-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Clinical Medicine and Diagnostics
p-ISSN: 2163-1433 e-ISSN: 2163-1441
2015; 5(4): 70-79
doi:10.5923/j.cmd.20150504.03
Peri-Auricular Percutaneous Neurovascular Stimulation as a Non Narcotic Treatment Alternative for Acute and Chronic Pain
Christopher R. Brown DDS
Director of Medical Resources, Innovative Health Solutions
Correspondence to: Christopher R. Brown DDS , Director of Medical Resources, Innovative Health Solutions.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Peripheral Electrical Nerve Stimulation (PENS) has been proven to be an effective treatment for acute and chronic pain. Implementation of transillumination allows visualization of auricular neurovascular bundles enhancing the ability of the clinician to directly access branches of cranial nerves V,VII, IX, X, peripheral branches of the lesser and greater occipital nerves, as well as branches of the superficial temporal and the posterior auricular arteries. A recently FDA cleared device (Neurostim System/NSS) reduces sympathetic activity and increased parasympathetic activity by electrical stimulation via percutaneous implantation of needle arrays into the dermis of the peri-auricular region. The needle arrays are attached to an externally affixed generator placed behind the ear by a wire harness allowing physician applied ambulatory treatment of chronic and acute pain potentially reducing the need for central acting opioids.
Keywords: Neurovascular, Non narcotic, Percutaneous, Sympathetic, Para-Sympathetic
Cite this paper: Christopher R. Brown DDS , Peri-Auricular Percutaneous Neurovascular Stimulation as a Non Narcotic Treatment Alternative for Acute and Chronic Pain, Clinical Medicine and Diagnostics, Vol. 5 No. 4, 2015, pp. 70-79. doi: 10.5923/j.cmd.20150504.03.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
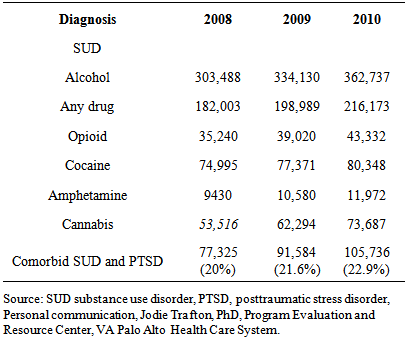
- Prescription pain medication abuse has taken on epidemic proportions. According to rehab-international.org it is estimated that two million people in the United States are addicted to hydrocodone alone and abuse has nearly quadrupled within the last ten years. The same source estimates that between 1994 to 2001 patients visiting the emergency room as a result of opiate analgesic abuse has increased by more than 115%. [1] These conditions are not just limited to chronic conditions. According to the latest Mayo Clinic study up to 25% of patients who were prescribed narcotics for acute post-surgical pain or musculoskeletal pain were still on narcotics one year after the initial prescription [2].Prescription opioid dependency is a growing problem in the armed forces veterans’ population as well as the general population. Substance abuse disorder (SUD) is not only an independent problem with Veterans but is also co-occurring with Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). It is estimated that more than 2 in 10 veterans with PTSD also have SUD. Concurrently almost one out of three Veterans seeking treatment for SUD also suffer from PTSD. [3]The number of patients seen in Veteran’s medical centers with various substance abuse has been increasing as measured from 2008-2010 (see table 1) [4].
|
2. Brain Anatomy
- Sympathetically maintained and or medicated pain (nociception) is processed in the brain by a complex feedback loop. The nociceptive stimuli via a cranial nerve/nerves entering the nucleus tractussolitarious. The impulses tracked into the hypothalamus, the thalamus, the hippocamous and circuits throughout the neuro-matrix interconnecting the synaptic impulses via the limbic system. The major parasympathetic connection is the vagal nerve (X) the stimulation of which alters signalsreducing sympathetic functions. This affects the hypothalamic-adrenal-thyroid- pituatary axis often negatively affecting homeostasis.The trigeminal nerve (V) progresses through the trigeminal nucleus into the medulla sending sympathetic signals into the gray matter of the spine altering afferent signals. The result of cranial nerve stimulation is the alteration of both efferent afferent signals.The alteration of these signals can assist in reducing pain and subsequently reverse the resulting neuro-plasticity returning the neuro-matrix to homeostasis. While traditionally this has been accomplished by medications there is growing evidence to support alternative, non chemical ways to address the issues of chronic pain and narcotic consumption.
3. Electro-Acupuncture
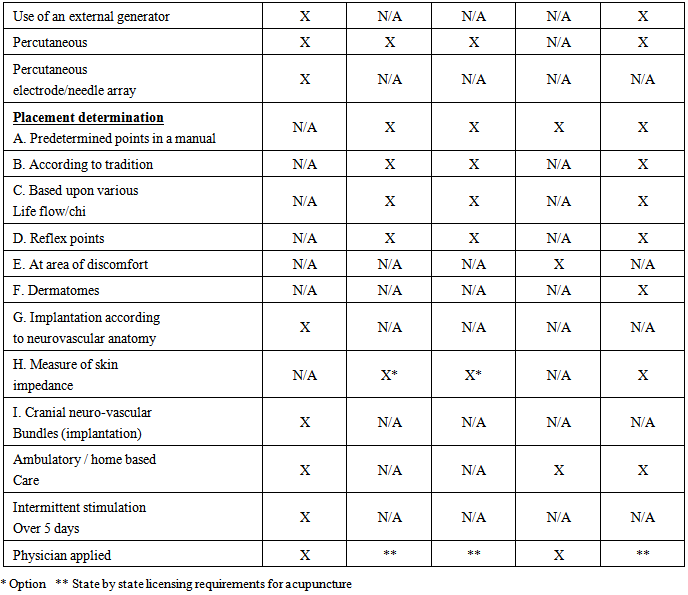
- The NIH 1997 consensus conference supports the use of electro-acupuncture for adult pos-operative and chemotherapy nausea, vomiting, and nausea for pregnancy, postoperative dental pain, menstrual cramps, tennis elbow, and addiction, stroke rehabilitation, carpel tunnel syndrome, headache, and fibromyalgia [11].The complete mechanisms of actions are not fully understood however evidence suggests that endogenous opioid peptides are released and produce analgesic affects [12] although no valid reproducible mechanism of action has been indicated.The theory and placement of acupuncture needles, heat, pressure, laser, and electrical, are based upon specific “points” (which vary according to which variation/ philosophy of acupuncture is referenced) altering chi (body energy flow), reflex points, and flow of heat/cold. The purpose is to correct imbalances through channels known as meridians.
4. TENS
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical- Neural Stimulation) is designed to deliver sufficient electrical stimulation via surface electrodes so that the current density produced by the electrical field is able to excite the afferent fibers in an adjacent nerve. [13] Surface electrodes are attached to the outer skin and conductivity is enhanced by using a conducting gel. Different skin and underlying tissues produce a non- homogeneous impedance resulting in an unpredictable application of the electrical charge. By definition TENS is transcutaneous rather than percutaneous or implanted. It is primarily used for musculoskeletal pain.
5. P-STIM
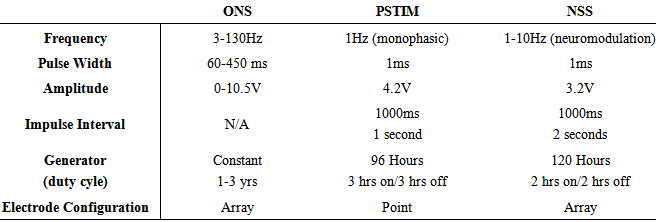
- The P-Stim is a physician or acupuncturist applied ambulatory electro-acupuncture device. The device consists of an externally affixed battery powered generator, and 3 wire leads attached to three needles. The needles are designed to be percutaneously applied and stimulate auricular acupuncture points. [14, 15] The acupuncture points are located by the use of the Multi-Point Stylus (Beigler, GmbH, Mauerbach, Austria). The Multi-Point Stylus locates acupuncture stimulation points in the auricle by “taking measurements of the skin’s impedance, which are converted into visual and acoustic signals.” (product package insert) The theory is there is a low impedance in the skin directly over an acupuncture point. This point location technique is common among various electro-acupuncture procedures using various designs of ohm meters. The generator is designed to run for 3 hrs on, 3 hrs off for a total of 96 hours. The device is disposable and for single use only.
6. PENS
- There is a clear delineation between percutaneous electrical neural stimulation and electro-acupuncture. [16]As opposed to acupuncture, the location of PENS needles is determined by neurological and vascular proximity within a sclerodermal, myodermal or dermatological distribution rather than theories of energy flowor reflex points. [17, 18] Percutaneous electrical neural stimulation therefore provides in-direct stimulation to the nerves [19] via a battery-operated pulse generator which delivers current that can be varied in form, intensity, frequency, and is differentiated by “the use of fine needles inserted through the skin to stimulate peripheral sensory nerves” [20] The PENS needles are always placed in the proximity of the pain for indirect stimulation.
7. Neuro Stim Systems (NSS)
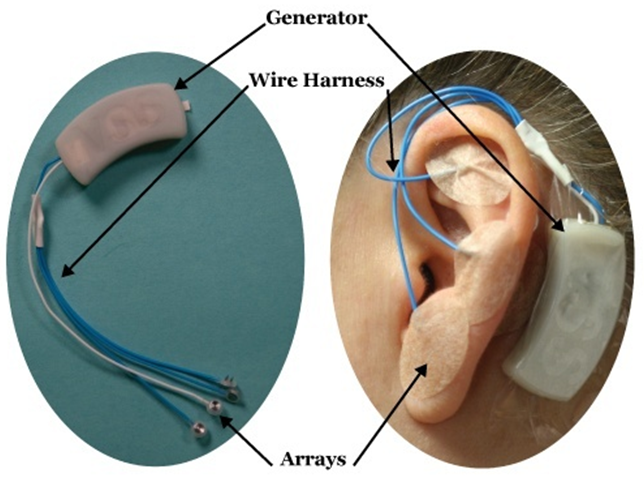
- The Neuro Stim System (NSS) is a physician applied, peripheral nerve stimulator which consists of a battery powered externally affixed generator, 4 wire leads attached to 3 electrode/ needle arrays and one single point needle. The arrays are designed to produce a field effect similar to surgically implanted peripheral neurostimulators. The electrode/needle arrays are implanted according to the individual’s arterial and cranial nerve anatomy. The exact location of the implantation is determined by both knowledge of auricular neuro- anatomy and visualization of the neurovascular bundles by a patented transillumination technique (Christopher R. Brown DDS, MPS). The electrode / needle array must be percutaneously implanted to within. 5-1mm of the neurovascular bundles to allow for proper energy transfer according to Coulomb’s and Ohm’s laws. The implantation locations are therefore determined by a properly trained physician based on neurovascular anatomy and will vary from person to person.Once the arrays are implanted the patient is observed for clinical signs which includes auricular vasodilation, warming of the tissue, lack of site implantation pain, bleeding, and symptom reduction similar to observation guidelines for surgically implanted peripheral neuro-stimulators. The generator is designed to turn on and off every two hours and have a total run time of 120 hrs. The NSS is a disposable, single use device. (see Table 2a, b, c for comparisons)
|
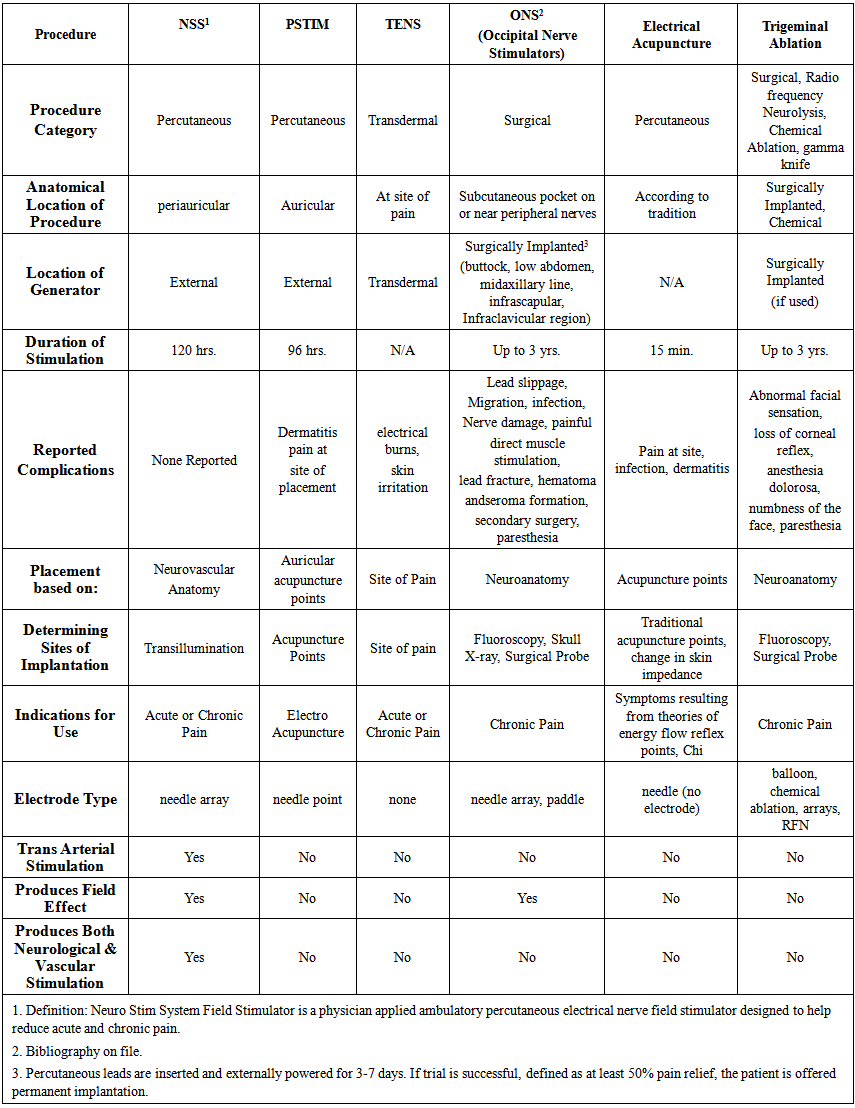 | Table2b. |
|
8. Clinical Application of the NSS Neurostimulator for the treatment of Acute and Chronic Pain
- The NSS peripheral nerve field stimulator is the only ambulatory, physician applied, minimally invasive application of neuromodulatingelectrical neural stimulation implanted into or near the neurovascular bundles of the external ear verified by transillumination. A generator located behind the affected ear, produces electrical stimulation impulses which are transferred via an electrode/ needle array to branches of cranial and/or occipital nerves and sympathetic fibers of the arterial branches (see photos).The NSS neurostimulator allows for continuous, intermittent (2 hrs on and 2 hrs off) neuromodulatingneurovascular stimulation for 120 hours while allowing the patient to remain ambulatory during the treatment of both acute and chronic pain. Percutaneous electrode implantation into the skin of the ear allows for direct access to branches of Cranial Nerves V, VII, IX, X as well as branches of the occipital nerves. [21] Direct access to the arterial branches of the head and neck are accessible [22] and reduction of sympathetic stimulation results in an increase of vascular flow rate, reduction of vascular resistance, and increase of perfusion [23, 24] The arterial branches of the superficial temporal artery (STA) and the posterior auricular artery (PAA) form a rich interconnecting complex network the terminal branches of which anastomose thoughout the ear. (Fig. 1)
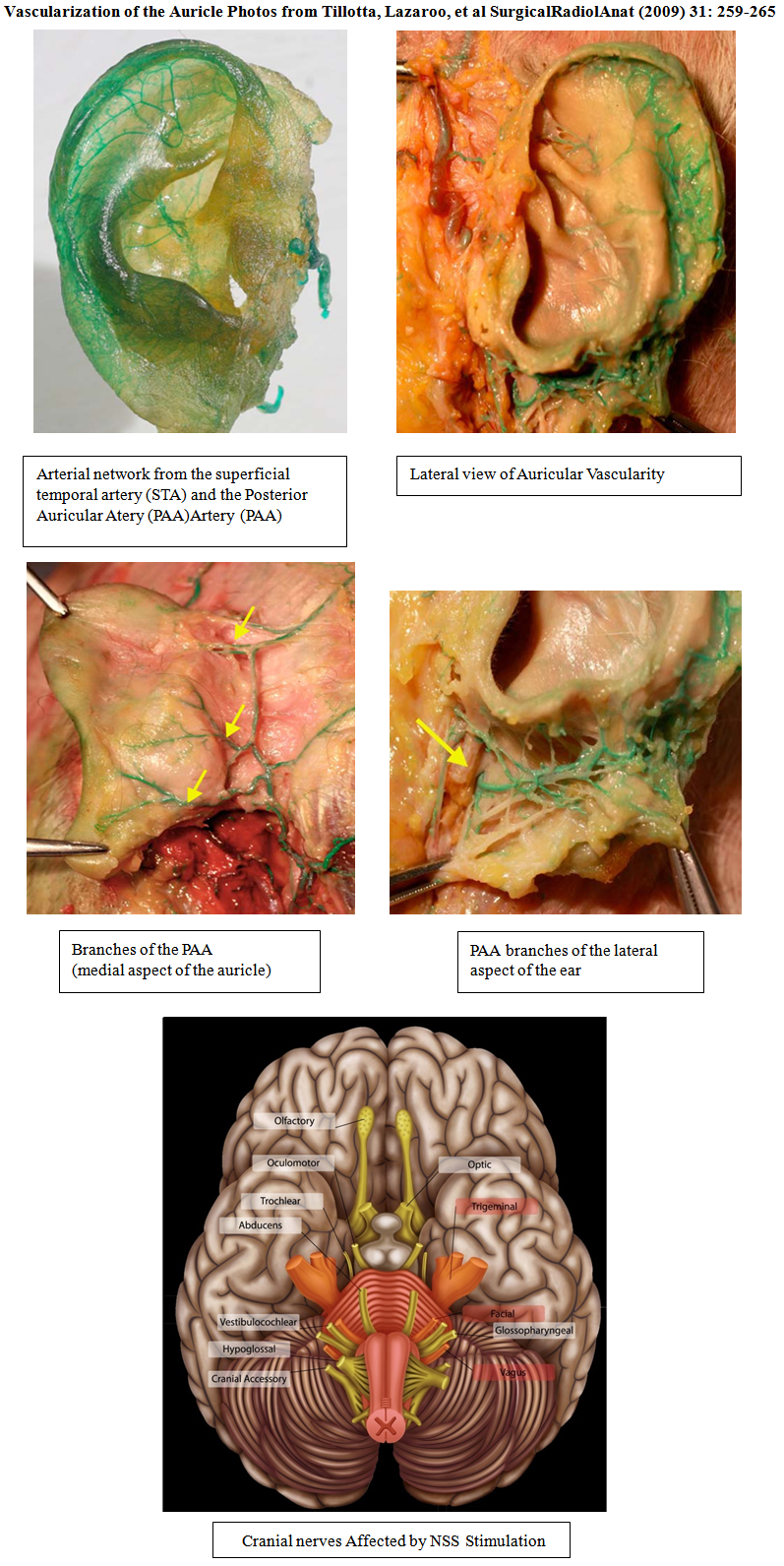 | Figure 1. |
 | Figure 2. |
9. Clinical Efficacy of the NSS
- The initial clinicaltrial of the NSS procedure (published in Clinical Medicine and Diagnostics) indicated a 65%decrease of reported VAS pain scores, reduction of opioid consumption, an increase in physical activities, and an improvement of sleep after peri-auricular percutaneous placement as indicated by neurovascular anatomy visualized by transillumination. Inclusion and exclusion criteria were established as well as reported previous treatments. [33] The reduction of pain, peripheral inflammation / ischemia, and an increase in vascular flow has also been indicted with NSS treatment co-joined with surgical debridement in Chronic Fibrosing Osteomyelitis (CFO). [34] Sympathetically maintained or mediated clinical conditions which respond well to NSS treatment are central sensitization syndrome, migraines, fibromyalgia, muscular pain, co-morbid nausea/vomiting, co-morbid anxiety/depression, chemically induced peripheral neuralgia (CIPN), and post-surgical sympathetic responses such as swelling/edema.The mechanism of induced analgesia is speculated to be as a result of neuro-modulation (inhibition of small C fibers) [35] and an increase of endogenous morphine - like substances within the central nervous system (CNS) [36] The NSS neurostimulator achieves a rapid onset of analgesia and is a safe, additive, non-addictive, non-pharmaceutical approach to pain management in a clinical setting.The auricular percutaneous neuromodulation of the neurovascular bundles may also alleviate other symptoms commonly associated with CSS (central sensitization syndrome) which involves “hyper-excitability” of the CNS resulting in headaches, body pain, confusion, sleep disturbances, and chronic fatigue [37]. Direct access into the spinal cord via the lesser and greater occipital nerves, cranial nerves, and sympathetic reduction along with endogenous endorphin production, may account for the reduction of these symptoms. Electro-analgesia is thought also to be mediated by three types of CNS opioid receptor sites: mu, sigma, and kappa [38] producing a more regionalized analgesia effect indicated by percutaneous neuromodulation stimulation of the auricular neurovascular bundles.The decrease in the use of oral analgesics including opioids has been noted as well with the NSS neurostimulator [39]. All symptom reduction and behavioral changes noted in the APS Bulletin and University of Birmingham review [40, 41] correlate well with those found with the NSS peripheral neurostimulator.Other percutaneous electrical neural stimulation methods stimulate in only 15, 30-45 minute applications applied twice per week over the course of several weeks. An increase in analgesia was noted by the longer duration of various applications. [42] All noted percutaneous electrical neural stimulation techniques are designed to follow dermatomes [43] while the NSSneurostimulatordirectly implants into the cranial nerves, neurovascular bundles, and the soft tissue surrounding them. Auricular neurovascular bundles/ arterial branches are initially visualized by transillumination utilizing an Auricular Transilluminator (IHS, Versailles, IN) via a specific clinical technique. Utilization of transillumination is essential to help verify the most optimal electrode implantation into the underlying neurovascular bundles. The positive results achieved by the stimulation is dependent on the precise placement of the electrode near the neurovascular bundles. The precise neurovascular application, electrode arrays, and clinical technique, including transillumination clearly separates the use of the NSS. Placing the patent pending electrode array directly into the neurovascular bundles is a technical advancement of previously published methodology, experimental approach, and rationale. The NSSneurostimulationsystem allows for direct, physician applied, ambulatory, continual treatment with outcome measured results. The treatment is ambulatory with the patient wearing the device affixed to the skin distally to the ear (as illustrated) for five days. If problems should arise the patients are instructed to call the treating clinician or can be removed themselves by taking a hot shower and getting the device wet. The patient is instructed to return the device to be disposed of in a sharp’s container.The use of electrical stimulationhas reduced the need for analgesic drugs such as NSAIDS, and central acting Opioids. [44] This may also help alleviate the dependencies, addictions, and other common complications found with opioid use such as immunosuppression, constipation, and hyperalgesia. [45-48] Electrical neural stimulation such as the NSSneurostimulator can be considered as an evidence based, non-pharmaceutical adjunct or replacement for opioid and non-opioid analgesics and should be considered asa viable non narcotic treatment option for chronic pain with sleep disturbance co-morbidity. [49]The APS bulletin (vol 9, Number 2, March/April 1999 White, MD PhD, Phillips, et al) compared findings from a group of publications [50] as well as did The University of Birmingham, Alabama. [51] and collectively noted positive results consistently with peripheral neural stimulation.
10. Summary
- The use of percutaneous electrical neural stimulation is a non-narcotic alternative to acute and chronic pain and is the only physician applied ambulatory, continuous, evidence based therapy which is designed to be directly implanted into auricular neuro-vascular bundles ascertained by neurovascular anatomy verified by auricular transillumination. Preliminary data indicates the use of the NSSneurostimulatoralso substantially reduces the need for analgesics including NSAID’s and central acting opioids potentially reducing the co-morbidities of unwanted significant side effects often associated with analgesic pain control. The use of percutaneous electrical neural stimulation has been shown as a viable alternative to escalating opioid and non-opioid dosages even in the management of cancer pain. [52-55]Periaucular percutaneous neurovascular stimulation is an easily applied, cost effective, safe, non pharmaceutical neurological based treatment alternative which has patient reported outcomes reducing ancillary health care costs associated with acute and chronic pain, improve sleep, and reduce opioid use. Because of the length of application of the NSSneuro-stimulator both actively (two hours) and duration (five days), a longer residual effect is often noted as a result of potential neuroplastic changes and endogenous endorphin production. The use of the NSSnerve field stimulator can be used primarily or as an adjunct with other means of treatment such as oral medications, injectables, surgical procedures, physical and manipulative therapy, exercise, and nutrition, will integrate well into the established medical model. Use in out- patient and hospital post-operative situations holds great promise for reduced healing time, pain control, and reduction of opioid consumption.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML