-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Composite Materials
p-ISSN: 2166-479X e-ISSN: 2166-4919
2016; 6(2): 48-54
doi:10.5923/j.cmaterials.20160602.02

Physical and Mechanical Properties of Chemically Treated Bagasse Fibre for Use as Filler in Unsaturated Polyester Composite
Josephine Taiye Omole, Benjamin Dauda
Department of Textile Science and Technology, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Josephine Taiye Omole, Department of Textile Science and Technology, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

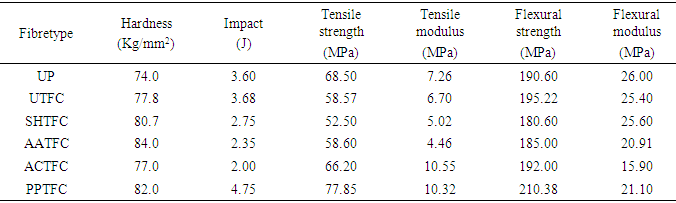
In this research, physical and mechanical properties of bagasse fibre/unsaturated polyester composite was studied after chemically treating four different portions of the bagasse fibre with Sodium hydroxide, Acetic acid, Potassium permanganate, and Acrylic acid. The results obtained showed that Potassium permanganate treated fibre composite had better fibre/matrix adhesion, improved compatibility, higher fibre/matrix interaction and good wetting. The tensile strength was found to be 77.85MPa as compared to 68.50MPa of the untreated fibre composite. The water absorption level was found to be lower than the untreated fibre composite except for the unsaturated polyester composite which is as expected and was at an average of 5%. The hardness and impact strength were also improved for all chemically treated samples. However, in the case of flexural strength not much effect was seen as the flexural modulus of Potassium permanganate treated fibred dropped at 21.1MPa and sodium hydroxide treated fibre composite was 25.60MPa, Acetic acid treated fibre composite had a modulus of 20.91MPa and Acrylic acid treated fibre composite was 15.90MPa, all of which were lower than the untreated fibre composite. Scanning Electron Microcopy (SEM) studies was also carried out which revealed higher interaction in Potassium permanganate treated fibre composite.
Keywords: Bagasse fibre, Chemical modification, Scanning electron microscope, Interphase, Debonding
Cite this paper: Josephine Taiye Omole, Benjamin Dauda, Physical and Mechanical Properties of Chemically Treated Bagasse Fibre for Use as Filler in Unsaturated Polyester Composite, International Journal of Composite Materials, Vol. 6 No. 2, 2016, pp. 48-54. doi: 10.5923/j.cmaterials.20160602.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The inability of synthetic fibres to degrade upon disposal, high processing cost of fibre from synthetic polymers and the pollution caused by this synthetic waste and its effect on the environment has led to the emergence of natural fibre as a cost-effective substitute for synthetic fibres [1-5]. The Advantages of natural fibres include low cost, availability, biodegradability, low density, high specific strength and stiffness, excellent absorbance properties, and high impact energy absorption [24-30].Fibre reinforced polymer composite research is on the increase due to the aforementioned advantages of natural fibres; however, they are not without their limitation. Natural fibres are hydrophilic while the traditional polymer matrices are hydrophobic and therefore limit full adhesion and compatibility [22-25]. One way of improving this adhesion and compatibility is by modifying the fibre surface prior to its use in the composite [3, 6, 7]. The modification is expected to 1. Make the fibres more align 2. Remove pectin wax, lignin, and hemicellulose that cover the fibre surface and enhance its water absorption 3. Roughen a little the fibre surface thereby creating micropores which are actually the sites for interlocking that improves interaction between the fibre and the polymer matrix [4-10]. The aim of this study is to state the likely suitable chemical modification method for the variety of bagasse fibre used as far as the four chemicals used (acetic acid, acrylic acid, sodium hydroxide and potassium permanganate) is concerned. The inclusion of Potassium permanganate in this research was to explore its efficiency, comparing it to conventional chemicals used in previous research (particularly Sodium hydroxide and Acetic acid).In this research, the bagasse fibres were chemically treated using Sodium hydroxide, Acetic acid, Potassium permanganate, and Acrylic acid. The composite produced was then subjected to physical and mechanical testing in order see the effect the chemicals had on the properties; the effect which depends to some extent on certain factors such as source, age, maturation, period of cultivation and separating techniques [20, 22]. One of the vital factors for obtaining good fibre reinforcement in the composite is the bonding strength between the fibre and the matrix which is directly linked to adhesion [11, 14, 16, 19]. Due to the presence of hydroxyl and polar groups, moisture absorption of natural fibre is very high which leads to poor interfacial bonding [23].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Bagasse fibre was extracted manually from sugarcane after milling out the juice using a process described by Asegekar and Joshi in 2013. The sugarcane was obtained from a farm in Hunkuyi village of Zaria town through the faculty of Agriculture, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria-Kaduna state, Nigeria and was of the variety NG57-258.The unsaturated polyester was supplied by NYCIL chemicals Enterprise LTD. Ikeja-Lagos, Nigeria.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Fibre Surface Modification
- Processed bagasse fibres of length 5-6cm were divided into 5 portions, 1 was left as untreated while others were chemically treated using 2wt%NaOH, 2% CH3COOH, 2wt% KMnO4, and 1% CH2=CHCO2H for 3hours at 70°C. Each treatment was followed by thorough rinsing to neutralize pH, sundried and then oven dried to constant weight.
2.2.2. Composite Preparation
- The bagasse fibre/unsaturated polyester composites were prepared using hand lay-up technique. This technique is known for its ease of use, low cost, and suitability of mass production. The fibres were first arranged parallel in the mold, followed by the application of the Unsaturated Polyester (USP) to fill every cavity within the mold. They were then cured at room temperature.The formula below was used in determining the fibre volume fraction of the mold.
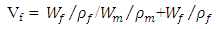 | (1) |
2.3. Testing
2.3.1. Mechanical Testing
- Tensile strength and modulus following ASTMD638-06 and three point bending (flexural) test following ASTMD790-08 were carried out using a universal testing machine (TIRA model 4204). The bagasse fibres were measured prior to testing with a sample gauge length of 80mm, a gross head speed of 10mm/min and a sample dimension of 150mm long and 30mm wide.For the three point bending test, the length to thickness ratio was 15:1. All tests were taken at an average value of 5 samples.
2.3.2. Water Absorption
- This experiment was performed following the ASTMD570 standard. The samples were first oven dried to constant weight (W0) at a temperature 0f 50-60°C and all samples were cut to an equal size of 50 x 50 mm and placed in water cans and removed at 5days interval. Using an analytical weighing balance, each samples removed were weighed (W1). The percentage water absorption by weight as a function of immersion time was thus calculated using the formula below:Water absorption (%) = [W - WO / WO] X 100Where, W = final weight and WO = initial weight.
2.3.3. Impact Strength
- Charpy impact testing machine (model SI-IC3) following ASTM E23 was used in carrying out this test. It was subjected to a 15joule energy impact at 3.21m/s suspended with a pendulum mass of 25kg.
2.3.4. Rockwell Hardness
- This test was carried out on a DIN 53505 EN ISO 868 machine that measures in Kg/mm2 using ASTM D2240. Hardness test helps to determine the resistance of the material to indentations and all other forms of deformity. The test was based on the rate of penetration by an indenter into the sample. The test was done at various points on the sample to obtain an average.
2.3.5. SEM Analysis
- The internal morphology of the produced composites was studied by microscopic analysis using the phenom pro X model Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). SEM is a surface analytical technique used to generate magnified topographical images of a material surface 20x to over 100,000x. In this research, the captures were done to a magnification of 1500x.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Tensile Strength and Modulus
- The result obtained as shown in table 1, indicates that the Potassium permanganate treated fibre composite (PPTFC) had the highest strength at 77.85MPa.This shows that Potassium permanganate improved the tensile strength of the untreated fibre composite which recorded 58.57MPa. This is indicative of the ability of Potassium permanganate to modify the fibre. Sodium hydroxide treated fibre composite (SHTFC), Acetic acid treated fibre composite (AATFC), and Acrylic acid treated fibre composite (ACTFC) recorded values of 52.50MPa, 58.60MPa, and 66.20MPa respectively. The results for Sodium hydroxide and Acetic acid might be easily considered an anomaly as these agents have been reported to improve fibre composite strength. However, the poor tensile strength could be due to the variety of bagasse used, method of collection, processing, and environmental conditions [17, 20].
|
3.2. Flexural Strength and Modulus
- The result of the flexural tests shows the PPTFC at 210MPa has more tendency to accommodate higher stress than other treated fibre composites just before yield point, that is, during application it is more likely to resist any major deformity, bending or fracture for a long time but in terms of modulus at 21.10MPa which is lower than the untreated fibre composite at 25.40MPawhich means that the PPTFC has a higher deflection. A study on different varieties of bagasse fibre revealed that the modulus of bagasse fibre is generally low [20]. The flexural test tells how much of bending in various directions that the material can accommodate and to what extent. SHTFC has been proved by other research to be promising using other fibres, hence, its negative response here may be due to the bagasse variety, processing and handling [11, 12, 15, 18].
3.3. Rockwell Hardness
- In fig.1a, the AATFC at 84kg/mm2shows that it is the hardest, however looking at previous test results (such as tensile, flexural, etc) PPTFC had better improved properties. PPTFC hardness at 82kg/mm2 and UNTFC at 77.882kg/mm2 confirms further the efficiency of Potassium permanganate to modify the fibre and enhance its mechanical properties.
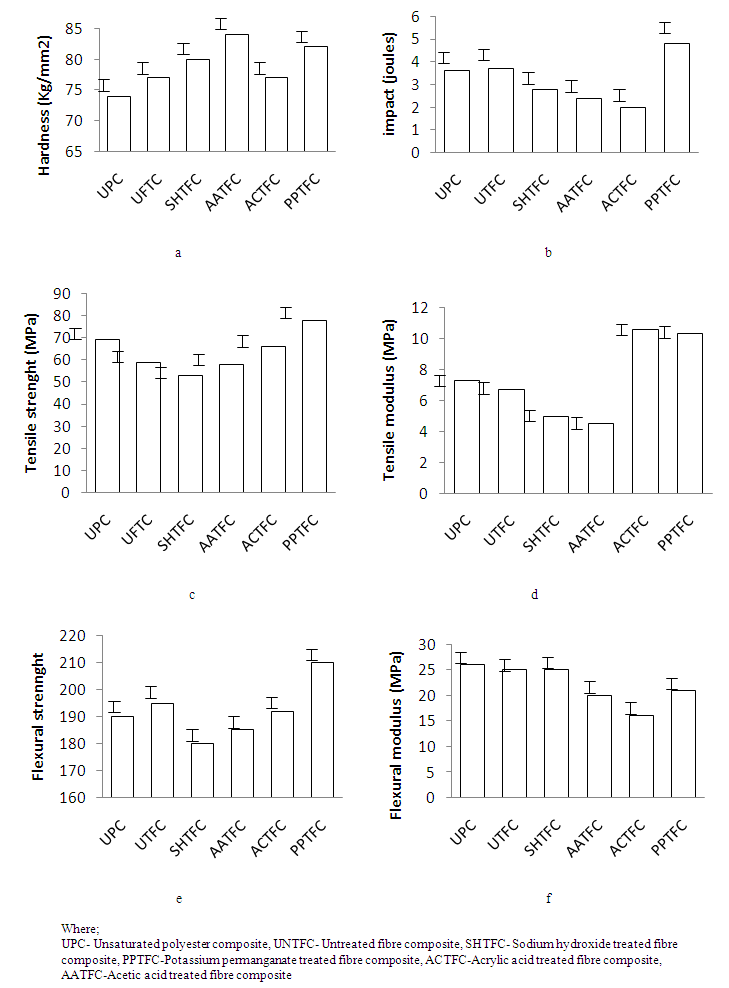 | Figure 1. Showing graph of a-hardness, b-impact, c-tensile strength, d-tensile modulus, e-flexural strength, and f- flexural modulus |
3.4. Impact Test
- Impact is associated with the force the material is subjected to at first impact and this dependent on the time speed for which the force is applied. PPTFC was more resistant at about 4.8 joules which is about 40% higher than the UTFC at about 3.7 joules. This implies that the PPTFC composite is strong and also the chemical succeeded in making the fibre more hydrophobic than it was prior to treatment and is thus now reinforcing. The SHTFC, AATFC and ACTFC at 2joules, 2.4joules, and 2.75 joules respectively can only be used as fillers.
3.5. Water Absorption
- From Figure 2 below, it is observed that all the composite samples absorbed water; however, PPTFC absorbed the least amount at 2.8% after 720hours of the experiment. The untreated fibre composite absorbed as high as 7% which is expected due to its hydrophilic nature and the presence of OH, polar groups, and other waxy substances. The SHTFC, AATFC, and ACTFC absorbed more water than PPTFC which is again an indication that Potassium permanganate treatment might be more ideal for chemical modification of bagasse fibre composite. Although the unsaturated polyester composite absorbed water, which was unexpected as the weight should remain constant throughout the water absorption treatment. This may have been due to cracks and voids during production or curing.
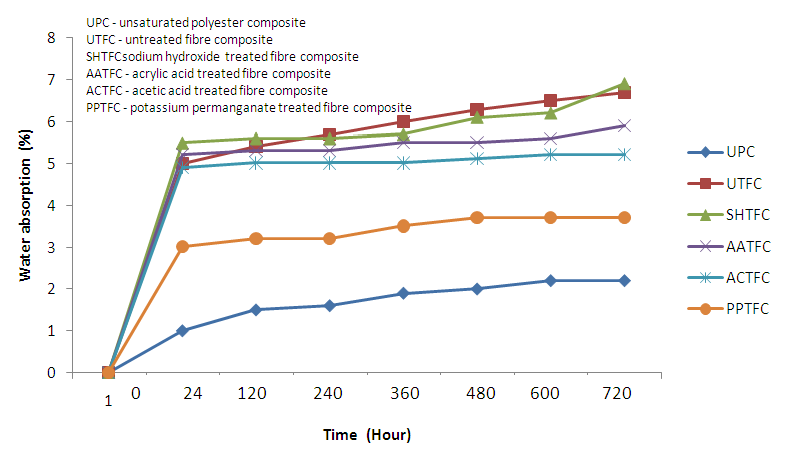 | Figure 2. Graph of water absorption as function of immersion time |
3.6. SEM Analysis
- Figure 3 below shows the micrographs of the treated and untreated composites. This reveals the effect of chemical treatments on the interface of the composite. Looking at Fig.3a showing for UTFC, it does not show distinctively the presence of the fibre and the USP which is indicative of the fact that the adhesion and interaction was very poor; but it shows cracks which may have been due to processing. Fig.3b (micrograph for SHTFC) shows that the lumen found in cellulosic natural fibres did not collapse which is inconsistent with previous experiments [1]. Hence the wide cavity that enhances the ability of the fibre to absorb and retain water is still present, and this is most likely responsible for the poor result exhibited by the composite. The failure of Sodium Hydroxide to collapse the lumen might be as a result of the variety of fibre used. Fig. 3c shows micrograph of AATFC which reveals that the surface of the fibres became too coarsened than needed as the fibres began to pull out which is detrimental to fibre/matrix adhesion. Also, the production of micropores that promotes interlocking was not created. The USP can barely be seen, this means that interaction between the fibre and the matrix was poor and may have contributed to the poor bonding strength exhibited by the composite. It is observed in Fig.3d (ACTFC) that the fibres lacked the roughness required to improve adhesion andinadequate interlocking sites (micropores) for fibre/ matrix union. These might have contributed to the composite’s poor performance as observed in the tests. PPTFC micrograph shows Fig.3e that the lumen found in cellulosic natural fibres collapsed sufficiently to prevent the cavities from retaining water within the fibre. The SEM showed good bonding of the fibre/matrix at the interphase. The surface was coarse and microspores present to aid adhesion. This therefore is visual evidence of the effectiveness of Potassium Permanganate as a possible ideal agent for the modification of Bagasse fibre.
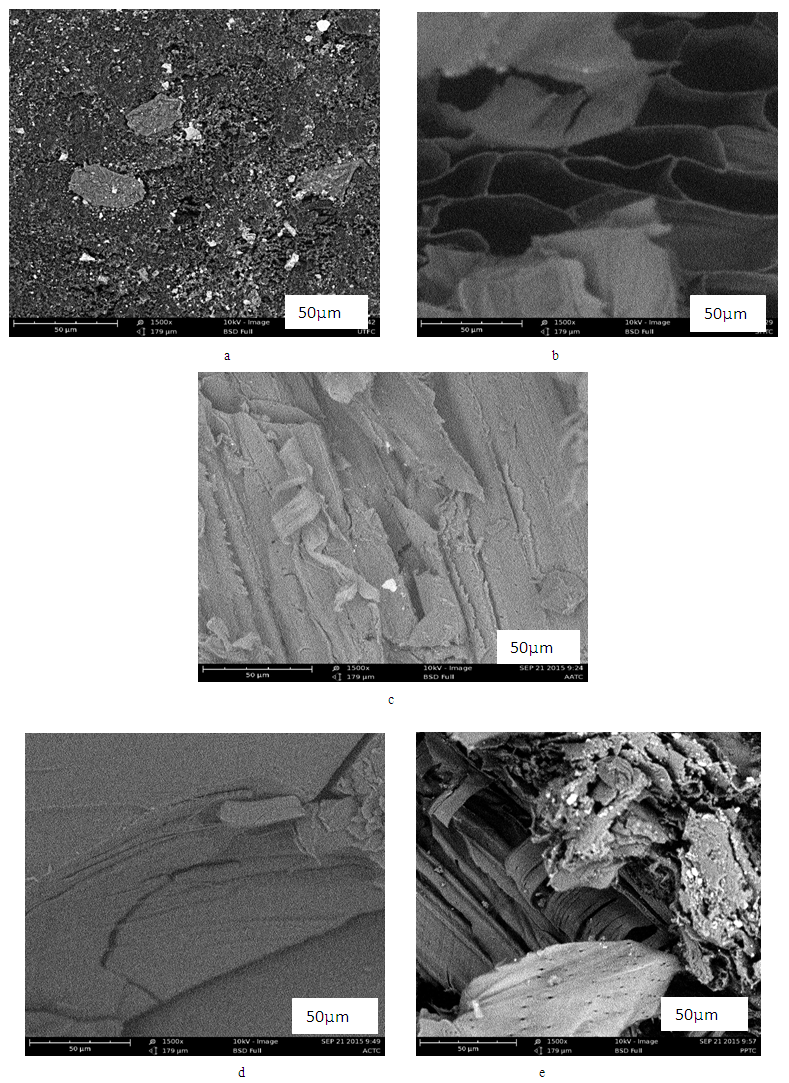 | Figure 3. SEM micrographs of a-UTFC, b-SHTFC, c-AATFC, d-ACTFC, and e-PPTFC |
4. Conclusions
- Potassium permanganate treated fibre composite (PPTFC) seem more promising for use as reinforcement in natural fibre composite, this is evident in the results obtained in all the tests carried out. The hardness and impact test of PPTFC shows that the composite has a good resistance to indentations and other major deformations that the composite may be exposed to during use. The tensile, flexural and scanning electron microscopy analysis also indicates that the PPTFC has improved fibre/matrix adhesion, that bonding strength is quite high compared to other treated composites, which is why it had improved fibre/matrix interaction and compatibility. A good number of interlocking sites must have been created which has led to its improved mechanical properties. The water absorption result was also positive.Other treated fibre composites (SHTFC, AATFC, and ACTFC) may only be used as fillers, as their results in all the tests and analysis exposes their inability to reinforce. This is most likely due to the variety of bagasse fibre used and not the inefficiency of the chemicals used.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML