-
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Composite Materials
p-ISSN: 2166-479X e-ISSN: 2166-4919
2016; 6(1): 34-41
doi:10.5923/j.cmaterials.20160601.05

Investigation on Tensile Properties of Plain and Nanoclay Reinforced Syntactic Foams
H. Ahmadi1, G. H. Liaghat1, 2, H. Hadavinia2
1Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran
2Department of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, Kingston University, London, UK
Correspondence to: H. Ahmadi, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2016 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

Tensile properties of plain and nanoclay reinforced epoxy matrix syntactic foams with three different sizes of ceramic microballoons are investigated experimentally. Nine series of plain syntactic foams with 20, 40 and 60 volume fractions of microballoons are prepared and tested to study the volume fraction and size effects. Also nano syntactic foams specimens with six different weight fractions of nanoclay (0, 1, 2, 3, 5 & 7%) are tested and the effect of nanoclay content on the tensile properties is investigated. In addition to tensile tests, fracture modes of all syntactic foams are considered thoroughly by using scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
Keywords: Syntactic foam, Ceramic microballoon, Nanoclay, Tensile properties, Experimental analysis
Cite this paper: H. Ahmadi, G. H. Liaghat, H. Hadavinia, Investigation on Tensile Properties of Plain and Nanoclay Reinforced Syntactic Foams, International Journal of Composite Materials, Vol. 6 No. 1, 2016, pp. 34-41. doi: 10.5923/j.cmaterials.20160601.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Application of lightweight materials is widely increased in aeronautical, marine and civil structures. Among these materials, foams with a significant weight saving have an important role, but their applications are limited by their low strength and modulus. So, developing some methods for introducing porosity in materials without causing serious effects on mechanical properties is the topic of many researches during recent years. Syntactic foam is a kind of porous material with walled hollow particles (microballoon) in a matrix material [1]. Desired properties for this material can be obtained by choosing appropriate material for matrix and microballoons. Metal, polymer or ceramic can be selected for matrix and microballoons can be made of ceramic, glass, carbon or polymer. A wide range of possible volume percentages of microballoons gives opportunity to tune the desired properties [2]. Most of the studies performed have been on the mechanical and fracture properties of syntactic foams under compression [3-6], flexural [7-9] or thermal degradation [10, 11]. However few published works have been reported on tensile properties of syntactic foams. Gupta and Nagorny [12] investigated the effect of hollow glass microballoons volume fraction on the tensile properties and fracture modes of syntactic foams. They observed that the tensile strength decreases with an increase in the volume fraction of microballoons. The similar results have been reported by Wouterson et al. [13]. Gupta et al. [14] focused on the synthesis and characterization of vinyl ester/glass microballoon syntactic foams. They found that specific tensile strength and specific tensile modulus of foams are comparable with their neat resin and are higher for some samples. Gouhe and Demei [15] tested four types of hollow polymer particles as filler in UV-heat-cured epoxy resin. The tests show that tensile strength and specific properties of all foams decrease with increasing the particle content. Also the results showed that the mechanical properties of syntactic foams specially depend on microballoons’ material. Among the published papers ceramic microballoons are considered in few cases. Ceramic microballoons are being developed for structural applications or electric appliances like piezoelectric transducers and low dielectric constant substrates [16, 17]. Mechanical properties are obviously the primary concern for ceramic microballoon filled syntactic foams. Interest for exploiting the benefit of low density of syntactic foams has made it necessary to characterize these materials for tensile loading and study various parameters affecting their properties. It has been studied that use of nanoclay in the structure of neat polymers such as epoxy, increases tensile strength, tensile modulus and impact resistance [18-20]. Most of the published papers indicate that large number of interfaces that are created in a nanocomposite upon dispersion of nano particles results in increasing of strength of the composite matrix [21, 22]. Although, it is shown that nano-reinforcing of the matrix material of syntactic foams enhanced the mechanical properties of glass microballoon filled syntactic foams [23-27], the reports are few and the full potential of nano-reinforcing of the syntactic foams with different microballoons is not explored yet. In this paper, the tensile properties of nine types of plain syntactic foams (three microballoon sizes and three microballoon volume fractions) and neat epoxy are obtained experimentally to study the effects of volume fraction and microballoon size and material. Also, nano syntactic foams of 40% volume fraction of microballoons of only one type is prepared with six weight fraction of nanoclay (0, 1, 2, 3, 5 and 7 wt.%) in epoxy matrix. They are tested to study the effects of the presence of nanoparticles on the tensile properties. The fabricating method was evaluated by measuring density and porosity of fabricated foams. Also, extensive scanning electron microscopic observations are performed to establish the modes of failure and further to understand the mechanical properties.
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Materials
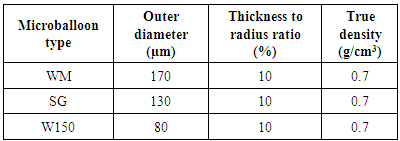
- The ceramic microballoons of syntactic foams are from OMEGA MINERALS Germany GmbH with the trade names of SG, WM and W150. Some typical properties of these microballoons are shown in Table 1. Epoxy resin, with the trade name of EPIKOTE 828 from Resolution Performance Products LLC and TETA hardener from Akzo Nobel Functional Chemicals are used for matrix material. EPIKOTE 828 is a medium viscous epoxy resin based on Bisphenol-A. TETA hardener is a low viscous aliphatic amine used for room temperature curing. The resin to hardener ratio specified by the supplier was 10:1. Density of the pure cured epoxy is measured to 1.18 g/cm3 according to ASTM C271 standard [28]. The nanoclay used is a natural montmorillonite modified with a quaternary ammonium salt that has the trade name Closite 30B, which is manufactured by Southern Clay Products, Inc. Its moisture is less than 2% and its density is about 1.98 g/cm3.
|
2.2. Fabrication
- Plain syntactic foams were fabricated by hand stirring mixing method. First, microballoons were added to resin gently and stirred with a wooden rod until a uniform distribution is ensured. Then the hardener was added to the mixture. For decreasing the undesirable phenomena effects, for 20 and 40 vol. % syntactic foams, final mixing last until the blend becomes a viscous paste. So, the floatation of the microballoons did not happen. On the other hand, for alleviating the matrix porosity of 60 vol. % syntactic foams, the uncured blend was degassed before moulding [5, 27, 29]. Nano syntactic foam samples consist of 40 vol.% of W150 microballoons. Five series of specimens with different nanoclay weight fraction in their matrix (1, 2, 3, 5, 7 wt.%) were prepared. For fabricating, the epoxy resin was preheated at 75˚C for approximately 24 hr in an oven to reduce the viscosity for better wetting of particles. Resin was then removed from the oven and nanoclay was incorporated in the required amount and the mixture was stirred by a mechanical shear mixture at 500 RPM for 30 minute. As the next step, the mixture was ultra-sonicated for 15 minutes with the cycle of 0.5 and the amplitude of 60% [30]. During this process, nanoclay clusters break into nanoclay platelets and the resin can penetrate into the nanoclay galleries. Sonication caused temperature increasing and a large number of micro-bubbles. So, degassing of the mixture was important. After cooling the mixture to room temperature, the microballoons were added and the mixture was hand stirred until a uniform distribution was insured. The hardener was added to the mixture as the last step. Finally the blend, both plain and nano syntactic foam, was transferred to a stainless steel mould which was smeared with mould releasing agent. The mixture was cured for 48h at room temperature. The test specimens were cut from cured slabs by water-jet cutting machine.
2.3. Specimen Coding
- Preventing from ambiguity, the following nomenclature for specimens has been used as: SF-XX-YY. SF is the abbreviation of syntactic foam. The name of microballoon is used instead of XX and volume percentage of microballoon in epoxy is used for YY. For example SF-SG-40 is the syntactic foam with 40 volume percentage of SG microballoons. For nano syntactic forms the nomenclature of NSF-XX-Y has been used. Since the microballoon volume percentage of all the nano syntactic foam samples are 40%, the nomenclature has not included this value. XX show the type of microballoon and Y represents the nanoclay weight fraction of the samples. For example: NSF-W150-5 is a nanoclay syntactic foam with 40% volume fraction of microballoon and 5% weight of nanoclay in epoxy.
2.4. Test Procedure
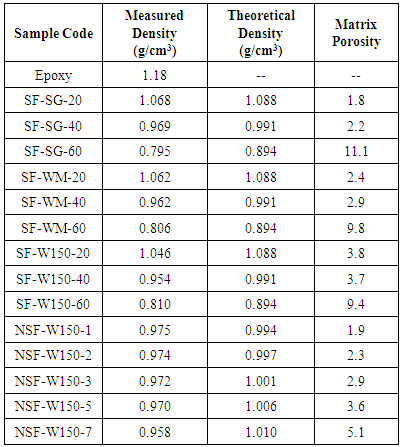
- ASTM standard C271 was applied to measure the density of all fabricated specimens. The weights and volumes of at least five pieces of 25×25×13 mm3 size from each type were measured to calculate the foam density. The tensile samples were cut according to ASTM standard D638 [31] into dog-bone test specimens. The test was carried out using Instron 5500 testing machine system (Figure 1) and at cross head speed of 1 mm/min. At least five specimens of each type of syntactic foams were tested. Strain data was collected by an extensometer with 25 mm gauge length.
 | Figure 1. Dog-bone test specimen and tensile testing machine |
 | Figure 2. Matrix porosity in syntactic foam |
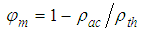 | (1) |
|
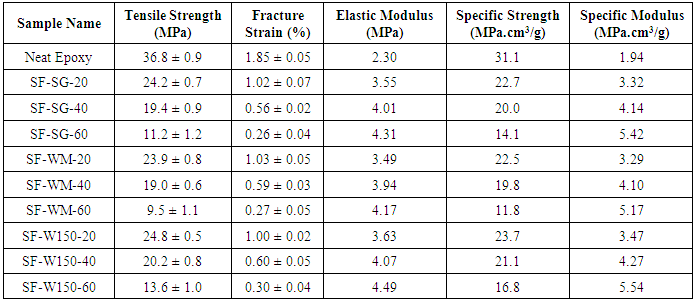
2.5. Effect of Volume Fraction
- The results of tensile strength, elastic modulus, fracture strain, specific strength and specific modulus are shown in Table 3. The results state that with increasing the microballoon content of the foams, the strength of them decreased. It means that the strength of syntactic foam strongly depended on the content of matrix as the main constituent of load bearing. But it did not have a linear relation between increase of strength and volume fraction as shown in Figures 3 & 4. By adding 20% microballoons to epoxy resin the strength decreased about 33-35%. Actually adding microballoons created some imperfections such as unwanted porosity and weak interfacial surfaces between microballoons and matrix. These facilitated the crack propagation inside the foam. The SEM figures of the fracture surfaces of tested specimens validated this claim. Reviewing the fracture surfaces, both damage mechanisms of microballoon fracture and propagation of crack along the weak interface of microballoons and matrix can be seen (Figure 5). It was expected that in well prepared syntactic foams, bonds between microballoons and matrix remained intact and this will force the crack to propagate along the matrix or fracture the microballoons. In SEM figures of this work, debonding between microballoons and matrix was rarely observed and it can be deduced that the interfacial bonding is strong.
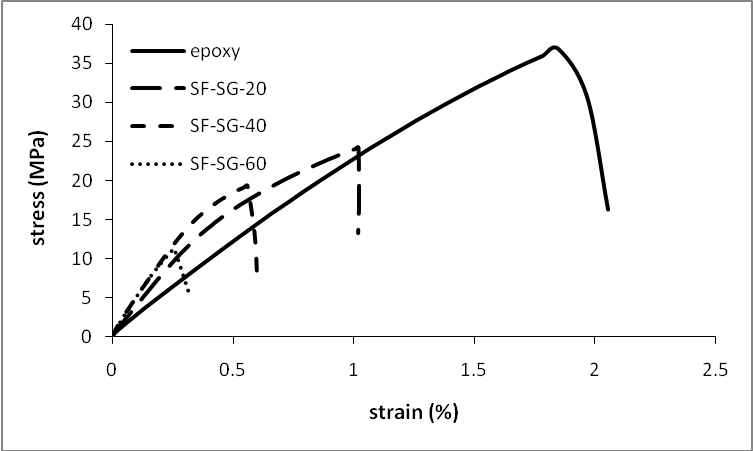 | Figure 3. Stress – Strain curves for neat epoxy and SG microballoons syntactic foams with different volume fractions |
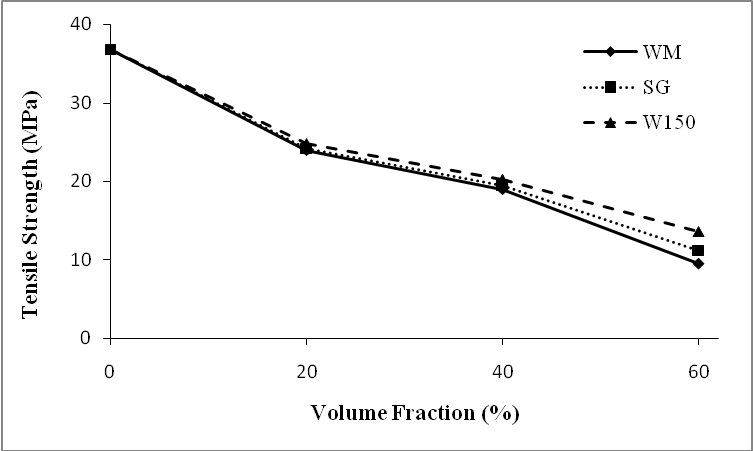 | Figure 4. Effect of microballoon volume fraction on the tensile strength of syntactic foams |
 | Figure 5. Crack paths through microballoon, matrix and interfacial surfaces between them in SEM figures from fractured surfaces |
|
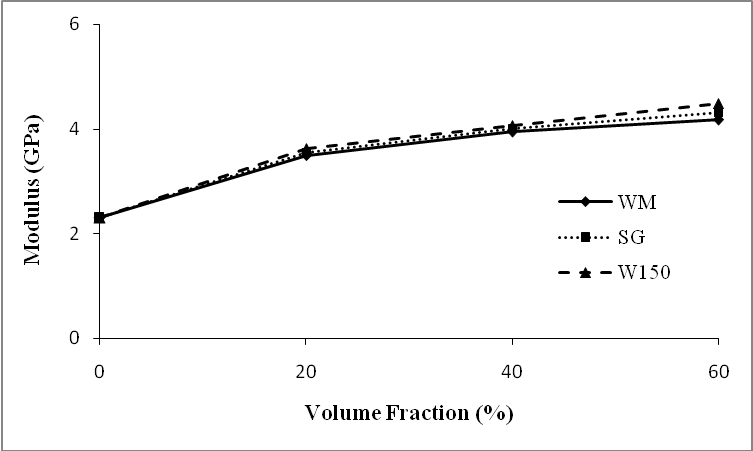 | Figure 6. Effect of microballoon volume fraction on the tensile modulus of syntactic foams |
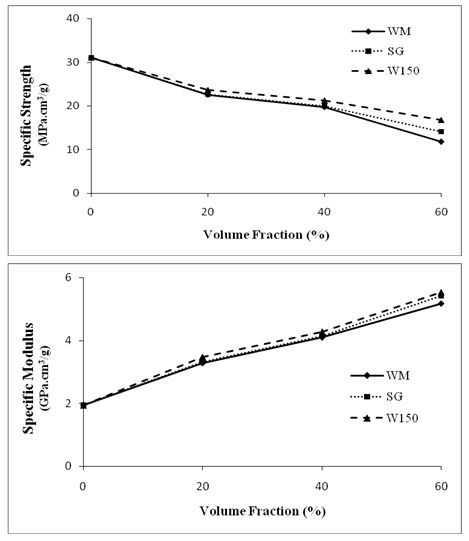 | Figure 7. Effect of microballoon volume fraction on specific strength and specific modulus |
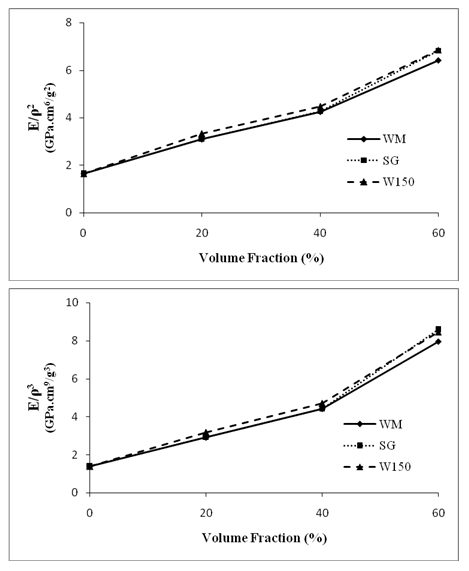 | Figure 8. Effect of microballoon volume fraction on E/ρ2 and E/ρ3 of syntactic foams |
2.6. Effect of Microballoon Size
- The results of tensile tests for nine types of syntactic foams with the different microballoon volume fractions and different microballoon sizes are presented in Table 3 and Figures 9 & 10. The results show that the microballoons’ size did not affect the fracture strain significantly. Of course its effect on the tensile modulus was about 4-7 %. Actually syntactic foams with smaller microballoons had higher modulus and as the microballoon content increased, the difference became more.
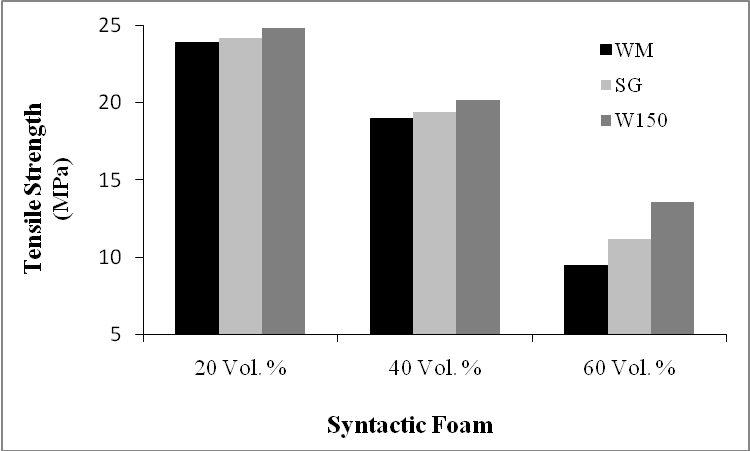 | Figure 9. Comparison of the tensile strength of syntactic foams with different microballoon size |
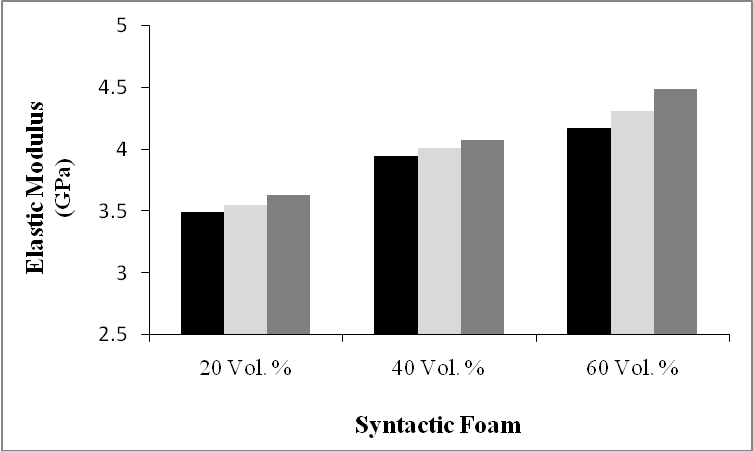 | Figure 10. Comparison of the elastic modulus of syntactic foams with different microballoon size |
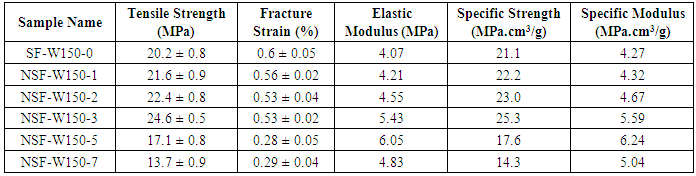
2.7. Effect of Nanoclay Weight Fraction
- As mentioned before, presence of limited amount of nanoclay in epoxy would enhance its mechanical properties. In this study, the effect of nanoclay in epoxy matrix of syntactic foam has been investigated. Six types of nano syntactic foams were prepared with W150 microballoons and 40 % volume fraction. Nanoclay weight fraction of epoxy matrix of these syntactic foams were 0%, 1%, 2%, 3%, 5% and 7%. The stress - strain curves are illustrated in Figure 11. Also, the comparative results for tensile strength and modulus are in Figures 12 & 13. Generally, presence of nanoclay in epoxy matrix, made nano syntactic foams more brittle. As the nanoclay content increased, the fracture strain decreased and the tensile modulus increased. The tensile modulus of NSF-W150-5 was the most and nearly twice the tensile modulus of NSF-W150-0.
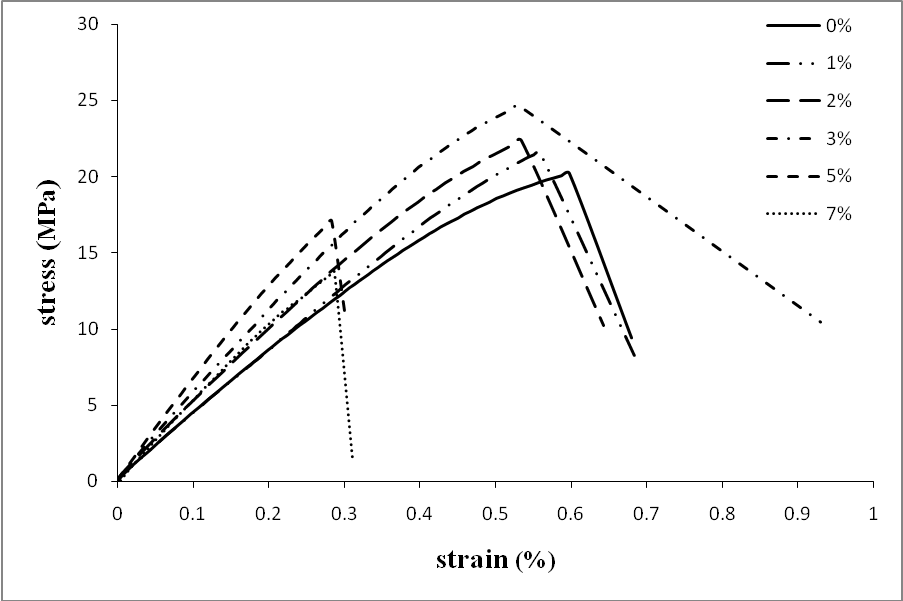 | Figure 11. Stress – Strain curves for nano syntactic foams with 40% W150 microballoon volume fraction and different nanoclay content |
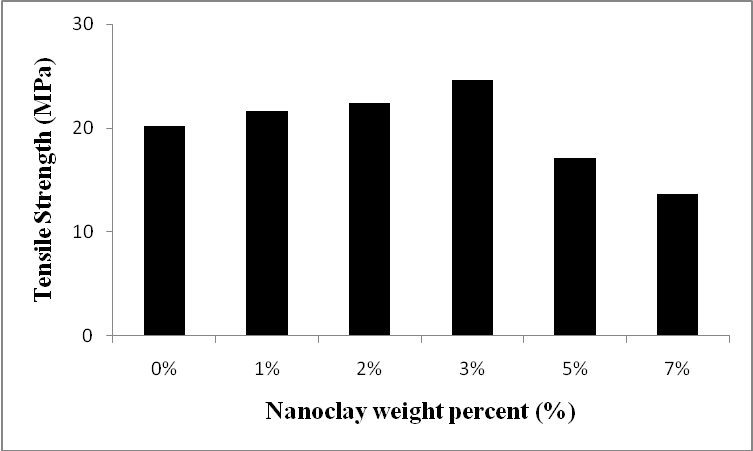 | Figure 12. Effect of nanoclay weight fraction on the tensile strength of syntactic foams with 40% W150 microballoon volume fraction |
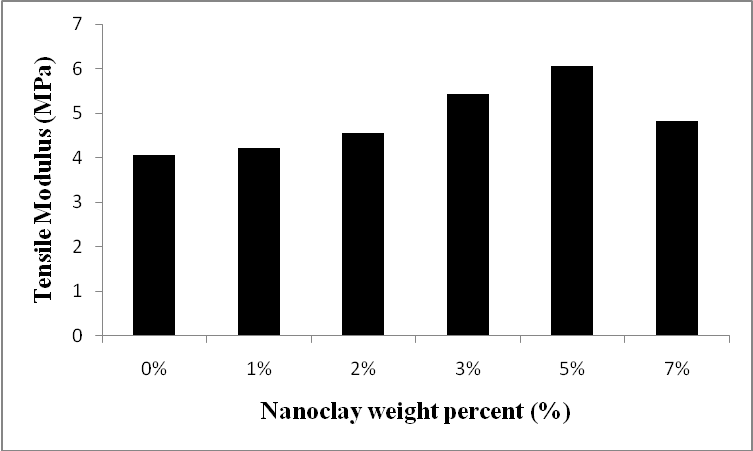 | Figure 13. Effect of nanoclay weight fraction on the elastic modulus of syntactic foams with 40% W150 microballoon volume fraction |
|
3. Conclusions
- Tensile properties of ceramic microballoon/epoxy matrix syntactic foams with different volume fraction and microballoons’ size were investigated in this work. The fracture strain and tensile strength of syntactic foams are significantly influenced by the microballoon content. It is found that both of them decreased as the volume fraction increased. Contrary to glass microballoons, introducing the ceramic microballoons in epoxy enhanced the tensile modulus as the volume fraction increased. SEM images showed that the cracks propagated along the matrix and microballoon materials. Interfacial bonding of microballoon surface and matrix was strong enough that debonding rarely occurred. Microballoons’ size effect on the mechanical behavior is also investigated and results show that syntactic foam with bigger microballoons has less strength than syntactic foam with smaller microballoons. Also, it should be indicated that the fracture strain and the tensile modulus did not change significantly. Tensile properties of nanoclay reinforced syntactic foams were studied, too. Adding nanoclay to the matrix of syntactic foams resulted in increasing the tensile modulus and decreasing the fracture strain. Increasing nanoclay content up to 3% enhanced the tensile strength but more nanoclay had a reverse effect and decreased it.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML