-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Composite Materials
p-ISSN: 2166-479X e-ISSN: 2166-4919
2015; 5(5): 133-141
doi:10.5923/j.cmaterials.20150505.05
Olive Oil Waste Filled High Density Polyethylene Bio-Composite: Mechanical, Morphological and Water Absorption Properties
Raid Banat1, Mohammad M. Fares2
1Department of Chemistry, Al al-Bayt University, Mafraq, Jordan
2Department of Applied Chemical Sciences, JUST, Irbid, Jordan
Correspondence to: Raid Banat, Department of Chemistry, Al al-Bayt University, Mafraq, Jordan.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
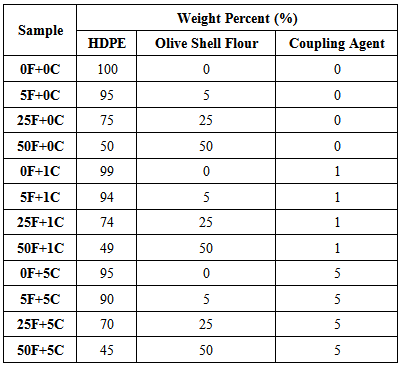
The effect of olive shell flour, Exocarp & Mesocarp, on the mechanical, morphological, and water uptake properties of high density polyethylene (HDPE), with and without using coupling agent, were investigated. In this research, HDPE filled with olive shell flour at 0, 5, 25, and 50 wt. % loading level in the absence and presence of 1% and 5% coupling agent. Environment-friendly composites were fabricated by extrusion and compression molding processing technologies. Tensile strength of the composite decreases with the increase of the filler loading; and increases in the presence of coupling agent. The modulus of elasticity at 5 and 25 wt. % filler showed higher values on the order of 5% compared to that of neat HDPE. The impact strength was increased for low filler loading level (5 wt. %) on the order of 16% and decreased for medium and high filler loading level (25 and 50 wt. %) on the order of 61% and 91% respectively. The interfacial properties of the polymer composites were improved at low filler loading level 5 wt. % and enhanced by the addition of 5 wt. % coupling agent (5F+5C). Morphological illustrations reflect the mechanical behavior findings and the effect of coupling agent on the enhancement of the composite interfacial adhesion. Water uptake of the composite; increased with filler content and decreased in the presence of coupling agent. The results of the study demonstrate that olive shell flour can be used as reinforcement for HDPE bio-composite material.
Keywords: Olive oil waste, HDPE composite, Coupling agent, Mechanical & physical properties
Cite this paper: Raid Banat, Mohammad M. Fares, Olive Oil Waste Filled High Density Polyethylene Bio-Composite: Mechanical, Morphological and Water Absorption Properties, International Journal of Composite Materials, Vol. 5 No. 5, 2015, pp. 133-141. doi: 10.5923/j.cmaterials.20150505.05.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- Agro crop residues can serve as a source material for bio-energy and developing bio-based polymer composites [1-3]. Wastes of biomass based fillers are increasingly used as reinforcement material for thermoplastic composite materials [4-6]. In order to minimize the negative effects on the environment of certain plastic structures, promoting clean technologies and recycled products, the use of olive stone as plastic filler was studied [7-9]. The preparation of composite samples by mixing olive stone and polypropylene to produce a new thermoplastic polymer was performed [10, 11]. There are industrial films that have developed a homogeneous polymer compound incorporating olive stone as a natural and biodegradable raw material [12-14]. Products such as panels, pipes, tubes or profiles amongst others, have been elaborated by extrusion and injection technologies [15].The olive oil extraction processes generates huge amounts of solid lignocellulosic waste, representing 30-35% by weight of the olive fruit. The chemical composition of which; mainly composed of lignin, hemicellulose and cellulose. Olive waste has a growing potential as a reinforcement filler materials among many other uses [16-18].Modern olive oil mills use centrifugal separation methods where the olive cake (waste) residues represent 35% of the whole olive fruit, and composed of oil 9%, shell 22%, water 24% and stone45%. The mentioned values varied depending on the process used for olive oil production [19-21].In literature, most studies were performed on the olive stone part (Endocarp) and no specific research mention the use of the olive shell part, skin and pulp or (Exocarp & Mesocarp) as a reinforcement filler material. In this study a novel biodegradable composite material containing olive shell flour dispersed into HDPE was manufactured and studied. In general natural fiber composites can be classified into green or partially green composite based on the polymer matrix in use [22]. In the last two decades the developments of such kinds of polymer composite reduce the consumption of non-biodegradable polymer matrix which partially fulfills the global environmental needs toward less hazardous materials. The aim of this study was to formulate less hazardous composite form HDPE and OSF and to investigate the effect of olive shell flour at different weight fractions on the physical and mechanical properties of HDPE composites. Moreover, commercially available coupling agent was used to evaluate its effect on olive shell flour/HDPE polymer composite.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- The composites were prepared using homopolymer HDPE (ExxonMobil HDPE HMA 018) as the polymer matrix. This HDPE is an easy flow grade with a melt flow index of 30 g/10 min (according to ASTM D1238 standard) to facilitate the dispersion and processability of the composite material. Fusabond M603 resin, a random ethylene copolymer incorporating a monomer, which is classified as being a maleic anhydride equivalent, was kindly provided by Dupont Company and used as coupling agent to improve the interface adhesion and to promote the compatibility of powder/matrix composite. Olive waste was kindly provided by local olive oil processing plant in Jerash region/Jordan and used after certain conditioning as a filler material.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Olive Pulp and Skin Flour Preparation
- Olive waste was obtained from the residues of the olive oil production. After the separation of the olive oil, the residue is composed of skin, pulp, and stone. The solid residue was used without any chemical or solvent treatment. Then the residue was dried and separated into shell (pulp and skin) and stone by means of screening ventilation. The resulting shell residues were ground into fine flour that represents about 10-15% of the whole olive fruit. Olive shells (pulp and skin) were grinded using Pulverisette 9 vibrating cub mill (Fristch, Germany). The obtained particles mesh size was measured with a set of sieves from 140 to 325. Olive shell flour was oven dried at 103°C ± 2°C for 24 h to adjust moisture content to approximately 1.5%.
2.2.2. Compounding and Composite Processing
- Before processing (Figure 1) HDPE and flour are dried at 103°C± 2°C for 24 h. Compounding is achieved by a parallel co-rotating twin screw extruder (TSE 20, L/D: 40:1, diameter 22 mm, 8 × 78 mm2 flat die) with 7 heating zones (temperature profile: 160°C / 180°C / 180°C/175°C / 175°C / 170°C /180°C). Screw speed rate is 60 rpm and feed rate is 3 kg/h.
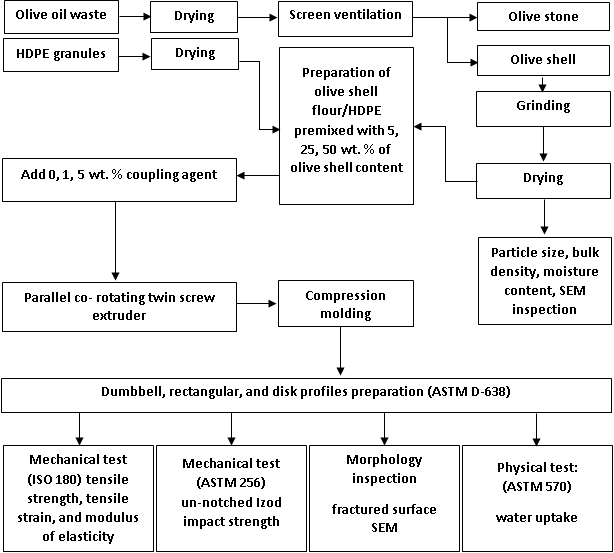 | Figure 1. Process for olive shell flour filled high density polyethylene composite production |
|
2.3. Bulk Density Measurement of Olive Shell Flour
- Bulk density of olive shell flour filler was measured by using conventional standard method, where the volume of 50 g olive shell flour was determined by using high precision graduated cylinder, after 24 h drying at 80°C.
2.4. Moisture Content
- Aluminum dish was weighted using digital balance. Samples (10 g) with mesh size 140-325 were placed in the dish and the dish and sample were weighted. The sample and the dish were then placed in drying oven and kept at 103 ± 2°C for 48 h until constant weight was reached. The moisture content was calculated according to equation (1)
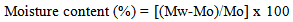 | (1) |
2.5. Mechanical Characterization
- The specimens were stored at 23°C and 30% relative humidity for 48 h. Afterwards, composites were assayed in a computer control electrical universal testing machine (WDW-5), fitted with a 5 kN load cell and operating at a rate of 1 mm/min. Tensile strength and Young’s modulus were analyzed using dog-bone specimens according to ISO 180. The un-notched Izod impact strength was measured according to ASTM: D256 using digital display Izod impact testing machine (FI-68) provided with impact speed of 3.5 m/s, a hammer of 2.270 kg weight and 335 mm arm length. Results were obtained from the average of at least 5 samples.
2.6. SEM
- For morphological characterization, Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) photomicrographs were taken on the fractured surface of the specimens from tensile measurement. Fractured surface was made conductive through sputter-coating for 40 s at a beam current of 38–42 mM·L−1 with a 100 Å layer of gold/palladium alloy in vacuum chamber. Investigation was done using Quanta 600 SEM. Representative micrographs were taken in the magnification of the order 800-1000 for all samples.
2.7. Water Absorption Test
- The water absorption of the composite was conducted according to ASTM D570 standards. Samples (50 mm diameter disks, 6.23 mm thick) were oven dried at 50°C. Composite samples were then immersed in distilled water (23ºC for 24h) and taken out after a constant interval of time, wiped with tissue paper, and weighted in high precision digital scale balance with a resolution of 0.001g. The water absorption uptake was recorded on daily basis for 30 days after which the water absorption % was calculated accordingly to equation (2).
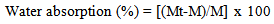 | (2) |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Size of the Olive Shell Flour
- Olives shell flour fractions with mean sizes of approximately 140-325 mesh, was obtained using vibrating cup mill Pulverisette 9. 70% of the flour was in the range of less than 50µm particle size. Flour fractions were subsequently retained for further investigation.
3.2. Density and Moisture Content Measurements of Olive Shell Flour
- The bulk density of olive shell flour was found to be 0.71 g/cm3 and the moisture content was determined to be 1.5% for all flour samples used in processing of the composites material.
3.3. Mechanical Characterization of Composites
3.3.1. Tensile Stress and Strain
- Experimental results represent the mean value of at least five specimens tested. Figure 2 shows the olive shell flour/HDPE composite tensile stress variation in the absence and in the presence of coupling agent as a function of filler content.
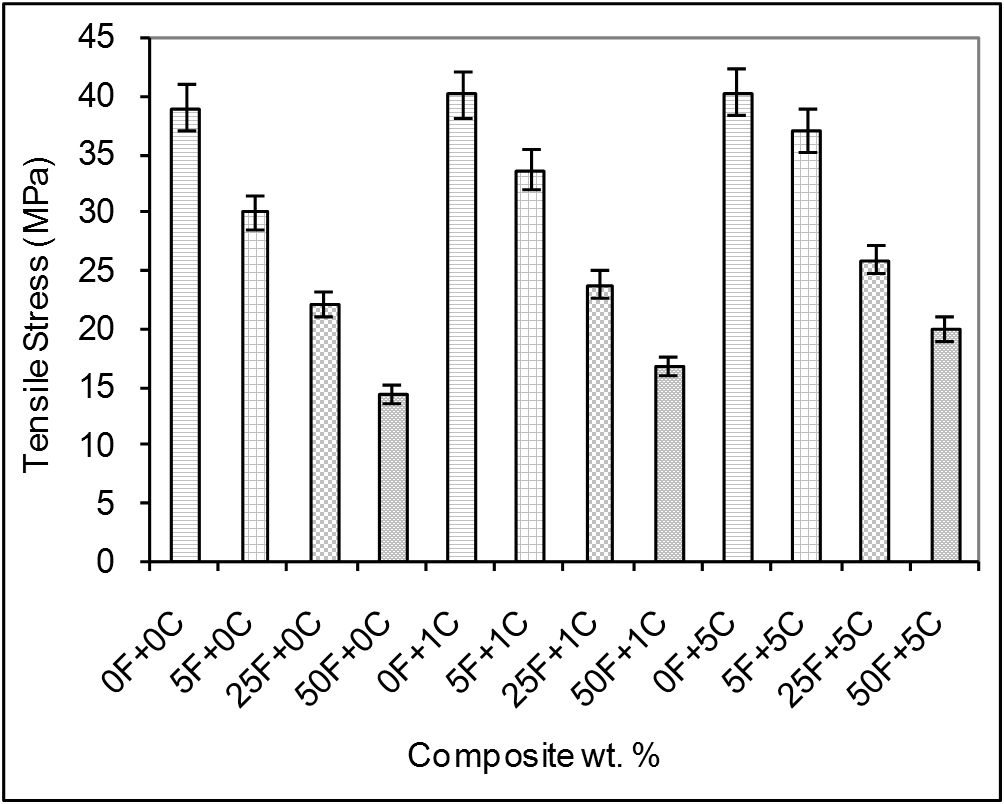 | Figure 2. Comparison of tensile stress of olive shell flour/HDPE composites as a function of the filler and coupling agent loading. F: filler % (olive shell flour) and C: coupling agent % |
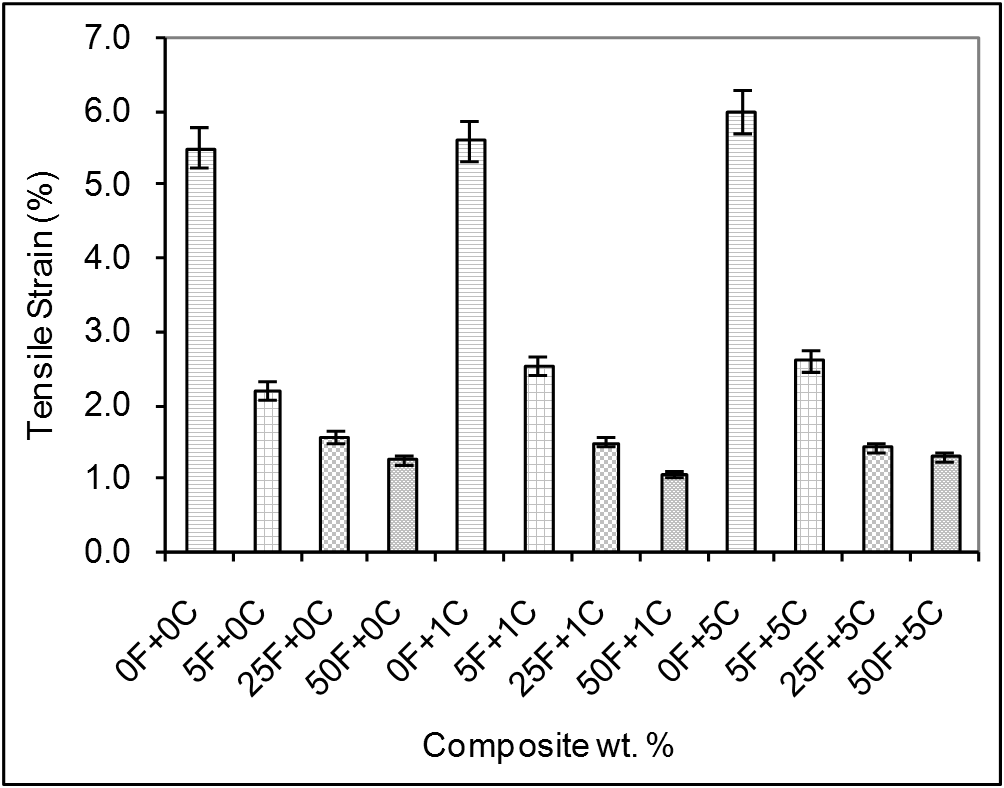 | Figure 3. Comparison of tensile strain of olive shell flour/HDPE compoites as a function of the filler and coupling agent loading. F: filler % (olive shell flour) and C: coupling agent % |
3.3.2. Modulus of Elasticity
- Modulus of elasticity of olive shell flour/HDPE specimens measured in tensile test. Figure 4 shows the variation of the tensile modulus as a function of the olive shell flour content of the composites. Tensile modulus gradually increases at low level filler loading (5F) followed with a decrease attributed to the filler agglomeration phenomena at medium (25F) and high (50F) level filler loading. For the composite with 5 wt. % olive shell content, the highest modulus was observed in specimen with 5% filler and 0% coupling agent (5F+0C), on the order of 4% compared with the modulus value of neat HDPE. This was probably due to the improved dispersion quality of olive shell flour particles in the polymeric matrix at low filler loading level. In case of medium and high filler loading level (25F and 50F) the modulus of elasticity showed a decreasing trend on the order of 4% and 13% respectively. The use of %1 and %5 coupling agent enhanced the modulus of elasticity on the order of % 8 and %17 for low level loaded filler content (5F+1C and 5F+5C ) respectively. Addition of %1 and %5 coupling agent to composites of medium and high filler loading level enhanced the modulus values on the order of %4 for each addition and for both composites.
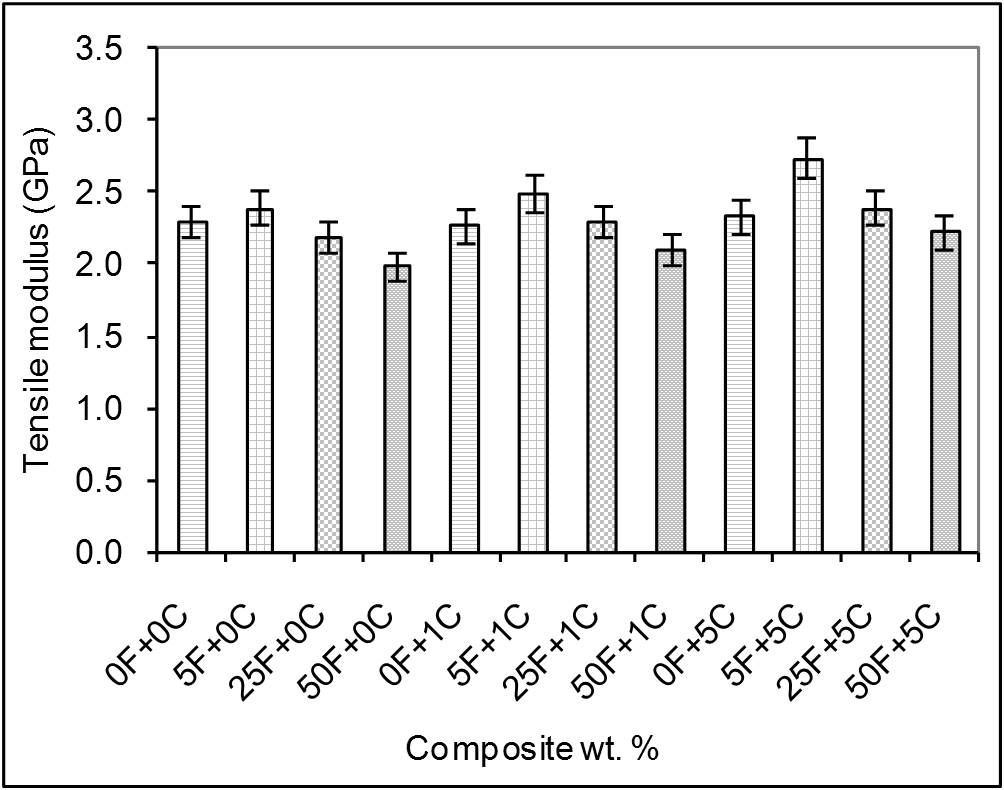 | Figure 4. Comparison of tensile modulus of olive shell flour/HDPE composites as a function of the filler and coupling agent loading. F: filler % (olive shell flour) and C: coupling agent % |
3.3.3. Un-notched Izod Impact Strength
- The impact strength is the ability of a material to withstand fracture or the amount of energy required to propagate a crack. It depends on certain factors such as fiber and matrix strength, load transfer efficiency, resistance to crack propagation, bonding strength, volume fraction, fiber distribution, and geometry [23]. The measured values of the impact strengths are presented in Figure 5.
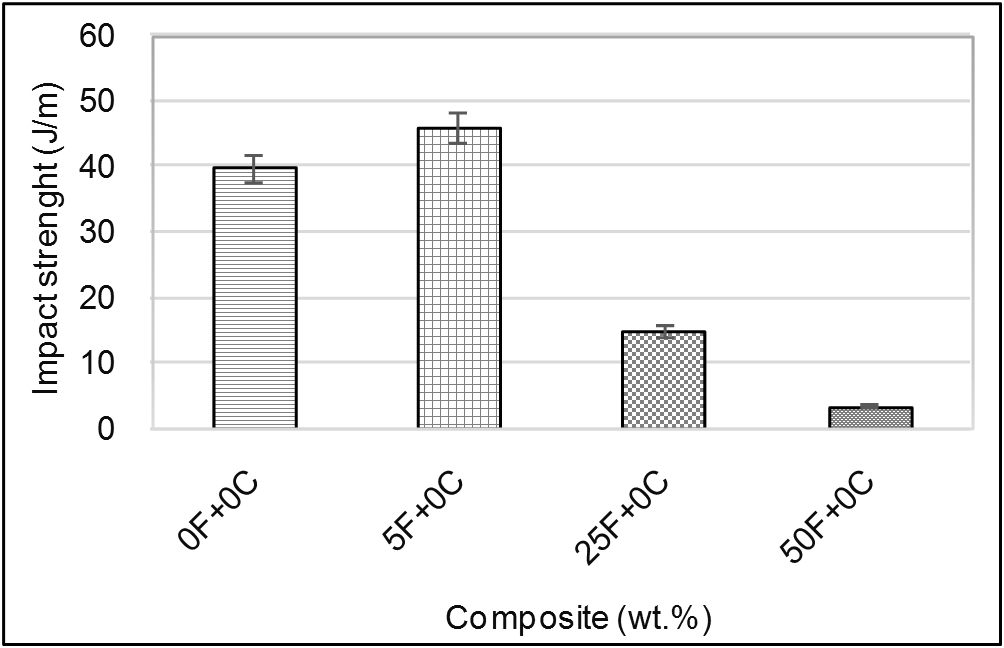 | Figure 5. Effect of olive shell flour loading on the impact strength of the olive shell flour/HDPE composite. F: filler % (olive shell flour) and C: coupling agent % |
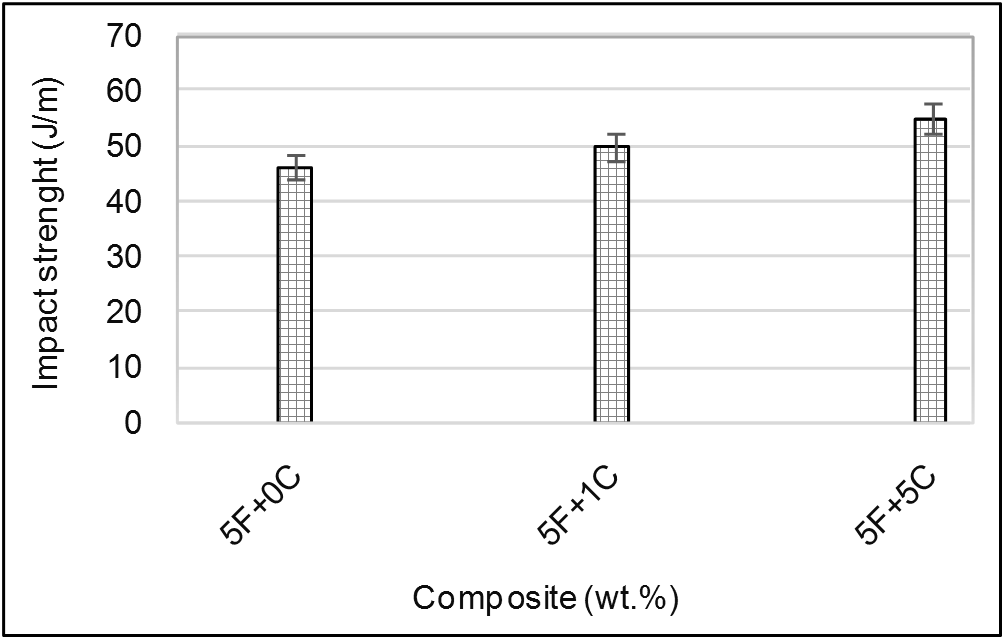 | Figure 6. Effect of coupling agent loading on the impact strength of 5% olive shell flour/HDPE composite, F: filler % (olive shell flour) and C: coupling agent % |
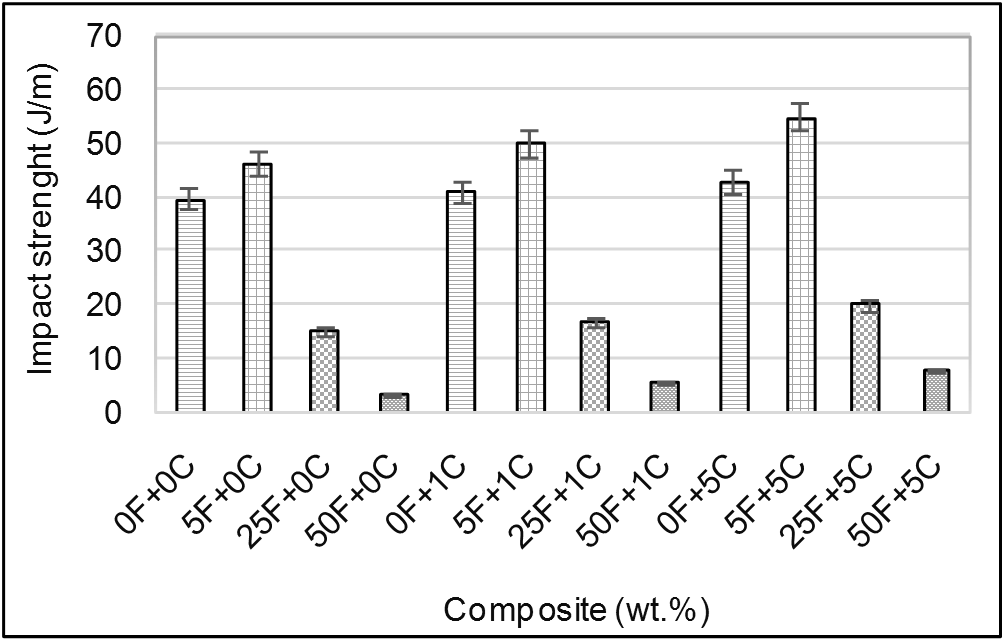 | Figure 7. Comparison of impact strength of olive shell flour/HDPE composites as a function of the filler and coupling agent loading. F: filler % (olive shell flour) and C: coupling agent % |
3.4. Fractured Surface Morphology
- The obtained olive shell flour particles mesh size was measured with a set of sieves from 140 to 325 meshes. Figure 8 represents the morphology of the olive shell flour which apparently showed irregular particle shapes with particle size distribution range from 40 to 100 µm. The assumption of obtaining spherical particle shape is not a realistic one, since a complex shape of particles usually exists.
 | Figure 8. SEM micrograph of the olive shell flour |
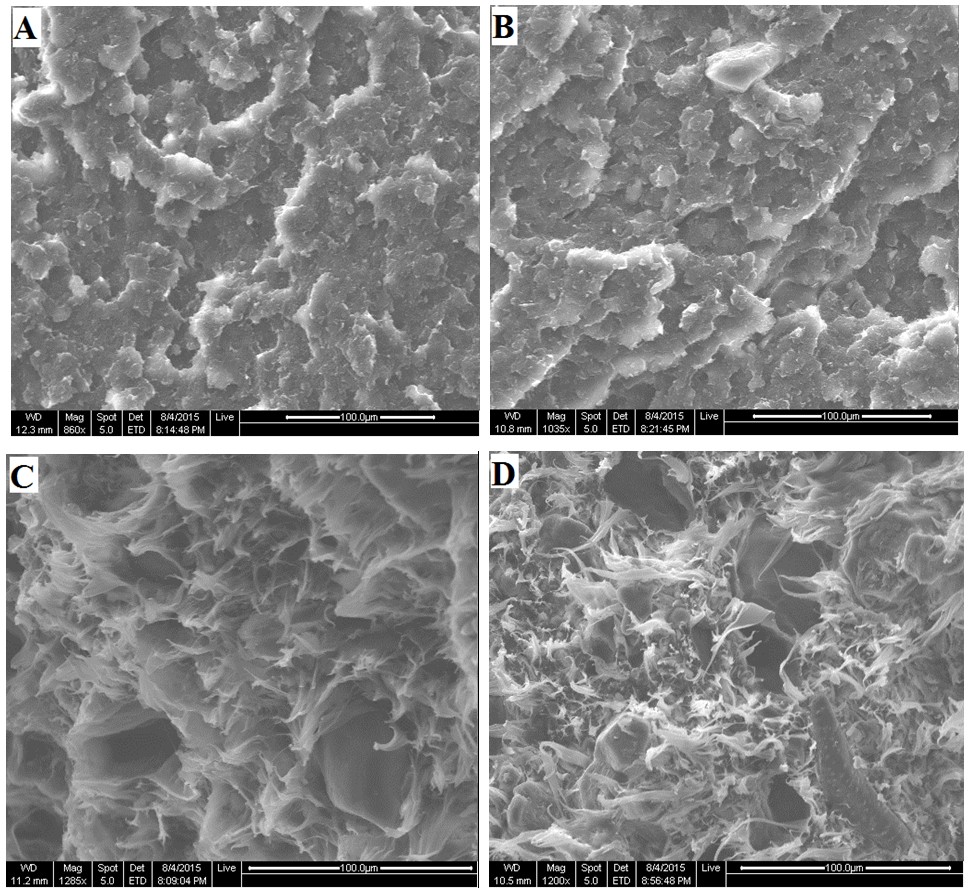 | Figure 9. SEM micrographs of the tensile fractured specimens of olive shell flour/HDPE composite at different filler content (A) 0, (B) 5, (C) 25, and (D) 50 wt.% |
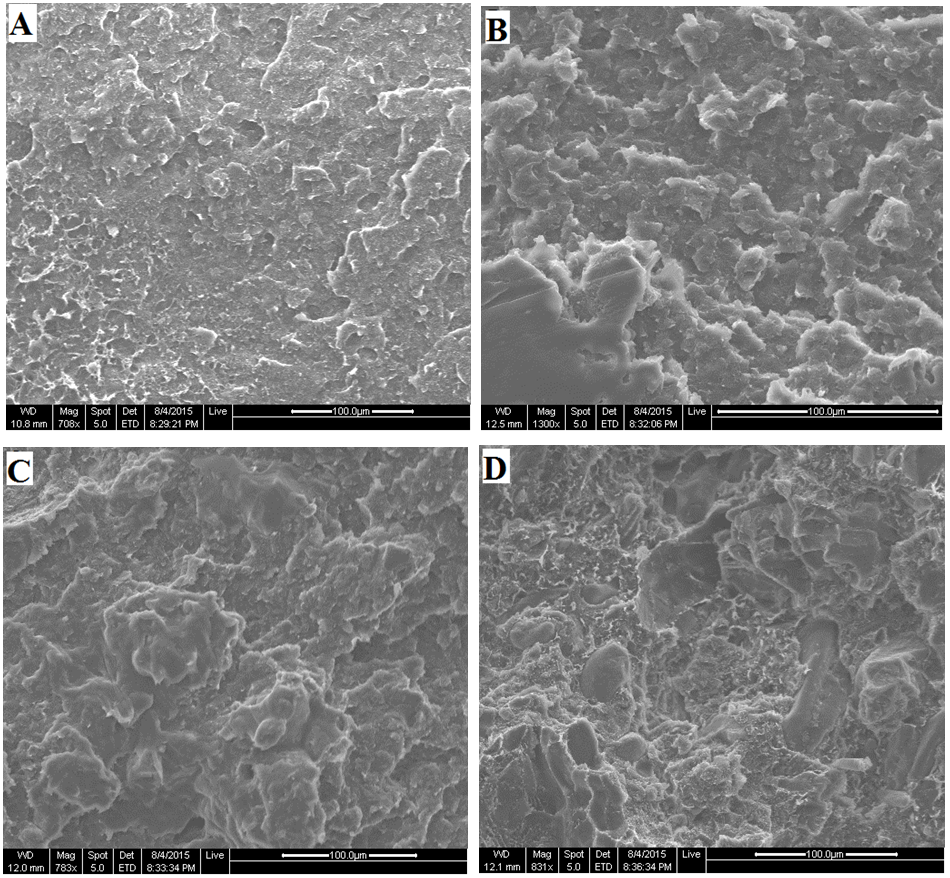 | Figure 10. SEM micrographs of the tensile fractured specimens of olive shell flour/HDPE composite with %1 coupling agent at different filler contents (A) 0, (B) 5, (C) 25, and (D) 50 wt.% |
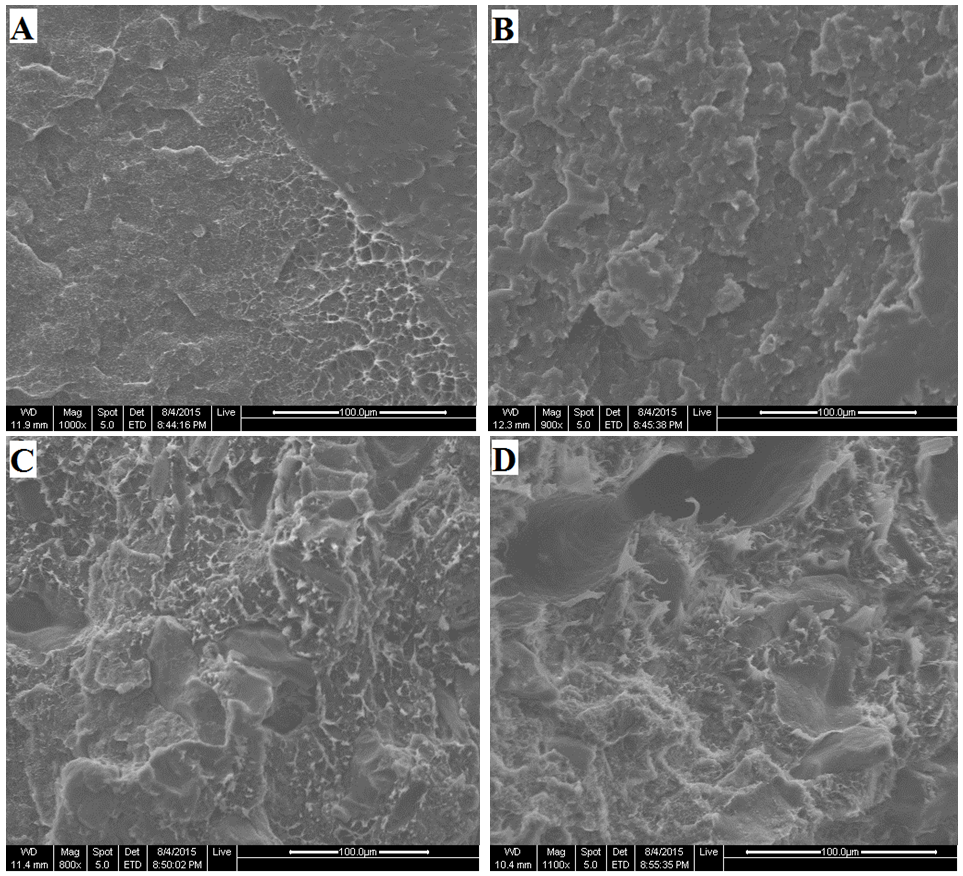 | Figure 11. SEM micrographs of the tensile fractured specimens of olive shell flour/HDPE composite with %5 coupling agent at different filler contents (A) 0, (B) 5, (C) 25, and (D) 50 wt.% |
3.5. Water Absorption Properties
- Composites based on lignocellulosic fillers are sensitive to water environment. The mechanical properties of such polymer composites are in general adversely affect by water contact. The filler hydrophilic characters and the poor interfacial adhesion of the filler polymer matrix are believed to induce such adverse performance for the polymer composite. Water absorption % vs. time at different filler and coupling agent loading level is shown in Figure 12. The water absorption % increased rapidly at the first stage of absorption and then gradually slowed down until saturation region was reached after about 20 day’s immersion in water.
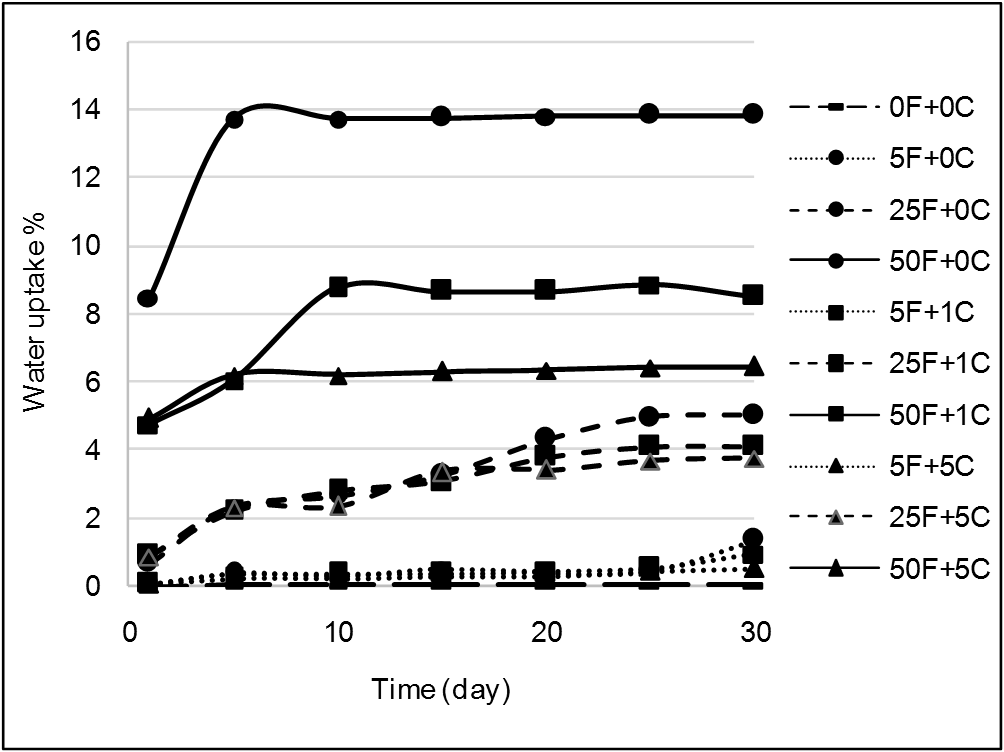 | Figure 12. Water absorption of olive shell flour filled high density polyethylene composite as a function of time |
4. Conclusions
- In the present work a novel composite material containing olive shell flour (pulp and skin) dispersed in HDPE matrix was manufactured and studied. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of olive shell flour at different weight fractions without and with coupling agent on mechanical, morphological, and water uptake properties of HDPE matrix composite. Olive shell flour/HDPE composite with 5, 25, and 50 wt. % olive shell flour contents are under taken in an extrusion and compression molding processes. In the production of the polymer composites with the desired olive shell flour content, one can use a single stage process, in which olive shell flour, coupling agent, and polymer are directly fed into the hopper. The results indicate the variation of the composite properties with varying the filler and coupling agent content. Composites, with low filler loading, showed good performance when compared to composite with high filler content. The tensile stress and modulus of elasticity reduction at medium and high filler loading may be due to the poor interfacial bonding between olive shell flour and HDPE. The decline in mechanical properties could be reversed and even improved on the use of definite proportion of coupling agent in the polymer composite. From a general point of view interfacial adhesion is the main disadvantage encountered during the incorporation of natural lignocellulose materials into polymers. Therefore suggestions to achieve a better interfacial bonding are accomplished by using coupling agent. Olive shell flour can be used as reinforcements in HDPE by the help of certain coupling agent, so that a bio-based composite is produced. Morphological illustrations and water uptake results were in good agreement with the mechanical properties variation with filler and coupling agent contents. The developed partially green OSF/HDPE polymer composite would be considered as an alternative to conventional polymers in packaging application.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- The authors would like to express their gratitude to Scientific Research Support Fund (Jordan) and Al al-Bayt University for their financial support of this research through SRF grant )Bas/2/03/2013).
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML