-
Paper Information
- Paper Submission
-
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Archive
- Author Guidelines
- Contact Us
American Journal of Chemistry
p-ISSN: 2165-8749 e-ISSN: 2165-8781
2024; 14(4): 45-50
doi:10.5923/j.chemistry.20241404.02
Received: Oct. 20, 2024; Accepted: Nov. 6, 2024; Published: Nov. 12, 2024

Phytochemical Investigation of Three Medicinal Plants Grown as Leafy Vegetables in Burkina Faso
Alphonsine Ramdé -Tiendrébéogo1, 2, Benjamin Ouédraogo2, 3, Jules Yoda1, Felix Kini1
1Department of Traditional Medicine, Pharmacopoeia – Pharmacy (MEPHATRA-PH), Health Sciences Research Institute (IRSS /CNRST), Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso
2International Research Laboratory IRL 3189 Environment, Health, Societies (CNRST, USTTB, UCAD, UGB, CNRS)
3Department of Physics and Chemistry, UFR/ST, University Ledea Bernard Ouedraogo (ULBO), Ouahigouya, Burkina Faso
Correspondence to: Alphonsine Ramdé -Tiendrébéogo, Department of Traditional Medicine, Pharmacopoeia – Pharmacy (MEPHATRA-PH), Health Sciences Research Institute (IRSS /CNRST), Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Scientific & Academic Publishing.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY).
http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/

The aim of this study was to investigate the phytochemical composition and antioxidant activity of three medicinal plants whose leaves are used as vegetables in Burkina Faso: Adansonia digitata, Moringa oleifera, and Senna obtusifolia. The leaf powder was extracted by decoction to obtain aqueous and hydroethanolic extracts. Analyses were performed to identify the major compounds of biological interest present in each plant extract by thin layer chromatography (TLC). Total phenolics and flavonoids were determined by the Folin-Ciocalteu and AlCl3 methods, respectively. The antioxidant activity was evaluated using the DPPH method. Phytochemical screening revealed the presence of chemical groups of interest in the extracts, namely tannins, flavonoids and saponosides. Senna obtusifolia had the highest total phenolic content with 169.31 ± 0.28 mg EAG/gES. The highest total flavonoid content was obtained with the hydroethanol extract of Adansonia digitata (79.72 ± 3.33 mg EQ/gES). The best antioxidant power was obtained with the hydroethanol extract of Moringa oleifera, with an IC50 of 13.75 ± 1.95 µg/mL, indicating its potential to neutralize free radicals. These results underscore the importance of these leafy vegetables as potential sources of phytocompounds of therapeutic interest and natural antioxidants.
Keywords: Phytochemical study, Adansonia digitata, Moringa oleifera, Senna obtusifolia
Cite this paper: Alphonsine Ramdé -Tiendrébéogo, Benjamin Ouédraogo, Jules Yoda, Felix Kini, Phytochemical Investigation of Three Medicinal Plants Grown as Leafy Vegetables in Burkina Faso, American Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 14 No. 4, 2024, pp. 45-50. doi: 10.5923/j.chemistry.20241404.02.
Article Outline
1. Introduction
- The use of natural plant resources for nutritional and therapeutic purposes is an ancestral practice deeply rooted in the cultural traditions of many parts of the world, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa. In Burkina Faso, a Sahelian country in West Africa, the local population has developed a rich empirical knowledge of the indigenous flora and has mobilized its benefits to meet their nutritional and health needs for generations.A preliminary study carried out in the province of Oubritenga, located in the Central Plateau region of Burkina Faso, identified twenty-five (25) drought-adapted local plants with both nutritional and therapeutic virtues and high utility values [1]. Among these traditionally used plants, three species stand out for their exceptional nutritional and medicinal virtues: Adansonia digitata, Moringa oleifera, and Senna obtusifolia, called Tohega, Arzan tiiga, and Sogoda, respectively, in the local language (Mooré).Adansonia digitata, the emblematic tree of the Sudano-Sahelian landscape, plays a central role in the culture and traditional diet of Burkina Faso. All parts of this tree (leaves, pulp, seeds, bark) are widely used in various culinary forms: Vegetables, soft drinks, cooking oil, etc. This plant has also been recognized for centuries for its medicinal properties, especially in the treatment of fever, diarrhea and stomach upset [2]. Moringa oleifera is a fast-growing herbaceous plant found in many regions of Burkina Faso. All parts of the plant (leaves, flowers, pods, seeds) are consumed for their exceptional nutritional qualities. Moringa oleifera is used in traditional medicine for its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and anti-hypertensive properties. This plant, nicknamed “the miracle tree”, has thus established itself as one of the most nutritious and health-promoting foods in many rural communities [3].In traditional medicine, Senna obtusifolia is known for its laxative and purgative properties, as well as its beneficial effects on liver and kidney function. Although its use is less widespread than that of Adansonia digitata or Moringa oleifera, Senna obtusifolia remains an important plant resource for traditional health care in certain regions of the country [4]. Despite their ancestral use in food and traditional medicine in Burkina Faso, scientific knowledge on the phytochemical composition and biological activities of these three plants is still relatively limited, especially in the specific context of the central plateau region of Burkina Faso. This is the background of the present study, which aims to characterize the phytochemical profile and antioxidant activity of these three nutritious plants cultivated in Zitenga, in the central plateau region of Burkina Faso.
2. Methodology
2.1. Plant Material
- The plant material consisted of the leaves of Adansonia digitata, Moringa oleifera, and Senna obtusifolia as show in Figure 1, harvested from a community garden in Zitenga (Oubritenga province in the Central Plateau region of Burkina Faso). The harvested leaves were thoroughly washed and dried in an airy room away from sunlight and dust (for 2 weeks), then ground into a powder.
 | Figure 1. Leafy vegetables under cultivation (September 2022, Zitenga) |
2.2. Moisture Content
- The residual moisture content of each plant powder was obtained using the thermogravimetric method, the principle of which is based on loss on drying [5]. To do this, one (1) g of weighed plant powder was placed in a tared watch glass. The assembly was placed at 105°C for one (1) hour and thirty (30) minutes in a ventilated oven. After cooling in a desiccator, the product was weighed again. The operation was repeated until a constant weight was obtained. The residual moisture content of the plant drug was determined using the following formula:
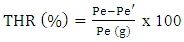 Pe = Plant material test sample (g);Pe' = Test sample after drying (g).
Pe = Plant material test sample (g);Pe' = Test sample after drying (g).2.3. Extraction
- Extracts were prepared by aqueous and hydroethanolic decoction of Adansonia digitata, Moringa oleifera and Senna obtusifolia leaf powders. The aqueous and hydroethanolic decoctions were prepared according to the following procedure: A 50 g test sample of the plant powder was dispersed in 500 mL of distilled water or 500 mL of a 70/30 ethanol-water mixture, which constituted the hydroethanol solvent. The mixture was boiled for 30 min. After cooling, the mixture was filtered through a fine-mesh nylon cloth. The filtrate was centrifuged at 2000 rpm for 10 min, then dried in a ventilated oven and stored for further analysis. Extraction yield was determined by dividing the mass of dry extract obtained by one hundred (100) grams of dry plant matter test sample.
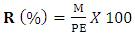 R: yield (%)M: dry extract mass (g)PE: plant material test sample (g)
R: yield (%)M: dry extract mass (g)PE: plant material test sample (g)2.4. Phytochemical Screening
- The phytochemical screening was carried out on chromatoplates (60 F254, glass support 20 x 20 cm, Fluka silica gel) according to the methods described in the literature [6]. Thin layer chromatography (TLC) was used to identify the main chemical groups such as steroidal, terpene, phenolic and alkaloidal compounds. Each dry extract was solubilized in its extraction solvent at a concentration of 10 mg/mL (10 mg in 1 mL solvent) and 5 µL was applied to the TLC plate. Chromatograms were developed over an 8 cm path in appropriate solvent systems.Several specific reagents were used to detect these groups of compounds. Sulfuric vanillin reagent and Burchard Libermann reagent for terpenes and sterols; 5% (V/V) methanolic KOH reagent for coumarins; NEU reagent for flavonoids; FeCl3 reagent for tannins and phenolics; and sulfuric anisaldehyde reagent for saponosides.
3. Evaluation of the Content of Bioactive Compounds
3.1. Determination of Phenolic Compounds
- Phenolic compounds were determined by the Singleton method using Folin-Ciocalteu reagent (FCR) [7]. The reaction mixture consisted of 25 µL extract at 0.1 mg/mL, 105 µL FCR 0.2 N, incubated for five minutes in the dark. To this mixture, 100 µL sodium carbonate solution (75 g/L in distilled water) was added. The mixture was incubated for one (1) hour in the dark and the absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 760 nm using a spectrophotometer against a tannic acid standard curve. Assays were performed in triplicate and results were expressed as milligrams of Equivalent Tannic Acid per gram of dry extract (mg ETA/g). The total phenolic content of the extract was evaluated according to the formula:
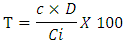 T = Content in mg Equivalent Tanic Acid per gram of extract C = sample concentration read (μg ETA/mL) on standard curve D = Dilution factor of the sample to be assayed Ci = initial concentration of sample solution to be assayed
T = Content in mg Equivalent Tanic Acid per gram of extract C = sample concentration read (μg ETA/mL) on standard curve D = Dilution factor of the sample to be assayed Ci = initial concentration of sample solution to be assayed3.2. Total Flavonoids Assay
- The flavonoid assay was performed according to the method of Kumaran [8], adapted by Abdel-Hamed [9]. To 100 μL of concentrated extract (1 mg/mL), 100 μL of aluminum trichloride (2% in methanol) was added. The absorbance was read at λ = 415 nm after 40 min incubation against a blank (100 µL methanol and 100 µL AlCl3). The appearance of a stable yellow color allows the evaluation of the flavonoid content of the sample by UV spectrophotometry using a BioRad spectrophotometer (model 680 Japan) in comparison with a reference solution of quercetin (0-70 μg/mL). Assays were performed in triplicate and results were expressed as milligrams of quercetin equivalent per gram of dry extract (mg EQ/g). The flavonoid content of the extract was calculated using the formula:
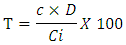 T = Content in mg Equivalent Quercetin in 100 g extract C = sample concentration read (mg EQ/mL) on standard curve D = Dilution factor of the sample to be assayed Ci = initial concentration of sample solution to be assayed
T = Content in mg Equivalent Quercetin in 100 g extract C = sample concentration read (mg EQ/mL) on standard curve D = Dilution factor of the sample to be assayed Ci = initial concentration of sample solution to be assayed3.3. Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity Using the DPPH Method
- The DPPH (2,2-Diphenyl-picrylhydrazine) method for measuring antioxidant activity is based on the ability of a compound to reduce the DPPH° radical (Figure 2). The reduction results in a color change of the solution from purple to yellow in the presence of an anti-radical compound. The reaction is then quantified by measuring the absorbance of the solution spectrophotometrically at a wavelength of 490 nm. The color change from purple to yellow is proportional to the antioxidant power.
 | Figure 2. Reduction of DPPH by an antioxidant |
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Moisture Content
- Moisture content is a crucial factor to take into account when storing and processing plant raw materials. The results are shown in the following Table 1.
|
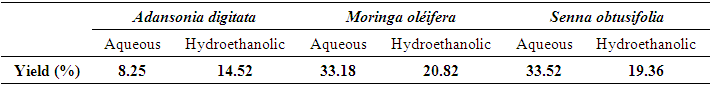
4.2. Extraction Yield
- The various plant material extraction operations gave variable yields, which are recorded in the following Table 2.
|
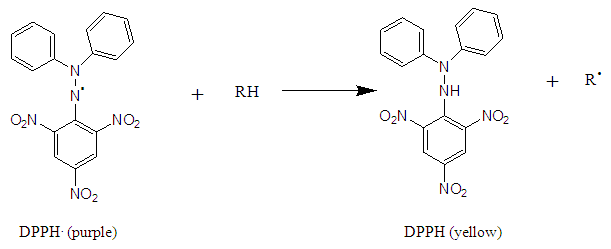
4.3. Chemical Groups
- The various fractions were characterized by TLC in order to highlight the chemical groups of interest. The results obtained are illustrated by thin layer chromatography (TLC) and reported in the following Figure 3.
 | Figure 3. TLC to detect secondary metabolites |
4.4. Bioactive Compound Content and Antioxidant Activity
- Total phenolic content, total flavonoid content and antioxidant activity were determined successively with aqueous and hydroethanolic decoctions. The results obtained are presented in histogram form in the following Figure 4.
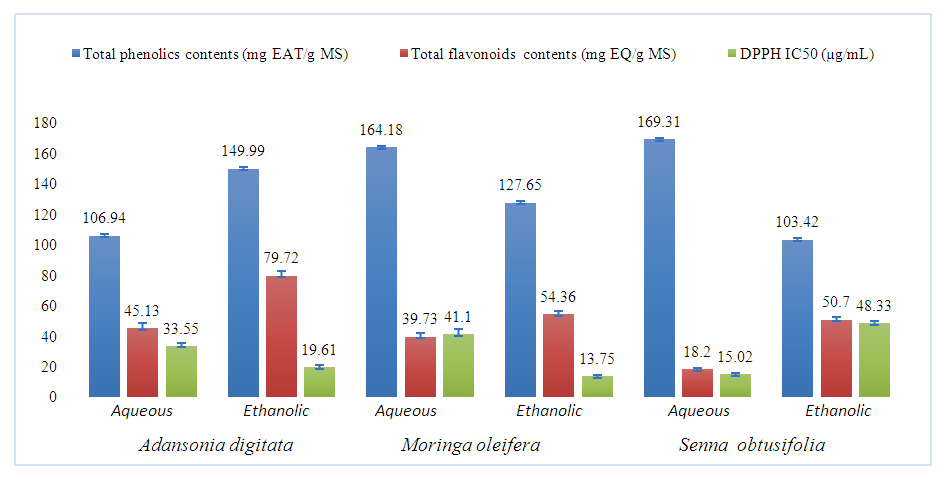 | Figure 4. Contents of total phenolics, total flavonoids and antioxidant activity |
5. Conclusions
- This study assessed the phytochemical profile and antioxidant activity of three leafy vegetables, Adansonia digitata, Moringa oleifera and Senna obtusifolia. The phytochemical screening revealed the presence of chemical groups of interest in the extracts, namely tannins, flavonoids and saponosides, known for their therapeutic properties. The results obtained provide a scientific basis for the development of improved traditional medicines or nutraceuticals for the prevention of various diseases related to oxidative stress or other diet-related chronic diseases.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
- We thank the National Fund for Research and Innovation for Development (FONRID) for financing the project.
 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML