-
Paper Information
- Next Paper
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
International Journal of Composite Materials
p-ISSN: 2166-479X e-ISSN: 2166-4919
2014; 4(5A): 41-44
doi:10.5923/j.cmaterials.201401.06
Similar Interpenetrating Epoxy Structures for Reconstruction of Concrete Constructions
Vadim A. Lissenko
Department of Architectural Structures, Renovations and Reconstruction of Buildings, Structures and their complexes, Odessa State Academy of Construction and Architecture, Odessa, Ukraine
Correspondence to: Vadim A. Lissenko, Department of Architectural Structures, Renovations and Reconstruction of Buildings, Structures and their complexes, Odessa State Academy of Construction and Architecture, Odessa, Ukraine.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Repair, restoration, preservation and reconstruction of concrete structure are closely connected to problems of a joint, seam, crack, and cavity. For this purpose a combination of traditional methods and materials with new ones is effective especially, in particular the compounds. Therefore, the creation of new types of composites with improved physical and mechanical properties, with raised level of durability, is an urgent problem. Considering a network of polymer mortar, it is necessary to note the existence of defects, arising by virtue of a statistical property polymerization at the so-called structural mechanism of their hardening. In the beginning much ramified elements is formed, which are connected among them by through passage circuits, and as the reaction proceeds in heterogeneous milieu, it results to dissimilarity of network structure. The paper aims at presenting certain results of lengthy tests carried out in Odessa State Academy of Building and Architecture: physical and mechanical properties and durability of epoxy-polyester adhesives used for restoration and repair of architectural monuments. The effect of augmentation of durability is obtained owing to especially composed matrixes based on the interpenetrating networks, special means of the technological treatment and superfine organic and inorganic charger addition.
Keywords: Concrete repair, Polymeric materials, Hybrid-matrixes, Epoxy composites, Strength, Durability
Cite this paper: Vadim A. Lissenko, Similar Interpenetrating Epoxy Structures for Reconstruction of Concrete Constructions, International Journal of Composite Materials, Vol. 4 No. 5A, 2014, pp. 41-44. doi: 10.5923/j.cmaterials.201401.06.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- To assist in restoration, reconstruction and repair of the objects, which are of a great social and industrial significance, innovative polymer solutions (mortars) - PS, and polimerconcretes - PC have been developed [1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10]. Their life cycle give the positive effects of micro phase interaction in the complicatedly organized matrix, which is reinforced with charges, introduced following the principle of selective. Designed and thoroughly studied was a variety of hybrid matrix formed based on such systems or networks as polymer-polymer (PPN), interpenetrating polymer (IPN), homogeneously interpenetrating polymer (HIPN), and semi - interpenetrating polymer network [4, 13, 16]. The effect of the optimization of their properties is obtained by technological means, besides synthesizing new based system and characterized by 20 - 110% greater, if compared with traditional ones, strength indexes at different kinds of loading, and 30 - 120% greater atmosphere resistance. Their initial stresses level is 8 - 10 times, and creeps train 20 - 65% lower, lower technological viscosity and less defective matrix provide for PS (mortars) a longer life [2, 14, 15, 17].A general principle of designing disperse filled monolith - forming PS (mortar), namely, a principle of selective adsorption was finally suggested. It is that certain matrix components are selectively adsorbed at the surface of specially selected combination charges , and thus provide for redistribution of the matrix constituents, clearing it of low molecular impurities which are migrating trough inter- cluster regions and concentrating at the surface of active charges (organic, as a rule). This leads to curing matrix defects and improving its interaction with structure-forming charger and base, thus increasing cohesion and adhesion indexes of the system. Based on the principles of the system analysis, a probabilistic mathematical model of controlling the service life of adhesion polymer solution (mortar) as “aging” system was suggested its evolution being described by stochastic process.
2. Polymer Epoxy Composites Particle Shape
- Restoration, preservation, reconstruction and repair are closely connected to problems of a joint, seam, crack, and cavity. For this purpose, a combination of traditional methods and materials with new ones is effective especially, in particular composition polymeric materials. Considering a network of polymer mortar, as has been formed system, it is necessary to note its existence of defects, arising by virtue of a statistical property polymerization at the so-called structural mechanism of their hardening: in the beginning very ramified elements is formed, which are connected among themselves by through passage circuits, and, as the reaction proceeds in heterogeneous milieu, it results in dissimilarity of network structure. Besides, oligomers are dissimilar with distinction number of functional groups and molecular mass. All these will results in formation dissimilarity of network structure [4, 13]. If ratio picked up correctly (stoichiometrically) then oligomer-hardening agent a spatial, rather rigid network is formed having by virtue of the specified above reasons, increased existence of defects. In seams and joints of loaded constructions in such compositions at high levels of tension creep deformations, the growth of which much outstrips deformations of concrete and stone.The specified defects result in decrease of durability, that puts a scientific problem of transition to new generation of matrixes - hybrid, representing already at a level of microstructure in a known sense composite materials: polymeric, oligomeric and polymeric, polymeric mixtures, half-interpenetrating networks (HIN), homo-interpenetrating networks (HIN). The essence of received compositions consists in creation of hetero-phaseous systems, which then pass in a harden condition, being or mix of thermodynamically incompatible oligomers, or system, generated from two or several networks, the components of each of which are not capable to chemical interaction and penetrate one in other, creating some reciprocally balancing structure, where elements of one system relax tension in other, as the process of formation of each structure separately has various kinetic gradient in time [4, 7]. The postulate forecast of parameters change was confirmed in a process of optimization of structures at tests for durability at a bend, compression, shift, studying of the module of elasticity, factor of linear temperature expansion, at the short-term and long application of load, viscosity, durability. The results of research allow to make conclusions that the hybrid matrixes in comparison with one-base compositions have raised parameters of stability at various kinds of an intense condition (20-85%), lower internal tension (up to 5 time), creep deformations (25-45%), raised resistance to atmospheric and aggressive influence (30-120%), lowered technological viscosity, smaller existence of defects of a matrix, that increase of durability provides. A scientific problem of transition to new generation of hybrid - matrixes, representing already at a level of microstructure in a known sense composite materials: polymeric, oligomeric and polymeric, polymeric blends, half-interpenetrating networks (HIN), homo-interpenetrating networks (HIN) is put. The idea of creation of similar matrixes is rather fruitful and successfully develops in our country and abroad. The essence of received compositions consists in mixture of chemical noninteracting components and in creation of heterophasic systems, which then pass in hardened state, representing or blends of thermodynamically incompatible oligomers, or systems, generated from two or several networks, the components of each of which are not capable to chemical interaction and penetrate one in other, creating reciprocally balancing structure, where elements of one system relax tension in other, as the process of formation of each structure separately has various kinetic gradient in time. The basic principle, fixed in a basis of this approach to creation of hybrid matrixes of the second generation, is using not one, but two or several base resins, that is justified also from the economic point of view, as does not require of synthesis of new base components and alignment of their industrial production, and allows to use binding heavy manufacture, receiving systems with considerably improved parameters. Composites are developed purposefully for use in seams and joints of stone and concrete constructions, and their durability (D) is determined multicriterial generalized dependence, in which each everyone of three basic criteria characterizes probability of achievement by a composite of a limiting condition:

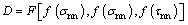 Where: 1. f (σкд) - limiting state of a composite, determined by value of tensions and deformations at short-term action and long action of load at various kinds of an intense condition. The durability of a composite in a joint, seam is determined by probability P (t) of occurrence in a seam, unit, crack of tensions, achieving 0.5σdestr (destructive tension) of composite or achievement of value of deformation, critical for polymer mortar in an interval from 0 up to t under various conditions of work;2. f (σis) - limiting value of internal tensions (initial stress) of a composite at stages of formation and operation. The durability of a composite in a seam and joint, and also of adhesive connection is determined by probability P (t) of occurrence in a composite of internal tensions, achieving 0.5R of material of a joint at a stretching or shifts;3. f (τdeg) - aging (degradation) of superficial layer, determined by intensity of growth of composite defection in a joint under the formula:
Where: 1. f (σкд) - limiting state of a composite, determined by value of tensions and deformations at short-term action and long action of load at various kinds of an intense condition. The durability of a composite in a joint, seam is determined by probability P (t) of occurrence in a seam, unit, crack of tensions, achieving 0.5σdestr (destructive tension) of composite or achievement of value of deformation, critical for polymer mortar in an interval from 0 up to t under various conditions of work;2. f (σis) - limiting value of internal tensions (initial stress) of a composite at stages of formation and operation. The durability of a composite in a seam and joint, and also of adhesive connection is determined by probability P (t) of occurrence in a composite of internal tensions, achieving 0.5R of material of a joint at a stretching or shifts;3. f (τdeg) - aging (degradation) of superficial layer, determined by intensity of growth of composite defection in a joint under the formula:
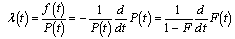 Where f (t) - density of distribution of an operating time up to a refusal of controllable value of defection.
Where f (t) - density of distribution of an operating time up to a refusal of controllable value of defection.3. Experimental Results
- The character of variation (degradation) superficial layer of offered composites was supervised through an original technique of visualization of the images with use of electrical and topographical effect in photo emulsions, which are well recommended in electronic and space engineering and which we applied for the first time for research building materials. An essence of the technique is in an opportunity to receive a picture of accumulation defects and potentially of defective zones by their electrostatic registration on a photographic film with limiting minimum of their size up to 0,03 microns. The researched structures of modified epoxy composites were rendered on metal, concrete, stone plates, were exposed to conditioning and were exposed in conditions of atmospheric influence of a cold and moderate climate in cities Novosibirsk, (Russia, Siberia), Odessa and Ilyichevsk (southern Ukraine). In terms with conformity with ST SEH 1767-96 were removed electrical topographical charts from researched samples, then on them a scale network was rendered and statistical quantity of defects was counted up. Kinetics of entirety variation of a superficial layer was counted up on parameter specific relative defection αrel
 αrel = (χt - χ1) / (χ1· F),where χ1 - initial quantity of defects, χt - quantity of defects in time t, F - area of electrical topographical charts.
αrel = (χt - χ1) / (χ1· F),where χ1 - initial quantity of defects, χt - quantity of defects in time t, F - area of electrical topographical charts.4. Discussions
- Kinetics curves of change of relative specific defection are satisfactorily described by logarithmic dependencies, and meaning of destruction parameter (the limiting state) is correlated, as it was shown, with the appropriate meaning τdeg, which is limiting for compositions of one chemical nature, as the processes of degradation, occurring on atomic, molecular and super molecular levels, submit to the same physical laws, and, means, the limiting deviation αrel will be identical at researched compositions of various recipes [4, 6]. The curves, constructed in half-logarithmic coordinates, turns to a bunch of direct lines, leaving from a beginning of coordinates, if t = 0, αrel = α1. By receiving meaning for αrel in points t1, t2, … tn (depending on duration of test) and extrapolating them up to a horizontal, appropriate to approach of a limiting state lim αrel, we receive prediction durability of structures.
5. Conclusions
- Principles of formation of hybrid matrixes from oligoepoxids, modified by polyesters, acrylic resins, constructed by such principles: a) «compound in compound», b) interpenetrating, half-interpenetrating networks, c) homo - interpenetrating networks, in the course of hardening of which the process of micro phase division and formations of microheterogeneous structures with a new complex of a final product, achievable by technological receptions, based on fundamental rules of physical chemistry and not requiring synthesis of new base components, takes place. It is shown, that one of the determining criteria of durability of a composite joint is aging (degradation) of superficial layer, determined by change of protective and decorative properties, which are offered to define with value of relative specific defection according to a technique of electrical and topographical fixing. Based on electrical and topographical researches of aging (kinetics of defection) superficial layer the diagrams have been traced for prediction of durability of unfilled and dispersible reinforced structures in conditions of Ukraine and Siberia [11, 12, 18, 19].
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML