-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Clinical Medicine and Diagnostics
p-ISSN: 2163-1433 e-ISSN: 2163-1441
2015; 5(5): 81-89
doi:10.5923/j.cmd.20150505.01

Study of Serum Dickkopf-1, and Golgi Membrane Protein in Egyptian Patients with Colorectal Cancer
Wafaa M. El-Zefzafy1, Zakia Abu-Zahab2, Maisa A. Abdelwahab3, Lamyaa Ismail Ahmed4
1Department of Tropical Medicine, Faculty of Medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
2Department of Clinicalpathology, Faculty of Medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
3Department of Vascular Surgery, Faculty of Medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
4Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
Correspondence to: Wafaa M. El-Zefzafy, Department of Tropical Medicine, Faculty of Medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Background: Colorectal cancer is considered as a major cause of morbidity and mortality throughout the world. Colonoscopy is highly sensitive and specific for detection of lesions. It is likely that the combination of screening methods is more effective than the use of any methodalone. Serum Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) and Golgi membrane protein (GP73) has emerged as a promising biomarker for colorectal cancer diagnosis. However, their diagnostic accuracy is quite variableAimofthework: to study serum Dickkopf-1, and Golgi membrane protein in Egyptian patients with colorectal cancer as well as their correlation to CEA, CA 19-9 & other -biochemical parameters and determine the possibility to use them as a diagnostic tool for colorectal cancer.Patientsandmethods: This study included 30 patients divided into 2 groups: group I: comprised 15 patients with CRC, group II: comprised 15 patients with other colorectal disease together with 15 healthy control. The diagnosis was established on the basis of history, clinical, laboratory, endoscopic and histological data. CBC, ESR, liver, kidney function tests, CEA, CA 19-9, were also done. Results:There was highly significant increase in DKK1 in group I, II in comparison to control group with no significant difference between group I, group II and no significant difference in GP73 between the studied groups. There was highly significant decrease in Hg& increase in ESR level in GI in comparison to control group while no significant difference in WBCs was detected among the studied groups.In GI there were significant positive correlations between GP73 levels, Hg, RBCs, ESR while in GII a significant positive correlation between GP73 levels & CA19-9 and between DKK1& CEA was found. Conclusions: DKK1 is involved in the pathogenesis of colorectal diseases including colorectal cancer but the exact value of serum DKK1 & GP73 as a diagnostic tool for colorectal cancer requires additional investigation.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer, Golgi membrane protein (GP73), Dickkopf-1 (DKK1), Diagnostic biomarker
Cite this paper: Wafaa M. El-Zefzafy, Zakia Abu-Zahab, Maisa A. Abdelwahab, Lamyaa Ismail Ahmed, Study of Serum Dickkopf-1, and Golgi Membrane Protein in Egyptian Patients with Colorectal Cancer, Clinical Medicine and Diagnostics, Vol. 5 No. 5, 2015, pp. 81-89. doi: 10.5923/j.cmd.20150505.01.
1. Introduction
- Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains one of the most frequently diagnosed cancers worldwide and it is characterized by a low survival rate due to diagnosis in advanced stages, which leads to high mortality rates [1].Patients show a better prognosis when the neoplasm is diagnosed early. Among the variety of screening strategies, the methods range from invasive and costly procedures such as colonoscopy to more low-cost and non-invasive tests such as the fecal occult blood test [2].Unfortunately, most colorectal cancers are "silent" tumors. They grow slowly and often do not produce symptoms until they reach a large size. Fortunately, colorectal cancer is preventable, and curable, if detected early. After potential curative surgery, ~30% of the patients will eventually develop metastases, often in spite of adjuvant therapies, such as chemotherapy and radio-chemotherapy [3].The Dickkopf (DKK) family encodes secreted proteins, consisting of DKK-1, DKK-2, DKK-3, DKK-4, and a unique DKK-3-related gene, called Soggy. They contain two discrete cysteine-rich domains, in which the positions of 10 cysteine residues are supremely conserved among family members [4].The Dickkopf (DKK) protein is Highly expressed in thyroid, small intestine, stomach, liver, placenta, pancreas, uterus, abdominal cavity, bladder and skin. Weaker expression has been detected in colon and spleen. It is involved in embryonic development through its inhibition of the WNT signaling pathway [5].Dickkopf-1 is a 35kDa secreted protein involved in embryonic development; it plays a critical role in cell patterning, proliferation, and fate determination during embryogenesis as a potent inhibitor of the Wnt signaling pathway [6].Previous studies have shown that the expression of DKK-1 was down-regulated significantly in human colon cancer, gastric cancer , melanoma, hepatoblastoma and hepatocellular carcinoma, this means that the function of DKK-1 may differ depending on the cancer type , and its role as an antagonist of Wnt signaling is lost in these cancers [7].Golgi membrane protein 1 (GOLM1) also known as Golgi phosphoprotein 2 or Golgi membrane protein (GP73) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GOLM1gene [8] Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been described for this gene [9]. The Golgi complex plays a key role in the sorting and modification of proteins exported from the endoplasmic reticulum. The protein encoded by this gene (GOLM1gene) is a type II Golgi transmembrane protein. It processes protein synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and assists in the transport of protein cargo through the Golgi apparatus. The expression of this encoded protein has been observed to be up regulated in response to viral infection [10], prostate cancer [11], lung adenocarcinoma tissue [12] and liver cancer [13]. Abnormal glycosylation of cellular glycoconjugates is a common phenotypic change in many human tumors. An altered Golgi pH may be responsible for these cancer-associated glycosylation abnormalities [14].Aim of the work: to study serum Dickkopf-1, and Golgi membrane protein in Egyptian patients with colorectal cancer as well as their correlation to CEA, CA 19-9, other -biochemical parameters, and determine the possibility to use them as a diagnostic tool for colorectal cancer.
2. Subjects and Methods
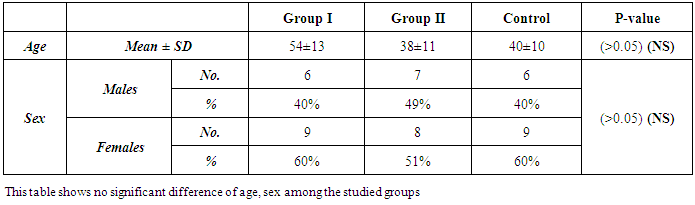
- This study was conducted on 30 patients admitted to the Tropical, Surgery and Internal Medicine Departments of Al-Zahraa University Hospital, Cairo Governorate; Egypt in the period from December 2014 to July 2015. The patients were 13(46.5%) males and 17 (56.5%) females. Their ages ranged from 25 to 75 years. The study also included 15 healthy subjects who were clinically, laboratory and ultrasonographically free served as a control group.The inclusion criteria include: adult patients with one or more of the following clinical picture: bleeding per rectum, diarrhea, constipation, alternating bowel habit, abdominal pain, flatulence, presence of mucous in the stool, weight loss, and or anorexia. The exclusion criteria include: Patients with local causes of bleeding per-rectum e.g. piles, fissure, patients with suspected toxic megacolon, colonic obstruction, colonic perforation, colectomy or proctocolectomy, known cases of other malignancy.Patients were divided into 2 groups:Group I (GI): comprised 15 patients with CRC, they were 6 males (40%) and 9 females (60%). Their ages ranged from 30 to 75 years with mean ± SD (54±13).Group II (GII): comprised 15 patients with other colorectal disease, they were 7 males (49%) and 8 females (51%). Their ages ranged from 25 - 69 years with mean ± SD (38±11).All patients were subjected to the following:I-Clinical part of the work:A: Detailed history: with special emphasis: Symptoms of lower GIT: diarrhea, constipation, alternating bowel habit, abdominal pain and its relation to bowel motions, bleeding per rectum, history of weight loss, anorexia, symptoms of anemia and family history (malignancy of the GIT or elsewhere in the body).B: Complete physical and PR examination: to examine the tone of the sphincter, any obvious lesions at the anus and lower rectum and if the endoscopic preparation has been adequate.II. Laboratory investigations: Blood samples were collected from the patients at the time of diagnosis, before any kind of treatment (surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy) as well as from the control group. Each blood sample was divided into three portions as follows:- First portion was collected into Na citrate-containing tube, and used for estimation of prothrombin time (PT) immediately on automated blood coagulation analyzer Sysmex CA1500 (Siemens AG, Erlangen, Germany) and for ESR estimation by Westergren´s method. - The second portion was collected into EDITA containing tube for CBC estimation using Coulter Counter T890 (Coulter LH 750 analyzer, Berlin, Germany).- The third portion was put in a plain tube, left to clot then centrifuged at 1600 rpm for 20minutes and serum was separated and used for estimation of: ● Liver and kidney function tests were done on Hitachi 911 auto-analyzer (Roche-Hitachi, Japan). ● CEA, CA 19-9 was determined on Immulite 1000 from SIEMENS (Germany).● Human Dickkopf 1 (DKK1), Human golgi membrane protein 73 (GP-73) were detected by ELISA immunoassay Kits from CUSABIO (Reader Aз 1851& Washer 909) from das (Italy), Catalogue number CSB-E10104h. for (DKK1), & CSB-E11332h for (GP-73) Briefly, standards, samples and controls were pipette into wells, pre-coated with specific Antibody and any DKK1 or GP-73 present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After removing any unbound substances, a biotin-conjugated specific antibody is added to the wells. After washing, avidin conjugated Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) is added to the wells. Following a wash to remove any unbound avidin-enzyme reagent, a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of DKK1, GP-73 bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped and the intensity of the color is measured (Read at 450nm wave length). The levels were calculated from standard curve corresponding to the measured optical density. A standard curve is prepared relating color intensity to the concentration. The results were expressed as pg/mL for (DKK1), IU/ml for (GP-73). ● Colonoscopy and colonic biopsy: Patient preparation: The procedure was explained carefully to the patients including risk associated with the procedure. Bowel preparation: The colon was well prepared before endoscopy. The standard bowel preparation with low residue diet, laxatives and enemas can accomplish this goal.The standard 2 days preparation: Two days prior to endoscopy: clear liquid diet and citrate of magnesia 240 ml PO. One day prior to endoscopy: clear liquid diet and citrate of magnesia 240 ml PO and saline enemas until clear in the morning. The day of endoscopy: NPO after midnight and saline enemas until clear, given two hours before the procedure.Medications: Propofol (1%):5-10 mg slowly intravenous antispasmodic: Hyoscin N-butylbromide (Buscopan) 20mg intravenous, it produces good colonic relaxation for at least 5-10 minutes. Three biopsies were taken from any abnormal mucosa and were sent for histopathology. The fiberoptic colonoscopy Pentax was used. - CT Abdomen and pelvic for patients in G1 Tumor stage was determined according to the TNM staging classification system.Statistical analysis: Data were collected, reviewed and fed to the computer where statistical analysis was done using the Statistic Package for Social Science Version 17 (SPSS 17.0) for windows. Comparing groups was done using Student's t-test. Study of the relationship between variables was done using correlation coefficient (Pearson correlation). The level of significance was taken at P-value of <0.05" and high significant at P-value of < 0.001.
3. Results
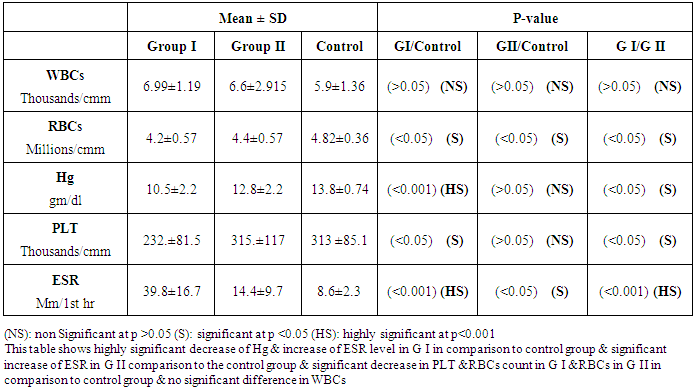
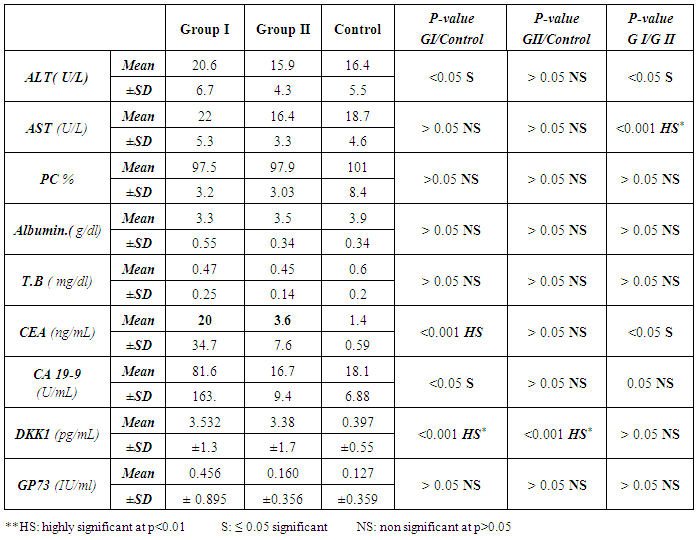
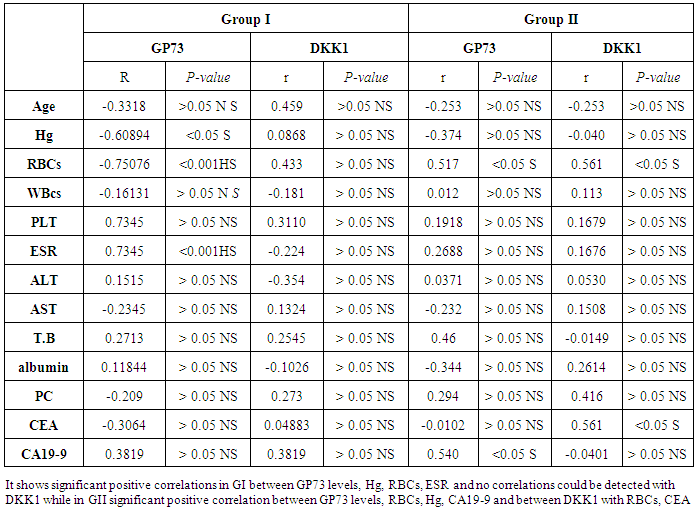
- The current study included 45 subjets (30 patients 13(46.5%) males & 17 (56.5%) females, their ages ranged from 25 to 75 years. and 15 healthy subjects as a control group. The results and data were collected and analyzed in tables 1-4 and figure 1-8.
|
|
|
|
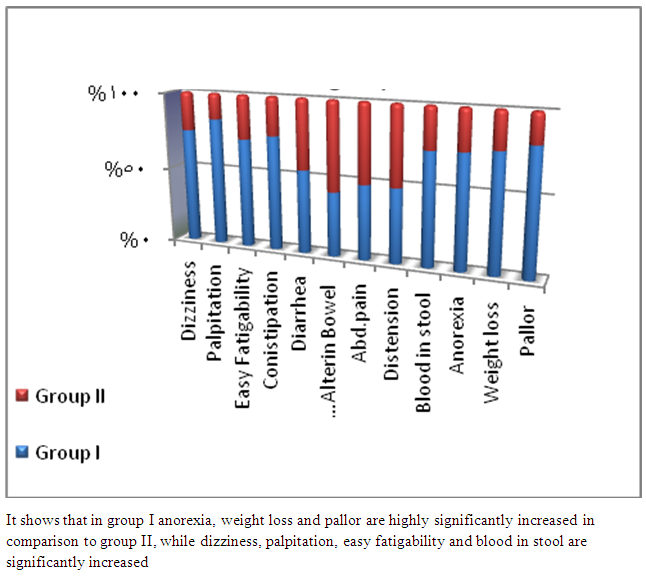 | Figure 1. Clinical manifestations in the studied groups |
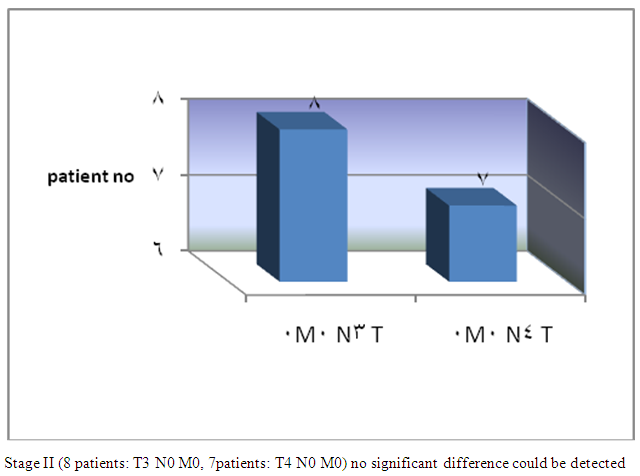 | Figure 2. Group I TNM staging |
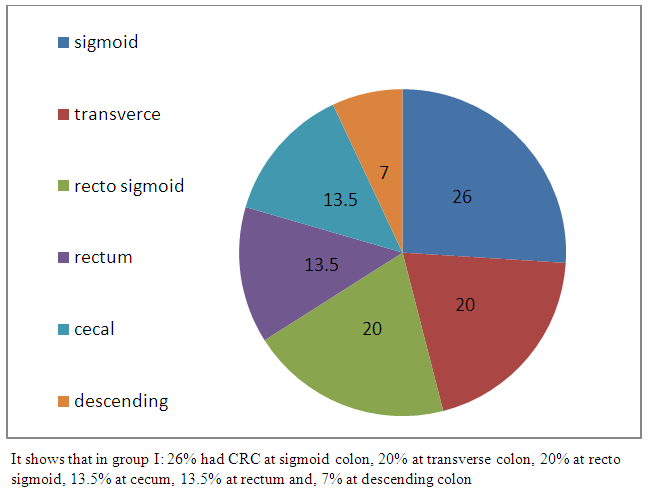 | Figure 3. Frequency and location of CRC in group I |
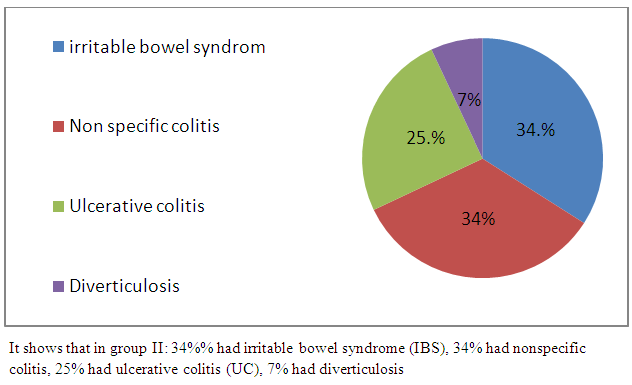 | Figure 4. Frequency of colorectal diseases in group II |
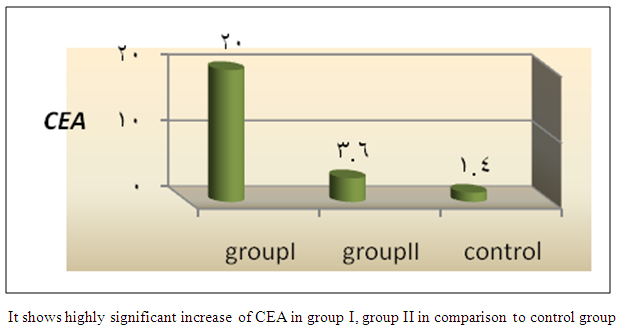 | Figure 5. Comparison of mean CEA among the studied groups |
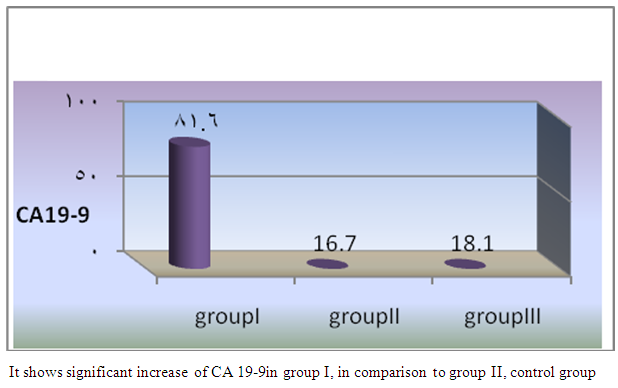 | Figure 6. Comparison of mean CA19-9 among the studied groups |
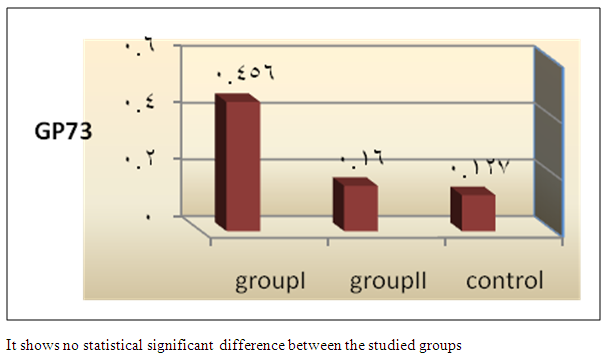 | Figure 7. Comparison of mean GP73 among the studied groups |
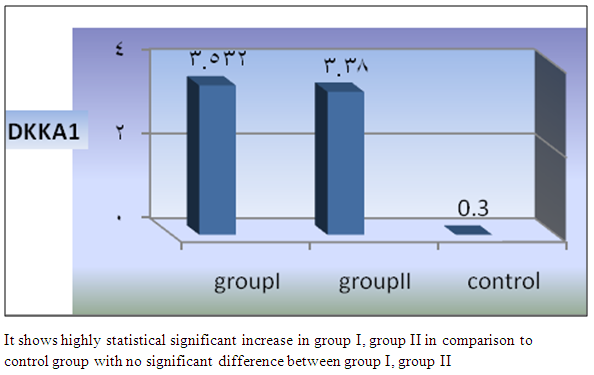 | Figure 8. Comparison of mean DKKA1 among the studied groups |
4. Discussion
- In Egypt, colorectal carcinoma is one of the most common malignant neoplasms, it is the fourth most common malignancy, representing 6.1% of cancers in Egypt [15].Colonoscopy is the gold standard for CRC diagnosis and multiple studies have provided indirect evidence regarding the higher benefits of colonoscopy compared with other methods. However, the costs and risk of complications, besides discomfort, have made this and other invasive tests such as flexible sigmoidoscopy, poorly accepted for population [16].The alternative is to develop a blood-based screening test based on biomarkers which poses minimal risk to patients, easy to perform, can be repeated at shorter intervals, identify the high risk population and can replace colonoscopy as a first-line screening tool, and therefore would likely lead to a much higher participation rate and therefore early detection and thereby reduce CRC incidence rate [17].Due to the heterogeneous nature of CRC, a single biomarker is unlikely to have sufficient sensitivity or specificity for use as a stand-alone diagnostic screening test and a panel of markers may be more effective [18] Serum Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) and Golgi membrane protein (GP73) has emerged as a promising biomarker for CRC diagnosis. However, their diagnostic accuracy is quite variable. The aim of our work was to study serum Dickkopf-1, and Golgi membrane protein in Egyptian patients with colorectal cancer and their correlation to CEA, CA 19-9 & other -biochemical parameters and determine the possibility to use them as a diagnostic tool for colorectal cancer. As regard the personal data of our patients, the mean age of CRC (GI) was 54±13 with no significant difference in age and sex, while Alteri et al., (2014) [19] noted that the median age at colon cancer diagnosis, 69 years in men and 73 years in women. Incidence of colorectal cancer is strongly related to age where 95% of CRC cases were diagnosed in those aged 50 and over [20].Concerning the clinical manifestations, anorexia and weight loss are highly significantly increased in group I in comparison to group II. This is in agreement with, Mantovani et al., [21] who mentioned that during cancer progression, it induces changes in the host immune system and energy metabolism that affect the clinical status of the patient so profoundly that it can result in death.Tong et al., (2014) [22] noted that rectal bleeding patients aged more than 60 years had a 0.12 probability of identifying colorectal cancer, nearly two-folds the possibility of all-age patients. Change in bowel habit, weight loss, anemia seem to be the most important symptoms. Other conventionally stated alarm symptoms, such as abdominal pain, have modest diagnostic value.Muñoz et al., (2014) [23] mentioned that anemia (manifested clinically by pallor, easy fatigability, dizziness and palpitation) is one of the most frequent extra intestinal manifestations of colorectal cancer. Regarding laboratory results in the present work, there were highly significant difference in RBCs and HB, between group I and II. This is in acceptance with Tan et al., (2002) [24] who reported that iron deficiency anemia was one of the predictive factors of colorectal cancer and small intestinal cancer.In our study, there was highly significant difference in ESR between group I and II. Our results are in agreement with, Baicus et al., (2012) [25] who mentioned that one of features to significantly predict CRC was a raised (ESR). In addition, ESR is associated with increased risk of CRC in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) [26]. In our study, there was significant difference in platelet count, this is in agreement with Bambace and Holmes, (2010) [27] who reported that, complex interactions between tumor cells and circulating platelets play an important role in cancer growth and dissemination, and a growing body of evidence supports a role for physiologic platelet receptors and platelet agonists in cancer metastases and angiogenesis. Thus, there is an association between platelet number and metastatic cancer potential. Lee et al., (2006) [28] demonstrated that an elevated WBC is associated with an increase in both the mortality and incidence rates of colon cancer. In contrast, in this study there is no significant difference in WBCs between the studied groups.There was highly significant increase of CEA in GI in comparison to control group, while there was significant increase of CA 19-9 in GI in comparison to GII, control group. Interestingly, both the European Group on Tumor Markers (EGMT) and American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) groups in their guidelines, recommend the measurement of CEA in CRC patients in stage II or III every 2–3 months or every 3 months during at least 3 years after diagnosis [29].Screening programs can reduce mortality from CRC, emerging evi-dence suggests that a non-invasive blood-based test with high sensitivity and specificity for the disease, in particular early stage disease, may be advantageous to overcome perceived barriers to participation associated with the use of FOBT While non-invasive, the FOBT is not specific for CRC and it is not able to accurately detect early stage disease. Furthermore, the value of this test is hampered by poor patient compliance variations in analytical procedures such as different methods of stool collection and handling, the need for multiple test samples, and variations in the interpretation of test results [30].The Wnt pathway plays an important role in development and in regulating adult stem cell systems, and aberrant activation of the Wnt signaling pathway is a major trait of many human cancers, including colorectal cancer [7]. Dkk1 has been reported to be induced by Wnt signals as a component of a negative feedback loop in normal tissues [31]. In colorectal cancer, the autoregulatory mechanism of Dkk1 might be lost or abolished by epigenetic inactivation, and Dkk1 restoration in DLD-1 colon cancer cells reduces colony formation and tumor growth suggesting that the Dkk1 gene plays a tumor suppressor function in colorectal cancer [32].DKK-1 binds to low density lipoprotein receptor related protein-5/6 and blocks interaction with Wnt-1, resulting in β-catenin degradation and effects on proliferation [33]. DKK-1 also can suppress cell growth and induces apoptotic cell death by activating the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway [34].Regarding analysis of serum DKK1 there was highly significant increase in its levels in GI, GII in comparison to control group, Previous reports indicate that epigenetic silencing of secreted Wnt inhibitors, including Dkk-1, is a common occurrence in inflammatory bowel disease [35] and colorectal cancer [31]. Methylation of the WNT signaling genes is an early event seen in patients with IBD colitis and there is a progressive increase in methylation of the WNT signaling genes during development of IBD-associated neoplasia [36].Gonzalez-Sancho et al., (2005) [31] mentioned that DKK1 is correlated with advanced stages of colorectal tumorigenesis and Dkk1 protein overexpression is inversely related to the presence of metastasis and recurrence of colon cancer. Aguilera et al., (2006) [32] added that over expressing DKK1 in colon cancer cells or Hela cells [36] reduces colony formation and tumor growth in xenografts, suggesting a tumor-suppressor function for DKK1. In contrast to these reports, Soydinc et al., (2011) [37] found that serum DKK1 did not display any diagnostic potential in colon or rectal cancers. Further more, Liang-liang (2014) [38] found that serum DKK-1 level expression levels were significantly positively correlated with TNM stage, lymph node involvement, and distant metastases, high DKK-1 expression was independently associated with poor survival suggesting that DKK-1 might be involved in the carcinogenesis and metastasis of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), also it was correlated with lymphatic metastasis and tumor diameter in cervical cancer and associated with the prognosis of patients with cervical cancer [39] and in our study we could not correlate it with TNM stage as the studied cases were at same stage but we found significant positive correlations between DKK1 with RBCs, and CEA in GII while in GI no correlations could be detected.Xiao-Ting et al., (2014) [40] in their meta-analysis, found that the range of sensitivity and specificity of DKK1 in colorectal cancer detection were 30%-88% and 49%-100%, respectively. The pooled SEN and SPE of serum DKK1 were 0.55 and 0.86, suggesting that the diagnostic accuracy of serum DKK1 is very limited and heterogeneous and serum DKK1 had reasonable accuracy in terms of differential diagnosis between “normal” and “cancer”. This is in agreement with our result where there was highly significant increase in its levels in GI (CRC) in comparison to healthy control group with no significant difference between GI, GII.Increased (GP73) serum levels have been previously suggested as a specific finding for HCC. High tissue levels of (GP73) in adenocarcinomas of various organs including prostate, breast, colon, and some subtypes of renal cell carcinomas is reported which might confound the specificity of (GP73) as a serum marker for HCC [42]. Ultrastructural studies revealed severe alterations in colonocytes of rats with ulcerative colitis (UC) with areas of necrosis, desquamated epithelial cells as well as loss of intercellular junctions, and lobulated nuclei with heterochromatin accumulated in the nuclear envelope. Reduced endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, vacuoles, and electrodense and dilated mitochondria were observed. Mucin was released to the cytoplasm due to hypertrophy of goblet cells [43].Analysis of Golgi architecture in vivo using tissue microarrays revealed Golgi fragmentation in UC and colorectal cancer tissue [44]. An inappropriate Golgi pH may indeed be responsible for the abnormal Golgi structure and lowered glycosylation potential of the Golgi apparatus in malignant cells [14].In our study no significant difference in GP73 between the studied groups was found, also Block et al.,(2005) [44] did not find elevated GP73 levels in sera of nine patients with colorectal cancer, using immunoblots ,while patients with HBV-induced HCC had a 30-fold increase in the level of GP73. Our results are in contrary to Ozal etal; (2011) [41] who reported that serum GP73 seems to be a useful tumor marker in patients with colon cancer in the subgroup of liver only metastases. The reason for this discrepancy may be originated from racial difference, tissue specificity of different cancer, variable disease stage and the heterogeneity of CRC.We did not find a correlation in GI between GP73 levels and CA19-9 nor CEA while in GII there were significant positive correlations between GP73 levels, and, CA19-9, in contrary to Ozal etal; (2011) [41] who found the performance of CEA is similar to GP73 at the cut-off level of 15 ng/mL. Still, more data is needed to clarify whether carcinomas other than HCC or bile duct carcinoma (BDC) actively shed GP73 into the serum.
5. Conclusions
- Results of our studies show that DKK-1 is increased in serum of CRC patients, it may be involved in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. We did not find elevated GP73 levels in sera of colorectal cancer patients. DKK1 & GP73 cannot be used as a novel markers for diagnosis of CRC but they can be used in combination with current screening modalities, such as FOBT, FIT, or the recently reported plasma mSEPT9 test or stool-based DNA markers to further improve their diagnostic performance. Colonoscopy in elderly patients with iron deficiency anemia is highly recommended. Comparative study between serum and tissue levels of (DKK1) and (GP73) in colorectal diseases including CRC over a large scale is highly recommended to figure out detailed mechanism and their role in inflammation and malignancy.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML