-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Clinical Medicine and Diagnostics
p-ISSN: 2163-1433 e-ISSN: 2163-1441
2019; 9(5): 89-97
doi:10.5923/j.cmd.20190905.01

Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for Hippocampus Atrophy and Sclerosis Can Detect Convulsion Progression among Epileptic Children
Abdelmonem M. Mourad1, Mahmoud Mohamed Sabri2
1Radiology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Assuit University, Assuit, Egypt
2Neurology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Sohag University, Sohag, Egypt
Correspondence to: Abdelmonem M. Mourad, Radiology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Assuit University, Assuit, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background and Purpose: The purpose of the current research was to establish a link between gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) and creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for hippocampal atrophy and their correlation to recurrent seizures and clinical symptoms among epileptic kids. Methods: This study included male epileptics with tonic-clonic seizures and without them. Patients were chosen depending upon their therapy profile with Valproic acid (Depakine, 500 mg/day) and Carbamazepine (Tegretol, 400 mg/day) or combined therapy treatment. Axial T1 and T2 weighted images and FLAIR images were used for the MRI acquisitions. Results: Our study revealed that MRI of patients with tonic-clonic seizure had a relative dilation of the right temporal horn and right hippocampal abnormal outline with slightly atrophic changes and volume loss compared with a left region. Furthermore, gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) and creatine phosphokinase (CPK) has been slightly correlated with the extended seizure and rate of convulsions. Carbamazepine monotherapy is more effective in its role in reducing convulsions, which were improved in combination therapy (p < 0.01) than the Valproate. In addition, MRI flair and the increased signal intensity with T2-weighted protocol have a potential role in hippocampal atrophy and hippocampal sclerosis predictions. Conclusion: The hippocampal atrophy can be considered as one of disorder threat factors for convulsive tonic-clonic seizure, and the combined polytherapy of carbamazepine and Valproate can be considered as the combined polytherapy drugs of choice to decrease the convulsion rate among epileptic children.
Keywords: Hippocampal atrophy, Gamma-glutamyl transferase, Creatine phosphokinase, Epilepsy-MRI imaging, Monotherapy, Polytherapy, Antiepileptic drugs
Cite this paper: Abdelmonem M. Mourad, Mahmoud Mohamed Sabri, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for Hippocampus Atrophy and Sclerosis Can Detect Convulsion Progression among Epileptic Children, Clinical Medicine and Diagnostics, Vol. 9 No. 5, 2019, pp. 89-97. doi: 10.5923/j.cmd.20190905.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Seizures are the most common pediatric neurologic complications affecting from 4% to 10% of children within the first 16 years of life, and the highest incidence is among children younger than 3 years of age [1,2]. Epidemiologic studies have shown that every year, approximately 150,000 kids will be affected by a first-time, unprovoked seizure, and 30.000 will develop epileptic symptoms [1,3]. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive tool used to detect structural brain lesions [4,5] and provided a pivotal diagnostic technique for focal epilepsy diagnosis for approximately 30% of patients with partial epilepsy. Moreover, MRI sensitivity at 1.5 T for diagnosis of patients with partial epilepsy is between 82% and 86% [6,7].Although theoretically increased image resolution could be achieved by applying higher magnetic field strength, the few studies comparing the 3 T diagnostic output versus 1.5 T imagery when detecting structural lesions in focused pathology patients had contradictory conclusions about 3 T newly identified lesions rates (5–65%) [8,9]. One of the main causes of status epileptics is the low blood concentrations of antiepileptic drugs in patients with chronic epilepsy, cerebrovascular accidents, anoxia or hypoxia, metabolic causes, alcohol, or illicit drug withdrawal and miscellaneous causes [10-12]. The biochemical prognosis of Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) was considered as a marker of antioxidant inadequacy and increased oxidative stress from the liver that is [13] influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Moreover, GGT levels may be increased due to medications, such as carbamazepine, cimetidine, furosemide, heparin, methotrexate, oral contraceptives, phenobarbital, phenytoin, and valproic acid [14]. In addition, GGT is leaked into the serum possibly as a result of normal cell turnover and cellular stresses. Recently, GGT has been regarded as a clinical marker for the free-radical formation and pro-inflammation [15].Monotherapy is still considered as the treatment of choice for newly diagnosed epilepsy, which can be followed by poly-therapy in case of failure of a monotherapy regime. Moreover, the poly-therapeutic strategy has more concerns due to its drug load accompanied by increased toxicity [16,17]. Thus, combinations of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) should be carefully selected based on the potential for synergy that is not associated with unfavorable pharmacokinetic interactions and toxicity [18]. While clinical and radiological diagnostic efficiency of epilepsy has improved over the last few years, much has been achieved by reducing the amount of energy and the amount of time lost. In order to detect induced hippocampal atrophy in the epileptic child, this study seeks to create a correlative connection for additional diagnostic tools using radiological and biochemical technologies. The objective of the present study was constructed to 1) examine the activity of radiological techniques in the prognosis of epileptic status among children with convulsive repeated generalized tonic-clonic (GTC) seizures and non-convulsive status epileptics 2) the advantages of the polytherapy over monotherapy in controlling the seizures.
2. Materials and Methods
- The present study has comprised only (80) male children (mean age 11.21 ±2.2) with epilepsy, aged from 3-14 years. Epileptic children have categorized into the two main groups; non-convulsive epileptic status without a tonic-clonic seizure and did not get any type of treatment for the past three months and convulsive with a tonic-clonic seizure (60). The convulsive group with tonic-clonic seizure has been grouped into three groups, twenty individuals for each as follows; 1) Valproic acid (Depakine, 500mg/day), 2) Carbamazepine monotherapy (Tegretol, 400mg/day); 3) Regular combined therapy. The epileptic status has been defined as follows: three or more convulsions within the last hour and currently under episodic convulsions; two or more sequential convulsions without a consciousness recovery and currently with convulsions; a single convulsion which is currently at least 5 minutes. Seizures may have begun focally and evolved to become widespread; however, a loss of consciousness and widespread tonic / clonic seizures must be included. These definitions comply with present treatment norms. The levels of Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) and Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) enzymes have been checked before the initiation of therapy, and only patients with reference values have been included. The blood samples were drawn from peripheral veins after a minimum fasting period of 6 hours. The reference values for enzymes were as follows: CPK (55-232U/L) and GGT (8-40) IU/L.
3. MRI Acquisition
- In the study, children who could not fall asleep naturally were given oral chloral hydrate, of 10% concentration and the dose was adjusted as 50 mg/kg, the administration was given 30 minutes before an MRI scan. The MRI acquisitions were performed on a 1.5 Tesla MRI machine (Siemens Magnetom Symphony-Germany) with an 8-channel phased-array head coil The following sequences were used: axial T1 Weighted images with the following parameters, TR= 500-600, TE=20-25, slice thickness =2mm, flip angle 140°, Matrix = 320x320 and FOV =23cm.In addition, Axial and angled coronal sequences T2 Weighted images were done with the following parameters, TR= 3600, TE=120 Slice thickness =2mm, flip angle 130°, Matrix = 320x320 and FOV =23cm, Also FLAIR images were done; Axial, angled coronal and Sagittal with the following parameters, TR= 7000, TE=130 Slice thickness =2mm, flip angle 130°, Matrix = 320x320 and FOV= 23cm.
4. Statistical Analysis
- We calculate sample size according to Raosoft, and All statistical calculations were done using SPSS (Statistica Package for the Social Science version 25.00) statistical program at 0.05, 0.01 and 0.001 level of probability. Quantitative data with non-parametric distribution were done using Analysis of variance Kruskal Wills test. The confidence interval was set to 95% and the margin of error accepted was set to 5%. The p-value was considered non-significant (NS) at the level of P > 0.05, significant at the level of P< 0.05, 0.01 and highly significant at the level of < 0.001 [19].
5. Results
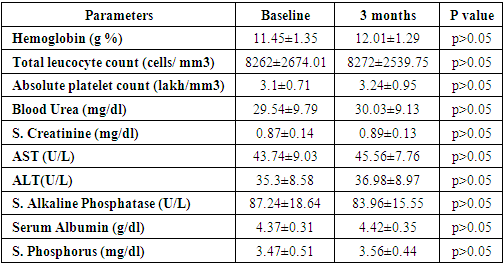
- The current research study revealed that no apparent significant differences in the baseline of biochemical characteristics of liver and kidney functions among all admitted children patients and the distribution of seizure between the different treated and control groups, as shown in the table (1).
|
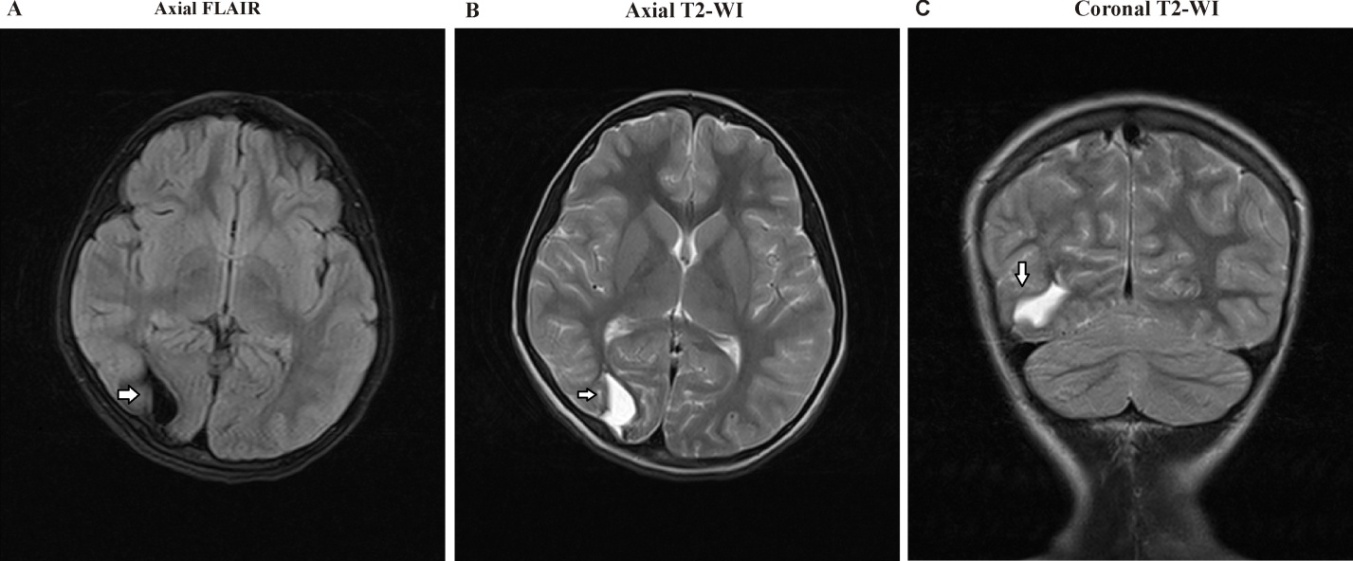 | Figure 4. A) axial FLAIR, B) Axial T2WI, and C) Coronal T2WI show a large Rt. occipital encephalomalacia area at the cortical, subcortical, and white matter regions |
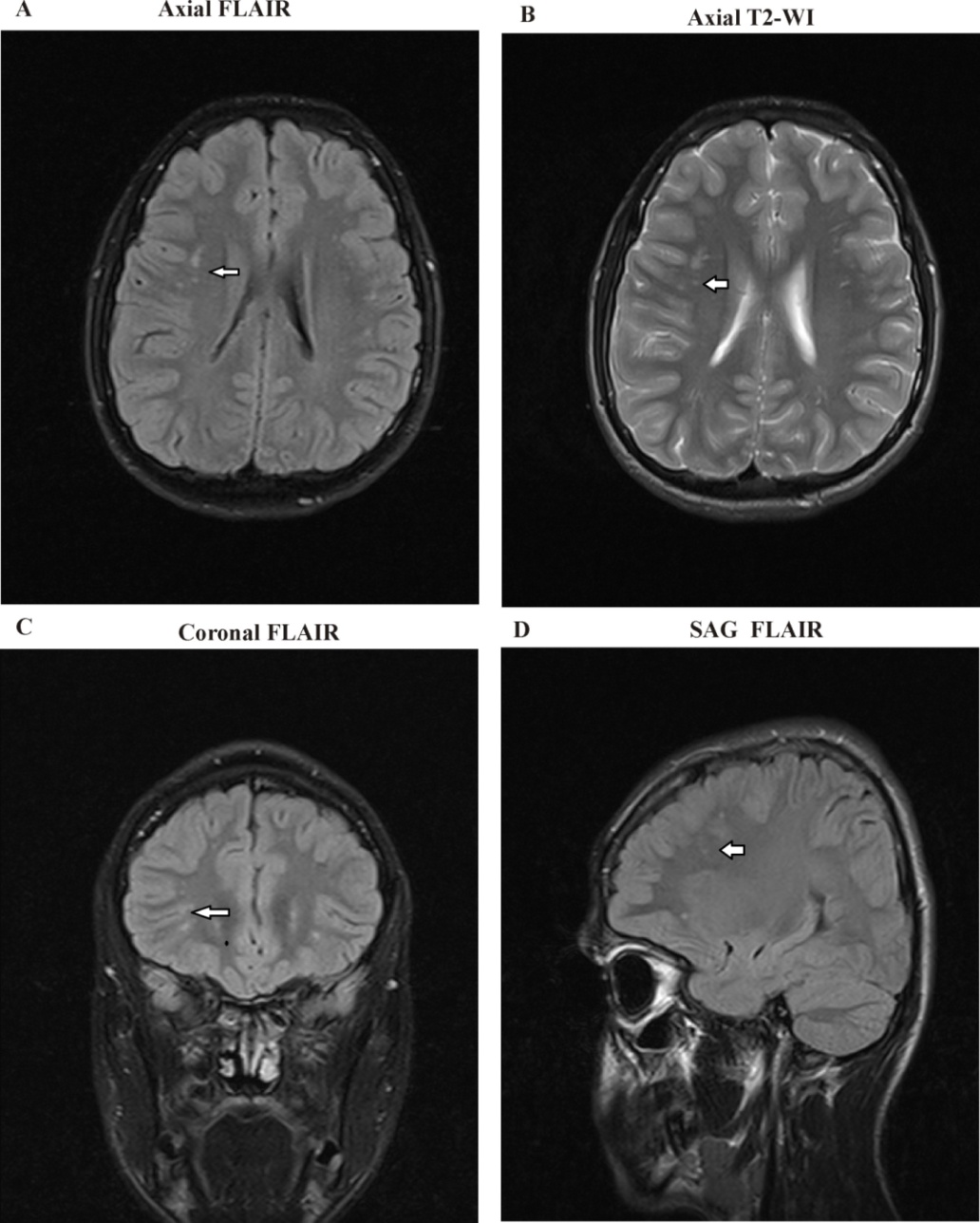
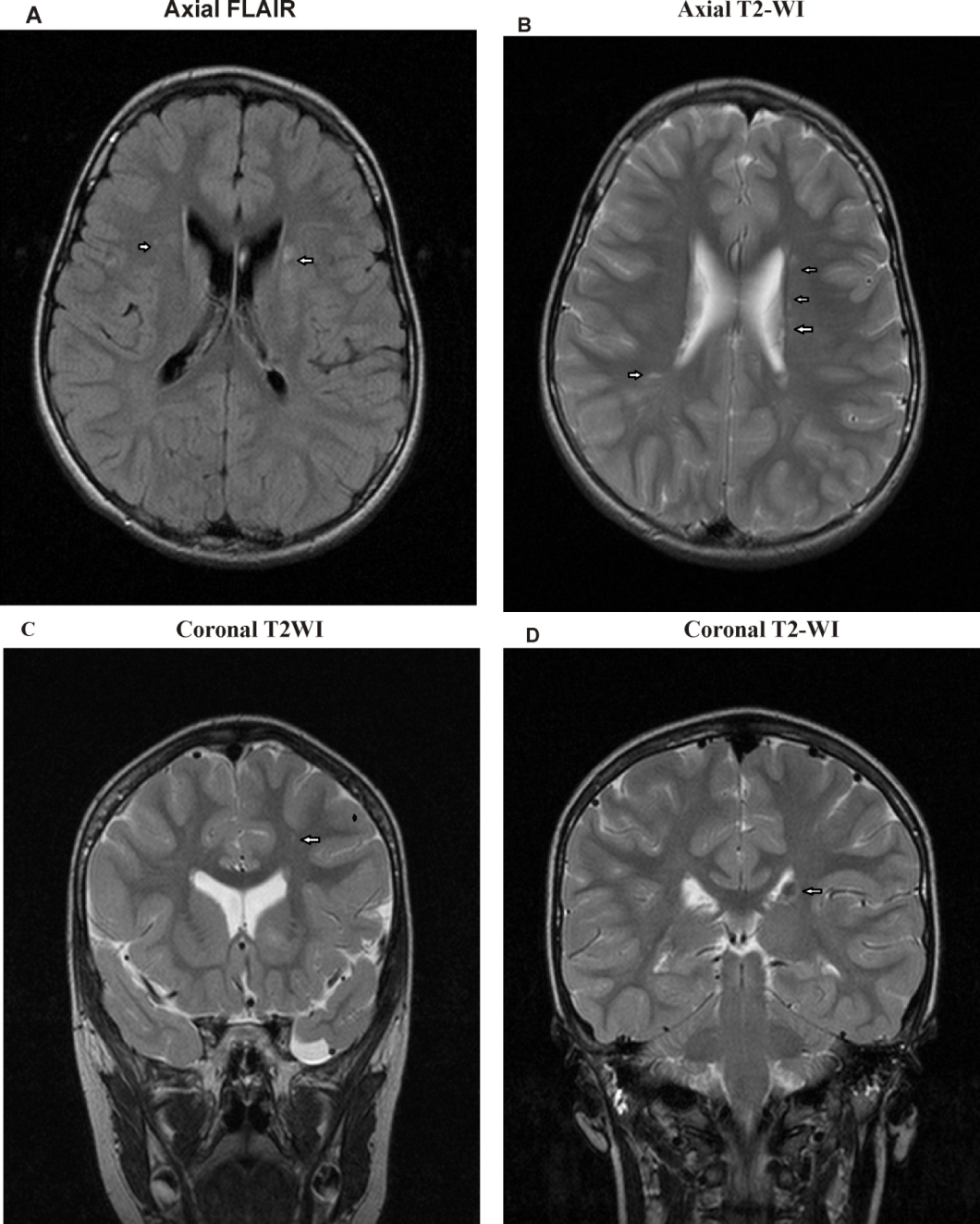 | Figure 5. A) Axial FLAIR B) Axial T2 WI and C) Coronal T2WI and D) Coronal T2WI Images show focal areas of mostly demyelination seen at the periventricular white matter regions |
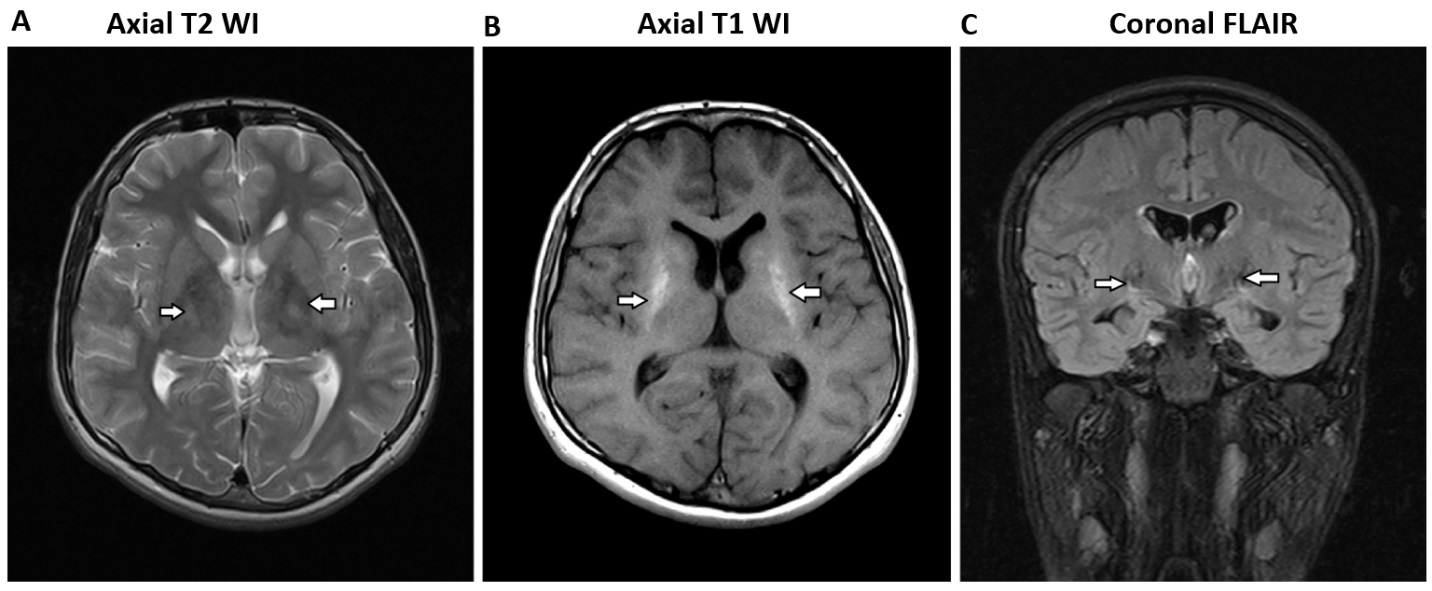 | Figure 6. A) Axial T2 WI, B) Axial T1 WI and C) Coronal FLAIR Images showed dense calcifications along both ganglionic regions, as was the bilateral cerebral hemispheres cortical regions |
6. Discussion
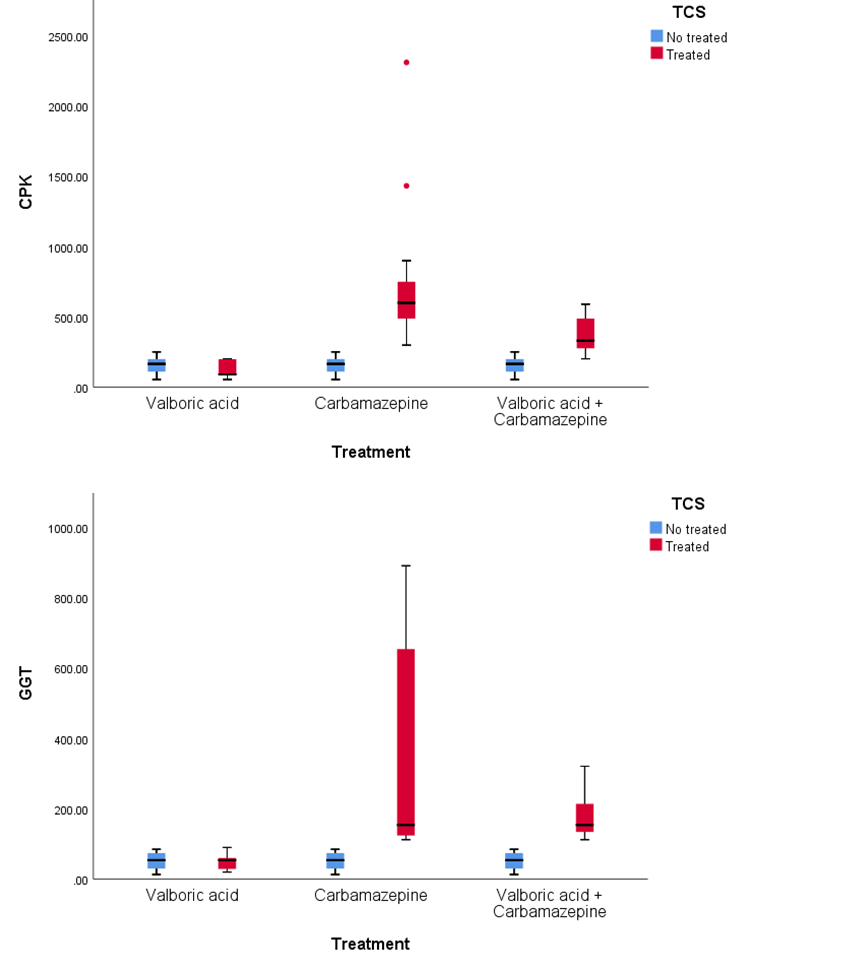
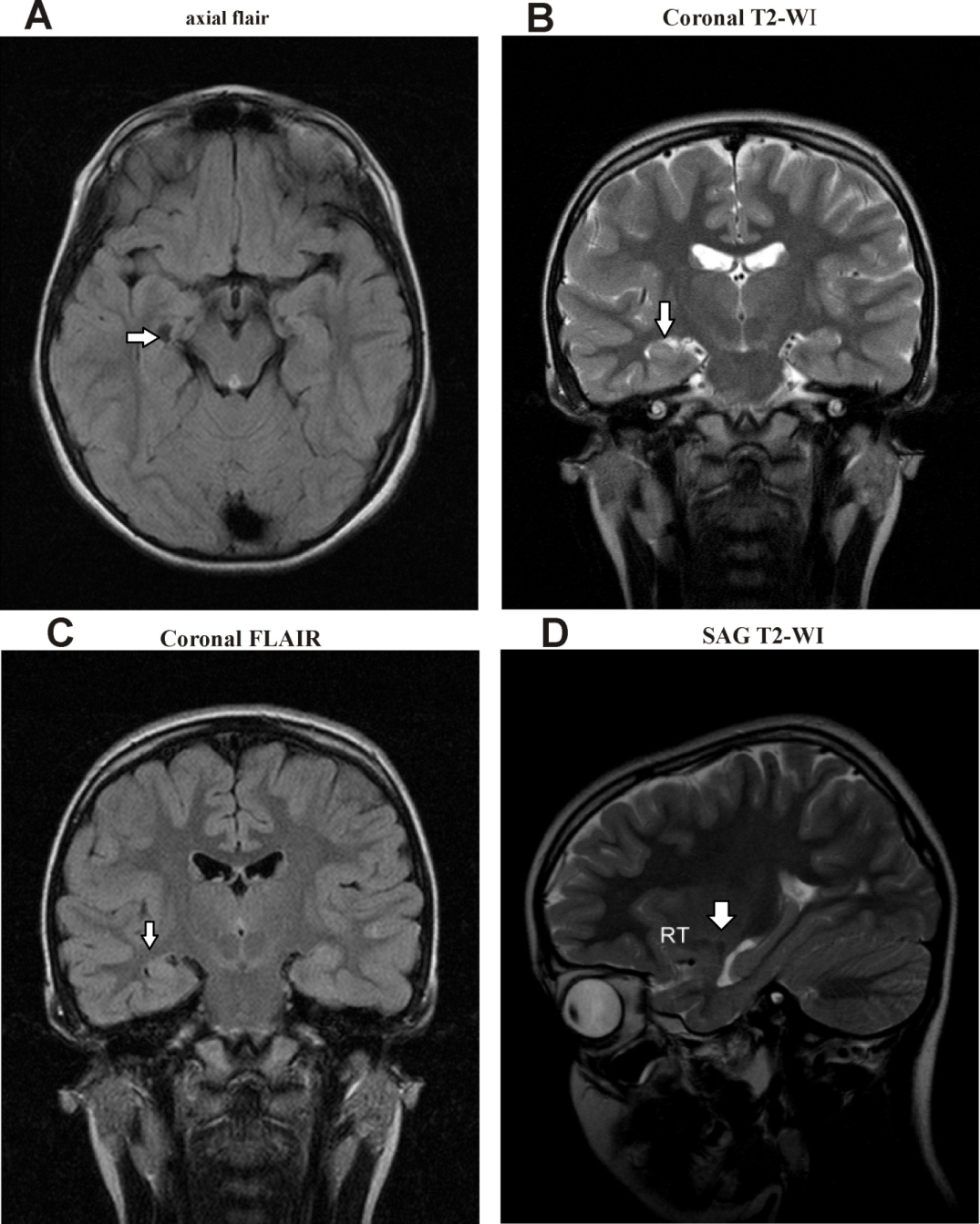
- Epilepsy is considered one of the neurological disorders that could be a consequence of diverse insults to the brain, including head trauma, stroke, vascular malformations, or congenital brain malformations [20]. Idiopathic epilepsies respond better to treatment than symptomatic epilepsies and should always begin with a single low initial therapeutic dose [21,22]. The present study data revealed that Carbamazepine is more active efficient in minimizing the rate of convulsions than valproic acid, and the combination therapy was more active than every separate medication. Magnet resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain also disclosed an essential diagnostic neuro-radiology tool that identified volumetric distribution amongst tonic-clonic seizure children with atrophy of the hippocampus and abnormality in temporary lobe epilepsy [23,24] reported MRI activities in a group of females with recurrent MDD in detecting the bilateral hippocampal atrophy.Sheline et al. [22] established a correlation between the magnitude of the decrease in hippocampal volumes and the duration of the depressive episode, and particularly with the untreated depression. Hitiris et al. [23] and Petrovski et al. [24] stated that the presence of bilateral hippocampal atrophy among epilepsy patients with depression might account for triggering worse seizure disorders and restraint to pharmacological, surgical therapy, or both.In the present study hippocampal sclerosis was diagnosed on the basis of MRI findings in 41% of children with convulsive tonic-clonic seizure using FLAIR and T2WI reported MRI features with increased signal intensity exposed hippocampal sclerosis including hippocampal atrophy with loss of internal architecture of the hippocampus on T2-weighted images, and loss of signal intensity on Ti-weighted images. Additionally, they characterized by identified mesial temporal sclerosis (MTS) as a volume reduction of the hippocampus and demyelination at the high parietal, white matter, and subcortical regions in T1-weighted images revealing the features of the epileptogenicity site [25-27]. Our results were consistent with Barkhof and Scheltens [28], who stated that T2-weighted fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) is considered one of the most useful contrast techniques for investigating the white matter diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS). Additionally, Simon et al. [29] explained that the brain imaging with T2-weighted FLAIR is used routinely to diagnose disease and to evaluate changes in lesion load due to its activity and high sensitivity to abnormalities and its excellent suppression of cerebrospinal fluid signal [30]. The current research has shown that carbamazepine is more active than Valproate in childhood against tonic-clonic seizure and sequential seizures. Seon et al. [31] described that, because of anticonvulsant activity in the liver, carbamazepine is anticonvulsant to enzymes producing CBZ 10,11 epoxide, CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP2C8, and anticonvulsant to the liver [32-34], due to the effect of cytochrome P 450 enzymes. Moreover, Valproate enhances the activity of histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition and the ability of cell growth and differentiation. Furthermore, Aldenkamp et al. [35] proved that Valproate (VPA) therapy has minor effects than other drugs that triggered its relevance to be the drug of choice for many epileptic children with minor neurologic adverse effects (sedation, ataxia, impairment of cognitive function) compared with other AEDs. Seon et al. [31] and Yılmaz et al. [36] showed that Carbamazepine and Valproate have different metabolisms through the smooth endoplasmic reticulum and endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria, respectively. On one side, our findings disagree with Davis et al. [37], who indicated that both generalized and partial convulsions had shown VPA to be efficient equal to that of carbamazepine monotherapies. On the other hand, our study has shown polytherapy's priority in the fight against seizure. Animals and in vitro studies have shown that GGT has several paradoxical effects on brain function and health. However, GGT induction may be performed as an oxidant protection adjustment [38,39]. GGT is possibly damaging as its extracellular activity can lead to free radicals production, lipid peroxidation, and mutagenesis that cause oxidative stress build-up in the body and brain [40-45].Preclinical studies may still provide valuable guidance for rational polytherapy in patients with epilepsy [46,47]. Studies involving pharmacological probes with well-defined selectivity towards specific neuronal targets may potentially offer a better understanding of synergistic mechanisms translating into better seizure protection. Moreover, our results can guide the development of therapeutics with a dual mechanism combined in one molecule [48].Carbamazepine activity may be due to its role in the sodium channel inhibition and decreasing neuronal firing in the SNR and enhancing the GABAergic neurotransmission [49]. Makarska-Bialek et al. [50] explained that Valproate and Carbamazepine polytherapy are the most clinically used antiepileptic drugs enhancing anticonvulsant effect and amelioration the episodic convulsions rate. Moreover, the neurological effect of VPA has been explained that it has the ability to inhibit GABA degradation and up-regulating their GABA levels and synthesis [51]. Also, Pugsley et al. [49] and Makarska-Bialek et al. [50] demonstrated the VPA inhibits NMDA receptors and induce the blockage of neuronal sodium channels [51,52].
7. Conclusions
- Based on the results, it can be concluded that the biochemical diagnosis CPK and GGT can be used as risk factors for epilepsy. Moreover, carbamazepine has more neuroprotective activity than Valproate in regulating mechanisms against convulsive behavior among epileptic children patients. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that MRI FLAIR and increased signal intensity on T2-weighted images can be used to detect the loss of internal architecture of the hippocampus and diagnosis of hippocampal sclerosis and atrophy which may be considered disease risk factors for convulsive tonic-clonic seizure. In our future research, we intend to concentrate on studying new therapeutic agents with various activity regimes of different polytherapy medications. These regimes will be intended to be directed against the recurrence of the convulsions and regulating the neural transmission of the hippocampus consistent with regulating the hippocampal activity action.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML