-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Clinical Medicine and Diagnostics
p-ISSN: 2163-1433 e-ISSN: 2163-1441
2015; 5(2): 17-21
doi:10.5923/j.cmd.20150502.01
Decrease in VAS Score Following Placement of a Percutaneous Peri-Auricular Peripheral Nerve Field Stimulator
Arthur Roberts 1, 2, Chris Brown 3
1Department of Oral Pathology, Medicine and Radiology, Indiana University School of Dentistry, Indianapolis, United States
2Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care, and Pain Medicine, University of Edinburgh, College of Medicine and Veterinary Medicine, Edinburgh, UK
3Private practice, 823 S Adams St, Versailles, IN
Correspondence to: Arthur Roberts , Department of Oral Pathology, Medicine and Radiology, Indiana University School of Dentistry, Indianapolis, United States.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
A cohort of 20 chronic pain patients in three separate clinics underwent a series of four one-week peri-auricular percutaneous nerve field stimulation (PENFS) treatments. A 65% improvement in VAS score was observed.
Keywords: Chronic pain, Percutaneous peripheral nerve fields stimulator
Cite this paper: Arthur Roberts , Chris Brown , Decrease in VAS Score Following Placement of a Percutaneous Peri-Auricular Peripheral Nerve Field Stimulator, Clinical Medicine and Diagnostics, Vol. 5 No. 2, 2015, pp. 17-21. doi: 10.5923/j.cmd.20150502.01.
Article Outline
- A cohort of 20 chronic pain patients in three separate clinics underwent a series of four one-week peri-auricular percutaneous nerve field stimulation (PENFS) treatments. A 65% improvement in VAS score was observed.
1. Methods and Materials
- During June, July and August 2014, in three separate Midwest centers, a cohort of 20 patients experiencing unremitting multiyear chronic pain underwent a series of four one-week for peri-auricular percutaneous peripheral nerve field stimulation (PENFS) treatments. Subject patients were selected sequentially.
2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- a. Inclusion Criteria-l Have consistent, daily pain (greater than 4 on the VAS for 30 days in a row) l The skin of the ear at the site of the Neuro-Stim System implantation must be intact and free of infectionl The participant must have vital signs (HR/breathing/ blood pressure) within stable acceptable medical limitsl Does not have any type of on - demand implantable electric devicesl Does not have a history of seizures l Is not pregnant (will be evaluated by asking verbally)l Is willing to participate and understand/sign the patient consentb. Exclusion Criteria-l Has intermittent, non daily painl Does not have at least one external earl The skin of the external ear is not intact or is infected.l Have inconsistent vital signs (fluctuating, extremely low blood pressure, tachycardia, etc)l Wear any type of implanted electrical device such as a brain shunt, vagal stimulator, pace maker, spinal pain pump, etc.l Has a history of seizuresl Is pregnantl Is unwilling to voluntarily participatel Hemophilial Psoriasis vulgarisThe devices used for the percutaneous peripheral nerve field stimulation were Neuro-Stim System (NSS ©) manufactured by Key Electronics, Jeffersonville, IN. (Figure 1)
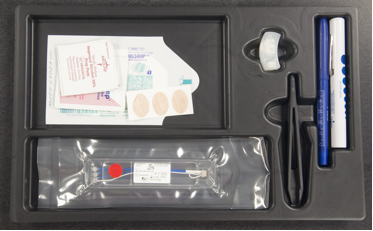 | Figure 1. NSS as received from manufacturer |
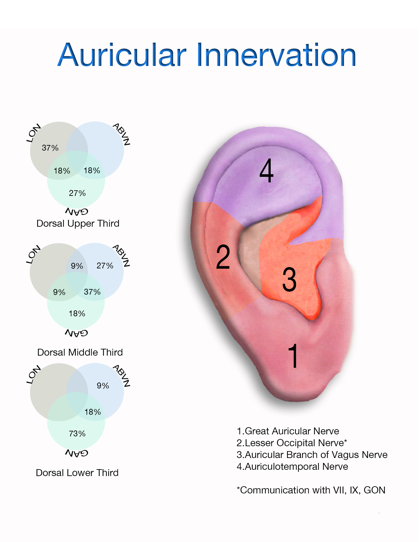 | Figure 2. Cranial nerve distribution in ear |
3. Procedure
- Vital signs were recorded, and pre-treatment pain levels were self-reported by the patient and recorded using the VAS pain scale.Patients were placed in a supine position, and observing sterile technique the peri-auricular area was cleansed with a 70% solution of isopropyl alcohol, and evaluated by IHS’s (Innovative Health Solutions) patent pending technique of trans-illumination to visualize and isolate the neuro-vascular bundles associated with the terminal afferent branches of the targeted cranial neurovasccular bundles nerves. The targeted areas were marked with a provided surgical pen on the ventral and dorsal.Steri-Strip© liquid adhesive was placed over the marked areas [1] The percutaneous electrodes were then implanted within one mm of the previously identified neuro-vascular bundles and secured with the provided oval bandages. The electrode harness was inserted into the solid-state integrated circuit generator. The generator with connected harness was attached behind the ear with the attached double-sided surgical tape by removing the tape backing and pressing firmly onto the skin for 15 seconds. (Figure 3)
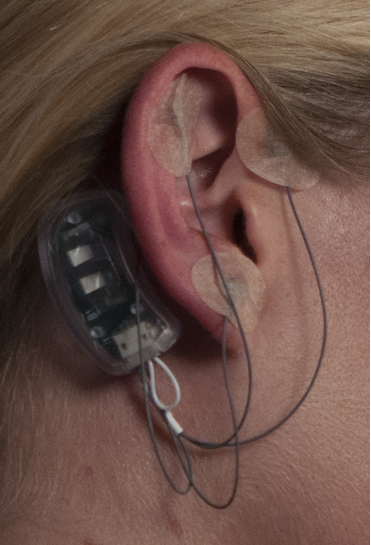 | Figure 3. NSS in place on patient |
4. Report of Findings
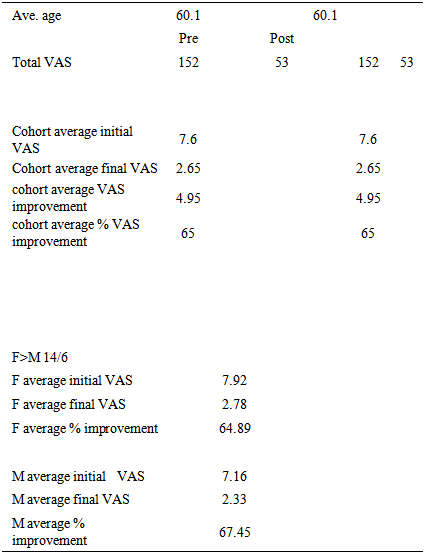
- Description of cohort:l n = 20l M = 6l F = 14l Average age 60.1l Age range 29-81l Average starting VAS 7.36l Average ending VAS 2.65l Average improvement in VAS: 4.71l Average percentage improvement in VAS: 65%
5. Adverse Reactions
- Potential overall risks/ discomforts involved are very minimal – Rare (event rate 1% - < 5%).The risks/discomforts may involve:l Discomfort upon insertion of the electrodes for < 5 minutes - Rare (event rate 1% - < 5%)l Discomfort at the lead placement site > 5 minutes – none observedl Bleeding at the electrode site if the neurovascular bundle is penetrated - Rare (none observed)l Localized discomfort if the electrodes should become dislodged during the wearing of the device - Rare (none observed)l Localized dermatitis - Rare (none observed)l Drop in blood pressure - Rare (event rate 1% - < 5%)l Syncope (fainting) - Rare (none observed)Potential adverse effects to supporting personnelSkin piercing with percutaneous needles - Rare (none observed)
|
6. Discussion
- Woolf, Wallace, Clauw, Melzack, and many others have repeatedly demonstrated the association of chronic pain conditions with central sensitization, autonomic dysfunction, disturbances in serotonin function, decreases in endogenous opioid production, and persistent inflammation of microglia. In addition, neuropsychiatric dysfunction is a common comorbid presentation in these patients. In this complex and integrated milieu, we are left to evaluate subjective pain and function levels as a measure of our outcomes. Recognizing full well the significant impact of the factors above, and multiple others, upon the neuromatrix we have set out to measure changes in VAS scores subsequent to the placement of a series of percutaneous peripheral nerve field stimulators. [2-22]The clinical application and efficacy of percutaneous electrical neural stimulation has been accepted throughout the physician community [23], has been verified for use in many acute and chronic pain conditions [24] and also been reported as an analgesic complementary therapy for the management of pain secondary to bony metastasis [25].This procedure distinguished from manual acupuncture [21], electrical acupuncture and/ or TENS [26, 27] although the physiological results may be similar [28].As opposed to acupuncture, the location of PENS needles is determined by neurological and vascular proximity rather than theories of energy flow or reflex points. [26, 29] Percutaneous electrical neural stimulation therefore provides in-direct stimulation to the nerves [30] via a battery-operated pulse generator which delivers current that can be varied in form, intensity, frequency, and is differentiated by “ the use of fine needles inserted through the skin to stimulate peripheral sensory nerves” [31].The reduction in symptoms of such systemic disorders such as fibromyalgia, knee pain, lower back pain, inflammation, edema/ ischemia are thought to be from the effect on the mid brain, endorphin production, and stimulation of spinal and peripheral inhibitory pain mechanisms via direct neurovascular stimulation and reduction of sympathetic fibers in the arterial walls. The NSS neurostimulation system allows for direct, physician applied, ambulatory, continual treatment.The use of electrical stimulation has been indicated for reducing the need for analgesic drugs such as NSAIDS, and central acting Opioids [32]. This may also help alleviate the dependencies, addictions, and other common complications found with opioid use such as immunosupression, constipation, and hyperalgesia. [30, 33-35]Reduction of pain and the reduced use of opioids may reduce the length of post operative hospital stays and therefore should be explored for reducing the chance of HAI’s ( hospital acquired infections ) [30, 36].Phillips, et al compared findings from a group of publications as did The University of Birmingham, Alabama and noted the following results with peripheral electrical neural stimulation [27, 37]:1. A reduction in VAS and other pain scores compared to sham needle placement and placebo in tension, migraine, and post traumatic headache [38]2. Decrease in frequency of Sciatica pain [39]3. Decrease post herpetic and diabetic neuralgia [40]3. A decrease in the use of oral analgesics (both opioid and non opioid)4. An increase in physical activity5. Improvement quality of sleep. [41, 42]The NSS is the first device specifically designed to provide ambulatory, percutaneous neuromodulating nerve field stimulation in the peri-auricular area utilizing the technique and concept of visualizing and targeting auricular neurovascular bundles. The 120 hr treatment (in two hour cycles) helps provide neurovascular stimulation over a much extended time compared to other PENFS techniques.All participants of the study reported use of prescribed central acting opioids (CAO) throughout their course of treatment and none reported satisfactory resolution of their pain. Long term efficacy of CAO in the control of chronic non- cancer pain is questionable and should be approached cautiously by both user and prescribers. FDA REMs guidelines have been established for evaluating the use of extended release and long acting opioids often used for the treatment of chronic pain. [43]The patient population for this clinical report of findings was not controlled for any specific pain entity but rather was included into the study based upon the inclusion and exclusion criteria as outlined specifically daily, consistent pain. This population is very broad in scope and therefore does not further define efficacy of the NSS for a specific use. Since the EAD generator itself is FDA cleared for a targeted population of acute and chronic pain the clinical evidence in this ROF is therefore supportive of the FDA clearance. Of further significance was the lack of any unacceptable clinical complications such as dermatitis, infections, bleeding at the site of implantation, drop in blood pressure, or syncope. None were reported at any of the three clinical sites. There was also no reports of injury (skin piercing) or otherwise of any of the participating clinicians. This presents a strong indication of clinical safety. The FDA clearance for the device has been placed in the “minimal risk” category and is further substantiated by this clinical report of findings.
7. Conclusions
- Initial clinical report of findings at three independent sites indicate the use of Neuro-Stim System (NSS) peri-auricular percutaneous electrical nerve field stimulation - PENFS) appears to be an effective, minimal-risk, non-narcotic alternative for reducing chronic pain. While further double blind and long-term studies are needed the initial findings indicate a significant reduction in patient reported pain. Because of the efficacy and minimal risk, the Neuro-Stim System (peri-auricular PENFS) should considered the by clinicians as a non-narcotic adjunct for chronic pain control.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML