-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Computer Science and Engineering
p-ISSN: 2163-1484 e-ISSN: 2163-1492
2024; 14(6): 121-128
doi:10.5923/j.computer.20241406.01
Received: Aug. 22, 2024; Accepted: Sep. 19, 2024; Published: Sep. 21, 2024

Cloud Computing and Its Impact on the Security of Financial Systems
Naga Rishyendar Panguluri
Senior IEEE Member, Software Engineering Manager, Researcher, USA
Correspondence to: Naga Rishyendar Panguluri, Senior IEEE Member, Software Engineering Manager, Researcher, USA.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

In the financial technology (fintech) sector, cloud computing has been a potentially disruptive technology and introduced considerable benefits in addition to some challenges. This research studies the impact of cloud computing on fintech systems and how it affects, what are its advantages & challenges. The research extends how cloud computing delivers improved scalability, agility, cost savings in financial technology operations and provides faster time to market for new services, better scale up and down as workloads change, and lower infrastructure costs. Further, also investigates challenges such as data security risks and compliance with regulations or the danger of being locked into the ecosystem. While its important of cloud computing for contemporary fintech and there should be strategic approaches to manage the type of implementation in a way that leverages advantages while mitigating potential risks while ensuring compliance to regulatory policies.
Keywords: Cloud computing, Fintech, Impact, Benefits, Challenges, Scalability
Cite this paper: Naga Rishyendar Panguluri, Cloud Computing and Its Impact on the Security of Financial Systems, Computer Science and Engineering, Vol. 14 No. 6, 2024, pp. 121-128. doi: 10.5923/j.computer.20241406.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Cloud computing is a technology that helps businesses to manage and utilize computing resources on demand. Cloud computing has been embraced by businesses & industries over the past decade. Cloud computing has the ability to offer services such as storage, compute cycles and applications over the internet in-lieu of on-premise servers or local infrastructure. It is a model with scalability, adaptability and an economic model that allows companies to consume resources according to demand.This transformative technology has been widely used by various financial institutions however there has been a wide debate on pros & cons of using cloud computing services in financial institutions. Harnessing the power of cloud computing, banks and financial service organizations can improve operational agility, innovate with new services faster and lower the costs for IT infrastructure. Cloud computing adoption raises new concerns in the security field. Most notably financial systems are vulnerable in large part because of the importance and regulation around such data. As more and more workloads are moved over to the cloud, enterprises find themselves in need to rethink security practices as standard on-premises controls may not always map directly across to these environments. These include risks from an information security point of view - data privacy, compliance with regulations such as GDPR and PCI-DSS or increasing exposure to cyber threats. Financial institutions need to enforce high levels of cloud security from their service providers with appropriate encryption, access controls and monitoring mechanisms in place to protect sensitive information. Furthermore, as cloud security is a shared responsibility (the provider secures the infrastructure while the client must secure their data), it demands an understanding of roles and responsibilities of each party.The adoption of cloud computing introduces a range of potential risks that financial institutions must navigate with prudence. Cloud service providers are entrusted with valuable customer information, and any compromise could have severe consequences, including financial losses and reputational damage, [1]. Cloud computing is one of the most powerful inventions that has grabbed the curiosity of technologists all around the world. Cloud computing has many advantages, but it also has a slew of security risks that no organization can afford to ignore. For a successful Cloud Computing adoption in a corporation, proper planning and awareness of emerging risks, threats, vulnerabilities, and potential solutions are necessary. As a result, determining the most effective solution instructions to increase cloud security has become important for all cloud operations, [2].Cloud computing is a definite boon not only to the financial sector but to all industries in the whole. Cloud security is among the many things that financial institutions have to consider when it comes down to digital transformation, and how they go about securing their operations could very well determine trust in their customer base.
2. Cloud Computing Security Services in Financial Industry
- The information that financial institutions work with is much too sensitive and the level of cloud computing security security plays a pivotal role.Financial data security is the main aspect in financial management processes (Buchanan and McMenemy, 2012, Menezes et al., 2001, Ogiela and Ogiela, 2014c). Systems which ensure the security of financial data represent one of the basic elements of efficient and safe management. As it is necessary to ensure the security of financial management processes, the data management systems currently operated by commercial organisations and enterprises are increasingly frequently focused on securely storing, processing, analysing and transmitting data (Buchanan and McMenemy, 2012, Hachaj and Ogiela, 2013, Ogiela and Ogiela, 2012, TalebiFard and Leung, 2011). [3-4]Financial institutions generally end up using a combination of the following cloud computing services security to provide robust protection:Data Encryption:At Rest: It secures the data stored in cloud storage and avoids unauthorized access of it.In Transit: This layer deals with encrypting the data which is being transacted between client and cloud services in order to preserve it from eavesdropping or interception.Data security and privacy is a major concern for the users while using software services on the cloud. When users want to compute on a cloud service, traditional encryption schemes can be applied to encrypt and transfer the data to the cloud service. However, the service provider must decrypt the data for input into their computational model and thus the data content is exposed. If users do not want service providers to know what they are computing, then computing on encrypted data preserving privacy is an important issue. Homomorphic encryption is an encryption method where computations can be performed on the ciphertext, and the decrypted result of these computations is the same as if the computations were performed on the plaintext. [5]IAM (Identity and Account Management:Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple types of verification to complete a process.Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Restricts access based on the user’s role within the organization, ensuring that individuals only have access to data and resources necessary for their job functions.Single Sign-On (SSO): Allows users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials, simplifying management and reducing the risk of password fatigue and compromise.Identity and access management (IAM) covers two very important aspects of securing technology assets against any cyber threat. The identity part of it helps validate whether the user is actually what they claim to be, and access element of IAM ensures the identified user can only access the resources that they are authorised to. IAM combines user access policies and authentication mechanisms, to control who can access what applications and data, and what they can do with them [6].Threat Detection and Monitoring:Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Aggregates and analyzes security-related data from across the cloud infrastructure to identify and respond to potential threats.Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): Monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and take action to prevent potential attacks.Financial fraud also represents an issue for cloud-based fintech systems. For example, criminal acts such as credit card information theft happen on a daily basis and in large numbers [7]. This fraud compromises legitimate credit card owners and causes financial and other forms of damage. Therefore, detecting fraudulent behaviour and tracking down malicious users represents a serious security challenge. Usually, anomaly detection techniques from machine learning (ML) are applied to identify suspicious behaviour patterns in payment datasets. In this way, ML provides predictions from available payment data and helps in further decision making [8]. Another problem for cloud and fintech systems is cyberattacks, which can violate information security or disrupt the functionality of a system [9]. Additionally, AI has become a target for so-called adversarial attacks in recent years [9]. For these reasons, ensuring security and privacy in the ubiquitous environment of fintech is of uttermost importance, [10,11].Firewalls and Network Security:Cloud Firewalls: Protect cloud-based resources from unauthorized access and threats by filtering incoming and outgoing traffic.Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Provide secure connections between the financial institution's network and the cloud environment.Installation of firewall and its maintenance is mandatory to ensure the protection. A firewall should be present in all external interfaces. A list of necessary port and services should be maintained. Assessment of firewall policies and rule sets and reconfiguration of router should be done in regular intervals. Build and deploy a firewall that denies access from ―untrusted ‖ sources or applications, and adequately logs these events. Build and deploy a firewall that restricts access from systems that have direct external connection and those which contain confidential data or configuration data, [13].Compliance and Governance:Regulatory Compliance Tools: Help ensure that cloud deployments meet industry standards and regulatory requirements, such as PCI-DSS, GDPR, and SOX.Audit Trails: Maintain logs of user activities and system changes for accountability and forensic analysis.Backup and Disaster Recovery:Automated Backups: Regularly backup data to prevent loss in case of hardware failure or other issues.Disaster Recovery Solutions: Enable quick restoration of services and data in the event of a significant disruption or failure. The organization data needs and its disaster recovery objectives need to be considered. To evaluate the risk, the types of disaster (natural or human-caused) need to be identified. The probability of a disaster occurrence needs to be assessed along with the costs of corresponding failures. An appropriate approach for the cost evaluation needs to be determined to allow a quantitative assessment of currently active disaster recovery plans (DRP) in terms of the time need to restore the service (associated with RTO) and possible loss of data (associated with RPO). This can guide future development of the plan and maintenance of the DRP, [12].Vulnerability Management:Regular Scanning and Patching: Identify and address vulnerabilities in cloud services and applications through automated scanning and patch management.Secure Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC):Application Security Testing: Includes practices such as static and dynamic analysis to identify security flaws in applications before deployment.Data Loss Prevention (DLP):Policy-Based Controls: Monitor and control data movement and usage to prevent unauthorized data transfers and leaks.Security Awareness and Training:User Education: Provide ongoing training for employees on best practices for cloud security, including recognizing phishing attempts and safe handling of sensitive data.These security services are either offered by cloud service providers called CSPs or they can also simply be third party solutions. Banks & financial Institutions often use a combination of these services to reinforce their security posture against potential threats and maintain compliance.Cloud architecture infrastructure for Banking and Financial Services Corporations operates on access control mechanism and trust over various cloud user. Having established the on demand service delivery model to operate, maintain, control and govern the cloud architecture, Banking and Financial Services Corporations deliver round the clock services to customers. Despite stringent security controls and minimum access level, the cloud users identify and exploit the cloud vulnerabilities. This leads to data leakages and loss of critical information. Depending upon the area of business and sophistication with which vulnerabilities have been exploited, frauds are committed and system are damaged by employees and third party contractors, [14].
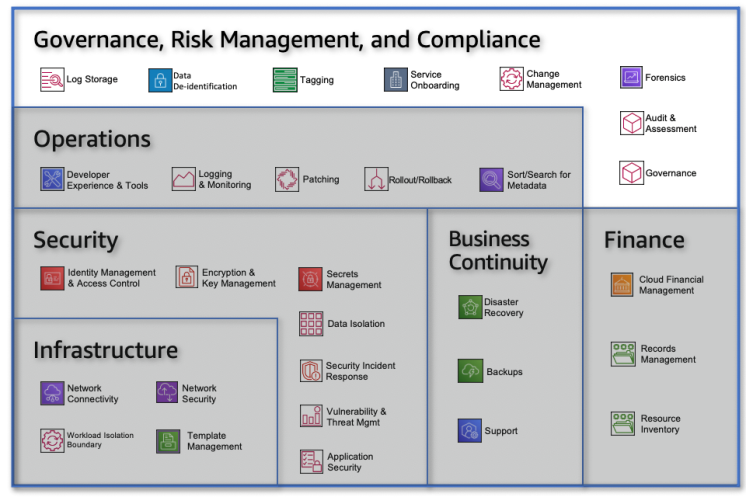 | Figure 1. Aws framework for financial institutions [19] |
3. Security Compliance in Financial Industry
- Cloud security services complying to regulations for financial institutions vary globally, reflecting regional regulations, standards, and best practices. Use of cloud services by its very design leaves the control of the computing infrastructure outside the control of the business using the cloud service. Many surveys have confirmed that this lack of control is a major concern for businesses when it comes to data security. Some technologies are better suited to protecting confidential information than others, [16].Amidst the fervent embrace of cloud computing within finance, the triad of data privacy, compliance, and security emerges as a cornerstone of organizational strategy. Financial institutions operate within a highly regulated environment, governed by stringent data protection laws, industry standards, and regulatory mandates (Halpert, 2011). Whether it be the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS), or industry-specific regulations such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), compliance is non-negotiable (Ruiter & Warnier, 2011). [17-18]Banks/Financial institutions must navigate these diverse requirements to ensure they maintain compliance while leveraging cloud technologies. Here’s a comprehensive overview of key global cloud security compliance considerations for the financial sector:United StatesGramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA): Regulations require banks/financial institutions to protect consumer financial information and maintain adequate privacy.Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS): an important compliance that mandates security measures for payment card data & financial transactions, applicable to cloud services handling card transactions.Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): Requires internal controls and accurate financial reporting, including controls over cloud-based systems.Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC): Provides guidance on managing risks in cloud computing environments, including security and privacy.CanadaPersonal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA): Requires organizations to protect personal data and be transparent about data collection and usage.Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions (OSFI) Guidelines: Includes guidance on technology and security risk management for financial institutions.European UnionGeneral Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Mandates stringent data protection and privacy practices, including data processing and storage in the cloud. Financial institutions must ensure that cloud providers comply with GDPR requirements for data protection and cross-border data transfers.EU-U.S. Privacy Shield: Previously governed transatlantic data transfers, now replaced by the EU-U.S. Data Privacy Framework.United KingdomUK Data Protection Act 2018: Complements GDPR requirements for data protection and privacy.FCA Guidelines: The Financial Conduct Authority provides specific guidance on cloud outsourcing and security for financial services firms.AustraliaAustralian Privacy Act 1988: Regulates the handling of personal information, including data in the cloud.Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) Standards: Includes standards for risk management, including cloud risk for financial institutions.SingaporePersonal Data Protection Act (PDPA): Governs the collection, use, and disclosure of personal data, including in cloud environments.Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) Guidelines: Provides guidelines for technology risk management, including cloud computing.BrazilGeneral Data Protection Law (LGPD): Regulates data protection and privacy similar to GDPR, with specific requirements for cloud data processing and storage.Central Bank of Brazil Regulations: Includes guidelines on technology risk management for financial institutions.United Arab EmiratesFederal Law No. 2 of 2019 on the Use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in the UAE: Includes provisions related to data protection and cybersecurity in cloud environments.Central Bank of UAE Guidelines: Offers guidance on IT and cybersecurity for financial institutions.Saudi ArabiaSaudi Data and Artificial Intelligence Authority (SDAIA): Oversees data protection and compliance, including for cloud services used by financial institutions.Beyond simple regulatory violations, failure to satisfy these requirements can have far-reaching financial repercussions, reputational damage, and increased vulnerability to data breaches. Notably, the broad range of services and features built into the AWS cloud platform give users a toolbox to comply with PCI DSS requirements. AWS offers a foundational infrastructure that is intrinsically secure, allowing organizations to build and deploy environments that seamlessly comply with PCI DSS requirements, [15].
4. Literature Review
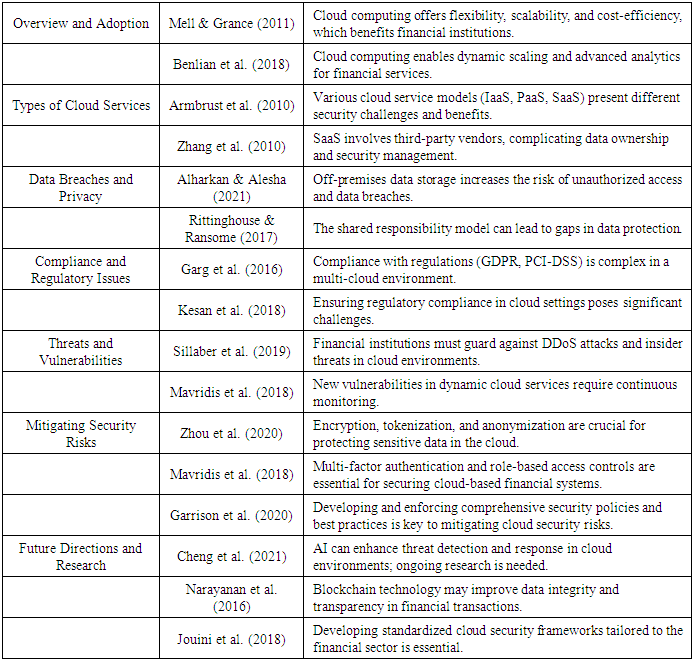
- The literature review on cloud computing and its impact on the security of financial systems, key studies highlight important research on data breaches, regulatory compliance, and evolving threats, emphasizing the need for security measures and ongoing research into advanced technologies.
|
5. Benefits of Cloud Services for Financial Assets
- Improved Compliance and Regulatory AdherenceStandards Compliance: financial sector to comply with industry regulations such as PCI-DSS, GDPR and SOX. An example would be, AWS Artifact which gives access to audit reports about compliance and security documentationAutomated Compliance Monitoring: Tools like AWS Config and AWS Security Hub helps organizations to have continuous monitoring and compliance management. Thereby, automating the process of adhering to regulatory requirements and standards.Operational Efficiency and Cost ManagementScalability and Flexibility: Leveraging cloud security services can adapt to the scalable nature of cloud environments, helping financial institutions scale up (or down) measures without requiring large upfront expenses on hardware or infrastructure.Cost-Effective Security Solutions: With cloud security services, financial firms bid adieu to the costs of running an on-premises appliance and can leverage pay-as-you-go models that allow them only for what they use - rationalizing their investments in securing their enterprise.Enhanced Risk ManagementCentralized Monitoring and Logging: Services such as AWS CloudTrail and CloudWatch offer the ability for comprehensive logging and monitoring. Helping enable financial institutions to track user activities, detect anomalies, and respond to incidents promptly.Automated Incident Response: AWS’s Systems Manager can automate responses to security incidents, reducing the time to address and mitigate potential threats.Improved Data Protection and PrivacyData Loss Prevention: Cloud Backup and Amazon’s S3 buckets ensure that financial data is regularly & timely backed up. Cloud services also extend protection from accidental deletion or tampering, supporting data integrity and availability.Sensitive Data Handling: Organisations use machine learning to classify and protect sensitive financial data, ensuring compliance with privacy regulations and safeguarding personal information.Global Scalability and AvailabilityRegional Security Compliance: Cloud security services include Region-specific compliance meaning that financial institutions get the ability to achieve local regulatory requirements as well as high availability and performance of cloud.To summarize, cloud security services improve the financial industry by reinforcing its stability and flexibility while keeping it cost effective with potential for higher dividends. All of the services are key to helping secure and protect data, mitigate risk management, allowing financial institutions to operate in the cloud.More and more financial service companies and organizations have shifted their online services to cloud platforms to provide customers with more convenient and accurate services. Working with a cloud service provider offers a wide variety of benefits for banks and financial institutions. This includes greater flexibility and scalability, lower costs, and improved organizational efficiency. However, at the moment, they pose a certain level of data security risk to financial organizations. For financial institutions, keeping data secure is of the utmost importance. Financial information is extremely sensitive, making it valuable and especially vulnerable. The cloud service providers are making significant efforts to develop the cloud industry in order to maintain optimal security, [20]. To enable security compliance in cloud computing solutions, financial institutions must adopt best practices for securing their cloud infrastructure. They must consider both the physical and logical security aspects, including access control, encryption, and data protection. Financial institutions must also ensure that their cloud solutions comply with regulatory requirements such as the GDPR and PCI DSS. The rapid adoption of cloud computing technologies has transformed the way organizations and individuals manage and store data, offering scalable solutions and cost efficiencies. However, this shift has introduced significant concerns regarding cloud security and data privacy. As organizations increasingly rely on cloud services, the need to address these concerns has become more pressing, [21].
6. Emerging Technologies
- Below are the few of emerging technologies relevant to the security of financial systems in the context of cloud computing:Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)AI and ML can enhance deployment with possible threat detection and recommend series of steps to prevent the damage. Forecasting based on analyzing vast amounts of data forming patterns and identifying unusual activities. Use of AI/ML helps business improve the accuracy and speed of identifying and responding to security threats, reducing the risk of breaches.Blockchain TechnologyOne of the highly discussed emerging technology is the Blockchain which provides a decentralized and immutable ledger for financial transactions which improves data integrity and transparency significantly. Use of Blockchain based application increases trust and security in transaction records, making it harder for malicious actors to alter or forge data.Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)One of the emerging approach is ZTA which operates on the principle of never trusting any user or system by default. Enforcing strict identity verification and access controls. Thereby reducing the risk of insider threats and any unauthorized access by ensuring that all users and devices are continuously validated before giving the access.Homomorphic EncryptionA new type of unique approach where the system allows data to be encrypted and processed without needing to decrypt it first. Enabling secure computations on sensitive data. Protects data privacy and security effectively while enabling only useful operations on encrypted data, which is particularly valuable for cloud environments.
7. Future Scope
- The road ahead for cloud computing in financial services looks highly promising. However, key areas in security for financial institutions adopting to cloud computing will see lot of advancements in areas as such as - Innovations in Cloud Security TechnologiesExisting cloud security technologies will improve to counter new threats. More secure financial systems will depend on innovations like improved encryption methods, more sophisticated threat detection devices and automated security responses.Better Security Measures And ProcessesThe tendency is likely to continue as banks lean on cloud technology more, which means stepping up security capabilities. It involves multi-factor authentication, zero-trust architecture and end-to-end encryption to secure data concerning transactions.Evolving Threat Landscape:Cyber threats are becoming more and more sophisticated, which means financial institutions will have to stay agile in how they defend against them. Cloud environments require strong defenses against ransomware, phishing and other innovations in attacks.Issues with Data Sovereignty and Privacy:Furthermore, this will also continue to be an issue from a data sovereignty standpoint where financial services organizations must make sure that storage and processing of data follows the reams of regulation at both local or global levels. It will involve weaving through complex legal with cloud vendors to meet all compliance needs.Incident Response & Recovery:Being able to detect, respond and recover rapidly will be essential. To mitigate ongoing and future threats, financial institutions will require holistic incident response plans that utilize cloud based resources for immediate detection and rapid recovery.A Security Ecosystem Approach:Looking to the future, we may see more enterprising collaborations on security ecosystems in which cloud providers, financial institutions and cyber vendors collaborate with each other to exchange threat intelligence and best practices. Working as a collective like this can improve security all round, making systems more resilient.Potential Security Challenges:As financial institutions are increasingly adopting cloud computing, they face several potential security challenges. In order to sustain growth and maintain trust financial institutions must address safeguarding sensitive information. One of major concern is that of data breaches, which can pose significant challenge exposing confidential customer financial data to unauthorized parties. Such data breach can occur due to vulnerabilities in the cloud infrastructure or because of inadequate access controls.Another significant challenge is regulatory compliance where financial institutions must adhere to controls and regulations posted by the authorities. Few of the regulations such as GDPR & PCI-DSS mandates stringent data protection measures which includes encryption, access controls & safeguard mechanism.Additionally, emerging threats also includes advanced persistent threats via APTs and sophisticated phishing attacks on customers of financial institutions. Addressing these challenges requires a holistic approach with combination of cloud security services, incorporating robust encryption, effective access controls, and proactive threat management.
8. Conclusions
- The emergence of cloud security services for financial institutions & service providers has indeed revolutionized the way they deal with a safer data system that helps them ensure proper compliance and operational efficiency. These security capabilities can greatly enhance the overall security posture of financial institutions as well as their ability to manage risks and comply with strict regulatory conditions.With advanced threat detection with Artificial intelligence, automated compliance monitoring and data protection features used by banks to protect highly-sensitive financial transaction data which further provides a secure and trusted environment. Furthermore, the scale and flexibility of cloud security services empower institutions to innovate rapidly changing in this hypercompetitive digital landscape without compromising its security whilst maximizing the cost efficiency.In conclusion, the use of cloud security services not only enables financial institutions to enhance their approach toward higher levels of safety and operational efficiency but also helps in securing them for further expansion and survivability within an industry that is rapidly changing.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML