still need to be worked out. These challenges range from the requirement to design AI governance frameworks with teeth, oversee the ethical implications of automation decision-making and ensure integration with legacy systems is a diplomatic process.In today’s technological scenario, artificial intelligence (AI) has predominantly taken over the charge of decision making in various sectors of business and advanced knowledge oriented platforms. AI has been around for long time yet remains a challenge. This excellent technology has been performing extraordinary improvement in our sphere of technical modernization. What’s more, with innovation and its proper management, there is greater development in scientific and engineering fields where impression of this improvement is noticeable. Along with AI, the emerging techniques of machine learning (ML) and their approaches are also getting attention due to their effective use. Recent advances in the innovation of AI and ML have tremendous contribution in Internet of Things (IoT) and Cloud computing-based new secured systems, [3].
3. Literature Review
- Literature review to present key findings, methodologies, and insights from various sources on the transformative effects of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on Cloud Computing.
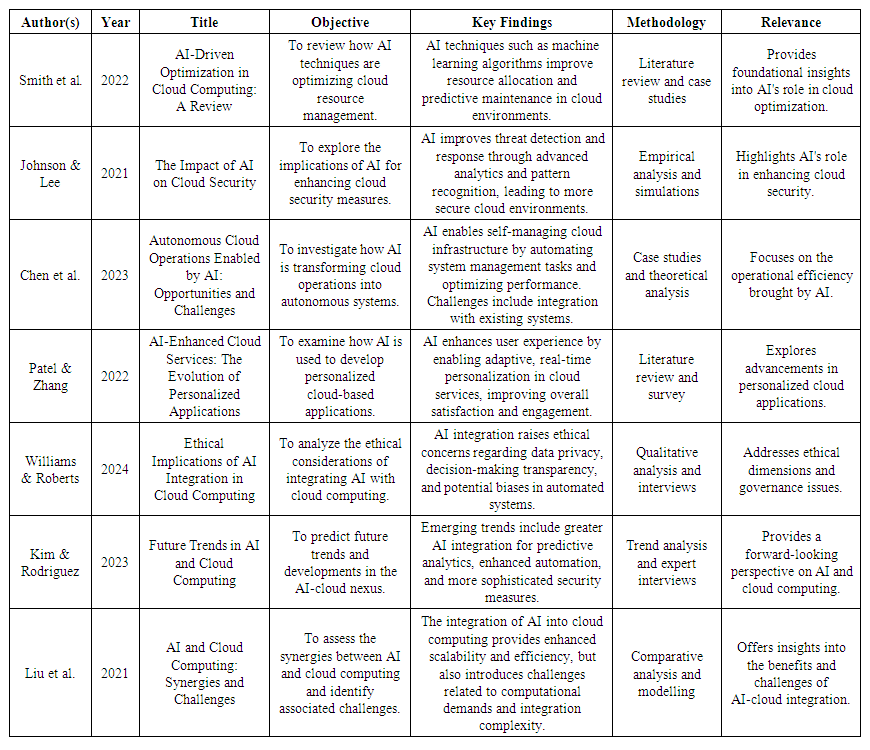 | Table 1 |
4. Cloud Computing Services with Capabilities of AI
- AI integration with Cloud Computing is changing the game by offering one of its kind cloud services ever. Technological developments such as the Artificial Intelligence-enabled platforms like Google Cloud’s autonomous management, Microsoft Azure’s security features and IBM Watson’s customized service provisioning are challenging to operationalize cloud consumption in several ways. These solutions, including artificial intelligence or other analytic capabilities tied to machine learning can provide performance optimization, security enhancements and unique user experiences. AWS SageMaker simplifies data analysis and Dropbox incorporates AI-powered productivity solutions to automatically categorize files and support fast searching. The necessary place for AI for future cloud computing evolution, modern-day cloud, is already changing consumer access services.Few of the examples of AI on cloud computing services-Autonomous Cloud ManagementGoogle Cloud's AI-Driven Operation: Google Cloud has implemented AI to enhance its cloud management capabilities. Its uses machine learning algorithms, which can automatically manage, optimize, and scale resources based on real-time data.Key Features:Auto-scaling: Automatically adjusting resources based on demand to ensure optimal performance leading cost-efficiency.Predictive Maintenance: Uses AI to predict potential issues before they occur. This technique can help in reducing downtime and improving reliability.Cost Optimization: Analyzes usage patterns and suggests or implements cost-saving measures.Smith and Johnson (2022) explore the transformative impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on autonomous cloud management in their study published in the Journal of Cloud Computing and Automation. Their research highlights how AI-driven automation is revolutionizing cloud management by enabling systems to self-manage, optimize resources, and predict failures, [11].AI-Powered SecurityMicrosoft Azure Security Center: Integrates AI technologies into its Security Center. The platform uses machine learning models to enhance threat detection and response capabilities by identifying unusual patterns and potential threats in real-time.Key Features:Advanced Threat Detection: Utilizes machine learning models to analyze vast amounts of data to detect anomalies that could indicate security breaches.Automated Response: AI-driven automation responds to threats swiftly, applying patches or adjusting security settings without manual intervention.Threat Intelligence: Continuously updates and refines security protocols based on the latest threat intelligence gathered through AI & models across datasets.Johnson and Smith (2021) examine the role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in enhancing cloud security in their article published in the International Journal of Cybersecurity and Cloud Computing. Their study details how AI-driven technologies are improving threat detection and response through advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms, [12]. Personalized Cloud ServicesIBM Watson on IBM Cloud: Watson hosted on IBM cloud offers AI-driven solutions for a range of applications, from customer service to data analysis. IBM Watson offers developers with advanced natural language processing and machine learning capabilities for personalized user interactions and improved service delivery.Key Features:Natural Language Processing: Machine learning technique to process text and contents and queries.Personalized Recommendations: Extend personalized content, product recommendations, and insights based on dataset and patterns.Custom AI Models: Allows businesses to build and deploy custom AI models tailored to specific needs and data.Patel and Zhang (2022) explore the impact of AI on personalizing cloud services in their article in the Journal of Computing and Personalization. They discuss how AI technologies are being utilized to create highly customized user experiences by analyzing individual preferences and behaviors, [13].Intelligent Data AnalyticsAmazon Web Services (AWS) SageMaker: is a fully managed service helping developers with a wide range of tools to build, train and deploy machine learning models with ease. Key Features:Automated Model Building: Uses algorithms to automate the process of model selection and hyperparameter tuning.Real-Time Analytics: Processes and analyzes data in real time to provide actionable data insights quickly. AI can significantly help businesses to make informed decisions. AI powered applications can help engineers and teams to help take data driven decision by analysis of datasets, identify patterns and extend recommendations for process optimization, optimal resource allocation, and aid in project management.Scalable Infrastructure: Leverages scalable cloud infrastructure to handle large volumes of data and complex computations.AWS offers a broad range of compute types designed to satisfy various requirements about cost, scalability, and performance. Because these instances are suitable for specific use cases and workloads, choosing the right compute type is essential. Effective compute type selection is essential for managing costs and allocating resources as efficiently as possible, [14].Enhanced Cloud-Based CollaborationDropbox's AI-Powered Collaboration Tools: Integrating AI into its cloud storage and collaboration platform to enhance productivity and streamline workflows and optimized storage approach.Key Features:Smart Search: enhances search capabilities by understanding context and providing relevant results much faster using AI.Automated File Organization: AI assists in automatically categorizing and organizing files based on type of contents and user behaviors.Collaboration Insights: offers behavior insights and recommendations for improving collaboration and improve productivity based on usage patterns.
5. Challenges & Factors
- The transformative effect of Artificial Intelligence in cloud computing is phenomenal but at the same time comes with certain privacy, regulatory and compliance issues, which need to be addressed. The last two decades have seen active research in the definition and evolution of cloud computing. Driven by innovation in networking and distributed architectures, cloud computing is a manifestation of distributed systems research since the initial conception of the client server model in 1958 [15]. Due to the rapid growth of cloud computing, it has been adopted as an important utility across all aspects of society, from academia, governmental institutions and industry. Characteristics of cloud computing such as dynamic, metered access to a shared pools of computing resources [16] have enabled the realization of new technologies and paradigms to fulfill the demands of emerging applications including scientific, healthcare, agriculture, smart city, and traffic management [17,18].Some of the key issues and considerations for how AI impacts cloud computing are:Data Privacy and SecurityChallenge: AI systems need a huge data set to operate with accuracy. Protecting such data from hackers and other breaches is key. This could allow attackers to gain access to sensitive data through AI, creating more security threats due to its integration.Solution: Necessary elements to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of data in cloud environments include good encryption (a strong cryptographic hash), security measures, defined access control, and firewalls.Costs of computation and resourcesChallenge: AI algorithms, especially deep learning models, are computationally heavy. Cloud-based artifacts for large-scale experiments are compute- and storage-intensive, to the point where it may overburden cloud infrastructure and incur high operational costs.Solution: Scaling infrastructure in the face of a growing demand for processing power and storage could necessitate additional investment in more advanced hardware, or optimization of existing resources.Integration ComplexityChallenge: Incorporating AI with operating cloud systems is very challenging and could be time-consuming without a proper skillset. These new AI technologies, in turn, may be incompatible with the legacy systems and can disrupt the entire system integration.Solution: Proper planning and may require upgrading systems, or implementing hybrid cloud solutions to upgrade with newer technologies to dated ones.Ethical and Bias ConcernsChallenge: AI models may encode unconscious biases in training data (often termed as model bias), causing ethical concerns and creating or sustaining discriminatory results. It is vital to ensure fairness and transparency in the making of any decision based on the output of AI.Solution: By creating a set of ethical AI guidelines, running continuous audits and incorporating multi-faceted datasets that are inclusive, biases like racism can be managed and ethical AI methods could be effectively put in place.Cost ManagementChallenge: Although AI can help make cloud operations more efficient, the up-front costs of implementing AI tech and scaling resources to accommodate these solutions can be significant. This comprises the price of training their own AI model, data transformation and life-time support.Solution: Businesses need to evaluate the ROI of AI projects and look out for strategies like savings by pay-as-you-go model and resource consumption efficiency.Scalability IssuesChallenge: It is often not very easy to scale AI-driven cloud services unless planned efficiently, as performance needs of different workloads can keep fluctuating. Keeping AI operations with the performance scale you need and without falling over requires great infrastructure management.Solution: Controlling scaling is necessary, and to accept all of the scalability concerns with different types of use case scenarios while maintaining low latency and performance may require usage of advanced auto-scalers or serverless computing.Regulatory ComplianceChallenge: Any deployment on cloud computing and with use of AI services, must adhere to many regulations (e.g., GDPR, industry standards) with regards to how AI is put on cloud computing. Regional compliance can be a major challenge to maintain with AI integration.Solution: Operating without keeping abreast of regulatory requirements and not factoring compliance checks into AI development or deployment processes can expose organizations to legal and financial liabilities.The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into cloud services further augmented capabilities, enabling predictive analytics, automation, and improved decision-making. The ongoing evolution of cloud computing continues to be shaped by technological advancements, emerging use cases, and the evolving needs of a diverse range of industries.
6. Future Scope
- The future of integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) with Cloud Computing is massive and rapidly growing and set to change a lot in the area of technology and business. Few of the areas where the future development of research has possibilities to go with next are:AI, Machine Learning (Advanced)Cloud providers to deliver higher-level AI and ML services as AI technologies evolve and become more advanced. This typically involves more advanced functions such as deep reinforcement learning, generative adversarial networks (GANs), and autonomous AI systems that can train and adapt in real-time.Significance: Improved AI services will allow for more advanced and individually tailored applications, leading to new use cases in areas of finance, healthcare, or autonomous systems.Edge Computing IntegrationThe merging of AI with capabilities of edge computing enables data to be processed and analyzed at the point of origin, thus cutting latency and bandwidth use. Real-time analytics and decision-making with applications which are AI-powered using edge devices would also undertake faster real-time analytics and decision-making, complementing cloud-based processing.Significance: The integration will help improve the performance of applications phenomenally that need a fast response time, such as smart cities, self-driving cars, IoT devices etc.Quantum Computing and AIQuantum computing offers the potential to unleash vast swaths of computation that was practically impossible prior to its arrival. The quantum-amplified AI model will solve complex problems at a much lower cost than the traditional system.Significance: Would eventually enable advances in drug discovery, cryptography and optimization that can only be achieved using quantum computers.AI-Driven Cloud AutomationFuture cloud platforms will use AI technologies not only to automate resource allocation, but all the way down to optimize infrastructure operations, monitor system health and perform predictive maintenance.Significance: AI-based automation will greatly reduce the operational overhead, enhance efficiency, and decrease manual interaction in managing cloud.Improved Data Privacy and SecurityFuture advancements will include developing enhanced security and privacy methods as AI further intertwines with cloud services. This entails figuring out an AI, which has the ability to detect threats, advanced encryption methods and automatic compliance monitoring.Significance: Enhanced security will reduce the likelihood of adverse impacts associated with cyber risks, containing a more stable trust in cloud computing offerings.Cloud Architectures Optimized for AIIn coming years, the technology landscape will definitely witness cloud architectures to be “AI ready” for yield optimization and resource allocation of bandwidth. It involves AI-boosted distributed computing frameworks as well as dedicated hardware to accommodate for AI workloads.Significance: More efficient cloud environments will include more performance AI, given to a broader and demanding variety of applications.The future dimension of AI in cloud computing is encapsulated by accelerated technological innovations and greater interaction with upcoming technologies concerning enhancing security, productive efficiency, management as well as improving user experience. Overall, its expected to make a meaningful dent in many areas and its positive impact for technology in relation to society, [19]. Security in traditional IT systems primarily focuses on protecting physical assets and internal networks. In contrast, cloud computing security must account for data that travels over the public internet and resides on shared infrastructure owned and operated by third-party service providers [20]. This shift poses unique challenges, such as ensuring data privacy, securing data transfer and storage [21], and managing a shared responsibility model between cloud providers and users. Quantum computing will make it possible for modern computers to perform computations, calculations, and problem-solving approaches at speeds, unimaginable with today's technology. Quantum computing along with artificial intelligence can provide a computation boost and the speed of processing complex data and datasets will increase significantly. Quantum computing is the future. It will not only increase the computation power but also help to answer the questions which remain unsolved because of the limitations of classical computers and algorithms, [22]. Cloud computing is a definite boon not only to the financial sector but to all industries in the whole. Cloud security is among the many things that financial institutions have to consider when it comes down to digital transformation, and how they go about securing their operations could very well determine trust in their customer base.
7. Conclusions
- To conclude, the transformative effect of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on Cloud Computing is one such transformative step in the digital technology revolution. The resultant synergy is transforming the industry by streamlining operational efficiency leading to innovation and opening new avenues across a multitude of industries. The way AI is able to automate intricate processes, control resources efficiently and provide tailored user experiences in the cloud is advancing rapidly.Regarding the future, AI has a broad and promising scope in cloud computing. Technology improvements such as AI cloud automation, the linkage with edge computing and potential breakthroughs in quantum computing are extra set to supply additional impetus. Furthermore, measures for improved data security, environmental sustainability and digital ethics will be required to shape the responsible evolution of these technologies.To the point that both AI and cloud computing are being blended into a transformative combination to not only to enrich our current capabilities but also poised for some future exciting innovation which will shape how we deal with technology and data around us. The continued research, development and collaboration in this area to ensure the maximum positive impact of these advances, and to solve the problems they inherit is paramount. As AI and cloud computing continue to evolve side by side, so will their interoperability, leading to a vision where technology weaves seamlessly into the fabric of society.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML