-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
Clinical Medicine and Diagnostics
p-ISSN: 2163-1433 e-ISSN: 2163-1441
2014; 4(6): 113-117
doi:10.5923/j.cmd.20140406.02
Innate Immunity Tests and CD69 in Septicemia of Infants
Nuha Hamdi1, 2, Fadel Al-Hababi2, Eatedal Ghareeb3
1Immunology and Clinical Pathology Department, Faculty of medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt
2Regional Labs, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
3Pediatric Oncology/Hematology Fellowship, King Saud medical City, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Correspondence to: Nuha Hamdi, Immunology and Clinical Pathology Department, Faculty of medicine (for girls), Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Introduction:Sepsis is systemic inflammatory syndromes triggered by viral or bacterial infections. Clinicians have long sought reliable markers to detect sepsis early in its course and to exclude diseases of non infectious origin. The role of the phagocytic function of monocyte, neutrophils, and T-lymphocyte cells in sepsis has been poorly investigated. Materials and Methods:The present study has been evaluate the activity of neutrophils, monocytes by phago and phagoburst tests and the activity of lymphocyte cells by CD69 on CD4, CD8 cells of patients with septicemia by flow-cytometry. Thirty five patients and twenty healthy individuals were enrolled in the study. Results:Our results were showing high significant difference of Phago test, PhagoBurst test of neutrophils, also CD69-CD4 and CD69-CD8 tests on T-cells. Conclusion:Our results need further researches to use these markers as early diagnostic and prognostic markers.
Keywords: CD69, Phago, Burst, Septicemia
Cite this paper: Nuha Hamdi, Fadel Al-Hababi, Eatedal Ghareeb, Innate Immunity Tests and CD69 in Septicemia of Infants, Clinical Medicine and Diagnostics, Vol. 4 No. 6, 2014, pp. 113-117. doi: 10.5923/j.cmd.20140406.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Sepsis remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in children despite improved understanding of the path physiology leading to better clinical management and survival [1]. Diagnosis of neonatal sepsis remains a major challenge as early signs of sepsis are often non-specific and the laboratory criteria are also not fully reliable [2]. The incidence of early- onset sepsis full term neonates is 0.1% while in premature ones is as high as 0.4 % [3]. The increased susceptibility of neonates to bacterial infections has been attributed to immaturity of innate immunity.The phagocyte system is an essential component of innate immunity [4]. Macrophages, monocytes and neutrophils have the ability to phagocyte bacteria and insert it in a cellular compartment (phagosome) which role as a cytotoxic agent [5]. These cells use bactericidal pathways that depend or in depend on oxygen as a weapon to eliminate infectious agents.The mechanism oxygen-independent involves chemo taxis, phagocytosis, degranulations and the release of lyses enzyme and bactericidal peptides [6], through the degranulation process occurred sections of several chemical compounds, especially MPO (myeloperoxidase) and LTF (lactoferrin), azurophilic granules and specific granules are released [7].Recently, flow-cytometric analysis of phago, phagoburst and antigens (CD11b, CD64, CD32, CD16, CD69, CD25 and CD45) has been performed to detect and follow up neonatal sepsis [8]. CD69, a protein expressed early on the surface of stimulated T cells, is used as a marker of activation and correlates with antigen specific proliferative response of lymphocytes [9, 10].The purpose of this study was to investigate the phago, phagoburst and CD69 T-cell activity as markers of neonatal septicemia.
2. Materials and Methods
- This study was conducted at Immunology department in Riyadh Regional lab in collaboration with neonatal intensive care unit at King Saud medical city.Subjects were classified into two groups:Group 1: included 35 patients (17 females and 18 male) in the first year of life admitted to hospital screened for septicemia in the first week of admission by sepsis score [11] and hematological sepsis scoring system and interpreted as suspected cases of sepsis (total score 7, score ≥ 3 is suggestive of sepsis) [12]. With exclusion criteria: infants with severe congenital abnormality, severe asphyxia and baby with severe low birth weight. Group 2: included 20 apparently healthy controls, matched by age and sex with the patients.Full clinical examination for symptoms and signs of sepsis. Laboratory investigations included complete blood picture, C-reactive protein and blood culture.Analysis was done for phago test, phagoburst test and CD69/CD4, CD69/CD8 fast immune test by FACSCanto™II flow-cytometry. Whole blood, collected in a vacutainer blood collection tube containing sodium heparin.Phagotest™ allows the quantitative determination of leukocyte phagocytosis (ingestion of bacteria). It measures the percentage of phagocytes which have ingested bacteria and their activity (number of bacteria per cell). The phagocytosis test kit contains fluorescein-labelled opsonized Escherichia coli bacteria and other necessary reagents. BD Biosciences (Cat.NO.341060). Heparinized whole blood is incubated with reagent B (FITC-labeled E.coli bacteria) at 37˚C, a negative control sample remains on ice. The phagocytosis is stopped by placing the samples on ice and adding reagent C (quenching solution). This solution allows the discrimination between attachment and internalization of bacteria by quenching the FITC fluorescence of surface bound bacteria leaving the fluorescence of internalized particles unaltered. After two washing steps with reagent A (wash solution) erythrocytes are then removed by addition of reagent D (lysing solution). The DNA staining solution (Reagent E), which is added just prior flow cytometric analysis, excludes aggregation artifacts of bacteria or cells.PhagoBurst test allows the quantitative determination of leukocyte oxidative burst. The Burst test kit contain unlabeled opsinized E. coli bacteria as particulate stimulus, the protein kinase C ligand phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) as high stimulus and the chemotactic peptide N-formyl-MetLeuPhe (fMLP) as low physiological stimulus, dihydrorhodamine(DHR) 123 as a fluorogenic substrate and necessary reagents. BD Biosciences (Cat.NO.341058) hepariniezed whole blood is incubated with the various stimuli at 37˚C, a sample without stimulus serves as negative background control. Upon stimulation, granulocytes and monocytes produce reactive oxygen metabolites (superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide, hypochlorous acid) which destroy bacteria inside the phagosome. Formation of the reactive oxidants during the oxidative burst can be monitored by the addition and oxidation of DHR 123. The reaction is stopped by addition of lysing solution, which removes erythrocytes and results in a partial fixation of leukocyte. After one washing step with washing solution, DNA staining solution is added to exclude aggregation artifacts of bacteria or cells. The percentage of cells having produced reactive oxygen radicals are then analyzed as well as their mean fluorescence intensity (enzymatic activity). CD69 fast immune assay: Lymphocyte response is measured after only 4 hour incubation with the stimulus in a three-color lyses/no wash flow-cytometric assay. BD Biosciences [Cat. NO.340365, for CD4FITC/CD69PE/ CD3PerCP, Cat.NO.340367 for CD8FITC/CD69PE/ CD3PerCP].
3. Results and Discussion
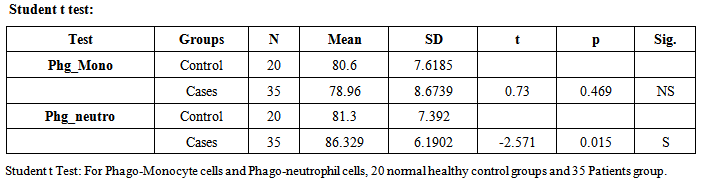
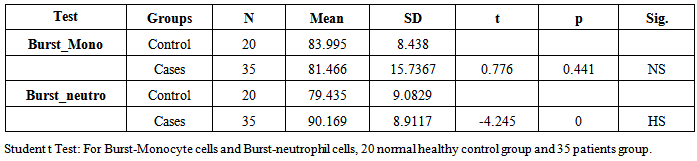
- The term sepsis implies the presence of infection with sign of systemic body response (tachycardia, tachypnea, fever, etc.) and condition of severe sepsis and septic shock, further disturbance in organ perfusion (impaired consciousness, hypoxia, oliguria) require fluid administration and inotropic and / or vasopressor drug, respectively [13].Sepsis is an enormously complex clinical syndrome that arises from the activation of an innate host response to danger. Sepsis is associated with infections of bacteria, viruses, fungi and endotoxins, whether or not being evidence by culture. The above systematic inflammatory response in humans occurs not only in sepsis but also in other non-infectious conditions such as pancreatitis, ischemia, server trauma, etc.).Early diagnosis increases the possibility of starting a specific therapy in time [14, 15].Infections by a variety of pathogens are a significant cause of morbidity and mortality during neonated and childhood. The susceptibility of neonates to bacterial infections has been attributed to immaturity of innate immunity. It is considered that one of the impaired mechanisms is the phagocytic function of neutrophils and monocytes [16]. Phagocytosisis the important factor that plays a role in acute inflammatory response due to its ability to destroy various pathogens efficiently [17]. A number of factors contribute to the efficient function of phagocytic system. These factors include the presence of adequate numbers of monocytes and neutrophils in peripheral blood, the ability to respond to signals from sites of inflammation, the migration to these sites and the capacity to ingest and kill the invaded micro-organisms [4, 5]. Neutrophils are considered to participate in the acute response against pathogens in many tissues [18].Neonatal sepsis is showing a very significant increase in phagocytosis activity due to qualitative and quantitative neutrophils changes as told by Ari Yunanto2013, and This result is agree with our result, 35 patients group show neutrophil phagocytosis mean±SD (86.329%±6.1902) and 20 health control group mean±SD (81.3%±7.392) p-value 0.015. But there is no significant change in monocyte phagocytosis (Table 1).
|
|
|
|
|
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
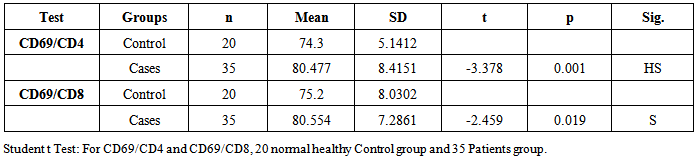
- Our study has demonstrated high significance of phagocyte and phago-burst tests activity of neutrophil cells, as innate immunity, and CD69 as T-cell marker activity in the first week of neonatal septicemia. And they may help in diagnosis and follow up of patients. Further research is needed to use these markers as early diagnostic onset markers of neonatal sepsis and as prognostic markers.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- The authors would like to thank Laboratory Specialist\ Latifa Bin Hubaish for her help.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML