-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Composite Materials
p-ISSN: 2166-479X e-ISSN: 2166-4919
2016; 6(4): 89-94
doi:10.5923/j.cmaterials.20160604.01

Preparation of Polypropylene/Silver Nano-Zeolite Plastics and Evaluation of Antibacterial and Mechanical Properties
Anh Quoc Le1, Van Phu Dang1, Ngoc Duy Nguyen1, Cao Tung Vu2, Quoc Hien Nguyen1
1Research and Development Center for Radiation Technology, Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
2University of Science, Vietnam National University in Ho Chi Minh City, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
Correspondence to: Quoc Hien Nguyen, Research and Development Center for Radiation Technology, Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Polypropylene (PP)/silver nanoparticles (AgNPs)-zeolite plastics were prepared by melt blending PP with AgNPs-zeolite at various AgNPs content of 0, 40, 80 and 160 ppm in a twin-rotating-screw extruder for inducing antimicrobial activity. Mechanical properties and antibacterial efficacy of the prepared PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastics were investigated. Results indicated that yield strength and tensile strength of PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastics were almost unchanged in comparison with that of the control PP while elongation at break was reduced from 562% (0 ppm) to 443% (160 ppm). The highly antibacterial efficiency (η~100%) was observed for the PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastics samples containing from 80 to 160 ppm of AgNPs. Thus, the prepared PP/AgNPs-zeolite masterbatch can be suitably used to fabricate a number of products like food containers, chairs, vials, etc. with highly antimicrobial activity.
Keywords: Polypropylene, Silver, Nanoparticles, Zeolite, Antibacterial
Cite this paper: Anh Quoc Le, Van Phu Dang, Ngoc Duy Nguyen, Cao Tung Vu, Quoc Hien Nguyen, Preparation of Polypropylene/Silver Nano-Zeolite Plastics and Evaluation of Antibacterial and Mechanical Properties, International Journal of Composite Materials, Vol. 6 No. 4, 2016, pp. 89-94. doi: 10.5923/j.cmaterials.20160604.01.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity have been most commonly used in consumer and medical products including clothing, respirators, household water filter, contraceptives, antibacterial spays, cosmetics, detergents, dietary supplements, cutting boards, sox, shoes, cell phones, laptop keyboards, food packaging, wound dressing, children’s toys, ect [1-6]. In addition, Mannewattanapinyo et al. reported that AgNPs could be relatively safe when administrated to oral (LD50 > 5,000 mg/kg body weight), eye and skin of the animal models [7]. Polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE) are among the most commercially important thermoplastic polymers with wide applications in the automotive, food and packaging industry, household appliances, and construction [8]. Several studies on the mechanical properties and antibacterial properties of polymers/silver composites have been carried out [8-11]. Typically, results of Aalaie et al. study indicated that PE/nanosilver film exhibited highly antibacterial efficiency (η>99.9%) for E. coli and S. aureus bacteria [8]. In addition, tensile strength and elongation at break of the PE/nano silver films with nanosilver filler from 0.5 to 1.5% were almost unchanged in comparison with that of the control PE film.In this study, PP was first mixed with AgNPs deposited in zeolite framework (AgNPs-zeolite) by extrusion compounding process to prepare PP/AgNPs-zeolite masterbatch. Then, PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastics with various AgNPs contents were prepared by mixing PP/AgNPs-zeolite masterbatch with PP resin. The mechanical properties and antibacterial efficacy of as-prepared PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastics were investigated. The development of these composite materials is with the purpose of fabricating them into a number of applications like food containers, chairs, vials, etc. with antimicrobial activity.
2. Experimental
2.1. Preparation of AgNPs-zeolite and PP/AgNPs-zeolite Plastics
- PP pellets (QR6701K), MFI = 10g/10 min and d = 905kg/m3, were a product of Sabic, Saudi Arabia. AgNPs-zeolite with the AgNPs size of about 30 nm and silver content of 1.2% (w/w) was a product synthesized by our research group as described in a previous paper [6]. In brief, 1.05 kg of zeolite 4A was suspended into a glass beaker containing 1.3 L water. Then, 1.05 L of HNO3 2N in water was added into zeolite suspension mixture for neutralization to pH ~6 and for final volume of about 4.2 L. 17.5 g of AgNO3 was dissolved in 300 ml water and then poured slowly into neutralized zeolite suspension mixture. Stirring was carried out for 2 h at RT for completed Ag+ exchange. A freshly prepared 50 ml hydrazine 25% (w/v) solution was added dropwise to the above Ag+/zeolite under stirring for 4 h at RT. Reduction reaction was stopped and let standing overnight for AgNPs/zeolite settling down at ambient temperature. Finally, AgNPs/zeolite product was filtered off using cotton fabric and dried at 110°C till to constant weight. PP resin in ground powder form (9 kg) and AgNPs-zeolite powder (1 kg) were premixed and melt blended in a twin-rotating-screw extruder (Brabender, Germany) for preparation of PP/AgNPs-zeolite masterbatch in form of pellets. Then, three PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastic samples with estimated AgNPs content at 40, 80 and 160 mg/kg were prepared by mixing a required amount of masterbatch with PP pellets in the extruder as mentioned above.
2.2. Characteristics of AgNPs-zeolite and PP/AgNPs-zeolite Plastics
- The as-prepared AgNPs-zeolite in powder form was characterized by transmission electron microscopy image (TEM, on a JEM 1010, JEO, Japan); by absorption UV-Vis spectrum (UV, on an UV-2401PC, Shimadzu, Japan); and by X-ray diffraction pattern (XRD, on a X Per’ Pro, PA Nalytical, Netherlands) for observation of formation and size determination of AgNPs on zeolite [6].The plastic samples in sheet form were prepared by heating pressure. The plastic sheets with thickness of about 2 mm were prepared for mechanical properties measurement on a Tensile tester Zwick/Roell Z 005, Germany according to ASTM D 638. The silver content in PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastic samples was determined by inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) on a Perkin-Elmer, Optima 5300 DV. AgNPs-zeolite aggregated on the surface of PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastic typically for sample with silver content of 160 mg/kg was visualized using scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM, Hitach S-4800, Japan).
2.3. Antibacterial Activity of PP/AgNPs-zeolite Plastics
- The antibacterial activity of PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastic samples against E. coli was evaluated following the method of Ahmadi et al. [12] with some modifications. Scheme of the antibacterial test was shown in Figure 1.
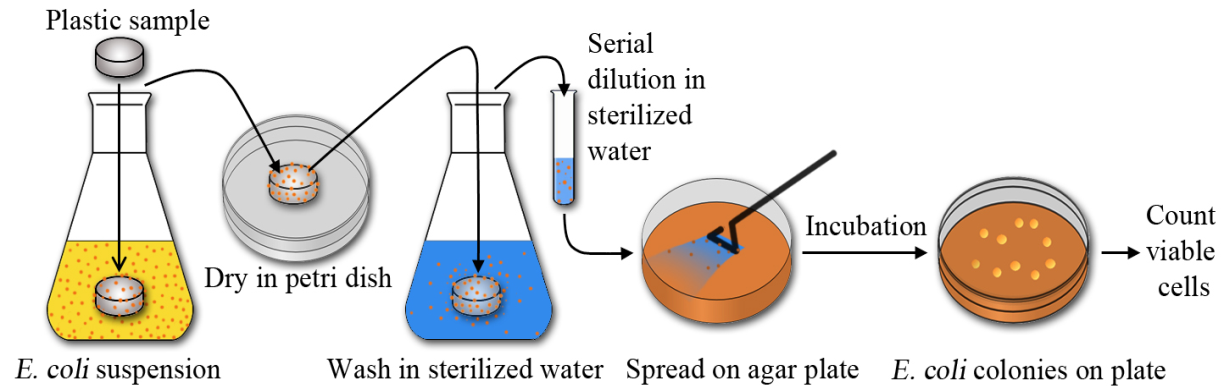 | Figure 1. Scheme of the antibacterial efficiency test for plastic samples |
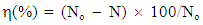 | (1) |
3. Results and Discussion
- In the UV-Vis spectrum of AgNPs-zeolite solution, a maximum absorption peak was appeared at λmax 429 nm which was confirmed to be a characteristic plasmon resonant peak of AgNPs [14], while the such a peak was destitute in Ag+-zeolite before reduction (Figure 2). Moreover, the XRD patterns shown in Figure 3 indicated that the AgNPs-zeolite has four typical diffraction peaks corresponding to 111, 200, 220, 311 crystal planes of silver with face centered cubic (fcc) structure [6, 18], whereas these peaks were not appeared in zeolite 4A. The UV-Vis spectra (Figure 2) and XRD patterns (Figure 3) authenticated the presence of AgNPs in zeolite framework.
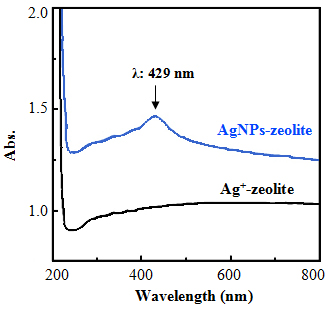 | Figure 2. UV-Vis spectra of Ag+-zeolite and AgNPs-zeolite |
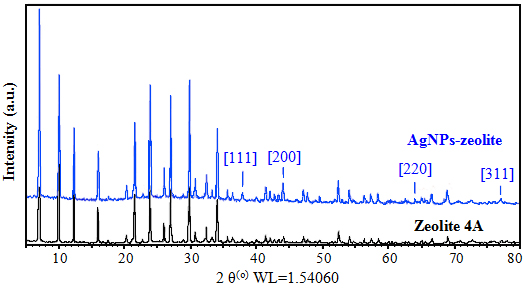 | Figure 3. XRD patterns of zeolite and AgNPs-zeolite |
 | Figure 4. TEM images of zeolite (left) and AgNPs-zeolite (right) |
 | Figure 5. Photographs of zeolite and AgNPs-zeolite |
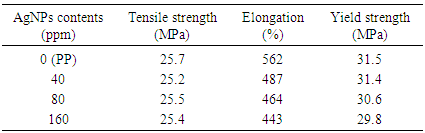
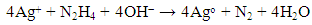 This reducing reaction lowers the pH of the solution and it remains in weak base due to reducing agent (N2H4.H2O) is added in more three time excess, according to stoicheiometry of the above reducing reaction. Dimitrijevic et al. also reported that hydrazine hydrate has been considered as preferred reducing agent and used for industrial scale production of silver powder for decades [15]. Therefore, this synthesis process of AgNPs-zeolite can be potentially to carry out on large scale. The schematic illustration of the synthesis of AgNPs into the zeolite framework from Ag+-zeolite by chemical reduction was also described by Shameli et al [14].The actual content of silver in PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastic samples was shown in Table 1. The obtained results of silver content in all three PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastic samples were slightly smaller in comparison with estimated values. Mechanical properties of PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastics were presented in Table 2.
This reducing reaction lowers the pH of the solution and it remains in weak base due to reducing agent (N2H4.H2O) is added in more three time excess, according to stoicheiometry of the above reducing reaction. Dimitrijevic et al. also reported that hydrazine hydrate has been considered as preferred reducing agent and used for industrial scale production of silver powder for decades [15]. Therefore, this synthesis process of AgNPs-zeolite can be potentially to carry out on large scale. The schematic illustration of the synthesis of AgNPs into the zeolite framework from Ag+-zeolite by chemical reduction was also described by Shameli et al [14].The actual content of silver in PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastic samples was shown in Table 1. The obtained results of silver content in all three PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastic samples were slightly smaller in comparison with estimated values. Mechanical properties of PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastics were presented in Table 2.
|
|
 | Figure 6. SEM micrographs of the neat PP (left) and PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastic (right) |
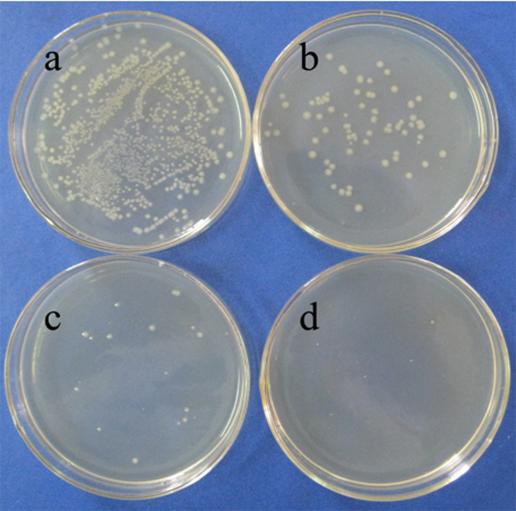 | Figure 7. E. coli colonies from the washing water of PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastics growth on agar plates: a) control (0 ppm), b) 40 ppm, c) 80 ppm and d) 160 ppm AgNPs |
|
4. Conclusions
- The AgNPs-zeolite powder with AgNPs size of about 10 – 30 nm was successfully synthesized by hydrazine reduction method. PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastics were prepared through masterbatch by melt blending method. PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastics with AgNPs content in the range from 80 to 160 ppm exhibited highly antibacterial efficiency (η ~100%). Furthermore, the tensile strength of PP/AgNPs-zeolite plastics was almost unchanged in comparison with neat PP. Thus, the as-prepared PP/AgNPs-zeolite masterbatch can be conveniently used to fabricate various products of antimicrobial plastics such as food containers, chairs, vials, etc.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- The authors would like to thank VINAGAMMA Center, VINATOM for financial support (Project No. CS/14/09-01).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML